NEET Biology Mcq Mendelism
Question 1. Principle or laws of inheritance were enunciated by
- Mendel
- Morgan
- Bateson
- Punnett
Answer: 1. Mendel
Principle or laws of inheritance were enunciated by Mendel. There are four principles or laws of inheritance based on monohybrid and dihybrid cross.
Question 2. Under which topic, Mendel’s work was published in ‘Natural History Society of Brunn’?
- Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance
- Experiments in Plant Hybridisation
- Experiment on Heredity and Variation
- Origin of Species
Answer: 2. Experiments in Plant Hybridisation
“genetics questions “
Mendel’s paper ‘Experiments on Plant Hybridisation’ was published in proceedings of Natural Science Society of Brunn in 1866.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 3. Mendel’s findings were rediscovered by
- De Vries
- Correns
- Tschermak
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
In 1900, three workers independently rediscovered the principles of heredity already worked out by Mendel. These workers were Hugo de Vries (Holland), Carl Correns (Germany) and Erich von
Tschermak (Austria).
Thus, option 4 is correct.
NEET Biology Mcq

NEET Biology Mendelism MCQs with answers
Question 4. Mendel’s law were true for situation in which
- Alleles are affected by their environment
- Alleles show complete dominance
- Alleles of a gene alter the affect of a different gene
- A given character is determined by more than one gene
Answer: 2. Alleles show complete dominance
Mendel’s law were able to predict accurately the pattern of inheritance for a situation in which alleles show complete dominance. Effect of the environment, other alleles, etc., were not explained by the Mendel. He was not aware of polygenic traits also.
“questions about genetics “
Question 5. Which of the following are the laws yielded by Mendel’s studies?
- Law of dominance
- Law of segregation
- Law of independent assortment
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Mendel’s studies yielded three laws of inheritance, i.e. the law of dominance, the law of segregation and the law of independent assortment. Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 6. It was during Mendel’s investigation that ….A…. and …..B….. were applied together in biology.
Choose the correct set of answers.
- A–statistical analysis, B–mathematical logic
- A–statistical analysis, B–physical logic
- A–statistical analysis, B–chemistry logic
- A–statistical analysis, B–genetic coding
Answer: 1. A–statistical analysis, B–mathematical logic
During Mendel’s investigation, statistical analysis (A) and mathematical logic (B) were applied
together in biology.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 7. Which one from those given below is the period for Mendel’s hybridisation experiments?
- 1856-1863
- 1840-1850
- 1857-1869
- 1870-1877
Answer: 1. 1856-1863
Mendel conducted hybridisation experiments on pea plant for 7 years between 1856 -1863 and his data was published in 1865.
Important MCQs on Mendelism for NEET
Question 8. Mendel conducted hybridisation experiments on garden peas for
- 7 years
- 6 years
- 5 years
- 4 years
Answer: 1. 7 years
Question 9. Choose the correct statement.
- Mendel died in 1884 without getting any recognition during his lifetime
- Correns converted two generalisations of Mendel into two laws of heredity
- Mendel had maintained statistical records of all the experiments
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
All the given statements are correct.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 10. During the experiments, Mendel called genes by the term
- Traits
- Characters
- Factors
- Qualities
Answer: 3. Factors
- Mendel proposed that inheritance is controlled by paired germinal units or factors, now called genes. They are present in all cells of the body and are transferred to the next generation
through gametes. - Factors or genes are thus, physical basis of heredity. They represent small segments of chromosomes.
Question 11. The botanical name of garden pea is
- Pisum sativum
- Lathyrus odoratus
- Mangifera indica
- Solanum tuberosum
Answer: 1. Pisum sativum
The botanical name of garden pea is Pisum sativum. It is herbaceous annual plant of the family–Fabaceae.It is grown virtually worldwide for its edible seeds.
Question 12. The experimental material in Mendel’s experiment was
- Pisum sativum
- Oryza sativa
- Mirabilis jalapa
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Pisum sativum
Gregor Johann Mendel conducted hybridisation experiments on garden pea (Pisum sativum) and proposed the laws of inheritance in living organisms.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 13. Pollination type adopted by Mendel in his experiment.
- Artificial pollination
- Cross pollination
- Natural pollination
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 2
Mendel conducted artificial pollination/cross-pollination using true breeding pea lines. A true breeding line is one that have undergone continuous self-pollination, shows stable trait inheritance and expression for several generation. Thus, option is correct.
Question 14. Mendel investigated characters in garden pea plant that were manifested in two ……………… trait.
- Similar
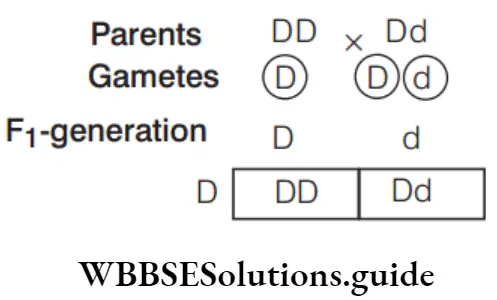
- Non-zygote
- Identical
- Opposite
Answer: 4. Opposite
Mendel investigated those characters in garden pea that were mainfested as two opposite traits, one was dominant and other one was recessive.
Question 15. Mendel was lucky to work on pea plants for his experiment because
- Pea flowers are normally self-pollinated, but can be readily cross pollinated
- There are several varieties in peas with observable alternative form of a trait
- The selected seven characters in the experiment are located on the same chromosome
- The selected seven characters were located on different chromosomes
Answer: 4. The selected seven characters were located on different chromosomes
- Mendel worked on garden pea. He choose only those characters which showed consistent results. He worked on seven characters.
- These characters showed complete independent assortment despite the seven characters chosen by him were present on four different chromosomes, i.e. 1, 4, 5 and 7.
“genetic questions “
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET Question 16. The number of contrasting characters studied by Mendel for his experiments was
- 14
- 4
- 2
- 7
Answer: 1. 14
Mendel selected 7 pairs or 14 characters of true breeding pea plant varieties for his experiment.
Question 17. Mendel’s laws of inheritance are applicable only for
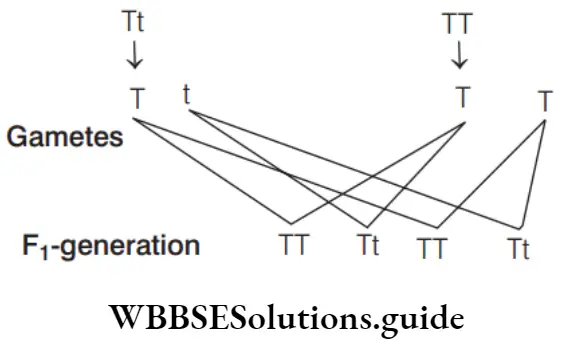
- Protista
- Monera
- Diploid organism
- Haploid organism
Answer: 3. Diploid organism
- Mendel’s laws of inheritance are applicable for the organisms, which are multicellular and diploid and form haploid gametes during sexual reproduction.
- This law is applicable to organism having single gene pair containing two alleles, one dominant over the other. Protista and Monera, both are the unicellular organisms.
Question 18. Which of the following is correct about Mendel’s statement?
- 7 characters, 7 pair traits
- 7 paired characters, 7 traits
- 7 characters, 7 traits
- 7 pair characters, 7 pair traits
Answer: 2. 7 paired characters, 7 traits
Mendel conducted cross breeding experiments on garden pea (Pisum sativum). He studied the inheritance of 7 different pairs of contrasting characters or 7 traits in this plant, but considered only one pair at a time.
Question 19. Which one of the following traits of garden pea studied by Mendel was a recessive feature?
- Green pod colour
- Round seed colour
- Axial flower position
- Green seed colour
Answer: 4. Green seed colour
Recessive traits studied by Mendel were are wrinkled seed coat, green seed colour, white flower colour, constricted pod shape, yellow pod colour, terminal flower position, dwarf stem height.
Mendelian genetics MCQs for NEET with solutions
Question 20. The colour based contrasting traits in seven contrasting pairs, studied by Mendel in pea plant were
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer: 3. 3
Out of the seven pairs of contrasting traits studied by Mendel in pea plants, yellow seed colour, violet flower colour, green pod colour were three colour based traits.
Question 21. Mendel selected Pisum sativum for his experimental investigations among various plants available in the Monastery garden. Which of the following can be a reason for this?
- It has a short life cycle
- It has distinctive, contrasting traits like tall and dwarf plant
- It easily undergoes self-pollination
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
- Mendel selected Pisum sativum due to following features Pure varieties of pea are available.
Pea plants show a number of easily detectable contrasting characters. - The flower structure of pea allow controlled breeding. Pea flower normally remains closed and undergoes self- pollination. It is an annual plant with short lifespan and gives result within 3 months. A large number of seeds are produced per plant.
- The plant is grown easily and does not require after-care except at the time of pollination. Though pea plant is self- pollinated, but it can be cross breed manually. F1 hybrids are fertile.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 22. Mendel studied seven pairs of contrasting characters for his breeding experiment with Pisum sativum. Which of the following characters were not considered for his experiment?
- Pod shape
- Leaf shape
- Plant height
- Pod colour
Answer: 2. Leaf shape
“gene questions “
The seven pairs of contrasting characters studied by Mendel were Tall or dwarf nature of plants Axillary or terminal flowers Green or yellow coloured pods Smooth or wrinkled seed shape Inflated or constricted pods Yellow or green seed colour White or violet flowers. Thus, he did not considered leaf shape.
Question 23. Among the following characters, which one was not considered by Mendel in his experiments on pea?
- Stem – Tall or dwarf
- Trichomes – Glandular or non-glandular
- Seed – Green or yellow
- Pod – Inflated or constricted
Answer: 2. Trichomes – Glandular or non-glandular
Nature of trichomes, i.e. glandular or non-glandular was not considered by Mendel. Whereas stem, seed and pod were considered.
