Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers Common Diseases in Human
Question 1. Koch’s postulates include which of the following?
- The organism must be regularly found in the body of the potential
- Must be isolated and grown in an artificial medium
- Inoculated culture in a healthy person must cause disease and should be recorded again
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
- Koch’s postulates are as follows
- The microorganism must be found in abundance in all organisms suffering from the disease, but should not be found in healthy organisms.
- The microorganism must be isolated from diseased organisms and grown in pure culture artificial medium.
- The cultured microorganism should cause disease when introduced into a healthy organism.
- The microorganism must be reisolated from the inoculated, diseased experimental host and identified as being identical to the original specific causative agent.
Common Diseases In Humans NEET
Question 2. It is not possible to apply Koch’s postulates to
- Diphtheria
- Cholera
- Leprosy
- Tuberculosis
Answer: 3. Leprosy
- Koch’s postulates are not applicable for leprosy and syphilis.
- Mycobacterium leprae causing leprosy produces endospores on which
- Koch’s postulates are not applicable, because Mycobacterium leprae cannot be cultured in vitro.
- Koch’s postulates are applicable for diphtheria, cholera and tuberculosis.
“mcq on malaria “
Question 3. Koch’s postules are not applicable to
- Smallpox
- Diphtheria
- Tuberculosis
- Typhoid
Answer: 1. Smallpox
Koch’s postulates are applicable for diphtheria, tuberculosis and typhoid, but not for smallpox.
Common Diseases In Humans NEET
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
NEET Biology Common Diseases in Humans MCQs with Answers
Question 4. Consider the following statements.
- A pathogen or an infectious agent is a microorganism, such as a virus, bacterium, fungus that causes disease in its host.
- The pathogens multiply in the host body and interfere with normal vital activities, resulting in morphological and functional damage.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
Common Diseases In Humans NEET
Question 5. A reservoir of infection is the one in which
- Large-scale infection occurs
- The pathogen resides without producing disease
- The pathogen passes its sexual phase
- The pathogen passes its asexual phase
Answer: 2. The pathogen resides without producing disease
A reservoir is usually a living host of a certain species, such as an animal or a plant, inside which a pathogen survives, often (though not always) without causing disease in the reservoir itself.
Question 6. The period from the entrance of pathogens into the body and their multiplication to show initial symptoms of disease is known as
- Incubation period
- First period
- Climax period
- Infection period
Answer: 1. Incubation period
The period between infection due to the entrance of the pathogen and the appearance of first (initial) symptoms due to the multiplication of pathogens is the incubation period.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 7. The biological agents of the disease include
- Minerals, vitamins, proteins and carbohydrates
- Viruses, bacteria, fungi, helminths and other organisms
- Heat, cold, humidity pressure, radiations
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Viruses, bacteria, fungi, helminths and other organisms
- The biological agents that cause disease fall into five groups, i.e. viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoans and helminths (worms).
- Protozoa and worms are usually grouped together as parasites, and are the subject of the discipline of parasitology, whereas viruses, bacteria, and fungi are the subject of microbiology.
“human health and disease “
Common Diseases In Humans NEET
Question 8. The study of the causative agent of disease is called
- Aetiology
- Immunology
- Epidemiology
- Pharmacology
Answer: 1. Etiology
Aetiology is the study of the causative agent of a disease or the science that deals with such causes.
- Elephantiasis and dengue
- Malaria and yellow fever
- Ringworm and dengue
- Yellow fever and dengue
Question 9. Typhoid fever is caused by
- Salmonella
- Shigella
- Escherichia
- Giardia
Answer: 1. Salmonella
- Typhoid fever is caused by the bacteria, Salmonella typhi (S. typhosa). Other options are explained as
- Bacterial genus- Shigella causes shigellosis or bacillary dysentery.
- Escherichia coli is a facultative anaerobe found in the intestine of human beings.
- Giardia is a flagellate protozoan, which causes giardiasis prolonged diarrhoeal disease.
Question 10. The name of Mary Mallon is related with the disease
- Typhoid
- Cholera
- Malaria
- AIDS
Answer: 1. Typhoid
Mary Mallon (nicked name typhoid Mary born on September 23rd, 1869, in Cookstown, Country Tyrone, Ireland) was a famous typhoid carrier who allegedly gave rise to multiple outbreaks of typhoid fever. So, the name of Mary Mallon is related with the disease typhoid.
Common Diseases In Humans NEET
Question 11. Identify the common symptoms of typhoid.
- High fever and weakness
- Headache and loss of appetite
- Stomach pain and constipation
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Sustained high fever, weakness, stomach pain, constipation, headache and loss of appetite are some of the common symptoms of typhoid.
“common cold differs from pneumonia in that “
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 12. The typhoid pathogen is directly transmitted
- Through urine
- Through water
- Through blood
- Through hormone
Answer: 2. Through water
The pathogen of typhoid is directly transmitted through contaminated water and food, etc.
Question 13. Identify the correct pair representing the causative agent of typhoid fever and the confirmatory test for typhoid.
- Plasmodium vivax/UTI test
- Streptococcus pneumoniae/Widal test
- Salmonella typhi/Anthrone test
- Salmonella typhi/Widal test
Answer: 4. Salmonella typhi/Widal test
Show correct pair as Salmonella typhi is the causative agent of typhoid and its confirmatory test is the Widal test. It is based on antigen-antibody reaction.
Common Diseases In Humans NEET
Question 14. Salmonella typhosa causes
- An acute infection of the intestine that causes high fever and weakness
- Enlargement of the spleen and pain in the stomach
- Rose-coloured rashes on the body
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Typhoid fever is caused by Salmonella typhi (S. typhosa). Salmonella typhosa causes an acute infection of the intestine that causes high fever and weakness, enlargement of spleen and pain in the stomach and rose-coloured rashes on the body
Question 15. Complications of typhoid fever include
- Ulceration And Bleeding
- Haemorrhage
- Relapse
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Symptoms (complications) of typhoid are weakness, high fever, a rash of red spots on the chest and abdomen, chills, sweating and in serious cases, inflammation of the spleen and bones, ulceration or bleeding, delirium, relapse and erosion of the intestinal wall leading to haemorrhage.
Question 16. The widal test may come positive during _________ week of disease.
- First
- Second
- Third
- Fourth
Answer: 2. Second
The widal test is a diagnostic test for typhoid fever that measures agglutinating antibodies to O and H antigens of Salmonella typhi. However, it can show a false negative reading (high O-agglutination titers) in patients. But, the widal test mostly comes positive during the second week of the disease.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 17. Which cellular component of Salmonella typhi is responsible for its pathogenicity?
- Phosphorylated glucosamines
- Lipopolysaccharides
- Lipid A
- H-antigen
Answer: 2. Lipopolysaccharides
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) protects the typhoid bacteria from the environment. It is the cellular component of Salmonella typhi which is responsible for its pathogenicity.
Question 18. The natural host of S. typhi is
- Housefly
- Mosquito
- Cockroaches
- Man
Answer: 4. Man
S. Typhi is a highly host-adapted pathogen, humans comprise the only natural host and reservoir of this infection.
Common Diseases In Humans NEET
Question 19. The organism which causes pneumonia in human beings is
- Atrichous
- Monotrichous
- Amphitrichous
- Peritrichous
Answer: 1. Atrichous
Coccus forms are always atrichous. Pneumonia is caused by the Pneumococcus bacteria.
Important MCQs on Common Human Diseases for NEET
Question 20. Select the incorrect statement.
- Pneumonia is caused by
- Streptococcus and Haemophilus bacteria
- Pneumonia causes shirtlessness of breath
- Pneumonia mainly affects the liver
- All of the above
Answer: 3. Pneumonia mainly affect the liver
Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae are responsible for the disease pneumonia in humans, which infects the alveoli of the lungs. As a result of the infection, the alveoli get filled with fluid leading to severe problems in respiration.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 21. How does pneumonia spread?
- Due to droplets released from an infected person
- Infected released droplets inhaled by healthy person
- Sharing contaminated objects of an infected person
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
A healthy person acquires the pneumonia infection by inhaling the droplets/aerosols released by an infected person or even by sharing glasses and utensils with an infected person.
Question 22. Grey to bluish-coloured lips and nails are observed in a person suffering from
- Pneumonia
- Malaria
- Amoebiasis
- Typhoid
Answer: 1. Pneumonia
- Shortness of breath in bacterial pneumonia may cause a deprivation of oxygen in cells of the body. This can be seen evidently through a change in colour of the nails and lips.
- The nail bed turns white in colour resulting in white nail syndrome (leukonychia) and the lips may turn pale or bluish in colour.
- It can also cause blue colouration of the nails, lips and toes, known as cyanosis in severe pneumonia.
Question 23. The pathogen Haemophilus influenzae is responsible for the disease
- Influenza
- Pneumonia
- Plague
- Diphtheria
Answer: 2. Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a serious disease of the lungs caused by pathogens Streptococcus and Haemophilus influenzae (bacteria).
