NEET Biology Mcq Energy Flow
Question 1. Ecologists termed the transfer of energy from the sun to one organism to the next in a food chain as
- A Food Web
- A Top Consumer
- Energy Flow
- A pyramid of number
Answer: 3. Energy Flow
Energy after being accumulated by the primary producers is transferred through a food chain to different trophic levels (i.e. transfer of energy from the sun to one organism to the next in a food chain). This phenomenon is termed energy flow by ecologists.
ecosystem pyq neet
Question 2. The study of energy transfer in an ecosystem at different trophic levels is known as
- Bioenergetics
- Geobiocoenosis
- Holocoenosis
- Biosystem
Answer: 1. Bioenergetics
Bioenergetics is a field in biology that concerns with the study of energy flow through living systems. So, the study of energy transfer in an ecosystem at different trophic levels is known as bioenergetics.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 3. The ecosystem creates
- Food Chain
- Biomass
- Food web
- Both 1 and 3
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 3
Ecosystem creates food chain and food web. A food chain is a series of populations through which food and the energy contained in it, passes in an ecosystem. The various levels in the passage of energy are called trophic levels. Several food chains are linked together to form a complex of interrelated food chains called as food web.
Question 4. Source of energy in an ecosystem is
- Sun Up Cpmt 2002
- ATP
- Sugar Made By Plant
- Green plant
Answer: 1. Sun Up Cpmt 2002
Sunlight is the ultimate source of energy in an ecosystem as it is the only inexhaustible resource which is utilised by green plants (primary productivity) and is passed on to higher trophic levels through food chain.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answer
NEET Biology Energy Flow MCQs with Answers
Question 5. Energy enters in any ecosystem through
- Herbivores
- Carnivores
- Producers
- Decomposers
Answer: 3. Producers
The ultimate source of energy for the biosphere is solar energy, which is captured by producers through photosynthesis and stored in organic compounds. The stored energy in the form of food is transferred from producers to herbivores and then carnivores. So, energy enters in any ecosystem through producers.
“questions for ecology “
Question 6. Assertion A light is the energy which is stored as chemical energy in the form of food during photosynthesis. Reason (R) Light influences various activities of the organism like photoperiodism, etc.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 2. Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A. Light energy is stored in plants in the form of chemical energy during photosynthesis, i.e. in the form of glucose and ATP. Light also influences various other activities like photoperiodism, etc.
Question 7. Of the total incident solar radiation, the proportion of it reaching the ground is
- About 70%
- About 60%
- Less Than 50%
- More than 80%
Answer: 3. Less Than 50%
The source of energy in all ecosystem is solar energy. Less than 50% of the solar energy incident over earth is present in PAR (Photosynthetically Active Radiation). About 1-5% of incident solar radiation or 2-10% of PAR is captured for the photosynthetic organisms for the synthesis of organic matter (gross primary productivity).
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers

Important MCQs on Energy Flow for NEET
Question 8. PAR stands for
- Photosynthesis Active Respiration
- Photosynthesis Absorb Radiation
- Photosynthetically Active Radiation
- Photosynthetically Active Reaction
Answer: 3. Photosynthetically Active Radiation
The source of energy in all ecosystem is solar energy. Less than 50% of the solar energy incident over earth is present in PAR (Photosynthetically Active Radiation). About 1-5% of incident
solar radiation or 2-10% of PAR is captured for the photosynthetic organisms for the synthesis of organic matter (gross primary productivity).
“ecosystems questions and answers “
Question 9. The percentage of PAR that is captured by plants in synthesis of organic matter is
- 50-80%
- 10-20%
- 70-100%
- 2-10%
Answer: 4. 2-10%
Plants capture only 2-10% of the PAR and this small amount of energy sustains the entire living world.
Question 10. Energy transfers or transformations are never 100% efficient. This is due to
- Entropy
- Homeostasis
- Catabolism
- Anabolism
Answer: 1. Entropy
Entropy is the measure of system’s disorder, i.e. higher the entropy, the greater the disorder. In other words, it is the measure of the unavailability of a system’s energy to do work, so increase in entropy is accompanied by decrease in energy availability. Thus, energy transfer is never 100% efficient, as it is lost in different processes such as respiration, dissipation, maintain body temperature, etc.
Question 11. A biological model depicting the flow of energy from one trophic level to another.
- Energy link
- Food chain
- Phytoplankton cycle
- Photosynthesis
Answer: 2. Food chain
A biological model depicting the flow of energy from one trophic level to another is food chain.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 12. The direction of flow of energy in an ecosystem is
- Unidirectional
- Bidirectional
- Multidirectional
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Unidirectional
In an ecosystem, there is a constant unidirectional flow or transfer of energy from sunlight through plants and plant eating animals to flesh eating animals in the form of food.
Question 13. Flow of energy declines from lower to higher trophic level in an ecosystem. This is mainly explained by
- First Law Of Thermodynamics
- Second law of thermodynamics
- Both 1 and 2
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Second law of thermodynamics
According to second law of thermodynamics, ‘the transformation and transfer of energy do not occur spontaneously but involve degradation and loss in the form of heat’. So, flow of energy declines from lower to higher trophic level in an ecosystem.
“questions about ecosystem with answers “
Question 14. When food energy passes from herbivores to carnivores
- Some Energy Is Increased
- Some Energy Is Decreased
- Remain Unchanged
- Not relevant
Answer: 2. Some Energy Is Decreased
The actual percentage of energy that is transferred from one level to the next level is approximately 10%. About 90% of the energy is lost. Thus, we can say that when food energy passes from herbivores to carnivores, some energy is decreased.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 15. Which of the following processes does not affect the nutrient flow in an ecosystem?
- Migration
- Parasitism
- Predation
- Production
Answer: 1. Migration
Migration is the mass directional movements of large number of a species from one location to another. This process does not relate to the flow of nutrients in an ecosystem.
Question 16. Ecosystem is
- Always Open
- Always Closed
- Both Open And Closed Depending Upon Community
- Both open and closed depending upon biomass
Answer: 1. Always Open
Ecosystem is an open system. It receives input in the form of solar energy and matter. It results in productivity or synthesis of organic food. Food with its contained energy passes through various components of ecosystem.
Energy Flow in an Ecosystem MCQs for NEET
Question 17. The transfer of energy from one trophic level to another is governed by the second law of thermodynamics. The average efficiency of energy transfer from herbivores to carnivores is
- 5%
- 10%
- 25%
- 50%
Answer: 2. 10%
According to the 10% law, at each trophic level, only 10% of the energy is transferred to the next trophic level. So, the average efficiency of energy transfer from herbivores to carnivores is 10%.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 18. 10% law of flow of energy in ecosystem was proposed by
- Lindemann
- Carl Mobius
- Tansley
- Darwin
Answer: 1. Lindemann
Lindemann proposed the 10% law of flow of energy in an ecosystem. According to this law, only 10% energy is passed from one trophic level to other in a food chain.
“anthropogenic ecosystem “
Question 19. Only a small amount of the energy stored in food is available to the organism in the next trophic level. This is because
- There Are Lesser Consumers Than Producers In A Food Chain
- There Are Fewer Top Consumers Than Producers In A Food Chain
- Of Competition For Food Between Primary And Secondary Consumers
- Most of the energy is used for life processes
Answer: 4. Most of the energy is used for life processes
Only 10% of the herbivore productivity is utilised for raising productivity of primary carnivores. The rest is consumed in life processes, i.e. ingestion, respiration, maintenance of body heat and other activities.
Question 20. What per cent of incident sun radiation is utilised by plants?