Question 24. Which character was dominant among the 7 characters in Mendel’s experiment?
- Plant height–Dwarf
- Flower position–Terminal
- Pod colour–Green
- Seed colour–Green
Answer: 3. Pod colour–Green
Among the given options, green pod colour is dominant, whereas the other three are recessive traits.
Characters >Dominant traits > Recessive traits Seed shape > Round > Wrinkled Seed colour >Yellow > Green Flower colour >Violet >White Pod shape >Full or inflated > Constricted Pod colour > Green >Yellow Flower position >Axial >Terminal Stem height > Tall >Dwarf
Question 25. According to Mendelism which character shows dominance?
- Terminal position of flower
- Green colour in seed coat
- Wrinkled seeds
- Violet flower colour
Answer: 4. Violet flower colour
Question 26. Mendel was successful in discovering the principles of inheritance as
- He took pea plants for his experiments
- He did not encounter linkage between the genes for the characters, he considered
- He had in depth knowledge on hybridisation
- He was a famous mathematician
Answer: 2. He did not encounter linkage between the genes for the characters, he considered
Mendel took only those traits for his studies which did not show linkage, interaction or incomplete dominance. Mendel was lucky in selecting those traits whose genes did not interact. They were either present on different chromosomes or showed complete recombination.
Question 27. Mendel, while studying the garden pea (Pisum sativum) observed its seven traits. Which one does not match with its dominant character?
- Flower colour–Purple
- Flower position–Axial
- Pod colour–Yellow
- Seed shape–Round
Answer: 3. Pod colour–Yellow
Option does not match with its dominant character because yellow pod colour is a recessive character. Rest options represents the correct match with their dominant characters.
Question 28. Some of the dominant traits studied by Mendel were
- Round seed shape, constricted pod shape and axial flower position
- Green pod colour, inflated pod shape and axial flower position
- Yellow seed colour, violet flower colour and yellow pod colour
- Axial flower position, green pod colour and green seed
Answer: 2. Green pod colour, inflated pod shape and axial flower position
Question 29. The genes controlling the seven pea characters studied by Mendel are now known to be located on how many different chromosomes?
- Seven
- Six
- Five
- Four
Answer: 4. Four
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 30. Which of the following statements is not correct about pea plant?
- It is a plant with short annual life cycle
- Flowers are unisexual and cross pollinating
- They can undergo easy emasculation
- The offspring produced by cross-pollination are fertile
Answer: 2. Flowers are unisexual and cross pollinating
Statement in option is not correct and can be corrected as Flowers of pea plant are bisexual and self-pollinating. Rest statements are correct about pea plant.
Question 31. Mendel’s contribution for genetic inheritance was
- The idea that genes are found on chromosomes
- Providing a mechanism that explains patterns of inheritance
- Describing how genes are influenced by the environment
- Determining that the information contained in DNA codes for proteins
Answer: 2. Providing a mechanism that explains patterns of inheritance
Mendel gave the laws of inheritance, which provides the mechanism that explains the pattern of inheritance.
Question 32. In Mendel’s studies, inflated pod of pea is a/an
- Dominant character
- Incompletely dominant character
- Recessive character
- Abnormal character
Answer: 1. Dominant character
NEET quiz on Mendelism with solutions
Question 33. Among the seven pairs of contrasting traits in pea plant as studied by Mendel, the number of traits related to flower, pod and seed, respectively were
- 2, 2, 2
- 2, 2, 1
- 1, 2, 2
- 1, 1, 2
Answer: 1. 2, 2, 2
Mendel worked on garden pea and chose seven characters for his study. He studied 2 traits related to flower, i.e. colour and position, 2 traits related to pod, i.e. shape and colour and 2 traits related to seed, i.e. shape and colour and one trait related to stem, i.e. height.
Question 34. In Mendel’s seven contrasting traits of pea, total number of flower based characters studied by him was
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Answer: 1. 2
In Mendel’s seven contrasting traits of pea, total number of flower based characters tested by him was 2. These were flower colour and position.
Question 35. The recessive character in Mendel’s pea plant was
- Green pod
- Yellow pod
- Axial flower
- Round seed
Answer: 2. Yellow pod
Question 36. Which is correct about traits chosen by Mendel for his experiment on pea plant?
- Terminal pod was dominant
- Constricted pod was dominant
- Green pod colour was dominant
- Tall plants were recessive
Answer: 3. Green pod colour was dominant
Option is correct about traits chosen by Mendel for his experiment on pea plant as green pod colour is dominant. Other options are incorrect and can be corrected as Terminal constricted pod is recessive trait whereas tall plant height is a dominant trait.
Question 37. Match the following columns.
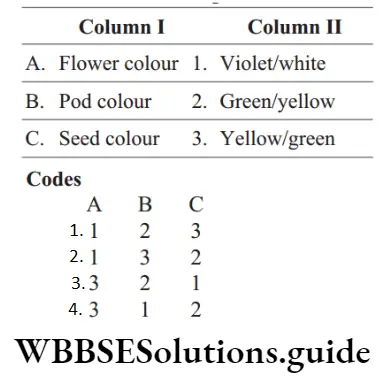
Answer: 1. A–1, B–2, C–3.
Question 38. In his classic experiments on pea plants, Mendel did not use
- Seed shape
- Flower position
- Seed colour
- Pod length
Answer: 4. Pod length
Mendel did not used pod length.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 39. Mendel always started his experiment (monohybrid and dihybrid cross) with
- Any pea plant
- A heterozygous plant
- A pureline plant
- A fresh new plant
Answer: 3. A pureline plant
For each of the characters that Mendel choose, he obtained pure lines of plants.
Question 40. The year 1900 AD is highly significant for geneticists due to
- Chromosome theory of heredity
- Discovery of genes
- Rediscovery of Mendelism
- Principle of linkage
Answer: 3. Rediscovery of Mendelism
In the year 1900, Hugo de Vries, Carl Correns and von Tschermak independently rediscovered the research carried out by Mendel and his experiments on heredity or variations and laid the basis of modern genetics. Thus, the year 1900 AD is highly significant for geneticists.
Question 41. Mendel studied inheritance of seven pairs of traits in pea which can have 21 possible combinations. If you are told that in one of these combinations, independent assortment is not observed in later studies, your reaction will be
- Independent assortment principle may be wrong
- Mendel might not have studied all the combinations
- It is impossible
- Later studies may be wrong
Answer: 2. Mendel might not have studied all the combinations
- Law of independent assortment is applicable to only those factors or genes which are located on different chromosomes.
- Probably the characters were present on same chromosome and showed linkage which Mendel might not have studied all the combinations.
Question 42. From his experiments, Mendel concluded that
- Recessive traits disappear in all crosses
- Individual characters blend with each factor
- Some factors are dominant
- Factors for the same trait are separated during fertilisation
Answer: 3. Some factors are dominant
On the basis of experiments performed, Mendel formulated that some factors are dominant. These
factors are able to express themselves in heterozygous condition, i.e. in the presence of other allele.
Question 43. Which of the following was not considered by Mendel?
- Test cross
- Linkage
- Back cross
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Linkage
- Two or more loci and their representative genes are said to be linked if they occur on the same
chromosomes. - Linkage was not considered by Mendel because the 7 pairs of characters chosen by Mendel were coincidently present on 7 different chromosomes, so the chances of linkage will negligible.
Question 44. Mendel failed to discover linkage because seven characters chosen by him were
- On 4 chromosomes on which they were closely placed
- On 4 chromosomes far apart
- On different seven chromosomes
- On different two chromosomes
Answer: 2. On 4 chromosomes far apart
Mendel could not find out linkage because all of his experimental characters of pea were present far apart from each other on 4 different chromosome. Linkage occurs between closely placed genes.
Question 45. The offspring of a cross between two individuals differing in at least one set of characters is called
- Polyploid
- Mutant
- Hybrid
- Variant
Answer: 3. Hybrid
The cross between two different homozygous lines produces an F1 hydrbid that is heterozygous, having two alleles, one contributed by each parent. For example, Triticale is the hybrid of crossing of wheat and rye.
Question 46. F1 -generation means
- First flowering generation
- First fertile generation
- First filial generation
- First seed generation
Answer: 3. First filial generation
The 1st generation obtained by crossing two parents is called as first filial generation or F1 -generation.
Question 47. F2 -generation is produced by
- Crossing F1 progeny with another plant having different trait
- Selfing the heterozygous progeny
- Selfing the parents
- A cross between recessive parents
Answer: 2. Selfing the heterozygous progeny
Mendel obtained F2 progeny from F1 plants by selfing the heterozygous progeny obtained from F1 cross.
Question 48. The recessive parental trait is expressed without any blending in the F2 – generation. We can infer, that F1plant produces gamete by the process of …A… and allele of parental pair …B… from each other and only one gamete is transmitted a gamete. Here, A and B are
- A–mitosis, B–aggregate
- A–meiosis, B–segregate
- A–meiosis, B–aggregate
- A–mitosis, B–segregate
Answer: 2. A–meiosis, B–segregate
Question 49. Monohybrid cross is
- A cross between two individuals differing in one trait
- A cross between two individuals having only one character
- A cross between the individuals of two different parents
- A cross between the two individuals that differ in two traits
Answer: 1. A cross between two individuals differing in one trait
A cross involving two individuals differing only in one character or trait is called monohybrid cross.
Question 50. Mendel’s first law is
- Law of segregation
- Law of independent assortment
- Law of variation
- Law of dominance
Answer: 4. Law of dominance
Mendel’s first law is known as law of dominance. According to this law, an individual, heterozygous for a pair of allele, expresses a trait pertaining to one allele, thus preventing other allele from expressing itself.