Common Diseases In Humans Class 12
Question 24. Diphtheria is characterised by
- Suffocation
- Hydrophobia
- Dehydration
- Gum bleeding
Answer: 1. Suffocation
Diphtheria is a serious, infectious disease caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheriae that produces a toxin and an inflammation in the membrane lining of the throat, nose, trachea and other tissues. The diphtheria toxin can damage the heart muscles and cause heart failure or paralyse the breathing muscles thus, causing suffocation.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 25. Diphtheria is caused by
- Poisons released from dead bacterial cells into the host tissue
- Poisons released by living bacterial cells into the host tissue
- Excessive immune response by the host’s body
- Poisons released by virus into the host tissues
Answer: 2. Poisons released by living bacterial cells into the host tissue
Diphtheria is a highly infectious disease caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae which liberates soluble toxin, i.e. poisons released by living bacterial cells into the host tissue. The toxin affects nerves and cause double vision, difficulty in swallowing and paralysis of breathing muscles and limbs.
Question 26. The disease whose vector is flea and pathogen is bacteria is
- Cholera
- Typhoid
- Plague
- Leprosy
Answer: 3. Plague
Plague is caused by Yersinia pestis (pathogen), a Gram-negative bacterium and transmitted by rat flea (vector). It is primarily a disease of rodents like rats, squirrels and carnivores like dogs, cats, etc. Man is incidentally attacked by rat fleas when the rat population decreases.
“virus infected cells secrete proteins called “
Question 27. Yersinia pestis is responsible for
- Syphilis
- Whooping cough
- Plague
- Leprosy
Answer: 3. Plague
- Plague is caused by Yersinia pestis, a Gram-negative bacterium.
- Other options are explained as Whooping cough or pertussis is caused by Bordetella pertussis, syphilis is caused by Treponema pallidum and leprosy (Hansen’s disease) is caused by Mycobacterium leprae.
Common Diseases In Humans Class 12
Question 28. Which is an endoparasite of skin?
- Xenopsylla
- Yersinia
- Ancylostoma
- Mycobacterium leprae
Answer: 4. Mycobacterium leprae
Mycobacterium leprae is the aetiologic agent of leprosy affecting the skin and peripheral nerves, So, it is an endoparasite of skin.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 29. Anti-Leprosy Day is observed on
- 24th March
- 30th January
- 1st December
- 5th November
Answer: 2. 30th January
Anti-Leprosy Day (Martyrdom Day of Mahatma Gandhi) is celebrated all over India on the 30th of January. World Leprosy Day, observed on the last Sunday of January, focuses on the target of zero cases of leprosy-related disabilities in children.
Question 30. When children play barefooted in pools of dirty water and flood water, they may suffer from diseases like
- Leptospirosis and bilharzia
- Malaria, amoebic dysentery and leptospirosis
- Bilharzia, infective hepatitis and diarrhoea
- Guinea worm infection, elephantiasis and amoebic dysentery
Answer: 1. Leptospirosis and bilharzia
- Leptospirosis is a bacterial zoonotic disease caused by spirochaetes of the genus- Leptospira that affects humans and a wide range of animals. Humans become infected through contact with water, food or soil containing urine from these infected animals.
- This may happen by swallowing contaminated food or water or through skin contact. Schistosomiasis or bilharzia is a life-threatening parasitic disease caused by a worm that lives in snail. Humans can be infected when they come in contact with water bodies where the snail lives.
- Thus, when children play barefooted in pools of dirty water and flood water, they may suffer from diseases like leptospirosis and bilharzia.
Question 31. Leprosy is diagnosed by which of the following set of symptoms?
- Fever, loss of pigmentation
- Deformity of fingers, scales, ulcers, loss of pigmentation, numbness of body parts
- Frequent watery stools and deformities in fingers or toes
- White spots on the skin without any scares or ulcers
Answer: 2. Deformity of fingers, scales, ulcers, loss of pigmentation, numbness of body parts
Early symptoms begin in cooler areas of the body and include loss of sensation. Signs of leprosy are painless ulcers, skin lesions, loss of pigmentation, deformity of fingers, eye dryness, reduced blinking and numbness of body parts.
Common Diseases In Humans Class 12
Question 32. Leprosy is also famous as
- Koch’s disease
- Hansen’s disease
- Pertussis
- Cholera
Answer: 2. Hansen’s disease
Hansen’s disease (also known as leprosy) is an infection caused by slow-growing bacteria called Mycobacterium leprae.
Question 33. The causative agent of Hansen’s disease is
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Mycobacterium leprae
- Corynebacterium diphtheriae
- Clostridium tetani
Answer: 2. Mycobacterium leprae
Hansen’s disease (also known as leprosy) is an infection caused by slow-growing bacteria called Mycobacterium leprae.
Question 34. Tetanus disease is caused by
- Virus
- Bacteria
- Fungi
- Mycoplasma
Answer: 2. Bacteria
Tetanus is an acute and serious infection of the central nervous system caused by bacterial infection of open wounds.
Question 35. ‘Lockjaw’ occurs in case of
- Tetanus
- Rigor mortis
- Tuberculosis
- Leprosy
Answer: 1. Tetanus
Tetanus is an acute, often fatal disease marked by tonic muscular spasm and hyperreflexia, resulting in lockjaw, generalised muscle spasm, opisthotonos and seizures.
Question 36. A person likely to develop tetanus is immunised by administering
- Preformed antibodies
- Wide spectrum antibiotics
- Weakened germs
- Dead germs
Answer: 3. Weakened germs
Tetanus toxoid is a vaccine consisting of growth products of Clostridium tetani treated with formaldehyde serving as an active immunising agent. Hence, a person likely to develop tetanus is immunised by administering weakened germs.
Question 37. Which of the following is a waterborne disease?
- TB
- Hepatitis
- Smallpox
- Cancer
Answer: 2. Hepatitis
Among given options, hepatitis is water-borne disease, whereas TB and smallpox are contagious diseases. Cancer is a non-infectious disease.
Common Diseases In Humans Class 12
Question 38. Doctors and nurses are more prone to get the infection of which of the following?
- Hepatitis-A
- Hepatitis-B
- Hepatitis-C
- Chronic hepatitis
Answer: 2. Hepatitis-B
Hepatitis B spreads through contaminated needles, sexual contact, mother-to-infant, close personal contact, blood transfusion and organ transplantation. In the hospital, doctors and nurses are more prone to hepatitis B if accidentally, they mishandle contaminated blood or needles.
Question 39. Which of the following is sexually transmitted disease?
- Hepatitis-A
- Hepatitis-B
- Hepatitis-C
- Hepatitis-D
Answer: 2. Hepatitis-B
Hepatitis B is a serious infection of the liver caused by a virus. The virus is found in blood, semen, vaginal fluids and saliva. It is the only sexually transmitted disease that has a safe and effective vaccine to protect against infection.
Question 40. Hepatitis virus serum is
- HIV
- HAV
- HAHBV
- HBV
Answer: 4. HBV
HBV is Hepatitis-B Virus. It was earlier known as serum hepatitis. Hepatitis B is caused by a highly contagious virus that infects the liver.
Question 41. Epidemic jaundice can occur in following conditions
- Hepatitis-a
- Hepatitis-b
- Hepatitis-c
- Hepatitis-d
Answer: 1. Hepatitis-a
- Hepatitis-A is a liver disease caused by the Hepatitis-A Virus (HAV).
- The virus is primarily spread when an uninfected and unvaccinated person ingests food or water that is contaminated with the faeces of an infected person.
- Today hepatitis-A has transformed from epidemic jaundice to a vaccine-preventable disease.
Common Diseases In Humans Class 12
Question 42. Hepatitis-B virus is a
- Hepadna Virus
- Variola Virus
- Retrovirus
- Picorna Virus
Answer: 1. Hepadna Virus
Hepadnaviridae is a family of viruses. Its best-known member is hepatitis-B virus. Diseases associated with this family include liver infections, such as hepatitis, hepatocellular carcinomas (chronic infections) and cirrhosis.
Question 43. Rhinovirus causes
- Common cold
- Malaria
- Aids
- Pneumonia
Answer: 1. Common cold
Rhinoviruses represent one such group of viruses, which causes one of the most infectious human ailments, the common cold.
Question 44. Which of the following viruses causes common cold-like symptoms?
- Adenovirus
- Simian virus-40
- T4 virus
- MSZ virus
Answer: 1. Adenovirus
Adenovirus is one or a group of DNA-containing viruses causing infection of the upper respiratory tract that produce symptoms resembling those of the common cold.
Bacterial Diseases In Humans NEET
Question 45. Symptoms of common cold are
- Cough and sore throat
- Nasal congestion
- Headache
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Symptoms of common cold are nasal congestion and discharge, sore throat, hoarseness, cough, headache, tiredness, etc.
Bacterial, Viral, and Fungal Diseases MCQs for NEET
Question 46. Common cold is not cured as it is
- Caused by a virus
- Caused by a gram-positive bacterium
- Caused by a gram-negative bacterium
- Not an infectious disease
Answer: 1. Caused by a virus
- The common cold is caused by some 100 types of rhinoviruses. It is one of the most common infectious disease in human.