- 0.01
- 0.001
- 10
- 20
Answer: 1. 0.01
Plant can utilise 1% (0.01) of total incident radiation. Sugarcane is the most efficient crop which utilises the 5% of total incident radiation and convert into photosynthetic product.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 21. The direction of energy flow is UP CPMT
- Producer → Carnivore → Herbivore → Decomposer
- Producer → Herbivore → Decomposer → Omnivore
- Producer → Herbivore → Carnivore → Decomposer
- Producer → Carnivore → Herbivore → Decomposer
Answer: 3. Producer → Herbivore → Carnivore → Decomposer
In an ecosystem, the direction of flow of energy is unidirectional. Producers (Green plants) → Herbivore → Carnivore → Decomposer
Question 22. The correct sequence of components through which energy may pass from initial source through an ecosystem is
- Sun → Autotrophs → Heterotrophs → Environment → Space
- Space → Environment → Heterotrophs → Autotrophs → Sun
- Sun → Space → Environment → Heterotrophs → Autotrophs
- Sun → Space → Environment → Autotrophs → Heterotrophs
Answer: 4. Sun → Space → Environment → Autotrophs → Heterotrophs
The correct sequence of components through which energy may pass from initial source through an ecosystem is Sun → Space → Environment → Autotrophs → Heterotrophs
Question 23. On an average, the proportion of assimilated energy consumed by herbivorous in respiration is
- 10%
- 20%
- 30%
- 60%
Answer: 4. 30%
With increasing trophic levels, the respiration cost also increases sharply. On an average, producers consume about 20% of their gross productivity in respiration. The herbivores consume about 30% of assimilated energy in respiration.
“ecological pyramid of grassland ecosystem “
Question 24. If an ecosystem is composed of only three trophic levels, then how much energy will be conserved at the IIIrd trophic level?
- 30%
- 20%
- 10%
- 0.1%
Answer: 4. 0.1%
In an ecosystem, if we start from 100% energy being captured from sun, the producers (I st trophic level) receives its 10%, first consumer will receive only 1% and second consumer (III rd trophic level) will have only 0.1% energy.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 25. Suppose 10,000 J of solar energy is incident on green vegetation. On the basis of 10% law of Lindemann, identify the amount of energy transferred to deer and then to tiger.
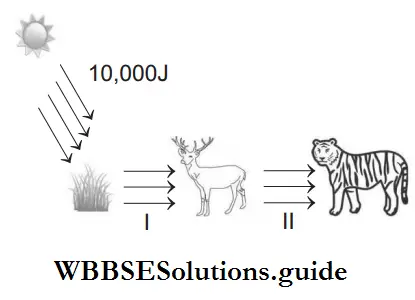
- 1-10 J, 2-1 J,
- 1-100 J, 2-10 J
- 1-10 J, 2-0.1 J
- 1- 0.1 J, 2-0.01 J
Answer: 1. 1-10 J, 2-1 J,
Only about 10% is stored at higher trophic level and the remaining 90% is lost in respiration, decomposition and waste in the form of heat. Since, 10,000 J of solar energy is incident on green vegetation, the latter having about 1% efficiency, trap about 100 J of energy and convert it into chemical energy by photosynthesis. The remaining 9980 J would be lost in the environment. The herbivore that feed on producers get 10% of the energy stored in plants, i.e. 10 J.
The remaining 90 J is lost to the environment. Carnivores feeding on herbivores would be able to store only 1 J of energy.
Topic-wise Energy Flow MCQs for NEET with Explanation
Question 26. If 20 J of energy is trapped at producer level, then how much energy will be available to peacock as food in the following chain? Plant → Mice → Snake → Peacock
- 0.02 J
- 0.002 J
- 0.2 J
- 0.0002 J
Answer: 1. 0.02 J
This is based on Lindemann’s 10% law. So, if plants trap 20 J energy then, Plant → Mice → Snake → Peacock 20 J 2 J 0.2 J 0.02 J So, energy available for peacock is 0.02 J.
Question 27. In an ecosystem, there is flow of energy at different trophic levels. This is as follows
- Primary consumers–Secondary consumers–Decomposers–Producers
- Producers–Primary consumers– Secondary consumers–Tertiary consumers–Decomposers
- Producers–Decomposers–Primary consumers–Tertiary consumers– Secondary consumers
- Producers–Primary consumers– Tertiary consumers–Secondary consumers–Decomposers
Answer: 2. Producers–Primary consumers– Secondary consumers–Tertiary consumers–Decomposers
The feeding level from producers to consumers is called trophic level. The energy flows unidirectionally through various trophic levels, i.e. Producers → Primary consumers → Secondary consumers → Tertiary consumers →Decomposers
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 28. Plants are
- Autotrophs
- Primary Producers
- Both 1 And 2
- Heterotrophs
Answer: 3. Both 1 And 2
In a food chain, a plant is primary producer. Producers are autotrophic organisms, which alone are able to manufacture organic food from inorganic raw materials in the process of photosynthesis.
Question 29. Biological equilibrium is equilibrium among the
- Producers
- Primary Consumers
- Decomposers And Producers
- Producers, consumers and decomposers
Answer: 4. Producers, consumers and decomposers
Biological equilibrium is equilibrium amongst the producers, consumers and decomposers. All these make a stable ecosystem by a dynamic balance.
Question 30. In a biotic community, the primary consumers are
- Carnivores
- Omnivores
- Detritivores
- Herbivores
Answer: 4. Herbivores
Consumers are organisms that feed on their previous trophic level.
Thus in a biotic community, primary consumers are herbivores, i.e. rabbit, etc.
Question 31. All the animals that depend on plants for food are called
- Decomposers
- Root Feeders
- Consumers
- Omnivores
Answer: 3. Consumers
Primary consumers are those who consume producers (i.e. green plants) so they are called herbivores and the animals or consumer who consumes the herbivores or primary consumers are called the secondary or tertiary consumers. Thus, all the animals that depend on plants for food are called consumers.
Question 32. What is true of ecosystem?
- Primary consumers are least dependent upon producers
- Primary consumers are out number producers
- Producers are more than primary consumers
- Secondary consumers are the largest and most powerful
Answer: 3. Producers are more than primary consumers
The organisms in an ecosystem are classified into three main categories, i.e. producers, consumers and decomposers. The consumers utilise materials and energy stored by the producers.
In a true ecosystem, producers are more than primary consumers (herbivores and carnivores).
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 33. Grasshopper is
- Primary Consumer
- Secondary Consumer
- Decomposer
- Primary decomposer
Answer: 3. Decomposer
A plant is a producer and the grasshopper is the primary consumer, which feeds on plant.
Question 34. These belong to the category of primary consumers.
- Insects and cattle
- Eagle and snakes
- Water insects
- Snakes and frogs
Answer: 1. Insects and cattle
Insects and cattle belong to primary consumers in their respective food chains as they are herbivores.
Question 35. Assertion Bacteria and fungi are microconsumers. Reason (R) Bacteria and fungi consume only a little part of living plants and animals.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 3. A is true, but R is false
A is true, but R is false. Microconsumers are microscopic organisms such as bacteria and fungi. These microorganisms breakdown the complex organic compounds of dead bodies of both plants and animals and absorb some of the decomposed products, while release most of inorganic compounds into the environment. From there, these are used by the plants. These are biotic components of an ecosystem.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 36. In a forest ecosystem, fungi is
- Secondary Consumer
- Tertiary Consumer
- Decomposers
- Primary producers
Answer: 3. Decomposers
Decomposers in any ecosystem or food chain are fungi, bacteria and saprophytic organisms.
Question 37. Assertion Herbivores are also called as first order consumers. Reason (R) They obtain their food directly from plants.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. Consumers of first order includes the herbivores which directly feed upon green plants (producers).
Question 38. Whale is
- Primary Producer
- Carnivorous Tertiary Consumer
- A Decomposer
- Herbivorous
Answer: 2. Carnivorous Tertiary Consumer
Carnivores that consume other carnivores are called tertiary consumers. Killer whales or orcas are a classic example of tertiary consumers. Killer whales hunt seals and sea lions.
NEET Biology 10% Law and Lindeman’s Law MCQs
Question 39. Match Column I with Column II
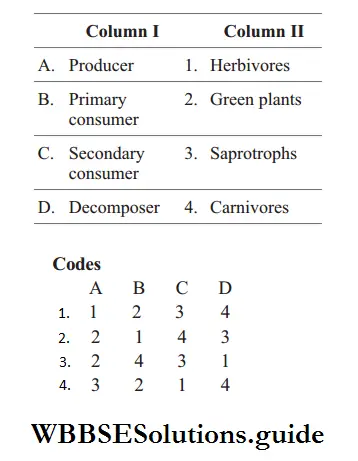
Answer: 2. 2 1 4 3
Question 40. A rat feeding upon potato tuber is
- Decomposer
- Producer
- Primary Consumer
- Carnivore
Answer: 3. Primary Consumer
Primary consumers include all the organisms that utilise plant products. The animals that eat plants as food are called primary consumers or herbivores, e.g. a rat feeding upon potato tuber.