Question 51. A pure tall plant can be differentiated from a hybrid tall plant
- By measuring length of the plant
- By spraying gibberellin
- If all plants are tall after selfpollination
- If all plants are dwarf after selfpollination
Answer: 3. If all plants are tall after selfpollination
A pure tall can be differentiated from a hybrid tall plant when crossed.

If all plants are tall after self pollination, it shows that is pure tall plant (dominant character).
NEET expected MCQs on Mendelism 2025
Question 52. The character which appears in F1 -generation is called
- Recessive
- Dominant
- Latent
- None of these
Answer: 2. Dominant
The characters that appear in the F1 -generation are called dominant traits and those that appear for the first time in the F2 -generation are called recessive traits.
Question 53. By seeing the ratio of F1 and F2 generation, Mendel proposed that something was stably passed down unchanged over successive generation and called this something as
- Alleles
- Genes
- Chromosome
- Factors
Answer: 4. Factors
- Based on the ratio of F2 and F1 – generation, Mendel proposed that something stable was being passed down from parent to F1 to F2 – generation and so on, unchanged, through the gametes.
- He called these things as factors, now known as genes. Genes therefore, are the units of inheritance required to express a particular trait.
Question 54. Mendel crossed tall and dwarf plants in F2 -generation and obtained both the tall and dwarf plants. This indicates
- Blending of characters
- Atavism
- Non-blending of characters
- Recessive traits are not expressed
Answer: 3. Non-blending of characters
Mendel crossed tall and dwarf plants in F2 -generation and obtained both the tall and dwarf plant. Dominant and recessive were expressed or appeared separately. This shows that there is no mixing or non-blending of characters.
Question 55. The phenotypic ratio of a monohybrid cross in F2 -generation is
- 3: 1
- 3:1:2
- 2 :1:1
- 9:3:3:1
Answer: 1. 3: 1
A Punnett square is used to understand a typical monohybrid cross conducted between true breeding tall plants and true breeding dwarf plants. The phenotypic ratio in F2 -generation,
in monohybrid cross is 3: 1.
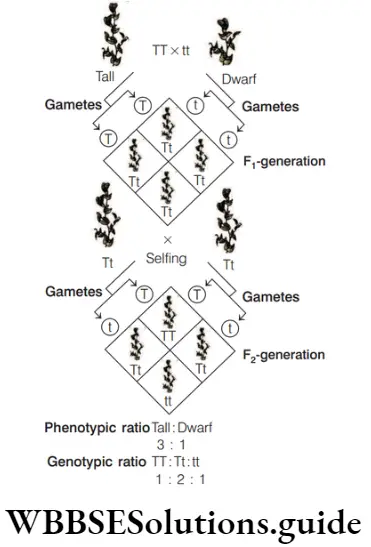
Question 56. The genotypic ratio of a monohybrid cross in F2 -generation is
- 3: 1
- 1 : 2: 1
- 2: 1: 1
- None of these
Answer: 2. 1 : 2: 1
Question 57. The allele which does not express in F1 -generation in the presence of another allele is
- Dominant
- Recessive
- Codominant
- Incompletely dominant
Answer: 2. Recessive
In F1 -generation, only dominant characters are expressed by dominant genes, while recessive genes and their expressions are suppressed.
Question 58. In Pisum sativum, the dwarfness of plant is a …………… character.
- Dominant
- Recessive
- Codominant
- Incomplete dominance
Answer: 2. Recessive
Question 59. Mendel’s work remain unrecognised for long time due to
- Communication was not easy.
- Concept of factors which did not blend was not accepted.
- Use of mathematics to explain biological problem was unacceptable.
- He could not provide any physical proof for the existence of factors.
Choose the correct option.
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 3 and 4
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: 4. 1, 2, 3 and 4
All the given statements are correct.
Question 60. Pure tall plants are crossed with pure dwarf plants. In the F1 -generation, all plants were tall. These tall plants of F1-generation were selfed and the ratio of tall to dwarf plants obtained was 3: 1. This is called
- Dominance
- Inheritance
- Codominance
- Heredity
Answer: 1. Dominance
The phenomenon given in the question expresses the monohybrid cross of Mendel. This is called the law of dominance. It states that when a pair of alleles or allelomorphs are brought together in F1 hybrid, then only one of them express itself while masking the expression of other completely.
Question 61. When alleles of two contrasting characters are present together, one of the characters expresses itself during the cross, while the other remains hidden. This is the
- Law of purity of gametes
- Law of segregation
- Law of dominance
- Law of inheritance
Answer: 3. Law of dominance
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 62. In genetics, the use of checker board was done by
- Mendel
- Correns
- Punnett
- Darwin
Answer: 3. Punnett
Punnett square (British geneticist, RC Punnett,1927) is a checker board used to show the result of a cross between two organisms. It was first done by Punnett.
Question 63. A graphical representation using which the probability of all possible genotypes of an offspring in genetic cross can be calculated is called
- Burnett square
- Morgan square
- Punnett square
- Test cross
Answer: 3. Punnett square
Punnett square was developed by British geneticist Reginald C. Punnett. It is a graphical representation to calculate the probability of all possible genotypes of offspring in genetic cross.
Question 64. Choose correct option for A, B, C and D in the given figure.
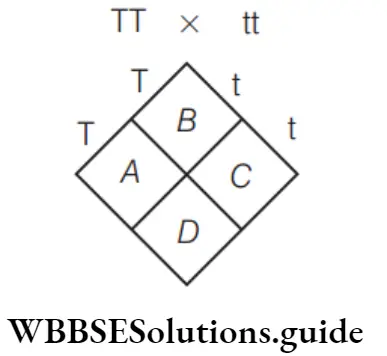
- A–tt, B–TT, C–TT, D–TT
- A–Tt, B–Tt, C–Tt, D–Tt
- A–TT, B–TT, C–Tt, D–TT
- A–Tt, B–Tt, C–Tt, D–TT
Answer: 2. A–Tt, B–Tt, C–Tt, D–Tt
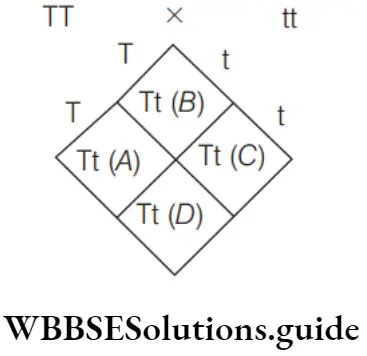
NEET Biology Mendelian inheritance MCQs with explanations
Question 65. Match the following columns.
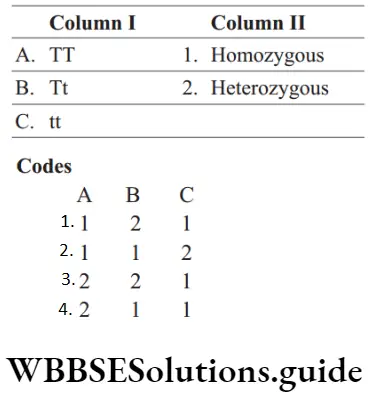
Answer: 1. A–1, B–2, C–1
Question 66. The technique of hybridisation used by Mendel was
- Back cross
- Double cross
- Single cross
- Emasculation
Answer: 4. Emasculation
The technique of hybridisation used by Mendel was emasculation, which means removal of anthers or stamens before anthesis, i.e. opening of flower to prevent self-pollination in bisexual flowers.
Question 67. The crossing of an organism with a double (homozygous) recessive in order to determine whether it is homozygous or heterozygous for a character under consideration is known as
- Back cross
- Test cross
- Reciprocal cross
- Dihybrid cross
Answer: 2. Test cross
Test cross is performed to determine the genotype of F1 plant. In a typical test cross, an organism showing dominant phenotype and whose genotype is to be determined is crossed with one that is homozygous recessive for the allele being investigated, instead of self-crossing.
The progenies of such a cross can easily be analysed to predict the genotype of the test organism.
Question 68. Which is a test cross?
- Ww × ww
- Ww × WW
- Ww × Ww
- WW × ww
Answer: 1. Ww × ww
A test cross is a cross between heterozygous F1 -generation and recessive parent, i.e. Ww
( F1 -generation) × ww (recessive parent).
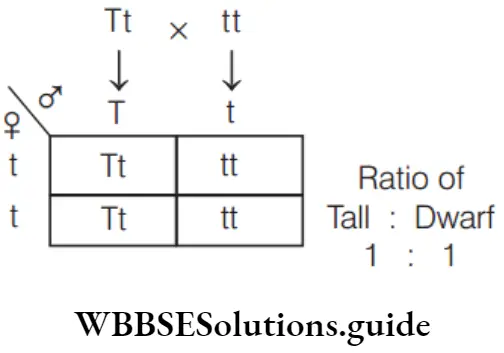
Question 69. In hybridisation, Tt × tt gives rise to the progeny of ratio
- 1: 1
- 2: 1
- 1: 2
- 1: 2: 1
Answer: 1. 1: 1
In a test cross, individual is crossed with recessive parent.
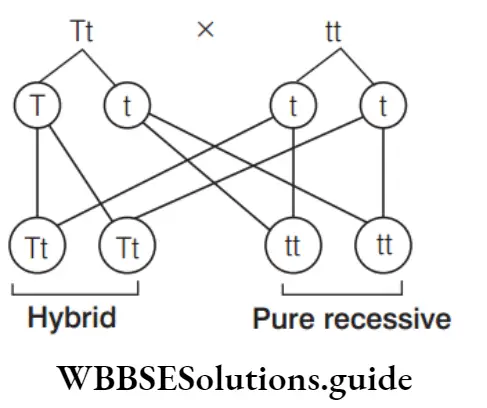
Ratio 1: 1
So, test cross gives rise to progeny whose ratio is 1: 1.
Question 70. The genotype of a plant showing the dominant phenotype can be determined by
- Test cross
- Dihybrid cross
- Pedigree analysis
- Back cross
Answer: 1. Test cross
Question 71. Select the correct statement.