- Antibiotics are substances that destroy or inhibit the growth of microorganisms, particularly disease-producing bacteria and fungi.
- Since the viruses do not possess cell wall and their own protein-synthesising apparatus, they are not attacked by antibiotics. Thus, the common cold is not cured as it is caused by virus.
Question 47. Common cold differs from pneumonia in that
- Pneumonia is a communicable disease, whereas common cold is a nutritional deficiency disease
- Pneumonia can be prevented by a live attenuated bacterial vaccine, whereas common cold has no effective vaccine
- Pneumonia is caused by a virus, while common cold by a bacteria
- Pneumonia pathogen infects alveoli, whereas common cold affects nose and respiratory passage, but not lungs.
Answer: 4. Pneumonia pathogen infects alveoli, whereas common cold affects nose and respiratory passage, but not lungs
Bacterial Diseases In Humans NEET
Question 48. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS)
- Is caused by a variant of pneumococcus pneumoniae
- Is caused by variant of the common cold virus (coronavirus)
- Is an acute form of asthma
- Affects non-vegetarians much faster than the vegetarian
Answer: 2. Is caused by variant of the common cold virus (coronavirus)
SARS is caused by a member of the coronavirus family of viruses (the same family that can cause the common cold). When someone with SARS coughs or sneezes, infected droplets spread in the air.
Question 49. Arbovirus causes
- Malaria
- Dengue
- Filariasis
- None of these
Answer: 2. Dengue
- Dengue fever is caused by an RNA-containing arbovirus (arthropod-born virus) of the Flavivirus group.
- Malaria is caused by Plasmodium vivax and filariasis is caused by any one of several thread-like parasite roundworms.
- The two species of worms most often associated with this disease are Wuchereria bancrofti and Brugia malayi.
Question 50. Aedes aegypti is a vector of disease
- Plague
- Malaria
- Dengue
- Kala-azar
Answer: 3. Dengue
The virus of dengue fever is transmitted by the bite of vector, Aedes aegypti (mosquito).
Question 51. Consider the following statements.
- A disease that has mosquito as a vector.
- The disease is also called as ‘breakbone fever’.
- Symptoms of this disease include high fever accompanied by severe headache, vomiting, etc.
- There are four different types of a virus that can cause this disease.
Identify the disease.
- Malaria
- Dengue
- Chikungunya
- Filariasis
Answer: 2. Dengue
- All given statements belong to dengue disease.
- Dengue is a disease in which the mosquito is a vector viz Aedes aegypti. There are four serotypes of a virus that can cause dengue.
- This disease is also known as breakbone fever as it involves severe pains of the joints and muscles along with high fever, severe headache, vomiting, bleeding gums, etc.
Bacterial Diseases In Humans NEET
Question 52. Smallpox is caused by a kind of
- Bacteria
- Virus
- Protozoans
- Helminths
Answer: 2. Virus
Smallpox is an acute highly communicable disease. It is caused by virus named Variola virus.
Question 53. How is smallpox transmitted?
- Droplets released through cough or sneeze from a patient
- Touching objects contaminated by bodily fluids of a patient
- The bite of a Musca domestica carrying the virus
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2)
- Smallpox is a disease caused by Variola virus causing high fever, rash in limbs or face and fatigue.
- This disease is transmitted only through person to person and does not involve any sort of vector.
- When a person comes in contact with the saliva or bodily fluids of an infected person then there can be a chance of small pox occurrence.
- The contact can occur through droplets released in cough or sneeze by the patient, touching or sharing objects contaminated by patient body fluids, etc.
Question 54. James Phipps and Ali Marvow are related to a viral disease that is no more now. The disease is
- TB
- Smallpox
- Cowpox
- Chickenpox
Answer: 2. Smallpox
- James Phipps and Ali Marvow are related to a viral disease that is no more now. The disease is smallpox.
- Smallpox can produce antibodies or antitoxins in human blood and it has no specific treatment, thus only prevention is vaccination.
- Smallpox outbreaks occurred long times ago, but the disease was totally eradicated after a successful worldwide vaccination programme.
Bacterial Diseases In Humans NEET
Question 55. Eradication of smallpox has been ossible due to the following except
- Use of highly effective vaccine
- Immunisation programmes
- Elimination of animal reservoir
- International cooperation
Answer: 3. Elimination of animal reservoir
Animal reservoir of smallpox does not exist, so its elimination has nothing to do with smallpox. Use of highly effective vaccines, immunisation programmes and international cooperation, are all related to the elimination of smallpox.
Question 56. Smallest animal virus is
- Poxvirus
- Coliphage
- Rhinovirus
- Poliovirus
Answer: 4. Poliovirus
Poliovirus is the smallest animal virus which is small RNA viruses. It is non-enveloped and about 20-30 amps in size.
Question 57. Polio is caused by a
- Bacteriophage
- Virus with a single-strand RNA
- Virus with a single-strand DNA
- Virus with double-strand DNA
Answer: 2. Virus with a single-strand RNA
Polio is caused by poliovirus which has single-strand RNA as genetic material.
Viral Diseases In Humans NEET
Question 58. The region in the body where the poliovirus multiplies is
- Nerve cells
- Muscle cells
- Intestinal cells
- None of these
Answer: 3. Intestinal cells
The virus multiplies in the lymphatic tissues of the alimentary canal, within the tonsils, Peyer’s patches of intestinal region, etc. It enters the regional lymphatics, then the bloodstream and finally to the spinal cord and brain.
Question 59. Antivenom injection contains preformed antibodies while polio drops that are administered into the body contain
- Activated pathogens
- Harvested antibodies
- Gamma globulin
- Attenuated pathogens
Answer: 4. Attenuated pathogens
Antivenom injection contains preformed antibodies while polio drops that are administered into the body contain attenuated pathogens. Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV) are of two types
- OPV sabin – Live attenuated vaccine
- OPV salk – Killed vaccine
Question 60. If a certain person shows production of interferons in his body, the chances are that he has got an infection of
- Typhoid
- Measles
- Malaria
- Tetanus
Answer: 2. Measles
Interferons are produced in response to viral infections, for example, measles. Whereas typhoid and tetanus are bacterial diseases. Malaria is caused by a protozoan.
Question 61. Common symptoms of measles are
- Dew drop-like rashes on skin and high fever
- Eruption of small red spots and inflammation of mucous membrane of nose
- Lacerating ulcers
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Eruption of small red spots and inflammation of mucous membrane of nose
- Clinical features of measles include fever and upper respiratory infection.
- Koplik’s spots can be seen on the buccal mucosa during this stage.
- The common symptoms of measles are eruption of small red spots and inflammation of mucous membrane of nose.
Viral Diseases In Humans NEET
Question 62. Mumps is an infection of
- Submandibular gland
- Submaxillary gland
- Parotid gland
- Sublingual gland
Answer: 3. Parotid gland
- Mumps is a very contagious infection of one or more of the salivary glands (parotid gland). These glands are located on either side of the face, below the ears.
- Mumps is spread from person to person through direct contact with saliva and discharges from the nose and throat of infected persons.
- Mumps can be spread by coughing, sneezing or even talking. The main symptoms are severe swelling and soreness of the cheeks and jaw.
- They usually start with neck or ear pain, loss of appetite, tiredness, headache and low fever. About a third of persons infected with the mumps virus have no symptoms.
Question 63. Which one of the following is an example of zoonosis disease?
- Measles
- Diphtheria
- Leprosy
- Rabies
Answer: 4. Rabies
- Infectious diseases transmitted from animal to man are called zoonosis.
- Zoonotic diseases are caused by harmful germs like viruses, bacteria, parasites and fungi coming into contact with the saliva, blood, urine, mucus faeces or other body fluids of an infected animal.
- Among given options rabies is an example of zoonosis disease.
- Other options are explained as Leprosy is a chronic granulomatous diseases of man involving primarily the skin.
Topic-wise Common Human Diseases MCQs for NEET with Explanation
Question 64. Hydrophobia is a feature of which disease?
- Poliomyelitis
- Measles
- Rabies
- Hepatitis
Answer: 3. Rabies
Hydrophobia is caused by a virus named rabies virus. It is introduced into the body by the bite of rabid dog or mad dog. Fear of water is the most important characteristic symptom of rabies.
Fungal Diseases In Humans NEET
Question 65. Chickenpox is caused by
- Adenovirus
- Varicella virus
- SV-40 virus
- Bacteriophage T2
Answer: 2. Varicella virus
Varicella zoster virus causes chickenpox as a primary infection in a non-immune individual.
Question 66. The painful skin condition, known as shingles, is associated with
- Chickenpox
- Rabies
- Influenza
- Polio
Answer: 1. Chickenpox
Chickenpox is viral disease. After the usual childhood case of chicken pox, the virus remains inactive in a person’s nerve cells. If reactivated later in life, it causes painful skin condition called shingles.