Question 41. The frog that feeds on an insect is a
- Primary Consumer
- Secondary Consumer
- Tertiary Consumer
- Decomposer
Answer: 2. Secondary Consumer
Primary consumer (insect) directly depends on the producer(plant) for food source. Secondary consumers (frog) include different organisms that feed on primary consumers (primary carnivore). Thus, the frog that feeds on an insect is a second consumer.
Question 42. Carnivores are
- Usually Primary Consumers
- Usually Secondary Consumers
- Usually Secondary Or Tertiary Consumers
- Usually Decomposers Rather Than Consumers
Answer: 3. Usually Secondary Or Tertiary Consumers
Carnivores are usually secondary or tertiary consumers as they feed on smaller animals.
Question 43. Match the following columns
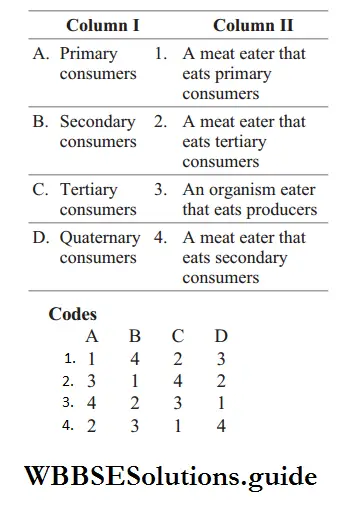
Answer: 2. 3 1 4 2
Question 44. Match the following columns.
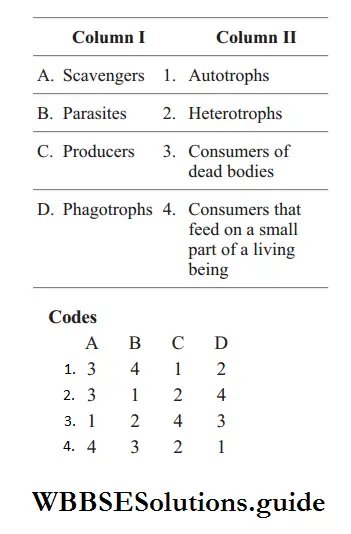
Answer: 1. 3 4 1 2
Question 45. Which of the following exist in maximum number in terms of genera and species?
- Herbivore mammals
- Carnivore mammals
- Aquatic mammals
- Terrestrial mammals
Answer: 4. Terrestrial mammals
Terrestrial animals are animals that live predominantly or entirely on land. They have the maximum number in terms of genera and species as they also include most of the herbivores like cows and carnivores animals like lion and even omnivorous like rats as well. Thus, they exist in maximum number in terms of genera and species.
Question 46. The primary producers of the deep sea hydrothermal vent ecosystem
- Green Algae
- Chemosynthetic Bacteria
- Blue-Green Algae
- Coral reefs
Answer: 2. Chemosynthetic Bacteria
In deep hydrothermal vents, chemosynthetic bacteria are present as there is no light energy available there.
Question 47. Consider the following statements.
- The excess of organic matter is stored by green plants for the utilisation by the herbivores.
- Work energy put by man in agriculture is used in the ecosystem.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
Question 48. Consider the following statements.
- Tertiary consumers are green plants.
- Microconsumers breakdown the dead protoplasm into simpler ones. They are last in the sequence of a food chain.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 1. Statement I is correct, but II is incorrect
Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect. Incorrect statement can be corrected as: Microconsumers breakdown dead protoplasm into simpler ones. They are first in the sequence of detritus food chain.
Question 49. If the primary producers are absent from any ecosystem which of the following will occur?
- Herbivores will not survive
- Carnivores will not survive
- Both will be disintegrated because of food absence
- No change will take place
Answer: 3. Both will be disintegrated because of food absence
In any ecosystem, if all primary producers are absent or removed, there will be reduction in primary productivity and biomass of producers.
No biomass will be available for transfer to next higher trophic levels, i.e. both will be disintegrated because of food absence.
Question 50. Fill up the blanks.
- Other name for herbivores…A… .
- Large …B… feed on secondary consumers.
- Secondary consumers are the source of nutrition for …C… .
- …D…is a network of many food chains.
Choose the correct option.
- A-secondary consumers, B-top predator, C-quaternary, D-Food web
- A-primary consumer, B-predators, C-tertiary consumer, D-Food web
- A-tertiary consumers, B-natural enemies, C-primary consumer, D-Food web
- A-quaternary consumers, B-alligator, C-top consumer, D-Food web
Answer: 2. A-primary consumer, B-predators, C-tertiary consumer, D-Food web
Question 51. Microconsumers are
- Primary Consumers
- Secondary Consumers
- Tertiary Consumers
- Decomposers
Answer: 4. Decomposers
Decomposers are also called microconsumers such as bacteria and fungi. They breakdown the complex organic substances of dead plants and animals to release most of inorganic substances back into the environment for their reuse by the producers.
Question 52. We refer to the following as the food chain.
- Large number of animals near a source of food
- Transfer of food energy from the green plants through a series of consumer organisms
- Large number of human beings forming a human chain near a source of food
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Transfer of food energy from the green plants through a series of consumer organisms
Transfer of food energy from the green plants through a series of consumer organisms is referred to as food chain.
Question 53. First link in any food chain is a green plant because
- Green Plants Can Synthesise Food
- They Can Eat Everything
- Fixed at one place
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Green Plants Can Synthesise Food
Green plants are called producers because they can synthesise food material in the presence of light (autotrophs). Thus, they form a first link in any food chain.
Question 54. Food chain consists of
- Plants
- Herbivores
- Carnivores
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
The food chain consists of producers, consumers and decomposers. Producers are plants. First order (Primary consumers) – Herbivores Third order (Tertiary consumers) – Secondary carnivores
Fourth order (Quaternary consumers) – Top carnivores.
Question 55. Food chain starts with
- N2-fixation
- Germination
- Respiration
- Photosynthesis
Answer: 4. Photosynthesis
Food chain starts with photosynthesis. The green plants always occupy first level in any given food chain and are commonly termed as the primary producers.
Question 56. Which of the following is the most diverse in a food chain?
- Herbivores
- Producers
- Omnivores
- Decomposers
Answer: 2. Producers
Producers are the most diverse in food chains. They are the direct and indirect source of food for all the trophic levels. They are always more in number and form largest population in a food chain.
Question 57. Consider the following statements.
- In a food chain, one organism holds only one position.
- In a food chain, the flow of energy can be easily calculated.
- In food chain, competition is limited to the members of same trophic level.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
Answer: 1. 1, 2 and 3
All given statements are correct. The transfer of energy from producers to top consumers through a series of organisms is called food chain. One organism holds only one position. The flow of energy can be easily calculated. It is always straight and proceeds in a progressive straight line. Competition is limited to the members of same trophic level.
Question 58. Given below are statements about food chain.
- The transfer of energy from producers to top consumers through a series of organisms is called food chain.
- A food chain is always straight and proceeds in a progressive straight line.
- In a food chain, there is unidirectional flow of energy from sun to producers and subsequently to series of different types of consumers.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- Only 2
- Only 3
- 1 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer: 4. 1, 2 and 3
All given statements are correct. A food chain is a sequence of populations or organisms of an ecosystem through which the food and its contained energy passes with each member becoming the food of later member of sequence. It is a single straight pathway through which food energy travels in the ecosystem. Energy flow in an ecosystem is always unidirectional or one way, i.e. Solar radiation → Producers → Herbivores → Carnivores. It cannot pass in the reverse direction.
Question 59. Which food chain correctly describes the flow of energy in an ecosystem?