- Genes located on same or different chromosomes, but distantly apart from each other assort independently.
- Genes which fails to assort independently are usually present very close, on the same chromosome
- Characters pass from parents to offsprings as factors, without blending or mixing
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
All the given statements are correct.
Question 72. Test cross is used to
- Check heterozygosity in F1-generation
- Check heterozygosity in F2 -generation
- Check independent assortment
- Check segregation
Answer: 1. Check heterozygosity in F1-generation
- Crossing of F1 individual having dominant phenotype with its homozygous recessive parent is called test cross and the progeny of test cross is called test cross progeny. Test cross was devised by Mendel to prove that F1 obtained by crossing two pure breeding parents is heterozygous or hybrid.
- If the unknown genotype is homozygous, half the progeny will exhibit the dominant trait and other half exhibit the recessive trait. So, a test cross is used to check heterozygosity in F1-generation.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 73. A test cross is carried out to
- Determine the genotype of a plant at F2
- Predict whether two traits are linked
- Assess the number of alleles of a gene
- Determine whether two species or varieties will breed successfully
Answer: 1. Determine the genotype of a plant at F2
When a tall plant from F1 or F2
has TT or Tt composition, its genotype cannot be predicted. Therefore, to determine the genotype of a tall plant in F2, Mendel crossed the tall plant from F2 with a dwarf parent. Thus, was called test cross.
Question 74. Ratio of progeny, when a red coloured heterozygous crossed with a white coloured plant in which red colour is dominant to white colour is
- 3: 1
- 1: 1
- 1: 2 :1
- 9: 3: 3: 1
Answer: 2. 1: 1
The given condition represents a test cross in which heterozygous red progeny is crossed with homozygous recessive white coloured parent. The test cross gives 1: 1 ratio in monohybrid condition, whereas 1: 1: 1: 1 in dihybrid condition.
Question 75. Law of purity of gametes put forward by Mendel was proved by
- Monohybrid cross
- Dihybrid cross
- Test cross
- Out cross
Answer: 3. Test cross
- A gamete may carry either the dominant or the recessive factor but not both, as we find in F1
individuals. This is why it is called either as ‘principle of segregation’ or as ‘law of purity of gametes’. - While 3: 1 ratio in F2 -generation of a monohybrid cross suggested that segregation of alleles does take place, the test cross confirmed it.
Question 76. The best method to determine the homozygosity and heterozygosity of an individual is
- Self-fertilisation
- Back cross
- Test cross
- Mono cross
Answer: 2. Back cross
The best method to determine the homozygosity and heterozygosity of an individual is back cross. Crossing of F1 (dominant phenotype) with any one of the parent is called back cross.
Question 77. When a plant of F1 -generation is crossed with homozygous dominant parents, it is known as
- Simple cross
- Test cross
- Back cross
- Special cross
Answer: 3. Back cross
Crossing of F1 (dominant phenotype) with any one of the dominant or recessive parent is called
back cross.
Question 78. Which of the statement is correct?
- Each back cross is a test cross
- Each test cross is a back cross
- Test cross and back cross are the same
- Reappearance of similar characters in a test cross is called a back cross
Answer: 2. Each test cross is a back cross
Statement in option is correct as each test cross is a back cross, but each back cross is not a test cross. Thus, test cross is a type of back cross.
Question 79. Hinny and mule are the example of
- Test cross
- Dihybrid cross
- Back cross
- Reciprocal cross
Answer: 4. Reciprocal cross
A hinny is a domestic equine hybrid that is the offspring of a male horse, a stallion and a female donkey, a jenny. It is the reciprocal cross to the more common mule, which is the product of a male donkey, a jack and a female horse, a mare.
Question 80. Two crosses between the same pair of genotypes or phenotypes in which the sources of the gametes are reversed in one cross, is known as
- Test cross
- Reciprocal cross
- Dihybrid cross
- Reverse cross
Answer: 2. Reciprocal cross
A reciprocal cross means that the same two parents are used in two experiments in such a way that if in one experiment A is used as the female parent and B is used as the male parent then in the other experiment, A will be used as the male parent and B as the female parent.
Question 81. Mendel’s reciprocal crosses gave identical results because
- Of segregation of characters
- Of complete dominance
- Characters are not sex-linked
- Of homozygous plants
Answer: 3. Characters are not sex-linked
- Mendel’s reciprocal cross gave the same results, i.e. when a white flowered female plant was crossed with a red flowered male plant, the F1 was red.
- In the reciprocal cross, red flowered female and white flowered male also gave a red flower. This was observed because the characters are not sex-linked.
Question 82. In monohybrid cross between pure tall and pure dwarf pea plant, how many types of genotypes are found in F2 -generation?
- 4
- 3
- 8
- 9
Answer: 2. 3
In monohybrid cross between pure tall and pure dwarf pea plant, three genotypes are found in F2 -generation, i.e. TT (pure tall), Tt (hybrid tall) and tt (dwarf).
Question 83. If a heterozygous tall plant is crossed with dwarf plant, what will be the ratio of dwarf plant in the progeny?
- 50 %
- 25 %
- 75 %
- 100 %
Answer: 1. 50 %
Heterozygous tall plant (Tt) will produce gametes T and t, whereas dwarf plant (tt) will produce gametes t. When heterozygous tall plant is crossed with dwarf plant, the progeny will show following combinations.
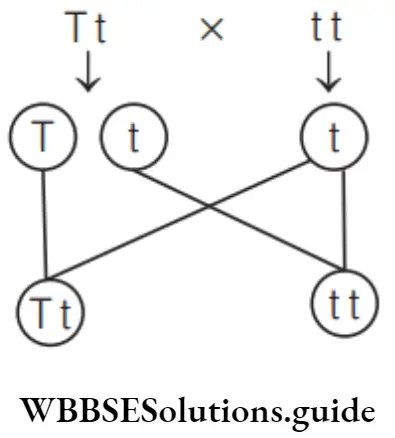
Thus, the population of tall and dwarf plants will be 50%.
Question 84. What result Mendel would have got, had he self-pollinated a tall F2 plant?
- TT and Tt
- All Tt
- No TT
- All tt
Answer: 1. TT and Tt
- In F2 -generation, two types of tall individuals are obtained pure tall (TT) and hybrid tall (Tt). Self-pollination of pure tall F2
- plant (TT) would give rise to all tall individuals of genotype TT, whereas self-pollination of hybrid tall F2
- plant (Tt) would give rise to tall and dwarf individuals of genotypes TT, Tt and tt. Thus, option 1 is most appropriate answer.
Question 85. F1 progeny of a cross between pure tall and dwarf plant is always
- Tall
- Short
- Intermediate
- Half short and half tall
Answer: 1. Tall
After crossing a pure tall plant with a dwarf one, the plants of F1 -generation are all tall.
Question 86. Mendel crossed true breeding tall and dwarf plant varieties in his experiment. The tall character dominant first appeared in F1 and recessive character dwarf appeared in
- F1
- F2
- F3
- F2 and F3
Answer: 4. F2 and F3
The recessive trait appears in F2 and F3 -generation, but not in F1 -generation.
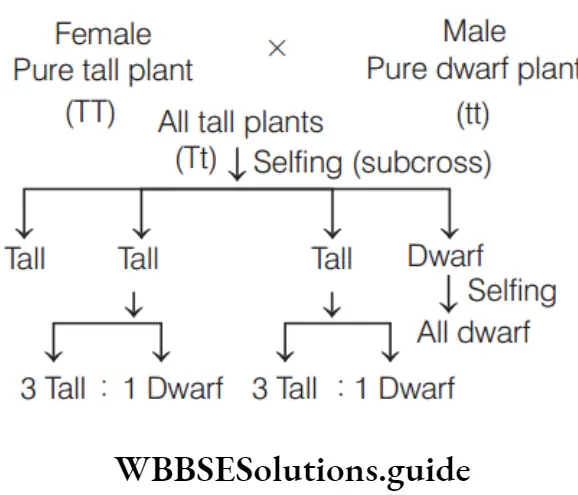
Question 87. The law of dominance is illustrated in the garden pea by
- Heterozygous tall × heterozygous tall
- Homozygous tall × homozygous tall
- Pure dwarf × pure dwarf
- Homozygous tall × pure dwarf
Answer: 4. Homozygous tall × pure dwarf
The law of dominance in garden pea is illustrated by TT × tt. The resultant F1 -generation would be tall (Tt) only.
Question 88. According to Mendel, plants of F1 -generation show
- Law of dominance
- Purity of gametes
- Independent assortment of genes
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Law of dominance
- Law of dominance states that in a heterozygous condition, the allele whose characters are expressed over the other allele is called the dominant allele and the characters of this
dominant allele are called dominant characters. - The characters that appear in the F1 -generation are called as dominant characters.Thus, plants of F1 -generation shows law of dominance.
Question 89. Match the following columns.