Question 67. The most common and most infectious childhood exanthemata is
- Rubella
- Variola
- Chickenpox
- Leprosy
Answer: 3. Chickenpox
Chickenpox (Varicella) is a highly contagious acute exanthematous disease that is most common in childhood. It is characterised by successive crops of lesions that progress rapidly.
Question 68. When is ‘Malaria Day’ celebrated?
- 5th June
- 25th April
- 15th August
- 20th September
Answer: 2. 25th April
World Malaria Day (WMD) is an international observance commemorated every year on the 25th April and recognises global efforts to control malaria.
Question 69. The primary host of Plasmodium is
- Man odisha
- Male culex
- Sheep
- Female anopheles
Answer: 4. Female anopheles
Plasmodium is a protozoan parasite, which causes malaria in human beings. The primary host of Plasmodium is female Anopheles mosquito.
Fungal Diseases In Humans NEET
Question 70. Motile zygote of Plasmodium occurs in
- The gut of female anopheles
- Salivary glands of anopheles
- Human RBCs
- Human liver
Answer: 1. Gut of female anopheles
Motile zygote of Plasmodium occurs in gut of female Anopheles. Zygote is formed in stomach of mosquito about 9-10 days after sucking the blood containing gametocytes, of an infected human.
Question 71. Plasmodium completes its life cycle in
- Multiple host
- Two hosts
- One host
- It does not involve a host
Answer: 2. Two hosts
Plasmodium completes its life cycle in two hosts (digenetic), i.e. man and female Anopheles mosquitoes.
Question 72. The infectious stage of plasmodium that enters the human body is
- Sporozoites
- Female gametocytes
- Male gametocytes
- Trophozoites
Answer: 1. Sporozoites
- The infective stage of Plasmodium that is inoculated into human blood by female Anopheles is a minute form called sporozoite.
- These are present in the saliva of female Anopheles mosquitoes. So, the malarial parasite is introduced into the blood of man as a sporozoite.
Question 73. Where will you look for the sporozoites of the malarial parasite?
- RBCs of humans suffering from malaria
- Spleen of infected person
- Salivary glands of freshly moultedn female Anopheles mosquito
- Saliva of infected female Anopheles mosquito
Answer: 4. Saliva of infected female Anopheles mosquito
When an infected female Anopheles bites a healthy person, Plasmodium in the form of ‘sporozoites’ are transmitted from saliva of mosquito into the human body.
Question 74. Infective stage ofPlasmodium in man is
- Merozoites
- Ookinetes
- Sporozoites
- None of these
Answer: 3. Sporozoites
Infective stage of malaria is sporozoite. Plasmodium enters the human body as sporozoites (infectious form) through the bite of an infected female Anopheles mosquito.
Question 75. The infectious form of malarial parasite inside a human migrates to the
- Erythrocytes of human
- Liver cells of human
- Stomach of mosquito
- Salivary gland of a mosquito
Answer: 2. Liver cells of human
- A mosquito causes malarial infection by taking a blood meal.
- First, sporozoites enter the bloodstream and then migrate to the liver of man.
Question 76. The poisonous substance released as a result of rupturing of schizont in the RBC of malaria patient is
- Haematin
- Haemoglobin
- Haemozoin
- Haem
Answer: 3. Haemozoin
In malaria the infected RBCs gets ruptured and result in the release of haemozoin into the blood. It causes chills, shivers and followed by fever.
Question 77. Haemozoin is released into the blood during the infection of plasmodium vivax at every
- 24 h
- 48 h
- 72 h
- 12 h
Answer: 2. 48 h
Haemozoin is released into blood during the infection of Plasmodium vivax at every 48 h.
Question 78. The relationship between malaria and female Anopheles mosquito was discovered by
- Grassi, Bignami, Batenetelli
- Charles Laveran
- Ronald Ross
- E Short
Answer: 3. Ronald Ross
The relationship between malaria and female Anopheles mosquito was discovered by Ronald Ross. Ross found malaria parasites growing as cysts (oocysts) on the stomach wall of an Anopheles mosquito (in 1897), which was previously fed on malarial patients.
Question 79. Sporogony of malarial parasite occurs in
- Stomach wall of mosquito
- Salivary glands of mosquito
- RBCs of man
- Liver of man
Answer: 1. Stomach wall of mosquito
Sporogony of malarial parasites occurs in stomach wall of mosquito (Anopheles). It is an asexual multiplication phase. The nucleus of the oocyst divides and followed by cytoplasmic division. Thus, several sporozoites are formed.
Fungal Diseases In Humans NEET
Question 80. Haemozoin is a toxic substance formed in case of malaria. It is produced by
- Globin protein of RBC
- Colour pigment of RBC
- Dead WBC
- Cryptozoic
Answer: 1. Globin protein of RBC
During erythrocytic schizogony, the haem of haemoglobin or globin protein RBCs changes to toxic substance, haemozoin which is responsible for malarial attack.
Question 81. During the erythrocytic schizogony of Plasmodium vivax, fine granules appear in the cytoplasm of infected RBC. They are known as
- Maurer’s dots
- Haemozoin granules
- Ferritin
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Haemozoin granules
Sporogony of malarial parasites occurs in stomach wall of mosquito (Anopheles). It is an asexual multiplication phase. The nucleus of the oocyst divides and followed by cytoplasmic division. Thus, several sporozoites are formed.
NEET Biology Immunity and Human Diseases MCQs
Question 82. Fertilisation of two gametes of Plasmodium and formation of zygote occurs in _______ of mosquito.
- Lungs
- Salivary Glands
- Liver
- Stomach
Answer: 4. Stomach
The Zygote of Plasmodium is formed in stomach of mosquito about 9-10 days after sucking the blood of an infected human.
Question 83. Maurer’s dots are observed in the erythrocytes of men if they are infected with
- Plasmodium malariae
- Plasmodium vivax
- Plasmodium falciparum
- Plasmodium ovale
Answer: 3. Plasmodium falciparum
Plasmodium falciparum causes malignant tertian malaria. It invades host RBC which does not get enlarged but greenish Maurer’s dots or clefts are seen.
Question 84. All stages of plasmodium get digested in stomach of female Anopheles except Rajasthan
- Sporozoite
- Gametocyte
- Erythrocyte
- None of these
Answer: 2. Gametocyte
The gametocytes of Plasmodium are not affected by the digestive enzymes of host mosquito.
Question 85. Which of the following malarial parasites has the longest incubation period?
- Plasmodium vivax
- Plasmodium falciparum
- Plasmodium ovale
- Plasmodium malariae
Answer: 4. Plasmodium malariae
- Plasmodium malaria is the causative organism of quartan malaria, which is characterised by the recurrence of fever every fourth day.
- Its incubation period is about 18-24 days which is greater among all the species of malarial parasites.
Question 86. Which species found in South America and West Africa is least harmful?
- P. ovale
- P. vivax
- P. falciparum
- P. malariae
Answer: 1. P. ovale
P. ovale is found is tropical Africa, causes mild tertian malaria. It is least harmful among four species of Plasmodium ovale.
Fungal Diseases In Humans NEET
Question 87. Cerebral malaria is caused by
- Plasmodium vivax
- Plasmodium ovale
- Plasmodium malariae
- Plasmodium falciparum
Answer: 4. Plasmodium falciparum
Plasmodium falciparum causes cerebral malaria which is life-threatening.
Question 88. Black water fever is caused due to
- P. vivax
- P. ovale
- P. falciparum
- P. malariae
Answer: 3. P. falciparum
Black water fever is caused by Plasmodium falciparum. It is called black water fever because patient produces dark coloured urine due to the destruction of erythrocytes.
Question 89. Malignant malaria is caused by
- Plasmodium falciparum
- Plasmodium ovale and malariae
- Plasmodium vivax
- Plasmodium malariae
Answer: 1. Plasmodium falciparum
Malignant tertian cerebral malaria is caused by Plasmodium falciparum, which is tropical in distribution.
Question 90. Benign tertian malaria is caused by
- Plasmodium vivax
- Plasmodium ovale
- Plasmodium malaria
- Plasmodium falciparum
Answer: 1. Plasmodium vivax
P. vivax causes benign tertian fever.
Question 91. Malarial infection can be prevented by
- Wire causing of doors and windows
- A sprinkling of kerosene on water bodies
- Introducing larvicidal fishes in ponds
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
- Malarial infection can be prevented by the use of antimalarial drugs and use of protection measures against mosquito bites.
- These include wire gausing of doors and windows, sprinkling of kerosene on water bodies, introducing larvicidal fishes in ponds, etc.
Question 92. Schuffner’s dots are seen in Red Blood Corpuscles (RBCs) of man due to which of the following diseases?
- Malaria
- Kala-azar
- Diabetes
- Filaria
Answer: 1. Malaria
- During malaria, the RBCs of man gets somewhat enlarged and irregular in shape.
- A number of orange or yellow eosinophilic granules of unknown nature, called Schuffner’s dots appear in its cytoplasm.