- Grass → Cow → Human
- Caterpillar → Leaf→ Human
- Cow → Grass → Human
- Rat → Bird → Buffalo
Answer: 1. Grass → Cow → Human
Food chain in option correctly describes the flow of energy in an ecosystem as Producers (Grass) → Herbivores (Cow) → Carnivores (Human)
Question 60. Which one of the following is the food chain operating in ponds, lakes or sea?
- Grass → Insects → Frog → Birds
- Algae → Small animals → Fish → Big fish
- Grass → Dear → Lion
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Algae → Small animals → Fish → Big fish
In ponds, lakes or sea, the operating food chain is Algae → Small animals→ Fish → Big fish
Question 61. The correct sequence of food chain is
- Grass → Insect → Birds → Snake
- Grass → Wolf→ Dear → Buffalo
- Grass → Snake → Insect → Deer
- Bacteria → Grass → Rabbit → Wolf
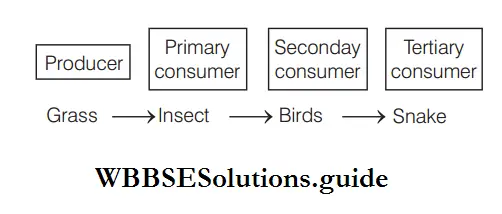
Answer: 1. Grass → Insect → Birds → Snake
The first trophic level in a food chain comprises of producers, i.e. green plants. Second trophic level is occupied by organisms which feed on producers (called herbivores). Third trophic level is occupied by organisms which feed on herbivores (called carnivores). Considering all these points in composing food chain, option represents the correct sequence of food chain, i.e.
Question 62. Which one of the following is a correct food chain?
- Grasshopper → Grass → Snake → Frog → Eagle
- Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Eagle
- Eagle → Snake → Grasshopper → Grass → Frog
- Frog → Snake → Eagle → Grasshopper → Grass
Answer: 2. Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Eagle
Option is a correct food chain as Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Eagle
Question 63. Select the incorrect food chain.
- Grass → Caterpillar → Butterfly → Deer → Lion
- Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Eagle
- Grass → Deer → Lion
- Phytoplankton → Zooplankton → Fish (perch) → Fish (bass) → Man
Answer: 1. Grass → Caterpillar → Butterfly → Deer → Lion
Option represents incorrect food chain because butterfly do not feed upon caterpillar, neither deer eat butterfly. Rest options represents correct food chains.
Question 64. Which of these is correct sequence for food chain?
- Insect → Fish → Zooplankton → Phytoplankton
- Phytoplankton → Zooplankton → Insect → Fish
- Fish → Insect → Zooplankton → Phytoplankton
- Zooplankton → Phytoplankton → Insect → Fish
Answer: 2. Phytoplankton → Zooplankton → Insect → Fish
Option is correct sequence for food chain. Phytoplanktons → Zooplanktons → Insect → Fish
Question 65. Identify the order in which the following organisms occur in a food chain. The organisms are Gerbil, Grass, Kite
- Kite → Grass → Gerbil
- Grass → Kite → Gerbil
- Gerbil → Grass → Kite
- Grass → Gerbil → Kite
Answer: 4. Grass → Gerbil → Kite
Option is the correct order in which the following organisms occur in a food chains as Producers (Grass) → Herbivores (Gerbil) → Carnivores (Hawk or Kite)
Question 66. Identify the possible link ‘A’ in the following food chain Plant → Insect → Frog → ‘A’→ Eagle
- Rabbit
- Wolf
- Cobra
- Parrot
Answer: 3. Cobra
Cobra is ‘A’ because frog is eaten by cobra and inturn, it is eaten by eagle.
Question 67. In grazing food chain, primary source of energy comes from
- Organic Remain
- Sun
- Water
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Sun
Sun is the primary source of energy in grazing food chain.
Question 68. This type of food chain begins with producers at the bottom most trophic level.
- Detritus food chain
- Grazing food chain
- Complex food chain
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Grazing food chain
Grazing Food Chain (GFC) is the most common food chain. In grazing food chain (e.g. grassland ecosystem), green plants (producers) constitute the bottom or first trophic level.
Question 69. In a grazing food chain, carnivores may also be referred to as
- Primary Producers
- Secondary Producers
- Primary Consumers
- Secondary Consumers
- Decomposers
Answer: 4. Secondary Consumers
The consumers that feed on herbivores are called carnivores. These carnivores are primary carnivores (secondary consumers). Those animals that depend on primary carnivores for food are called as secondary carnivores or tertiary consumers.
Primary and Secondary Productivity MCQs for NEET
Question 70. The food chain in which microorganisms breakdown the energy rich compounds is called
- Ecosystem Aiims 1999
- Detritus Food Chain
- Parasitic Food Chain
- Predator food chain
Answer: 2. Detritus Food Chain
Detritus food chain starts from dead organic matter and goes to detritus feeding organisms and on their predators. Such ecosystems are thus, less dependent on direct solar energy. These depend chiefly on the influx of organic matter produced in another system. So, the food chain in which microorganisms breakdown the energy rich compounds is called detritus food chain.
Question 71. Which of the following food chain may not be directly dependent upon solar energy?
- Grazing
- Detritus
- Soaking
- Depleting
Answer: 2. Detritus
Detritus food chain starts from dead organic matter and goes to detritus feeding organisms and on their predators. Such ecosystems are thus, less dependent on direct solar energy. These depend chiefly on the influx of organic matter produced in another system. So, the food chain in which microorganisms breakdown the energy rich compounds is called detritus food chain.
Question 72. The detritus food chain begins with
- Primary Producers J&K Cet
- Primary Consumers
- Secondary Consumers
- Dead organic matter
Answer: 4. Dead organic matter
The dead organic matter of plant or animal is called detritus. While a part of it remains on the soil surface as litter, the other part enters the soil. Many animals such as protozoans, nematodes, insects, etc., depend on detritus and hence, they are called as detritivores. From detritus, the chain proceeds to detritivores, then to carnivores and finally to top carnivores.
Question 73. Detritus food chain obtains energy from
- Organic Remains
- Air
- Radiation
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Organic Remains
In detritus food chain, primary source of energy is dead organic remains of plants and animals.
Question 74. Identify the food chain. Dead animal → Blow fly → Maggots → Common frog → Snake
- Grazing food chain
- Detritus food chain
- Decomposer food chain
- Predator food chain
Answer: 2. Detritus food chain
Detritus food chain begins from dead organic matter like dead remains of plants and animals.
Question 75. Which one of the following shows detritus food chain?
- Fallen leaves → Bacteria → Bivalve → Molluscs
- Small fish → Large fish → Crocodile
- Grass → Grasshopper → Frog
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Fallen leaves → Bacteria → Bivalve → Molluscs
The detritus food chains depend upon the dead organic matter either in the form of fallen leaves, etc., or dead animal bodies. Hence, the correct detritus food chain is Fallen leaves → Bacteria → Bivalve → Molluscs.
Question 76. In a food chain of grassland ecosystem, the top consumers are
- Carnivores
- Herbivores
- Either Carnivores Or Herbivores
- Bacteria
Answer: 1. Carnivores
Because carnivorous are not eaten by others, they are the top consumers.
Question 77. The organisms, which attack dead animals are
- First Link Of The Food Chain And Are Known As Primary Producers
- Second Link The Food Chain And Are Herbivorous
- Third Link Of The Food Chain And Are Tertiary Consumers
- Present at the end of food chain and are detritivores
Answer: 4. Present at the end of food chain and are detritivores
The organisms, which attack dead animals are present at the end of food chain and known as decomposers (detritivores). Decomposers are heterotrophic organisms, mostly bacteria and fungi, which feed on dead organic matter or detritus.
Question 78. In food chain, lion is a
- Primary Consumer
- Tertiary Consumer
- Secondary consumer
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 2
In a food chain, lion can be a secondary or tertiary consumer.
Question 79. During food chain, maximum energy is stored in Punjab, Manipal
- Producer
- Primary Consumer
- Decomposer
- Secondary consumer
Answer: 1. Producer
Producers constitute the first trophic level or base of a food chain. Maximum energy content is present in producers. They obtain the energy from solar radiations.