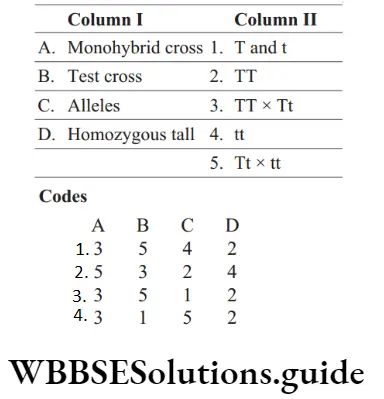
Answer: 3. A–3, B–5, C–1, D–2
Mendelism mock test for NEET preparation
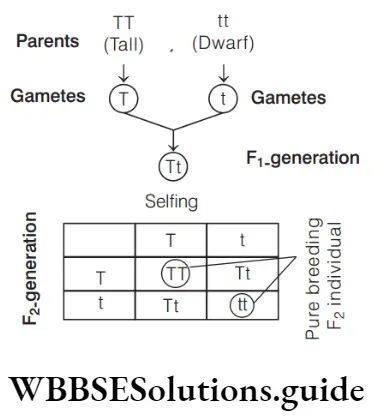
Question 90. A tall true breeding garden pea plant is crossed with a dwarf true breeding garden pea plant. When the F1 plants were selfed the resulting genotypes were in the ratio
- 1 : 2 : 1 :: Tall homozygous : Tall heterozygous : Dwarf
- 1 : 2 : 1 :: Tall heterozygous : Tall homozygous : Dwarf
- 3: 1 :: Tall: Dwarf
- 3: 1:: Dwarf: Tall
Answer: 1. 1: 2 : 1:: Tall homozygous: Tall heterozygous: Dwarf
When a tall true breeding garden pea plant is crossed with a dwarf true breeding garden pea plant and the plants were selfed, the resulting genotypes were in the ratio of 1:2:1, i.e. Tall homozygous : Tall heterozygous : Dwarf Parents :
Question 91. 3: 1 ratio in F2-generation is explained by
- Law of partial dominance
- Law of dominance
- Law of incomplete dominance
- Law of purity of gametes
Answer: 2. Law of dominance
3:1 ratio in F2-generation is explained by law of dominance.
Question 92. Mendel self-pollinated the F2 plant and found that …A… plants continued to generate dwarf plants in …B… and …C… generations. He concluded that the genotype of the dwarf is …D… . Choose the correct option for A, B, C and D.
- A–dwarf, B–F3, C–F4, D–homozygous
- A–dwarf, B–F3, C–F4, D–heterozygous
- A–tall, B–F5, C–F6, D–homozygous
- A–tall, B–F5, C–F6, D–heterozygous
Answer: 1. A–dwarf, B–F3, C–F4, D–homozygous
Question 93. The crossing of a homozygous tall pea plant and homozygous dwarf pea plant would yield plants in the ratio of
- 2 tall:2 dwarf
- All homozygous dwarf
- All heterozygous tall
- One homozygous tall: one homozygous dwarf: two heterozygous tall
Answer: 3. All heterozygous tall
Crossing of homozygous tall (TT) and homozygous dwarf (tt) would yield all heterozygous tall (Tt) plants in F1 -generation.
Question 94. From a single ear of corn a farmer planted 200 kernels which produced 140 tall and 40 short plants. The genotypes of these offsprings are most likely
- TT and Tt only
- TT, Tt and tt
- Tt and tt only
- TT and tt only
Answer: 2. TT, Tt and tt
- Mature corn plants produce ears that contain hundreds of seeds or kernels. Each seed is formed by the fertilisation of an egg by a male gamet.
- It has both the allele for height, i.e. T and t. So, the offspring produced by the crossing of Tt and Tt will have genotype as TT, Tt and tt. In this, 140 tall include TT and Tt gamete and 40 dwarf plants possess tt gametes.
Question 95. A plant is heterozygous for tallness (Tt). The possibility of t gamete fertilising either T or t is
- 1/8
- 1/2
- 1/4
- 1/6
Answer: 2. 1/2
Plant heterozygous for tall trait has two alleles, one governing tallness and other governing dwarf trait. This plant will produce two types of gametes, T and t. Hence, the possibility of fertilising either T or t is 1/2, i.e. 50%.
Question 96. In Mendelian monohybrid cross, phenotypic ratio in F2 is 3: 1. How many types of gametes are formed in F1 -generation?
- Only one type
- Two types
- Four types
- Eight types
Answer: 2. Two types
In a monohybrid cross only one trait of a character is crossed with other. Each character is governed by two alleles. Thus, after meiosis gametes formed in F1 -generation contain only one allele. The resultant gametes are hence of two types.
Question 97. F2 progeny of monohybrid cross shows
- Two phenotypes and two genotypes
- Two phenotypes and three genotypes
- Two genotypes and three phenotypes
- One phenotype and two genotypes
Answer: 2. Two phenotypes and three genotypes
F2 progeny of monohybrid cross shows two phenotypes and three genotypes. The cross between F1 progeny obtained from homozygous tall (TT) and homozygous dwarf (tt) plant yield (three types of genotypes) homozygous tall (TT), heterozygous tall (Tt) and homozygous dwarf (tt). The two phenotypes will be tall and dwarf.
Question 98. When red flowered plants are crossed with white flowered plants, the F2 -generation gives a ratio of 3:1. What do you conclude?
- That there are lethal genes
- That there is independent assortment
- That white colour is dominant
- That red colour is dominant
Answer: 4. That red colour is dominant
Crossing of red colour flower with white colour flower yield the progeny in ratio 3 : 1. As per law of dominance, the red colour flower is dominant, as it expressed maximally whereas the white colour in flower is a recessive trait.
Question 99. Haemolytic jaundice is caused by a dominant gene but only 20% of the people actually develop it. What proportion of the children would be expected to develop the disease if a heterozygous man marries a homozygous normal woman?
- 0.5
- 0.2
- 0.8
- 0.1
Answer: 4. 0.1
H allele is for haemolytic jaundice
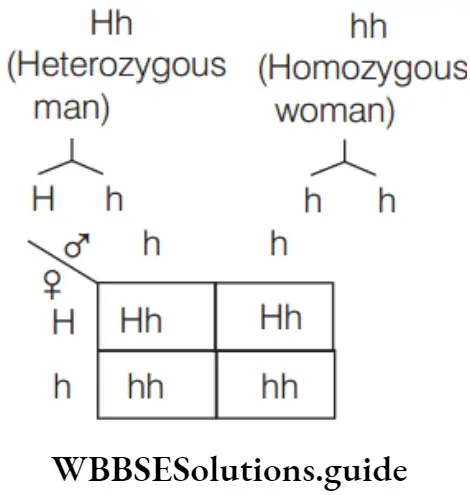
As shown above, there is 50% (half, 1/2) probability of progeny being haemolytic, but only 20% of people develop this disease so,
⇒ \(\frac{20}{100}\) × \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= \(\frac{10}{100}\)
= \(\frac{1}{10}\)
= 0.1
Question 100. If a heterozygous dominant plant (Tt) crossed with homozygous dwarf plant (tt), then the percentage of progeny having dwarf character is
- 60%
- 40%
- 50%
- 70%
Answer: 3. 50%
(Heterozygous tall) × (Homozygous dwarf)
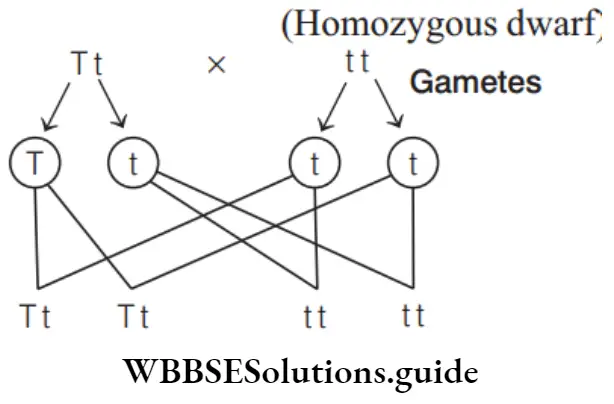
Phenotypic ratio 1: 1 (50% tall, 50% dwarf) Genotypic ratio 1: 1. Hence, percentage of progeny having dwarf character is 50%.
Question 101. Find out the percentage of dominant phenotype in cross between Pp and Pp. P-dominant, p-recessive
- 25%
- 50%
- 75%
- 100%
Answer: 3. 75%
Cross between Pp × Pp Gametes P, p; P, p Progeny PP, Pp, Pp, pp First three progeny 1, 2, 3 have the dominant traits, whereas the fourth progeny has recessive trait. Therefore, the ratio between dominant of recessive progeny is 3:1 or percentage of dominant progeny is 75%.
Question 102. Find the percentage of recessive phenotype in a cross between pp and Pp, where P refers to dominant and p refers to recessive.
- 5%
- 50%
- 75%
- 100%
Answer: 2. 50%
Percentage of recessive phenotype = 50% (pp)
Percentage of dominant phenotype = 50% (Pp)
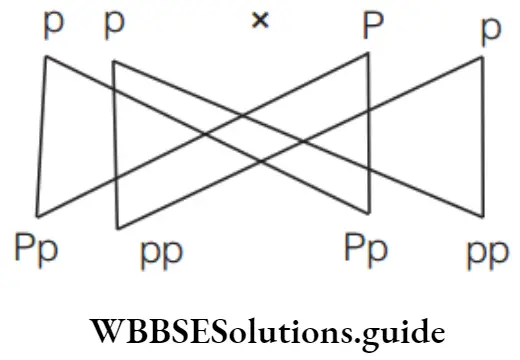
Question 103. Out of the four progenies obtained in F2 -generation by crossing pure tall and pure dwarf, how many of them will receive only recessive trait from both parents?
- All four
- One
- Two
- Three
Answer: 2. One
Only one progeny will receive recessive trait from both parents and therefore, it is dwarf (tt).
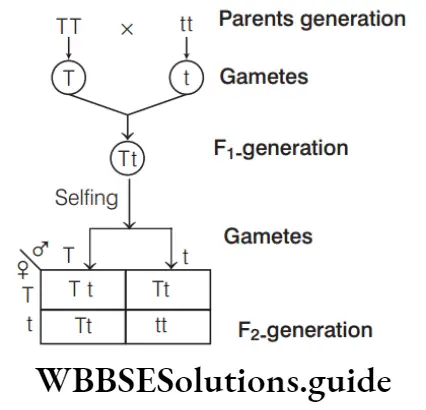
Question 104. Which of the following cross will produce terminal flower in garden pea?
- AA × Aa
- Aa × Aa
- Aa × AA
- AA × aa
Answer: 2. Aa × Aa
Axillary position (A) is dominant over terminal position. When Aa × Aa is crossed, we get 3:1 ratio, i.e. three axillary flowers and one terminal flower.