Fungal Diseases In Humans NEET
Question 93. Which one of the following conditions though harmful in itself, is also a potential saviour from a mosquito-borne infectious disease?
- Leukaemia
- Thalassaemia
- Sickle-cell anaemia
- Pernicious anaemia
Answer: 3. Sickle-cell anaemia
A sickle-cell anaemia-affected person is more resistant to mosquito-borne infectious disease because the sickle-cell-shaped RBCs are hostile to the protozoan, Plasmodium.
Question 94. The carnivorous fish used for the eradication of mosquito larva in stagnated water is
- Gambusia
- Anabas
- Rohu
- Catla catla
Answer: 1. Gambusia
The carnivorous fish used for eradication of mosquito larva in stagnated water is Gambusia. It is a large genus of fish in family Poeciliidae (order- Cyprinodontiformes).
Question 95. A malarial drug is obtained from
- Stem of mango
- Bark of cinnamon
- Bark of cinchona
- Leaves of Ocimum
Answer: 3. Bark of cinchona
Bark of Cinchona officinalis yields a drug called quinine which is used for the treatment of malaria.
Question 96. Which of the following diagnostic test is performed for the analysis of malaria?
- Widal test
- QBC test
- ELISA test
- Western blot test
Answer: 2. QBC test
- The QBC malaria test is a fluorescence microscopy-based malaria diagnostic test that speeds and simplifies malaria detection, with a combination of features and benefits unmatched by competing products.
- Increased sensitivity is compared to thick film analysis, with proven advantages in cases of low parasitemia.
Question 97. Chloroquine is used for treatment of
- Malaria
- Tetanus
- Cancer
- AIDS
Answer: 1. Malaria
Chloroquine phosphate is in a class of drugs called Antimalarials and amebicides. It is used to prevent and treatment of malaria. It is also used to the treatment of amoebiasis.
Fungal Diseases In Humans NEET
Question 98. Entamoeba histolytica is a human parasite usually found in
- Intestine
- Liver
- Blood
- Mouth
Answer: 1. Intestine
- Amoebiasis is an infection of intestine caused by the parasite, Entamoeba histolytica.
- So, Entamoeba histolytica is a human parasite usually found in the intestine.
Question 99. The causative agent of amoebiasis is
- Plasmodium
- Entamoeba histolytica
- Houseflies
- Contaminated food and water
Answer: 2. Entamoeba histolytica
Amoebiasis is caused by Entamoeba histolytica. It is commonly found in the upper part of the large intestine and is very often lodged in the liver, lungs, brain and testes.
Question 100. Entamoeba histolytica is
- A viral parasite
- A bacterial parasite
- A protozoan parasite
- A fungal parasite
Answer: 3. A protozoan parasite
Entamoeba histolytica is a gastrointestinal protozoan parasite that possesses a serious health problem with 50 million annual infections throughout the world.
Question 101. The infective stage ofEntamoeba histolytica is
- Spore
- Egg
- Trophozoite
- Cyst
Answer: 4. Cyst
- Entamoeba histolytica is a microscopic, monogenetic endoparasite of man.
- Infection to man depends upon intake of food or water contaminated with faecal matter containing tetranuclear or quadrinucleate cysts of E. histolytica.
- So, the infective stage of Entamoeba histolytica is cyst
Question 102. The infection ofEntamoeba takes place by
- Trophozoites
- Binucleate cyst
- Precystic stage
- Quadrinucleate cyst
Answer: 4. Quadrinucleate cyst
- Entamoeba histolytica is a microscopic, monogenetic endoparasite of man.
- Infection to man depends upon intake of food or water contaminated with faecal matter containing tetranucleate or quadrinucleate cysts of E. histolytica.
- So, the infective stage of Entamoeba histolytica is a cyst
Question 103. The encysted, non-motile and non-feeding infectious stage of Entamoeba histolytica is called Punjab
- Schizont
- Zygote
- Minute form
- Abiotic form
Answer: 3. Minute form
The precystic or minute form of E. histolytica is small, spherical, non-motile and non-feeding form. It measures 12-15 in diameter, vacuoles are absent. It lives in the lumen of large intestine and is non-pathogenic to man. But when the resistance of host’s body is low, it changes into magna form and invades the tissues of intestine.
Question 104. Carriers of entamoeba histolytica are
- Mosquito of the genus, anopheles
- Cattle
- Musca domestica (housefly)
- Healthy human host
Answer: 3. Musca domestica (housefly)
- Entamoeba histolytica is a monogenetic endoparasite of human causing amoebic dysentery.
- Musca domestica (houseflies) and cockroaches, carry viable cysts on their legs or in their intestine and transfer them to unprotected food stuffs.
Cancer, AIDS, and Malaria MCQs for NEET
Question 105. Which of the following can be considered to be the main source of amoebic dysentery?
- Contaminated food and water
- Water and food contaminated by the faecal matter
- Water and food contaminated by urine
- Water and food contaminated by polluted air
Answer: 1. Contaminated food and water
Amoebic dysentery is caused by an intestinal endoparasite, Entamoeba histolytica, found in large intestine of humans. Infection takes place through contaminated food and water.
Fungal Diseases In Humans NEET
Question 106. In Entamoeba histolytica, the presence of chromatid bodies is characteristic of
- Precystic stage
- Mature quadrinucleate stage
- Trophozoite stages
- Mature binucleate stage
Answer: 4. Mature binucleate stage
- The presence of chromatid bodies during life cycle of Entamoeba histolytica is characteristic of cystic stage (mature binucleate stage).
- During cystic stage, cytoplasm of E. histolytica contains one or two glycogen masses (reserve food) and one or more characteristic refractile bar-like chromatid bodies or chromidial bars with rounded ends.
Question 107. The pathogen of amoebiasis secretes ___________ enzyme which causes ulceration and acute diarrhoea.
- Haemolysin
- Proteolysis
- Cytolysin
- Hydrolysin
Answer: 3. Cytolysin
The pathogen of amoebiasis secretes cytolysin enzyme which causes ulceration and acute diarrhoea due to the destruction of intestinal mucosa.
Question 108. Common symptoms of amoebiasis include
- Constipation, stool with blood clots
- Abdominal pain and cramps
- Weakness
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Symptoms of amoebiasis disease include constipation, abdominal pain and cramps, weakness, stools with excess mucus and blood clots
Question 109. Amoebiasis can be prevented by
- Boiling untreated water
- Consuming cooked food
- Proper washing of fruits and vegetables before their consumption
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
- Entamoeba histolytica parasite can infect food and water so safety is of paramount importance. There are a few measures you can put in place to reduce the risk of amoebiasis, which include
- Boiling untreated water especially when travelling or camping.
- Washing fruit and vegetables before eating them.
- Washing your hands, utensils and kitchen worktops before and after food preparation.
- Ensuring that all food is cooked at the correct temperature.
- Washing your hands every time you visit the toilet or after you have been in contact with an infected animal.
- Ensuring that any cooked food is covered when left out to cool down.
Question 110. Identify the option that is not a symptom of disease caused by E. histolytica.
- Stools with excess mucus
- Constipation
- Abdominal pain
- Nasal discharge
Answer: 4. Nasal discharge
Nasal discharge is not a symptom of the disease (amoebiasis) caused by E. histolytica. Symptoms of amoebiasis disease include constipation, abdominal pain and cramps, stools with excess mucus and blood clots.
Question 111. The metazoan parasite transmitted through the contamination of food is
- Entamoeba
- Guinea worm
- Ascaris
- Filarial worm
Answer: 1. Entamoeba
- Entamoeba histolytica is a microscopic, monogenetic endoparasite (metazoan parasite) of man.
- Infection to man depends upon the intake of food or water contaminated with faecal matter containing tetranucleate or quadrinucleate cysts of E. histolytica.
Question 112. Kala-azar is caused by
- Trypanosoma cruzi
- Leishmania donovani
- Trypanosoma brucei
- Trypanosoma gambiense
Answer: 2. Leishmania donovani
Kala-azar is an infectious disease caused by an intracellular flagellate protozoan, Leishmania donovani.
Question 113. Phlebotomus argentipes is a vector for
- Leishmania donovani
- Trypanosoma cruzi
- Trypanosoma gambiense
- Trypanosoma evansi
Answer: 1. Leishmania donovani
Leishmania donovani is transmitted by a vector, Phlebotomus argentipes, which is also known as sandfly.
Question 114. Which of the following transmits visceral leishmaniasis?
- Phlebotomus
- Culex
- Both (1) and (2)
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Phlebotomus
Visceral leishmaniasis is transmitted by the bite of infected female Phlebotomus sandflies. The sandflies inject the infective stage from their proboscis during blood meals.
Question 115. Just as Xenopsylla is to Yersinia pestis, so is
- Glossina palpalis to Wuchereria bancrofti
- Culex to Plasmodium falciparum
- Homo sapiens to Taenia solium
- Phlebotomus to Leishmania donovani
Answer: 4. Phlebotomus to Leishmania donovani
- Xenopsylla or rat flea transmits the pathogen Yersinia pestis, responsible for plague.