Question 80. With regard to ecological food chain, man is a
- Producer
- Consumer
- Both 1 and 2
- Producer and decomposer
Answer: 2. Consumer
Man is a consumer because man cannot produce the food himself and he depends on plants (producers) for food.
Question 81. Cow in a food chain represents
- Primary Consumer
- Heterotroph
- Herbivore
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
A primary consumer or herbivore or heterotroph are animals which feed on plants or plant products, e.g. grasshoppers and several other insects, rabbit, hare, field mouse, deer, antelope, cow, elephant, zooplankton, tadpoles and some fishes.
Question 82. Nepenthes is a
- Primary Producer
- Consumer
- Both 1 and 2
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Both 1 and 2
Nepenthes is a chlorophyll containing plant, so it synthesises food by the process of photosynthesis and acts as a primary producer. Because of being an insectivorous plant, it consumes insects like grasshopper and other small insects, so, it is also a consumer.
Question 83. The planktonic forms are
- Autotrophs
- Heterotrophs
- Chemotrophs
- Insectivorous types
Answer: 1. Autotrophs
Planktons are drifting organisms that inhabit the water column of ocean, seas and bodies of freshwater and also shore. So they are autotrophs. Maximum contribution of oxygen is from phytoplankton.
Question 84. Zooplanktons are
- Primary Consumers
- Secondary Consumers
- Tertiary Consumers
- Quaternary consumers
Answer: 1. Primary Consumers
Zooplanktons are the microscopic organisms which exist as drifting organisms suspended in the oceans. These include protozoans, foraminiferans, dinoflagellates, etc. They feed upon phytoplanktons, thus they are primary consumers.
Question 85. The statement, ‘tiger is the apex of the food chain’, indicates
- Tiger Is Carnivore
- Tiger Has Many Enemies
- Tiger Has Maximum Biomass
- Tiger is dependent upon large number of herbivores and even large number of trees
Answer: 1. Tiger Is Carnivore
Tiger is dependent upon large number of herbivores and even more number of trees in forest. Thus, the given statement indicates tiger is carnivore.
Question 86. In the food chain, the saprophytic organisms are
- Producers
- Consumers
- Predators
- Decomposers
Answer: 4. Decomposers
A saprophyte or saprotroph is an organism which gets its energy from dead and decaying organic matter, i.e. decomposers.
Question 87. An organism contains carbon molecules which have passed through three levels of ecosystem. The organism.
- Primary Consumer
- Tertiary Consumer
- Predator
- Producer
Answer: 2. Tertiary Consumer
An ecosystem consists of biotic components like producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers (carnivores) and tertiary consumers and shows energy flow through these levels. Thus, carbon molecules in the form of food reach the level of tertiary consumer through three levels of ecosystem.
Question 88. If phytoplanktons are destroyed in the sea, then
- Algae Will Get More Space To Grow
- Primary Consumers Will Grow Luxuriantly
- It Will Affect The Food Chain
- No effect will be seen
Answer: 3. It Will Affect The Food Chain
Phytoplanktons are the main producers in the sea. The entire food chain depends upon production of food by the phytoplanktons. Thus, if phytoplanktons are destroyed in the sea, then it will affect the food chain adversely.
Question 89. When man eats fish which feeds on zooplanktons which have eaten small plants, the producer in the chain.
- Zooplanktons
- Small Plants
- Fish
- Man
Answer: 2. Small Plants
Small plants are producers in the food chain, these can prepare their food by the process of photosynthesis. Whereas, zooplanktons, fish and man are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, respectively
Question 90. In grass-deer-tiger food chain, grass biomass is one tonne. The tiger biomass shall.
- 100 kg
- 10 kg
- 200 kg
- 1 kg
Answer: 2. 10 kg
Only 10% of the mass is transferred from one trophic level to another in the form of energy. Thus in given food chain, the biomass of tiger shall be 10 kg.
Question 91. A lion eats a zebra that feeds on grass. The lion here is a
- Primary Producer
- Primary Consumer
- Secondary Consumer
- Quaternary Consumer
Answer: 3. Secondary Consumer
Producers (Grass) → Primary consumers (Zebra) → Secondary consumers (Lion)
Question 92. In an ecosystem, insectivorous plants are considered as
- Herbivorous
- Primary Producers
- Predators
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 2. Primary Producers
Insectivorous plants are autotrophs (primary producers) as they have chlorophyll. They do not eat insects for food, but use them as a source of nitrogen and phosphorus and use light to transform them into biomolecules.
Question 93. When frog eats grasshopper which thrives on green plants, the frog is
- Primary Producer
- Herbivore
- Primary Carnivore
- Top consumer
Answer: 3. Primary Carnivore
Primary consumer directly depends on the producer for food source. Secondary consumers include different organisms that feed on primary consumers (primary carnivore). Thus, when frog eats grasshopper (primary consumer) which thrives on green plants (producer), the frog is primary carnivore.
Question 94. If a big fish eats small fish which eats Hydra which in turn eats water fleas. Water fleas in turn eat phytoplaktons. In this chain, water fleas will be
- Producers
- Primary Consumers
- Secondary Consumers
- Top consumer
Answer: 2. Primary Consumers
In this food chain, water flea is primary consumers.
Question 95. In a food chain consisting of bear, algae, bugs and fish, the bear is a
- Tertiary Consumer
- Primary Consumer
- Secondary Consumer
- Primary producer
Answer: 1. Tertiary Consumer
Producers (Algae) → Primary consumers (Bugs) → Secondary consumers (Fish) → Tertiary consumers (Bear)
Question 96. Rabbits depend only on grass and other plants for survival. Hence, they are
- Decomposers
- Carnivores
- Producers
- Herbivores
Answer: 4. Herbivores
Herbivores (plant-eating animals) depend upon producers (plant) so, rabbits are herbivores.
Question 97. A wolf has just eaten a lamb. When tiger saw the wolf, it attacked and consumed it. The tiger in ecological terms is
- A Producer
- A Primary Consumer
- A Secondary Consumer
- A tertiary consumer
Answer: 4. A tertiary consumer
Grass(Producer) → Lamb (Primary consumer) → Wolf (Secondary consumer) → Tiger (Tertiary consumer)
Question 98. What will a man, who survives by feeding on both plants and animals and also consumes a primary consumer, be referred to as?
- Primary producer
- Primary consumer
- Secondary consumer
- Quaternary consumer
Answer: 3. Secondary consumer
Producers (Grain) → Primary consumers → Secondary consumers (Chicken). Thus, a man who survives by feeding on both plants and animals and also consumes a primary consumer, be referred to as secondary consumer.
Question 99. A purely vegetarian person acts as a
- Primary Producer
- Primary Consumer
- Secondary Consumer
- Tertiary consumer
Answer: 2. Primary Consumer
Primary consumers in an ecosystem are herbivores, which feed directly on producer (green plants). Thus, a purely vegetarian person acts as a primary consumer.
Question 100. Which one of the following is a primary consumer in maize field ecosystem?
- Lion
- Grasshopper
- Wolf
- Phytoplankton
Answer: 2. Grasshopper
In an ecosystem, producers (e.g. plants/ phytoplankton) belong to first trophic level, herbivores or primary consumer (e.g. grasshopper) to the second and carnivores or secondary consumer (e.g. lion, wolf) to the third trophic level.
Question 101. A snake feeding on a rat.
- Tertiary Consumer And Secondary Carnivore
- Primary Consumer And Herbivore
- Secondary Consumer And Primary Carnivore
- Primary consumer and secondary carnivore
Answer: 3. Secondary Consumer And Primary Carnivore
A primary consumer directly depends on the producer for food source. Secondary consumers include different organisms that feed on primary consumers. A snake eating a rat is an example of a secondary consumer (primary carnivore)
Question 102. Given flowchart represents grazing and detritus food chains. Grazing food chain : Grass → Rabbit → Lion Detritus food chain: Dead leaves → Woodlouse → Black bird The first trophic level of the grazing food chain and the detritus food chain respectively, are occupied by
- Grass And Dead Leaves
- Grass And Woodlouse
- Rabbit And Woodlouse
- Rabbit and black bird
Answer: 1. Grass And Dead Leaves
In grazing food chain, green plants or grass (producers) constitute the first trophic level. In detritus food chain, dead leaves constitute the first trophic level.