Among the given options, only Aa × Aa can produce terminal flower.
Question 105. Mendel crossed a pure white flowered recessive pea plant with a dominant pure red-flowered plant. The first generation of hybrids from the cross should show
- 50% white-flowered and 50% redflowered plants
- All red-flowered plants
- 75% red-flowered and 25% white flowered plants
- All white-flowered plants
Answer: 2. All red-flowered plants
The first generation of hybrids from the cross would show all red flowered plant, but they would exist in heterozygous state.
Question 106. A pea plant parent having violet coloured flowers with unknown genotype was crossed with a plant having white coloured flowers, in the progeny 50% of the flowers were violet and 50% were white. The genotypic constitution of the parent having violet coloured flowers was
- Homozygous
- Merozygous
- Heterozygous
- Hemizygous
Answer: 3. Heterozygous
In the question, a test cross between plants having violet coloured flowers ( F1 hybrid) with plants having white coloured flowers (homozygous recessive parent) produces progeny with violet and white flowers in equal proportion, indicating that F1 hybrids are heterozygous
Question 107. The leaf colour of certain plants is controlled by one gene. For that gene, the allele G = orange and g = green. You have a plant with orange leaves, but do not know whether that plant’s genotype is GG or Gg. If you cross your unknown plant with one of the plants whose genotype is listed below, you will be able to determine your unknown’s genotype. With which plant would you cross it?
- GG
- Gg
- Gg
- Either of parents
Answer: 2. Gg
- To know the genotype of dominant phenotype, we will cross that plant with the respective recessive phenotype. This is called test cross.
- The progeny of such cross can easily be analysed to predict the genotype of test organism. So here, to know the genotype of the leaf colour of that plant, test cross would be performed with the recessive homozygous, gg plant.
Question 108. Rrrr (progeny): Red (dominant) flowered (heterozygous) were crossed with white flower. The result will be
- 350 red: 350 white
- 450 red: 250 white
- 380 red: 320 white
- None of the above
Answer: 1. 350 red: 350 white
The cross of red dominant heterozygous progeny with white flower is shown below
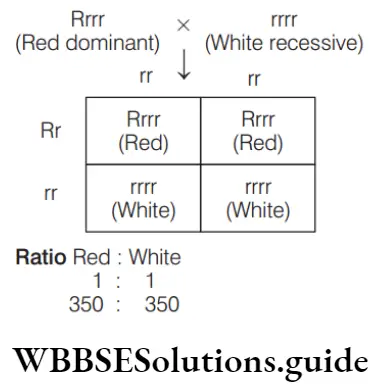
Thus, option 1 is correct.
Question 109. If a woman is homozygous normal and her husband is heterozygous for a genetically inherited recessive disease and they decide to become parents, what is the probability that they will have a healthy child?
- 1 out of 4
- 2 out of 4
- 3 out of 4
- 4 out of 4
Answer: 4. 4 out of 4
All of the children will be healthy since none of them can be homozygous recessive (aa).
However, there will be a 50% chance at each birth that the children will be carriers (Aa). The remaining 50% will be healthy homozygous dominant (AA).
Question 110. Mendel found that the reciprocal crosses yielded identical results. From that he concluded that
- There is independent assortment of trait
- Sex plays a role in deciding the dominance of a trait
- There is no dominance of any trait
- Sex has no influence on the dominance of traits
Answer: 4. Sex has no influence on the dominance of traits
- A cross with the phenotype of each sex reversed as compared with the original cross, to test the role of parental sex on inheritence pattern is called reciprocal cross.
- Reciprocal cross is made to eliminte the effect of cytoplasmic traits and to know whether the alleles are present on sex chromosome or autosomes.
- Mendel found that reciprocal crosses yielded identical results. From that, he concluded that sex has no influence on the dominance of traits.
Question 111. Match the following columns.
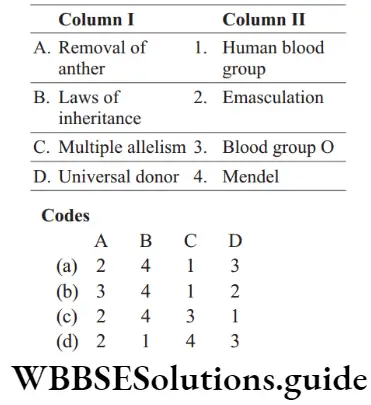
Answer: 1. A–2, B–4, C–1, D–3
Question 112. On inbreeding, the homozygous parents will produce
- All similar offspring
- 25% similar and 75% dissimilar
- 75% similar and 25% dissimilar
- 50% similar and 50% dissimilar
Answer: 1. All similar offspring
Inbreeding is the production of offspring from the mating or breeding of individuals or organisms that are closely related genetically. So, the homozygous parent will produce all similar offspring.
Question 113. What will be the genetic constitution of the offspring of a cross of individuals heterozygous (Zz) for an allele?
- All ZZ
- All zz
- 1/2 ZZ: 1/2 zz
- 1/4 ZZ: 1/2 Zz : 1/4 zz
Answer: 4. 1/4 ZZ: 1/2 Zz : 1/4 zz
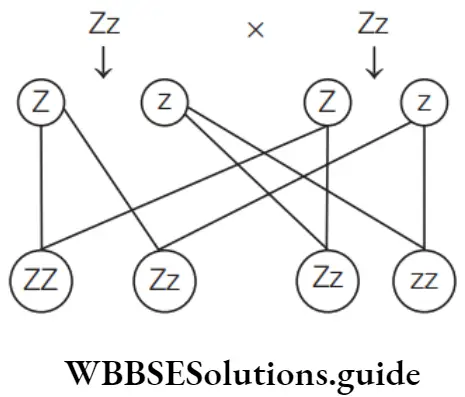
Thus, the genetic constitution of the offspring of a cross of individuals heterozygous (Zz) for an allele would be 1/4 ZZ: 1/2 Zz: 1/4 zz
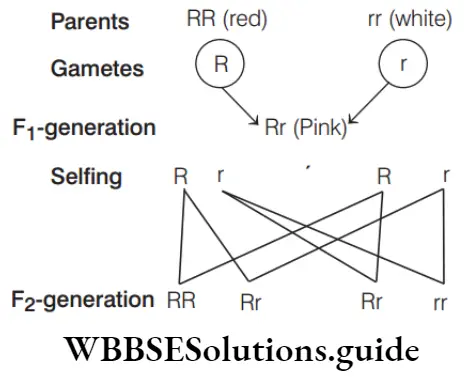
Question 114. Find out the genotype and phenotype of F1 -generation (R = dominant and red, r = recessive and white) from the given cross.
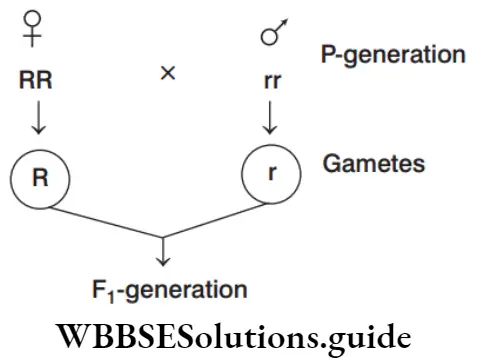
- Rr and white
- Rr and red
- Rr and pink
- RR and white
Answer: 2. Rr and red
Genotype is Rr and phnotype is red because the R is dominant so, the F1 -hybrid will be red.
Question 115. Identify a cross in which l/4th of the offsprings show recessive trait?
- Rr × RR
- Rr × rr
- Rr × Rr
- Both 2 and 3
Answer: 3. Rr × Rr
A cross between two heterozygous dominant individual (e.g. Rr × Rr) would yield 1/4 th of offspring with recessive trait (i.e. rr) in F2 generation.
Question 116. tt mates with Tt. What will be characteristic of offspring?
- 75% recessive
- 50% recessive
- 25% recessive
- All dominant
Answer: 2. 50% recessive
On mating tt with Tt, 50% offspring would be recessive and 50% would be heterozygous dominant.
Question 117. The proportion of plants that were dwarf and tall in F2-generation of Mendel monohybrid experiment
- 1/ 4 th and 3/4 th
- 3/4 th and 1/4 th
- 2/3 th and 1/3 th
- 1/3 th and 4/3 th
Answer: 1. 1/4 th and 3/4 th dwarf and tall respectivley Refer to cross in Ans. 103.
Question 118. In a monohybrid cross between two heterozygous individuals, the percentage of pure homozygous individuals obtained in F1 -generation is
- 25%
- 50%
- 75%
- 100%
Answer: 2. 50%
Let us consider a monohybrid cross between two tall heterozygous plants (Tt). The genotype of the offspring in F1 -generation will be TT, Tt,Tt and tt. Hence, half of the offspring (i.e 50%) are pure homozygous (TT and tt).
Question 119. Heterozygous purple flower is crossed with recessive white flower. The progeny has the ratio
- All purple
- All white
- 50% purple and 50% white
- 75% purple and 25% white
Answer: 3. 50% purple and 50% white
If we cross heterozygous purple flowers with parental flowers (recessive white flower) then we get 50% purple and 50% white.
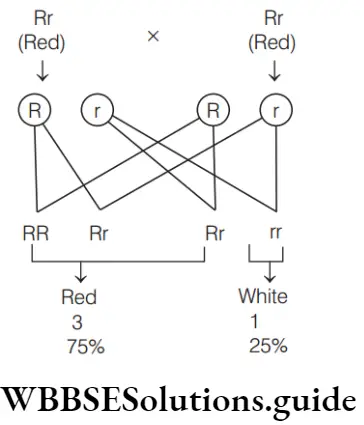
Question 120. If two pea plants having red (dominant) coloured flowers with unknown genotypes are crossed, 75% of the flowers are red and 25% are white. The genotypic constitution of the parents having red coloured flowers will be
- Both homozygous
- One homozygous and other heterozygous
- Both heterozygous
- Both hemizygous
Answer: 3. Both heterozygous
In given situation, genotype of parents having red coloured flowers will be heterozygous.