- Like this, the sandfly Phlebotomus transmits the protozoan Leishmania donovani which is the causative agent of kala-azar, oriental sore, etc.
Question 116. The test for kala-azar which has high percentage of positive findings is
- Stool test
- Blood culture
- Liver biopsy
- Rapid blood test
Answer: 4. Rapid blood test
- Serological testing is much more frequently used in areas, where leishmaniasis is endemic.
- A 2014 Cochrane review (which is a database of systematic review in health care) evaluated different rapid diagnostic tests.
- One of them, the rk39 immunochromatographic test gave correct, positive results in 92 people with visceral leishmaniasis.
- So, the test for kala-azar which has high percentage of positive findings is rapid blood test.
Question 117. Sleeping sickness is caused by
- Wuchereria bancrofti
- Trypanosoma gambiense
- Plasmodium
- Varicella zoster
Answer: 2. Trypanosoma gambiense
- Sleeping sickness is a dangerous disease of man in tropical Africa. Its causative agent is T. gambiense which is transmitted by a tse-tse fly, Glossina palpalis.
- Infestation of the lymph system leads to glandular swelling which is symptomatic for sleeping sickness.
Question 118. Trypanosoma, the causative agent of African sleeping sickness belongs to which class of Protozoa?
- Rhizopoda
- Mastigophora
- Sporozoa
- Ciliata
Answer: 2. Mastigophora
- Some Mastigophora are parasites , which depend on the infection of a host for the completion of their life cycle.
- These parasites cause disease in humans and other animals. One example is the trypanosomes, which cause African sleeping sickness and Chaga’s disease.
Question 119. Which of the following is the infective stage of Trypanosoma gambiense?
- Crithidial form
- Leishmanial form
- Metacyclic form
- Leptomonad form
Answer: 3. Metacyclic form
The infection to man by T. gambiense is always initiated by the bite of the tse-tse fly, Glossina palpalis, which harbours the infective metacyclic forms in the lumen of its salivary glands.
Question 120. ‘Trypanosomiasis’ is transmitted by or carrier of Trypanosoma in man is
- Housefly
- May fly
- Tse-tse fly
- Fruitfly
Answer: 3. Tse
Sleeping sickness or African trypanosomiasis is a parasitic disease transmitted by the tse-tse fly.
Question 121. Chaga’s disease is caused by
- Trypanosoma gambiense
- Trypanosoma cruzi
- Leishmania donovani
- Trypanosoma rhodisiensi
Answer: 2. Trypanosoma cruzi
- Chaga’s disease is an insect-transmitted parasitic disease common in South and Central America.
- It is caused by Trypanosoma cruzi, causes sleeping sickness. It is spread by triatomine or kissing bugs and is one of the major health problems in South America.
Question 122. Select the incorrect statement.
- African trypanosomiasis is caused by Trypanosoma brucei parasites
- Chagas disease is known as American trypanosomiasis
- Nagana disease is a form of trypanosomiasis that affects vertebrate animals such as cattle
- None of the above
Answer: 4. None of the above
All the given statements are correct.
Question 123. Assertion (A) Stool test is done to detect giardiasis. Reason (R) Giardia is enteric flagellate protozoan.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Stool test is done to detect giardiasis because Giardia is enteric flagellate protozoan.
- Giardiasis spreads through contaminated food or water. The parasite, Giardia lives in the intestine and is passed in stool
Question 124. Ascariasis is caused by
- Wuchereria bancrofti
- Brugia malayi
- Ascaris lumbricoides
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 3. Ascaris lumbricoides
Ascariasis is caused by the common roundworm Ascaris lumbricoides.
Question 125. Infection ofAscaris usually occurs by
- Eating imperfectly cooked pork
- Tse-tse fly
- Mosquito bite
- Drinking water containing eggs of ascaris
Answer: 4. Drinking water containing eggs of ascaris
- Ascaris, an intestinal parasite causes ascariasis. The eggs of the parasite are excreted along with the faeces of infected persons which contaminate soil, water, plants, etc.
- A healthy person acquires this infection through contaminated water vegetables, fruits, etc.
Question 126. The symptoms of ascariasis include
- Gastrointestinal discomfort, vomiting
- Nervousness, convulsions
- Diarrhoea, colic pain
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Symptoms of ascariasis disease include internal bleeding, muscular pain, fever, anaemia, blockage of the intestinal passage, impaired digestion, diarrhoea, nervousness, convulsions, colic pain, gastrointestinal discomfort and vomiting.
Question 127. Life cycle ofAscaris involves host
- One
- Two
- Three
- Five
Answer: 1. One
Man is the definitive host for Ascaris, so the life cycle of Ascaris involves one host.
Question 128. Ascaris larva reaches the host person’s heart through
- Subclavian vein
- Hepatic portal artery
- Pulmonary artery
- Post-caval vein
Answer: 4. Post-caval vein
- Ascaris lumbricoides is an endoparasite in the small intestine of man lying freely in its lumen. Ascaris larva reaches the host person’s heart through post-caval vein.
- A female worm lays enormous eggs which come out of the host body with faeces.
- Under favourable conditions, juveniles are formed in the egg. Such eggs, when reach in the stomach of man with contaminated food and drink hatch out juveniles.
- The juveniles undergo a journey within the body of man in following pathway bore through intestine → mesentric vein → hepatic portal vein → liver → hepatic vein → post-caval vein → right side of heart → pulmonary artery → lungs → bronchioles → bronchus ^ trachea → glottis → oesophagus → intestine.
- It takes nearly 10 days and during this period, juvenile moult four times to become an adult.
Lifestyle Diseases and Their Prevention MCQs for NEET
Question 129. Hexylresorcinol crystals in gelatin capsules are recommended in the treatment of
- Ascariasis
- Malaria
- Filariasis
- Ringworm
Answer: 1. Ascariasis
- Infection of ascariasis can be treated with a dose of antihelmintic hexylresorcinol crystals in gelatin capsule after about 12 hours fasting.
- The dose, followed by a fast of another 4 hours, kills the worms, which can be finally expelled by a purgative like sodium sulphate.
Question 130. Adult worms ofAscaris live in the
- Lumen of lungs
- Lumen of intestine
- Lumen of stomach
- Lumen of liver
Answer: 2. Lumen of intestine
- The development of Ascaris larva takes place outside the body of host in soil and their cleavage starts in shelled eggs.
- First moulting takes place in soil in shelled egg whereas second moulting takes place in alveoli of lung, respectively. The final moulting takes place in intestine. Thus, adult worms of Ascaris live in the lumen of intestine.
Question 131. Ascaris is most commonly found in
- Men
- Women
- Children
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 3. Children
- Ascaris is a genus of parasitic nematode worms known as the ‘small intestinal roundworms’.
- It is most commonly found in children as they become infected with this disease more often than adults. The illness often develops after a child puts his hands in his mouth after playing in soil contaminated by faeces containing the roundworm eggs.
Question 132. Which diagnostic test is/are used in diagnosis of ascariasis?
- Stool test
- Blood test
- Widal test
- All of these
Answer: 1. Stool test
Stool test is the diagnostic test used in diagnosis ofascariasis. Stool examination is done to find for ova and parasites. But eggs do not appear in stool until at least 40 days after the person is infected.
Question 133. Chenopodium oil is used in
- Tuberculosis
- Typhoid
- Ascariasis
- Smallpox
Answer: 3. Ascariasis
Chenopodium is an herb. Oil made from this herb is used as medicine in ascariasis. Despite serious safety concerns, people take Chenopodium oil to kill roundworms and hookworms in the intestine.
Question 134. Consider the following statements about ascariasis.
- The first larval stage is called rhabditi form larva.
- Infection takes place through consumption of contaminated vegetables, fruits and water
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
Question 135. The sites of the first, second and third moulting of the Ascaris larva are
- Soil, Lung And Intestine
- Liver, Stomach And Intestine
- Soil, Alveoli And Lung
- Soil, Intestine And Lungs
Answer: 1. Soil, Lung And Intestine
Question 136. The disease elephantiasis is caused by
- Protozoan
- Bacteria
- Elephant tick
- Filarial worm
Answer: 4. Filarial worm
Elephantiasis or filaria is caused by filarial worm, Wuchereria bancrofti and W. malayi. In elephantiasis, the legs become very heavy stout and elephant like. It spreads by the bite of female Culex mosquitoes.
Question 137. The causative agent of filaria is
- Wuchereria bancrofti
- Leishmania donovani
- Plasmodium vivax
- Trypanosoma gambiense
Answer: 1. Wuchereria bancrofti
Question 138. The disease filaria is transmitted by
- Housefly
- Sandfly
- Tse-tse fly
- Culex
Answer: 4. Culex
- Filariasis is transmitted by wide range of mosquitoes, depending upon the geographic area.
- In America, it is usually transmitted by Culex quinquefasciatus, whereas in Africa, common vector is Anopheles.