Question 103. Consider the following statements about grazing food chain.
- It starts with green plant called producers as first trophic level.
- Energy for grazing food chain comes from organic remain or detritus.
- A much less fraction of energy flows through this type of food chain in terrestrial ecosystem.
Which of the following statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer: 2. 1 and 3
Statements I and III are correct whereas statement II is incorrect. In grazing food chain, green plants (producers) constitute the first step (trophic level). A much less fraction of energy flows through this type of food chain in terrestrial ecosystem. Incorrect statement can be corrected as : dependent on influx from solar radiations for energy.
Question 104. Consider the following statements with regarding detritus food chain.
- Begins with dead organic matter and decomposers at the first trophic level.
- Large fraction of energy flows in this type of food chain in a terrestrial ecosystem.
- Energy for detritus food chain comes from sun.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer: 1. 1 and 2
Statements 1 and 2 are correct. Statement 3 is incorrect because, the detritus food chain depend upon the dead organic matter. A much large fraction of energy flows through this type of food chain. Energy for detritus food chains comes from organic remains or detritus.
Question 105. The bacteria which attack dead animals are
- First Link Of The Food Chain And Are Known As Primary Producers
- Second Link Of The Food Chain And Are Herbivorous
- Third Link Of The Food Chain And Are Tertiary Consumers
- The end of food chain and are decomposers
Answer: 4. The end of food chain and are decomposers
Bacteria attacking the dead animals represent the end of the food chain and are decomposers. These are the organisms that obtain energy from chemical breakdown of organisms.
Question 106. If all the decomposers are eliminated from food chain then which of the following is the incorrect option for given statement?
- Enhancement of mineral cycles
- Stoppage of decomposition of organic matter
- Imbalance in environment
- Stoppage of energy flow
Answer: 1. Enhancement of mineral cycles
Option is incorrect for given statement and can be corrected as Decomposers are also known as mineralisers as they release minerals trapped in organic remains. So, in the absence of microorganisms, the flow of mineral will stop. Rest options are correct for given statement.
Question 107. Consider the following statements concerning food chains.
- Removal of 80% tigers from an area resulted in great increase in growth of vegetation.
- Removal of most of the carnivores resulted in an increased population of deer.
- The length of the food chains is generally limited to 3-4 trophic levels due to energy loss.
- The length of the food chains may vary from 2-8 trophic levels.
Which of the above statements are correct?
- 1 and 4
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 3 and 4
Answer: 3. 2 and 3
Statements 2 and 3 are correct concerning food chains : Statements I and IV are incorrect and can be corrected as Removal of 80% tigers (i.e. tertiary consumer) from an area would result in decreased growth of vegetation because there will be increased numbers of secondary or primary consumers which feed on green plant. The length of food chains is limited to 3-4 trophic levels.
Question 108. There are mainly three types of food chains in natural ecosystems, i.e. grazing food chain, detritus food chain and parasitic food chain. In which of the ecosystem will you observe grazing food chain?
- Pond ecosystem
- Terrestrial ecosystem
- Ocean ecosystem
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
In a grazing food chain, energy is acquired, via photosynthesis through producers. In all the listed ecosystems, grazing food chain observed.
Question 109. Which of the following statements regarding food chain is false?
- In an aquatic ecosystem, grazing food chain is the major conduit for energy flow
- In terrestrial ecosystems, a large fraction of energy flows through detritus food chain
- The detritus food chain begins with dead organic matter
- Primary consumers belong to the first trophic level
- Animals like cockroaches and crows are omnivores
Answer: 2. In terrestrial ecosystems, a large fraction of energy flows through detritus food chain
Statement in option 4 is false regarding food chain and can be corrected as The primary consumers or herbivores belong to the second trophic level. Rest statements are true regarding food chain.
Question 110. Select the option that correctly identifies A, B and C in the given table.
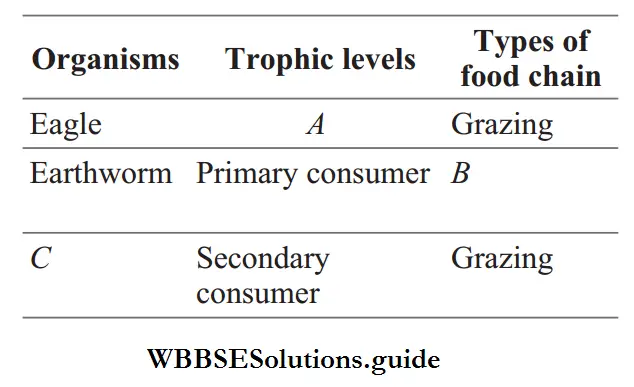
- A–Secondary consumer, B–Grazing, C–Algae
- A–Top carnivore, B–Detritus, C–Frog
- A–Scavenger, B–Grazing, C–Hawk
- A–Decomposer, B–Detritus, C–Perch
Answer: 2. A–Top carnivore, B–Detritus, C–Frog
Question 111. Match the names of organisms given under Column I with the ecological names given under Column II. Choose the correct option from the codes given below
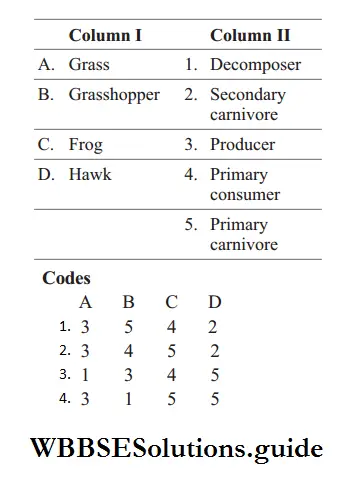
Answer: 3. 1 3 4 5
Question 112. The biomass of tiger is 10 kg in food chain. grass → deer → tiger, The grass biomass will be
- 100 kg
- 2000 kg
- 1 tonn
- 20 tons
Answer: 3. 1 tonn
According to 10% law, in the following food chain, grasses, deer tiger, if tiger have 10 kg biomass then deer will have 10 time more of this and grasses will have 10 times more of deer’s biomass. Thus, grass would have 1 tonn or 1000 kg of biomass.
Question 113. In an ecosystem, an organism occupies a specific place in a food chain called
- Branching lines
- Progressive straight line
- Trophic level
- Standing crop
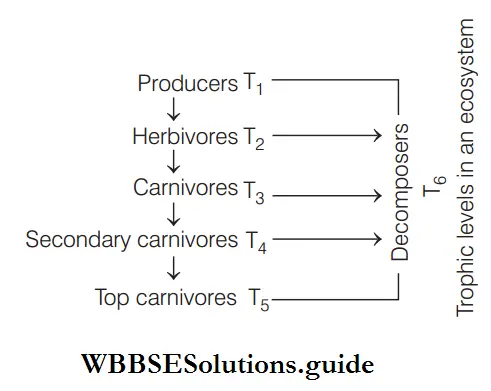
Answer: 3. Trophic level
Trophic level is a step or division of food chain which is characterised by the method of obtaining its food. The number of trophic levels is equal to the number of steps in a food chain.
Question 114. Organisms are classified into trophic levels based on their
- Habitat
- Source Of Nutrients
- Weight
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Source Of Nutrients
Organisms are classified into trophic levels according to the source of their nutrients.
Question 115. Generally, the food chain has how many trophic levels?
- One
- Two
- Four
- Three
Answer: 3. Four
Plants represent the first trophic level and the herbivores make the second trophic level. The primary carnivores constitute the third trophic level and the secondary carnivores, such as large fish, man, etc., constitute the fourth trophic level of an ecosystem. So, the food chain has four trophic levels.
Question 116. The number of trophic levels in a food chain is limited to 4 or 5 because
- The Amount Of Food Produced By Producer Is Limited
- Consumer’s demand is high
- 90% of the food energy is lost as heat at each transfer between trophic levels
- Activity of decomposer is poor
Answer: 3. 90% of the food energy is lost as heat at each transfer between trophic levels
The number of trophic levels in a food chain is limited to 4 or 5 because 90% of the food energy is lost as heat at each transfer between trophic levels.