Question 121. In a certain plant, red colour flower (R) is dominant over white colour flower (r). When a heterozygous Rr plant is crossed 64 offspring are obtained. The number of white offspring is
- 64
- 0
- 16
- 32
Answer: 3. 16
The given condition represents monohybrid cross in which dominance to recessive ratio is 3: 1. Out of the total 64 offsprings, the number of red offspring is 48 and white offspring is 16.
Question 122. If a pure tall pea plant is raised in nutrient deficient media such that it grows to the size of a dwarf plant and is then selfed, the progeny in normal media will be
- Dwarf
- All tall
- 50% tall and 50% dwarf
- 75% tall and 25% short
Answer: 2. All tall
Insufficient nutrient only changes the phenotype, but not the genotype of the plant. Hence, the pure tall pea plant still grow into all tall plants on returning to normal nutrient media.
Question 123. Pure red flowers were crossed with pure white flowers. Red is dominant. After selfing of F1 -generation, the proportions of plants producing white flowers in progeny would be
- 3/4
- 1/4
- 1/3
- 1/2
Answer: 2. 1/4
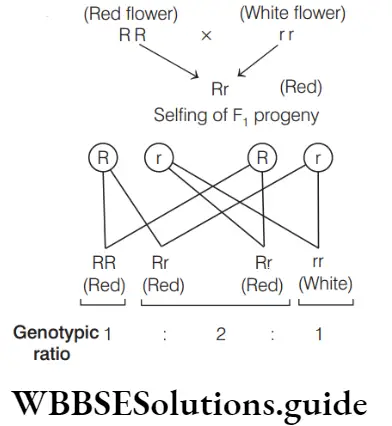
So, the proportion of white flower is 1/4.
Question 124. If a cross is made between AA and aa, the nature of F1 progeny will be
- Genotypically AA, phenotypically a
- Genotypically Aa, phenotypically a
- Genotypically Aa, phenotypically A
- Genotypically aa, phenotypically A
Answer: 3. Genotypically Aa, phenotypically A
If a cross is made between AA and aa, where ‘A’ is dominant over ‘a’,then the result will be according to Mendelian principles
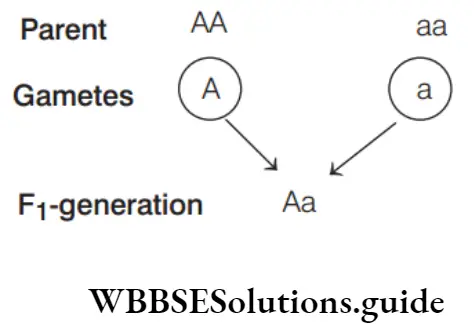
Genotype = Aa
Phenotype = Same as that of AA
Question 125. Percentage of homozygous offspring in a monohybrid F2 cross is
- 25%
- 0%
- 100%
- 50%
Answer: 4. 50%
- A monohybrid cross is a genetic mix between two individuals with homozygous genotypes, which result in an opposite phenotype.
- A monohybrid ratio is the phenotypic ratio of different types of individuals occurring in the F2-generation of a monohybrid cross.
- The percentage of homozygous offspring in a monohybrid F2 cross is 50%, which is homozygous dominant and recessive.
Question 126. 190 grains of jowar from single plant when sown produce 140 tall and 50 dwarf plants. The genotypes of these offsprings may be
- TT, tt
- TT, Tt
- Tt, Tt
- TT, Tt, tt
Answer: 4. TT, Tt, tt
- The phenotypes obtained from growing 190 grains of jowar are 140 tall and 50 dwarf. This is
approximately equal to 3:1 ratio. - Hence, this will be F2-generation and there will be 3 genotypes and two phenotypes. The genotypes will be TT, Tt, tt.
Question 127. When homozygous dominant parent is crossed with heterozygous parent, the percentage of offspring with different phenotype than either parent is
- 0
- 25
- 50
- 75
Answer: 1. 0
When homozygous dominant parent (TT) is crossed with heterozygous parent (Tt), the offspring produced is of same phenotype as that of parents.
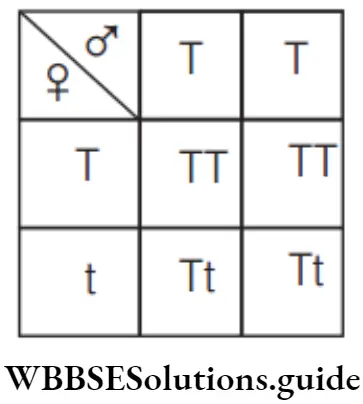
Hence , the percentage of offspring with different phenotype is ‘0’.
Question 128. If a cross between two individuals produces offspring with 50% dominant character (A) and 50% recessive character (a), then the genotype of parents are
- Aa × Aa
- Aa × aa
- AA × aa
- AA × Aa
Answer: 2. Aa × aa
If a cross between two individuals produces offsprings with 50% dominant character (A) and 50%
recessive character (a), then the genotypes of parents will be Aa and as
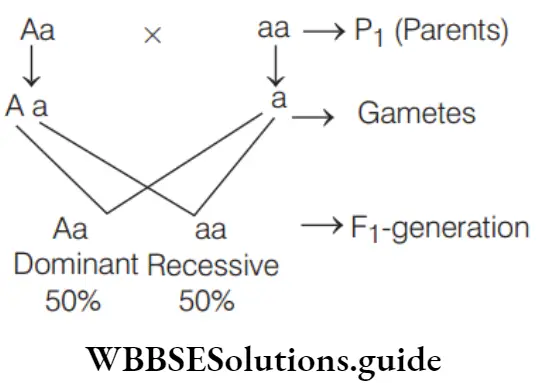
Question 129. One of Mendel’s pure strains of pea plants had green peas. How many different kinds of eggs could such a plant produce with regard to pea colour?
- 1
- 2
- 4
- 8
Answer: 1. 1
Since, the given pea plant is a pure strain, its genotype for green peas will be homozygous and thus, it will produce only one kind of gamete.
Question 130. A true breeding plant producing red flowers is crossed with a pure plant producing white flowers. Allele for red colour of flower is dominant. After selfing, the plants of first filial generation, the proportion of plants producing white flowers in the progeny would be
- 1/3
- 1/2
- 3/4
- 1/4
Answer: 4. 1/4
Genotype of true breeding plant producing red flower = RR Genotype of pure plant producing White flower = rr
Thus, white flower producing progeny is 1/4.
Question 131. Two pea plants were subjected for cross-pollination. Of the l83 plants produced in the next generation, 94 plants were found to be tall and 89 plants were found to be dwarf. The genotypes of the two parental plants are likely to be
- TT and tt
- Tt and Tt
- Tt and tt
- TT and TT
Answer: 3. Tt and tt
The genotypes of the two parental plants are likely to be Tt and tt. When, the parents are crossed, the next generation shows the following results
Total number of plants produced were 183 and tall: dwarf are 94 : 89, which is almost 1 : l (test cross ratio).
Question 132. When parents P1 and P2 were crossed, F2 progeny was produced with three fourth similar features in phenotype to P2 and F1 and one fourth possessed contrasting traits. If the traits being considered here are for height are, ‘T’ for tall and ‘t’ for short. What will be the possible genotype of P1 and one fourth of F2?
- tt and Tt
- Tt and tt
- Tt and Tt
- tt and tt
Answer: 4. tt and tt
The possible genotype of P1 and one fourth of F2 is tt and tt, respectively.
Question 133. Heterozyous tall (Tt) is crossed with homozygous tall (TT), the percentage of heterozygous tall in the progeny would be
- 25
- 50
- 75
- 100
Answer: 2. 50
A cross between heterozygous tall and homozygous tall is shown below
So, 50% heterozygous tall plants are produced.
Question 134. Offsprings of which of the following cross are all phenotypically alike?
- Dd × Dd
- Dd × dd
- DD × Dd
- Ww × Ww
Answer: 3. DD × Dd
The offsprings of cross DD × Dd would be dominant only. Thus, they are phenotypically alike, but differ genotypically.
Question 135. If ‘A’ represents the dominant gene and ‘a’ represents its recessive allele, which of the following would be the most likely result in the first generation offspring when ‘Aa’ is crossed with ‘aa’ ?
- All will exhibit dominant phenotype
- All will be of recessive type
- Dominant and recessive phenotype will be 50%
- Dominant phenotypes will be 75%
Answer: 3. Dominant and recessive phenotype will be 50%
‘A’ represents the dominant gene and ‘a’ represents its recessive allele. The result in the first generation offspring when Aa cross with aa is shown in cross below

Dominantphenotype
= Aa Homozygous recessivephenotype
= aa
Aa: aa → 1: 1
Question 136. Right handedness is dominant over left handedness. Most probable gene types with 2 right handed parents having left handed child is
- RR × rr
- Rr × RR
- RR × Rr
- Rr × Rr
Answer: 4. Rr × Rr
- Right handedness is dominant over left handedness. If both the parents are right handed, then they must have either pure right handed genotype or dominant right handed and recessive left handed genotype.
- But if they are having a left handed child, then the genotype of the child is (rr). So, both the parents should have recessive‘r’ gene in their genotypes. Hence, the probable genotype of both the parents is Rr and Rr, i.e. hybrid right handedness.
Question 137. Mendel’s principle of segregation is based on separation of alleles during
- Gamete formation
- Seed formation
- Pollination
- Embryonic development
Answer: 1. Gamete formation
The law of segregation states that when a pair of allelomorphs are brought together in the F1
hybrid, they coexist or remain together in the hybrid without blending or in any way contaminating each other and they separate completely and remain pure during the formation of gametes.