- In Pacific and Asia, filaria is transmitted by Aedes and Mansonia.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 139. The filariasis pathogens are transmitted to a healthy person through the bite of
- Female mosquito
- Housefly
- Cockroach
- None of these
Answer: 1. Female mosquito
The filarial pathogens are transmitted to a healthy person through the bite of female mosquito. Male mosquito do not act as vectors.
Question 140. Wuchereria is found in
- Lymph nodes
- Lungs
- Eye
- Gonads
Answer: 1. Lymph nodes
Wuchereria, the causative agent of filariasis is found in lymph nodes.
Question 141. In which disease does mosquito-transmitted pathogen cause chronic inflammation of lymphatic vessels?
- Elephantiasis
- Amoebiasis
- Ringworm disease
- Ascariasis
Answer: 1. Elephantiasis
Wuchereria, the causative agent of filariasis is found in lymph nodes.
Question 142. Filariasis is also called elephantiasis because
- Body part swell
- It is caused by elephant
- It is caused by ascaris
- It is caused by entamoeba
Answer: 1. Body part swell
- Filariasis is characterised by the swelling of the legs, scrotum and some other parts of the body.
- The disease is, therefore, commonly known as elephantiasis due to its resemblance to a leg of an elephant.
Question 143. Elephantiasis causing organism belongs to
- Aschelminthes
- Platyhelminthes
- Cnidaria
- Porifera
Answer: 1. Aschelminthes
The disease elephantiasis is caused by Wuchereria bancrofti, a member of phylum-Aschelminthes. It is an endoparasite of humans that lives in the lymphatic system.
Question 144. Which one of the following life cycle stages ofWuchereria bancrofti is infective to man?
- Microfilaria
- 1st stage larva
- 2nd stage larva
- 3rd stage larva
Answer: 4. 3rd stage larva
- There microfilariae develop into first-stage larvae and subsequently into third-stage infective larvae.
- The third stage infective larvae migrate through the hmocoel to the mosquito’s proboscis and can infect another human when the mosquito takes a blood meal.
- So, 3rd stage larva of Wuchereria bancrofti is infective to man.
Question 145. Third stage larva ofWuchereria bancrofti carried by Culex mosquito is called
- Cysticercus
- Merozoite
- Microfilariae
- Trophozoite
Answer: 3. Microfilariae
- The third infective stage of W. bancrofti carried by mosquito is called microfilariae.
- The slender microfilariae, 150-300 in length, are commonly found in the circulating blood or lymph of patients suffering from an infection of the filarial worms.
Question 146. Identify the site where Wuchereria bancrofti is normally found in human body.
- Muscles of the legs
- Blood vessels of the thigh region
- Skin between the fingers
- Lymphatic vessels of the lower limbs
Answer: 4. Lymphatic vessels of the lower limbs
- The site of Wuchereria bancrofti is lymphatic vessels of the lowerlimbs. Wuchereria bancrofti is a digenetic parasite which complete life cycle in two hosts. The final host is man harbouring the adult worm.
- The disease passes through four stages in human beings.
Question 147. In filariasis, the vector insect injects infectious larvae into
- Dermis of skin
- Blood stream
- Liver
- Tongue
Answer: 1. Dermis of skin
- The pathogen W. bancrofti spreads from one human being to another through mosquitoes like Culex and to a less extent by Anopheles and Aedes.
- Upon taking the blood meal, the vector insect injects infectious larvae into dermis of skin.
- The larvae then molt through two-three stages in about one year and gets matured to adult worms.
Question 148. Lymphatic filariasis affect
- Arms
- Vulva and breast
- Scrotum
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Filariasis affects the lymphatic system of body and hence all the parts like the arms, scrotum, vulva and breast, etc., get affected.
Question 149. Diethylcarbamazine is used in treatment of which disease?
- Malaria
- Ascariasis
- Filariasis
- Typhoid
Answer: 3. Filariasis
In the treatment of filariasis, 100 mg of diethyl carbamazine is used twice a day for 3 weeks and for 5 days every six month.
Question 150. The organism that causes elephantiasis belongs to
- Insecta
- Protozoa
- Nematoda
- Coelenterata
Answer: 3. Nematoda
Wuchereria bancrofti is a parasitic filarial worm which is a nematode.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 151. Assertion (A) Filarial worm is transmitted to humans by Culex mosquito. Reason (R) Culex prefers to breed in freshwater.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 3. A is true, but R is false
Female Culex carries filarial worm from one person to another. It prefers to breed in dirty water near human habitation.
Question 152. The secondary host ofTaenia is
- Snail
- Pig
- Man
- Dog
Answer: 2. Pig
Taenia solium is called pork tapeworm characterised by the absence of an alimentary canal. The intermediate (secondary) host is pig and primary host is man.
Question 153. The larval stage of Taenia solium is known as
- Hydatid cyst
- Cysticercus cellulose
- Cysticercus bovis
- Procercoid
Answer: 2. Cysticercus cellulosae
- At one time, the larvae and adult tapeworms were thought to be different species. For this reason, the larval stages are sometimes called by a different name.
- The larval stage of T. solium is sometimes called Cysticercus cellulosae. The larval stage of T. saginata is sometimes called Cysticercus bovis.
Question 154. _________ causes ringworm.
- Bacteria
- Virus
- Protozoans
- Fungi
Answer: 4. Fungi
Ringworm is a skin infection caused by a fungus species of Microsporum, Epidermophyton or Trichophyton.
Question 155. The athlete’s foot disease in humans is caused due to
- Bacteria
- Fungi
- Virus
- None of these
Answer: 2. Fungi
An athlete’s foot is caused by a fungi and is typically acquired by coming into contact with infected skin or fungus in the environment.
Question 156. ‘Athlete’s foot’ is caused by
- Tinea pedis
- Tinea capitis
- Candida albican
- Rickettsia
Answer: 1. Tinea pedis
Athletes’ food is a fungus infection of the skin between the toes by a type of ringworm Tinea pedis. The infection results in itching, dryness, skin abrasions, etc.
Question 157. Ringworm causes
- Athlete’s foot
- Groin jock itch
- Thickening, discolouring of nail
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Ringworm causes athlete’s foot, groin jock itch, and thickening and discolouring of nail.
Question 158. Ringworms are caused by
- Wuchereria
- Microsporum
- Haemophilus
- Epidermophyton
Choose the correct option
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 2 and 4
- 1 and 4
- 3 and 4
Answer: 3. 2 and 4
Ringworms are caused by Microsporum and Epidermophyton. Others are explained as Wuchereria causes elephantiasis and Haemophilus causes influenza.
Question 159. The pathogen Microsporum responsible for ringworm disease in humans belongs to the same kingdom of organisms as that of
- Taenia, a tapeworm
- Wuchereria,a filarial worm
- Rhizopus, a mould
- Ascaris, a roundworm
Answer: 3. Rhizopus, a mould
Microsporum is a member of Deuteromycetes of fungi and Rhizopus is also a fungi and member of Zygomycetes. So, Micosporum and Rhizopus belong to same kingdom.
Question 160. Dry, scaly lesions on the skin, nails and scalp are the symptoms of which of the following?
- Ringworm
- Skin allergy
- Botulism
- None of these
Answer: 1. Ringworm
- Symptoms of ringworm disease are
- Dry, scaly lesions on skin, nails and scalp.
- Lesions are accompanied by intense itching.
Question 161. Fungi belonging to genera Microsporum, Trichophyton and Epidermophyton causes
- Ringworm
- Skin allergy
- Amoebiasis
- Measles
Answer: 1. Ringworm
- A fungus parasitic upon the skin, usually a species of Microsporum, Epidermophyton or Trichophyton is responsible for ringworm.
- They are also called cutaneous fungus.
Question 162. Ringworm infection can be prevented by
- Avoiding sharing of clothes, sports equipment and towels
- Washing clothes in hot water with fungicidal soap after suspected exposure to ringworm
- Avoiding barefooted walking
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Ringworm infection can be prevented by avoiding sharing of clothes and all personal things, by washing clothes in hot waer with fungicidal soap after suspected exposure to ringworm avoiding barefooted walking.
Question 163. Plasmodium completes its life cycle in two hosts, asexual phase in __________ host and the sexual phase of life cycle in ______ host.
- Human, culex mosquito
- Human, female anopheles mosquito
- Human, aedes mosquito
- Human, male anopheles mosquito
Answer: 2. Human, female anopheles mosquito
Plasmodium completes its life cycle in two hosts, the asexual phase in human host and sexual phase of life cycle in female Anopheles mosquito.
Question 164. Which one of the following is not correctly matched?
- Glossina palpalis –Sleeping sickness
- Culex pipiens – Filariasis
- Aedes aegypti –Yellow fever
- Anopheles culicifacies–Leishmaniasis
Answer: 4. Anopheles culicifacies–Leishmaniasis
Glossina palpalis –Sleeping sickness is not correctly matched and can be corrected as Leishmaniasis is transmitted by sandfly Phlebotomus argentipes. Anopheles transmits malaria.
Rest options are correctly matched pairs.
Question 165. In present days, which of the following is most infective and found around us?