Question 117. The first trophic level in any kind of food chain is always a green plant because
- Of Their Wide Distribution
- They Alone Have A Capacity To Fix Atmospheric Co2, In The Presence/Absence Of Sunlight
- Their Richness In Chlorophyll
- Their capacity to convert light energy to chemical energy
Answer: 4. Their capacity to convert light energy to chemical energy
Trophic level is the specific place occupied by an organism in a food chain on the basis of its source of nutrition or food. Primary producers (green plants) belong to the first trophic level. They have prepare the food by photosynthesis by utilising radiant energy of sun, i.e. they have capacity to convert light energy to chemical energy.
Question 118. Each tropical level has a certain mass of living material at a particular time called
- Standing Crop
- Biomass
- Standing state
- None of these
Answer: 1. Standing Crop
Each trophic level has a certain mass of living material at a particular time called the standing crop. The standing crop is measured as the biomass of living organisms, as the number in a unit area.
Question 119. Standing crop means
- Amount Of Biomass Per Unit Area
- Energy Trapped By Producers
- Rate Of Energy Produced By Consumers
- Quantity of solar energy
Answer: 1. Amount Of Biomass Per Unit Area
Standing crop is the amount of living biomass per unit area present in an ecosystem.
Question 120. The trophic level of S-bacteria and cyanobacteria is
- Producer
- Consumer
- Saprotrophic Decomposer
- Primary consumer
Answer: 1. Producer
S-bacterium is chemosynthetic bacterium and cyanobacteria is a group of photosynthetic protists which can synthesise their own food material, i.e. producer.
Question 121. The second trophic level of longer food chains in a lake is
- Phytoplankton
- Zooplankton
- Benthos
- Fishes
Answer: 2. Zooplankton
The second trophic level of longer food chains in a lake is occupied by primary consumers or zooplankton.
Question 122. Snake generally belongs to
- Saprophytes Up Cpmt
- Primary Consumer
- Second trophic level
- None of the above
Answer: 4. None of the above
Snakes are the secondary consumers. Herbivores belong to
second trophic level and called as primary consumer. So, all the given options do not belong to snake.
Question 123. In trophic level, herbivore animal occupies which trophic level?
- 1st
- 2nd
- Intermediate
- 3rd
Answer: 2. 2nd
Herbivores are primary consumers and occupy the second trophic level. They are mainly dependent on the plants at first trophic level for their food needs.
Question 124. If bamboo plant is growing in a far forest then what will be its trophic level?
- First
- Second
- Third
- Fourth
Answer: 1. First
Bamboo is a plant, which can produce its own food. It occupies a first trophic level.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 125. In terrestrial ecosystem such as forest, maximum energy is found in which trophic level?
- T1
- T2
- T3
- T4
Answer: 1. T1
Maximum energy is found in first trophic level (T1 ), i.e. producers.
Question 126. Which of the following organisms occupy more than one trophic level in an ecosystem?
- Zooplankton
- Phytoplankton
- Frog
- Earthworm
Answer: 3. Frog
A single species may occupy more than one trophic level. Frog can be primary consumer as newly hatched tadpoles are mainly herbivores feeding on algae, detritus and plants. They become secondary consumers once their back legs develop.
They become fully carnivorous feeding on small water animals or even other tadpoles when food is scarce. So, frog occypy more than one trophic level in an ecosystem. Phytoplanktons are producers only which occupy first trophic level, zooplanktons which feed on phytoplanktons, occupy second trophic level and earthworm being detritivore occupy second trophic level in detritus food chain.
Question 127. Which one of the following animals may occupy more than one trophic level in the same ecosystem at the same time?
- Sparrow
- Lion
- Goat
- Frog
Answer: 1. Sparrow
Sparrow feeds upon grains hence called primary consumer and can also feed on insects, hence called secondary consumer at the same time in the same ecosystem.
Question 128. Which one of the following types of organisms occupy more than one trophic level in a pond ecosystem?
- Frog
- Phytoplanktons
- Fish
- Zooplanktons
Answer: 3. Fish
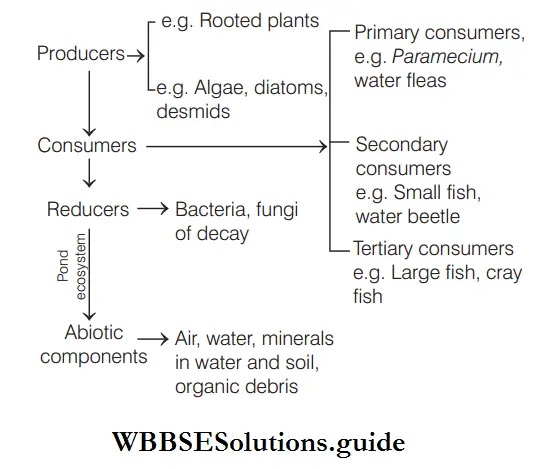
Fish occupy more than one trophic level in a pond ecosystem. A pond ecosystem is a delicate balance of fish, plants and other animals. Small fishes act as secondary consumer. They feed on primary consumer. Large fishes act as tertiary consumer. They feed on smaller fish.
Question 129. Mr. X is eating curd/yoghurt. For this food intake in a food chain he should be considered as occupying
- First Trophic Level Aiims
- Second Trophic Level
- Third Trophic Level
- Fourth trophic level
Answer: 3. Third Trophic Level
Mr. X eating curd/yoghurt should be considered as occupying third trophic level. Producers or green plants (first trophic level) are consumed by herbivore (second trophic level) and from them curd/ yoghurt (made from dairy breed) is derived. Thus, option is correct.
Question 130. In an aquatic ecosystem, the trophic level equivalent to cows in grasslands
- Phytoplanktons
- Zooplanktons
- Nektons
- Benthos
Answer: 2. Zooplanktons
In an aquatic ecosystem, the trophic level equivalent to cows in grasslands is zooplankton. They both occupy the second trophic level.
Question 131. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
- Biomass decreases from the first to fourth trophic level
- Energy content gradually increases from the first to the fourth trophic level
- The number of individuals decreases from the first trophic level to the fourth trophic level
- Energy content gradually decreases from the first to the fourth trophic level
Answer: 2. Energy content gradually increases from the first to fourth trophic level
The statement in the option is incorrect and can be corrected as The energy content decreases from the first (producer) to the fourth (consumer) trophic level. At each level, about 90% of energy is lost and only 10% is passed to the next level. The rest of other statements are correct.
Food Chain, Food Web, and Energy Pyramid MCQs for NEET
Question 132. Match Column I in trophic levels with Column II in their correct species examples in the grassland ecosystem. Select the correct option from the codes given below.
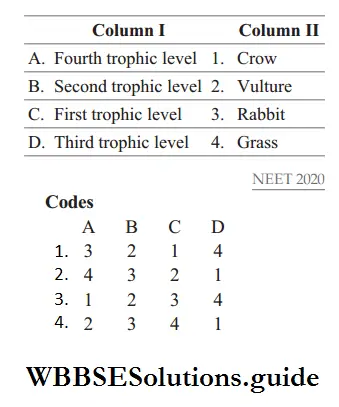
Answer: 4. 2 3 4 1
Question 133. Assertion Trophic levels are only observed in the plant kingdom. Reason (R) Food chains and webs are formed due to linked organisms on basis of their nutrition.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is false, but R is true
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 3. A is false, but R is true
A is false, but R is true. Assertion can be corrected as Trophic levels are observed in both plant and animal kingdoms.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 134. In an ecosystem, which one shows ‘one-way passage’?
- Free energy
- Carbon
- Nitrogen
- Potassium
Answer: 1. Free energy
The behaviour of energy in the ecosystem can be termed as unidirectional flow, i.e. from solar radiation → producers → herbivores → carnivores. This energy cannot pass in the reverse direction. There is decrease in the content and flow of energy with rise in trophic level. Thus, free energy shows one way passage in an ecosystem.