- Anopheles
- Aedes
- Culex
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
- Anopheles stephensi is most common Indian species. Other are Culex fatigans and Aedes albopictus.
- All given species are the most infective and found around us in present days.
Question 166. Which of the following sets of diseases is caused by bacteria?
- Cholera and tetanus
- Typhoid and smallpox
- Tetanus and mumps
- Herpes and influenza
Answer: 1. Cholera and tetanus
Cholera is caused by a bacterium, Vibrio cholerae and tetanus is caused by a bacterium, Clostridium tetani.
Question 167. Give the correct matching of causative agent/germ and disease.
- Anopheles – Malaria
- Leishmania – Sleeping sickness
- Glossina – Kala-azar
- Wuchereria – Filariasis
Answer: 4. Wuchereria – Filariasis
Question 168. Identify the group of diseases carried (transmitted) by insects.
- Typhoid, jaundice, tuberculosis
- Mumps, measles, smallpox
- Scabies, ringworm, swine flu
- Malaria, filaria, yellow fever
Answer: 4. Malaria, filaria, yellow fever
Mosquitoes are carriers of Malaria – Anopheles mosquito (female) Filariasis – Culex (female) Yellow fever – Aedes (female).
Question 169. Match Column 1 in causative organisms with Column 2 in their diseases.
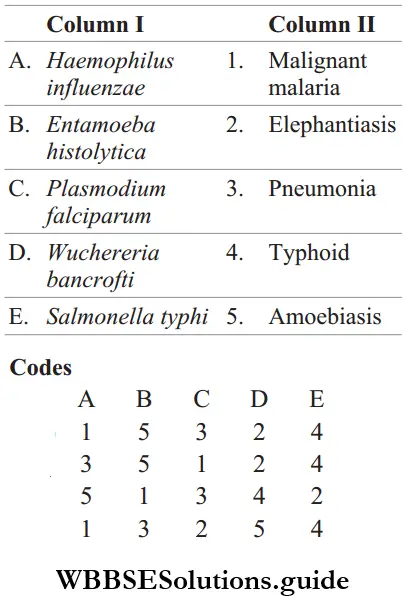
Answer: A-3, B-5, C-1, D-2, E-4
Question 170. Which one of the following options gives the correct matching of a disease with its causative organism and mode of infection.
- Disease → Causative organisms → Mode of infection
- Typhoid → Salmonella typhi → With inspired air
- Pneumonia → Streptococcus pneumoniae → Droplet infection
- Elephantiasis → Wuchereria bancrofti → Infected water and food
- Malaria → Plasmodium vivax → Bite of male Anopheles mosquito
Answer: 2. Disease → Causative organisms → Mode of infection
- Pneumonia disease is spreaded by the organism, Streptococcus pneumoniae and the mode of infection is by droplet infection.
- Other options are incorrectly matched pairs and can be corrected as Typhoid spreads through contaminated food and water.
- Elephantiasis is transmitted by mosquitoes. Malaria is transmitted by female Anopheles mosquito.
Question 171. The following table shows certain diseases, their causative organisms and symptoms.
- Diseases > Causative Organisms > Symptoms
- Filariasis > A > Inflammation
- Typhoid > B > High fever stomach pain
- C > Rhinoviruses > Nasal congestion and discharge
- Ascariasis > Ascaris > D
The correct option regarding A, B, C and D is
- A-Wuchereria, B-Salmonella typhi, C-Common cold, D-Internal bleeding, fever, anaemia
- A-Salmonella typhi, B-Ascaris, C-Typhoid, D-Stomach pain, headache
- A-Ascaris, B-Entamoeba histolytic, C-Pneumonia, D-Constipation, fever
- A-Entamoeba histolytic, B-Salmonella typhi, C-Common cold, D-Nasal discharge, high fever
- Answer: 4. A-Entamoeba histolytic, B-Salmonella typhi, C-Common cold, D-Nasal discharge, high fever
- A -Wuchereria, B-Salmonella typhi, C-common cold, D-Internal bleeding fever, anaemia.
Answer: 1. A-Wuchereria, B-Salmonella typhi, C-Common cold, D-Internal bleeding, fever, anaemia
Question 172. Heating food to 100°C will prevent all diseases except
- Salmonella infection
- Cholera
- Botulism
- Hepatitis-B
Answer: 4. Hepatitis-B
Hepatitis B is a viral disease and rest options are bacterial diseases. Hepatitis B is not transmitted through food but through sexual contact, contaminated syringes, etc. Thus, its transmission cannot be prevented by heating food at 100°C.
Question 173. 1. Wuchereria _______ and W _________ cause chronic inflammation of the organ.
2. ______ is an intestinal parasite that causes _________
3. ___________and _______ are responsible for ringworm.
4. Pneumonia and common cold are ________ diseases.
Most suitable combination to fill the blanks is
(1) 1. Bancrofti and malay
2. Ascaris, ascariasis
3. Microsporum, Trichophyton
4. Airborne
(2) 1. Microsporum, Trichophyton
2. Flatworm, ascariasis
3. Bancrofti and malayi
4. Waterborne
(3) 1. Entamoeba, Bancroft
2. Liverfluke, ascariasis
3. Trichophyton, malayi
4. Soilborne
(4) 1. Typhi, malayi
2. Wuchereria, ascariasis
3. Trichophyton, Bancroft
4. Airborne
Answer:
(1) 1. Bancrofti and malay
2. Ascaris, ascariasis
3. Microsporum, Trichophyton
4. Airborne
Question 174. In which one of the following pairs of diseases both are caused by viruses?
- Tetanus and typhoid
- Whooping cough and sleeping sickness
- Syphilis and AIDS
- Measles and rabies
Answer: 4. Measles and rabies
- Measles and rabies are caused by virus. Tetanus and typhoid are caused by bacteria.
- Whooping cough is caused by bacteria. Sleeping sickness is caused by parasitic flees.
- Syphilis is caused by bacteria, while AIDS is final stage of HIV viral disease.
Question 175. Match the following columns and select the correct option from the codes given below.
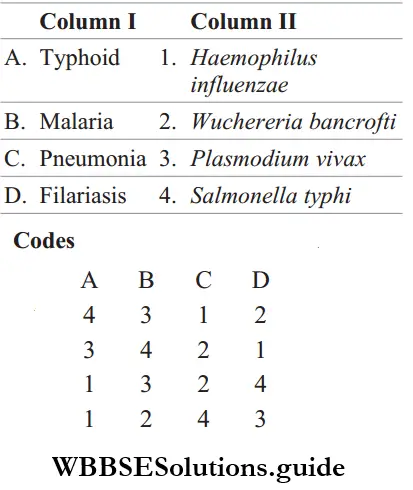
Answer: 1. A-4, B-3, C-1, D-2
Question 176. Match the following columns.
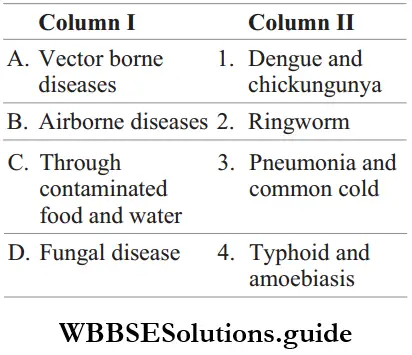
Answer: A-1, B-3, C-4, D-2
Question 177. Which of the following pair of diseases is caused by virus?
- Rabies, mumps
- Cholera, tuberculosis
- Typhoid, tetanus
- AIDS, syphilis
Answer: 1. Rabies, mumps
Rabies (hydrophobia) is caused by a virus named as rabies virus.
Mumps is an infectious disease causing fever, difficulty in opening the mouth and painful swelling of the parotid glands which lie just below the lobe of the ears. It is caused by a paramyxovirus.
Question 178. Which one of the following pairs of diseases are viral as well as transmitted by mosquitoes?
- Elephantiasis and dengue
- Malaria and yellow fever
- Ringworm and dengue
- Yellow fever and dengue
Answer: 4. Yellow fever and dengue
Yellow fever and dengue both are viral diseases as well as transmitted by mosquitoes
Question 179. Match the diseases in Column 1 with the appropriate items (pathogen/ prevention/ treatment) in Column 2.
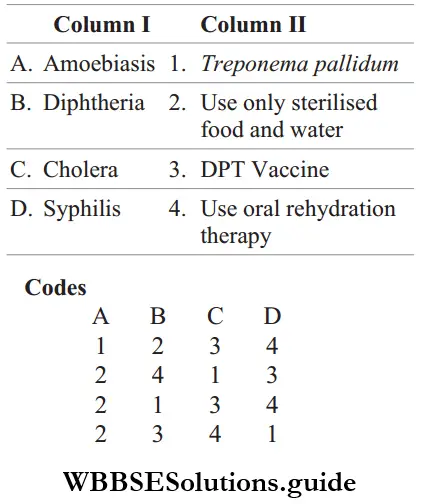
Answer: 4. A-2, B-3, C-4, D-1