Question 135. Relationships between different organisms can be best described by
- Food Web Dpmt 2001
- Pyramid Of Energy
- Pyramid of mass
- Eltonian pyramids
Answer: 1. Food Web Dpmt 2001
A food web is a network of food chains which become interconnected at various trophic levels, so as to form a number of feeding connections among the different organisms of a biotic community.
Question 136. Assertion A network of food chains existing together in an ecosystem is known as a food web. Reason (R) An animal like kite cannot be a part of a food web.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 3. A is true, but R is false
A is true, but R is false. Reason can be corrected as In the grazing food chain, the producers. (i.e. plants) are eaten by herbivores (i.e. rodents) and they are further eaten by carnivores, i.e. kite. Kites also eat small insects, snails, etc. Thus, kite can be a part of food web also.
Question 137. In a food web, each successive trophic level has
- Increased Total Energy
- More Total Energy
- Less Total Energy
- Non-estimated energy content
Answer: 3. Less Total Energy
In a food web, each successive trophic level has less total energy content. This is due to the reason that when energy is transferred from one level to the next, some energy is lost as heat to the environment.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 138. Extinction of a species in a food chain is compensated by
- Food Chain Up Cpmt 2007
- Ecological Pyramid
- Food web
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Food web
Food webs provide stability to the ecosystem. Most animals are polyphagous, i.e. they feed on more than one kind of organisms. If the population of a species decreases to an endangered level, its predators shift to another prey and the endangered species may get a chance to recover its population. Thus, extinction of species in a food chain is compensated by food web.
Question 139. A food web is more realistic than a food chain to depict feeding relationships. The reason for this is because
- It Compares The Number Of Consumers To The Number Of Microorganisms In An Ecosystem
- Food Chains Use Only A Small Sampling Of Organisms
- A Food Web Explains Why There Are More Producers Than Consumers
- Producers are usually eaten by different consumers and most consumers are eaten by more than one predator
Answer: 4. Producers are usually eaten by different consumers and most consumers are eaten by more than one predator
Food webs are more realistic because they show that the producers are usually eaten by many different consumers and most consumers are eaten by more than one predator. In contrast, food chain consider only one orgainsm being eaten by another.
Question 140.
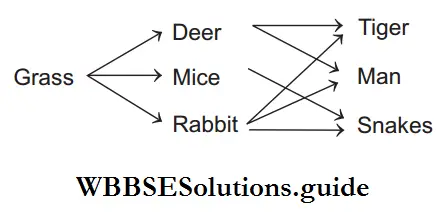
The above diagram represents
- Food Chain
- Food Web
- A Population
- Ecosystem
Answer: 2. Food Web
The given diagram represents a food web.
Question 141. If a single plant species is removed from a food web, then most likely.
- An Animal Species Will Fill The Unoccupied Niche
- Other Plants Will Produce Enough Food For Herbivores
- Dependent Herbivores Will Have To Find New Food Sources
- Carnivores will be unaffected by the loss
Answer: 3. Dependent Herbivores Will Have To Find New Food Sources
Herbivores are primary consumers, they are mainly dependent on the plants for their food needs. If a single plant species is removed, then they have to find new or other food sources.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 142. Consider the following statements about food web.
- One organism in a food chain can hold more than one position.
- The flow of energy is very difficult to calculate.
- A food chain can consist of branching lines too.
- Competition is amongst the members of same and different trophic levels.
Choose the option containing correct statements.
- 2 and 3
- 1, 3 and 4
- 2 and 4
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: 4. 1, 2, 3 and 4
All the given statements are correct.
Question 143. Identify the likely organisms (1), (2), (3) and (4) in the food web shown below.
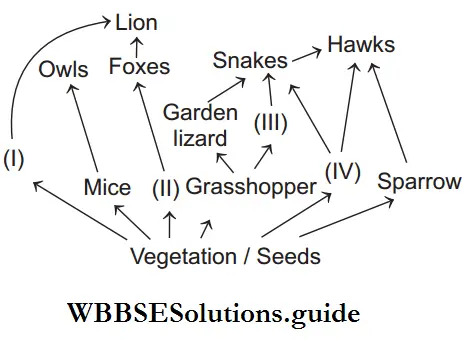
- Deer Rabbit Frog Rat
- Dog Squirrel Rat Deer
- Rat Dog Tortoise Crow
- Squirrel Cat Rat Pigeon
Answer: 1. Deer Rabbit Frog Rat
1-Deer, 2-Rabbit, 3-Frog, 4-Rat
Question 144. Identify A, B and C in the given flowchart.
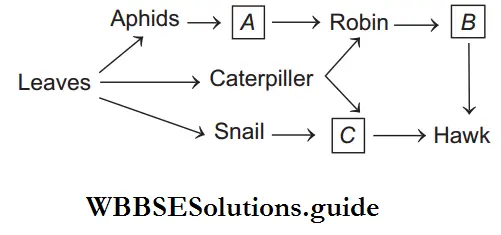
- A–Bulbul, B–Snake, C–Monkey
- A–Beetle, B–Lizard, C–Praying mantis
- A–Ladybird, B–Snake, C–Pigeon
- A–Lizard, B–Bird, C–Snake
Answer: 2. A–Ladybird, B–Snake, C–Pigeon
Leaves → Aphids → Ladybird → Robin → Snake → Hawk. Leaves → Snail → Pigeon → Hawk
Question 145. Given below is the diagram of a food web.
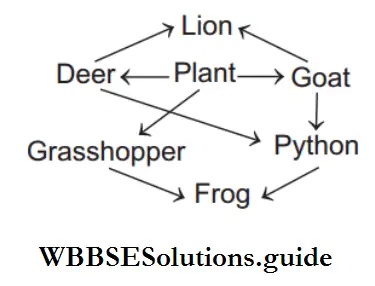
What is incorrect in the above diagram?
- Goats feeding on plants
- Deer and goat both occupying the same level in the trophic level
- Frog consuming python
- Lion being a carnivore
Answer: 3. Frog consuming python
Plant → Deer → Python Plant → Grasshopper → Frog Plant → Goat → Lion Plant → Goat → Python Plant → Deer → Lion Plant → Grasshopper → Frog → Python Thus, option is incorrectly shown in the diagram.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 146. Given food web contains some missing organisms A, B, C and D.
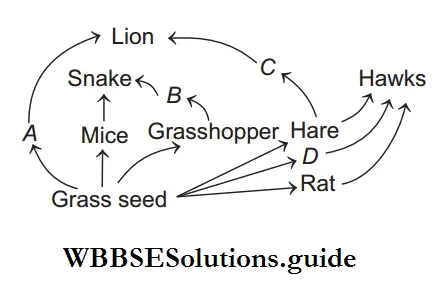
Identify these organisms and select the correct option.
- A–Deer, B–Frog, C–Foxes, D–Sparrow
- A–Dog, B–Squirrel, C–Deer, D–Hawks
- A–Cat, B–Eagle, C–Cow, D–Rat
- A–Eagle, B–Sparrow, C–Dog, D–Cat
Answer: 1. A–Deer, B–Frog, C–Foxes, D–Sparrow
Question 147. Study the food web given below and answer the questions that follows.
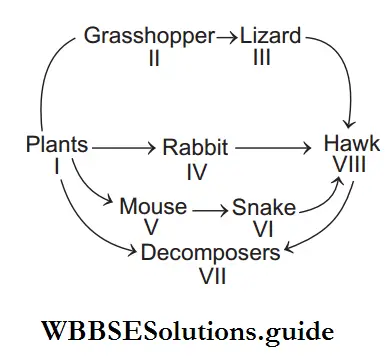
1. Which organisms act as secondary consumers?
2. Which organisms acts as primary consumers?
- 1 and 4 ; 1, 2 and 3
- 5 and 4; 2, 3 and 4
- 3 and 4 ; 2, 4 and 5
- 4 and 7 ; 6, 7 and 8
Answer: 3. 3 and 4 ; 2, 4 and 5
Secondary consumers are those which feed on primary consumers, i.e. carnivores. Primary consumers are animals, which feed directly on plants, i.e. herbivores.
- Lizard (3) and snake (4) act as secondary consumers.
- Grasshopper, (2) rabbit (4) and mouse (5) act as primary consumers.
Thus, option is correct.