Question 138. Law of segregation of gametes was proposed by
- Mendel
- Huxley
- de Vries
- Robert Hooke
Answer: 1. Mendel
Law of segregation of gametes was proposed by Mendel. It was the 2nd law given by him.
Question 139. Which of the following statement is/are correct regarding law of segregation?
- Alleles separate from each other during gametogenesis
- Segregation of factors is due to separation of chromosomes during meiosis
- Law of segregation is called as law of purity of gametes
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
- All given statements are correct regarding law of segregation. The principle or law of segregation is also called the purity of gametes.
- This law states that the two factors of a character present in individual keep their identity distinct separate at the time of gametogenesis (meiosis) or sporogenesis, factors get randomly distributed to different gametes and then get paired again in different offspring as per the principle of probability. The principal of segregation can be deduced in Punnett square.
Thus, option (4) is correct.
Question 140. According to Mendel’s principle of segregation, germ cells always receive
- One pair to four alleles
- One quarter of the genes
- One of the paired alleles
- Any pair of alleles
Answer: 3. One of the paired alleles
Law of segregation states that heredity characters in the form of allele segregate from each other during the formation of gametes. Half of the gametes carry one allele and other half carries other allele. So, germ cells receive one of the paired alleles.
Question 141. The law of segregation of characters is also called the law of purity of gametes because
- Gametes have only one of the two alleles for each character
- Gametes cannot be contaminated
- Gametes are very different type of cells
- Both tall and dwarf plants in 1:2
Answer: 1. Gametes have only one of the two alleles for each character
The law of segregation of characters as also called the law of purity of gametes because gametes have only one of the two alleles for each character.
Question 142. Law of Mendel which is not completely applicable is
- Codominance
- Law of segregation
- Law of independent assortment
- Law of dominance
Answer: 3. Law of independent assortment
Except codominance, other three options are laws of inheritance given by Mendel. Out of these, law of independent assortment is not completely applicable. This is applicable to only those factors or genes which are present on different chromosomes, i.e. non-linked gene.
NEET practice test on Mendelism and inheritance
Question 143. In garden pea, round shape of seeds is dominant over wrinkled shape. A pea plant heterozygous for round shape of seed is selfed and 1600 seeds produced during the cross are subsequently germinated. How many seedlings would have the parental phenotype?
- 400
- 1600
- 1200
- 800
Answer: 3. 1200
Since, this pea plant is heterozygous for round shape, its genotype would be Rr. Parents Rr × Rr (selfing) Progeny RR, Rr, Rr, rr Phenotypically, the ratio will be 3 : 1, i.e. only rr seedlings will show wrinkled phenotype, rest will show round shape (Parental phenotype).
∴ \(\frac{ 3}{4}\) × 1600= 1200
⇒ 1200 → Round shape (RR, Rr)
⇒ 400 → Wrinkled (rr)
Question 144. In wheat, when a green plant was self-fertilised, the progeny had 20 green seedling and 14 white seedling; this result indicates that the parents were
- True breeding
- Homozygous for one allele
- Heterozygous for one allele
- Heterozygous for two duplicate alleles
Answer: 3. Heterozygous for one allele
When green plant was self-fertilised, appearance of white seedling in progeny indicate parents were heterozygous for one allele, e.g. Gg × Gg. Where G represent dominant green allele and g is recessive white allele.
Question 145. Which of the following points further strengthened Mendelism?
- Law of independent assortment which was based on monohybrid cross
- Law of independent assortment which could be stated on the basis of segregation of gametes
- Incomplete dominance gave a new way to Mendel
- A character controlled by a pair of unit factors
Answer: 4. A character controlled by a pair of unit factors
Law of independent assortment is based on dihybrid cross. In this , two characters or genes do not influence each other and separate independently during gamete formation. The trait which did not appear in F1 – generation reappeared in F2. Mendel called the substance responsible for each trait as factor. He stated that a character is controlled by a pair of unit factos. Later, this factors were called alleles.
Question 146. Find odd one out.
- YyRr
- YyRr
- YYRr
- YYRR
Answer: 1. YyRr
The odd option is yyRr because the phenotype of this plant will be green round, whereas the phenotype of rest of the plants will be yellow round.
Question 147. What type of gametes will form by genotype rrYy?
- Ry, rY
- RY, Ry
- Ry, Yy
- RR, Yy
Answer: 1. Ry, rY
Only two types of gametes are formed by genotype rrYy, i.e. ry and rY.
Question 148. In Mendelian dihybrid cross, when heterozygous round yellow are selfcrossed, round green offspring are represented by the genotype
- RrYy, RrYY, RRYy
- Rryy, RRyy, rryy
- rrYy, rrYY
- Rryy, RRyy
- RrYy, rryy, Rryy
Answer: 4. Rryy, RRyy
In Mendelian dihybrid cross, when heterozygous round yellow (Rr Yy) are self crossed, round green offsprings- are represented by RRyy, Rryy genotypes.
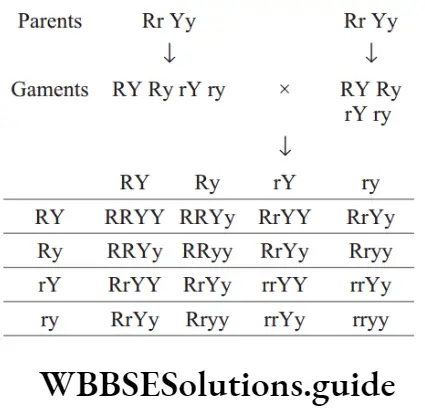
RR, Rr – Round rr – Wrinkled Yy, YY – Yellow yy – Green
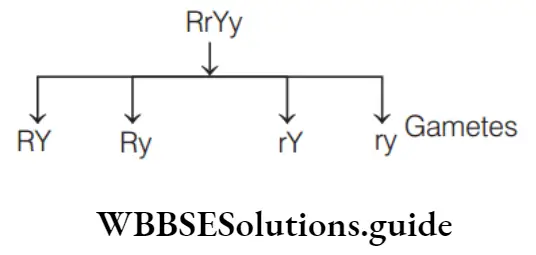
Question 149. The types of gametes formed by the genotype RrYy are
- RY, Ry, rY, ry
- RY, Ry, ry, ry
- Ry, Ry, ry, ry
- Rr, RR, Yy, YY
Answer: 1. RY, Ry, rY, ry
Number of gametes is calculated is 2n, where n = number of heterozygotes. RrYy is a dihybrid, so four types of gametes are formed ( )22 as RY, Ry, rY, ry.
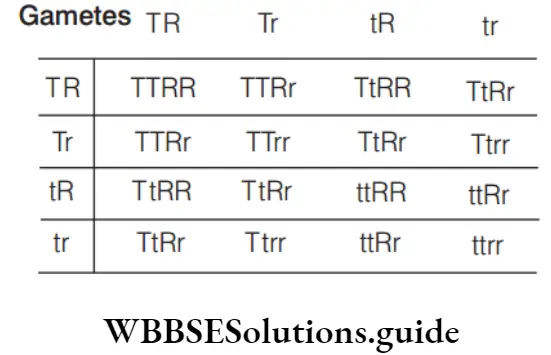
Question 150. A dihybrid plant on self-pollination, produces 400 phenotypes with 4 types of genotype. How many seeds will have genotype TtRr?
- 200
- 100
- 50
- 150
Answer: 2. 100
The self-pollination of a dihybrid plant yields the genotypic ratio of 1 TTRR: 2 TTRr: 1TTrr: 2Tt RR: 4 TtRr: 2Ttrr : 1ttRR: 1ttrr. The ratio of genotype Ttrr is 4/16. Hence, out of total 400 phenotypes, number of seeds having TtRr genotype will be 4/16 × 400 = 100 F -generation2 TtRr × TtRr
Question 151. When a pure tall plant (TT) having rounded seeds (RR) is crossed with dwarf plant (tt) having wrinkled seeds (rr) and their F1 progeny are crossed among themselves to produce F2-generation, how many phenotypes will be observed?
- 16
- 9
- 4
- 2
Answer: 3. 4
Four types of phenotypes will be observed. They are tall round, tall wrinkled, dwarf round, dwarf wrinkled.
Question 152. A cross between pure tall pea plant with green pods and dwarf pea plant with yellow pods will produce ………… tall F2 plants out of 16.
- 15
- 7
- 12
- 13
Answer: 3. 12
Tall is dominant over dwarf and yellow pods are dominant over green pods.
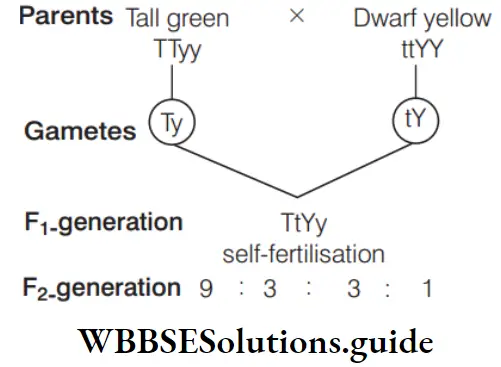
Tallgreen:Tallyellow:Dwarfgreen:Dwarfyellow Total tall plants = 12
Question 153. Assertion (A) In dihybrid cross, the two pairs of factors are located in two pairs of homologous chromosomes. Reason (R) Each chromosome bears two pairs of factors.
- A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 3. A is true, but R is false
- A is true, but R is false because, in a dihybrid cross, two different characters are crossed together. For example, a cross between round yellow seeds with green wrinkled seeds. Here, two characters both texture and colour are involved. Such a corss is called a dihybrid cross.
- These two characters are located on different homologous chromosomes. But a single chromosome does not bear two factors, they are located on two different chromosome.
Question 154. If there are 15 green wrinkled plants in a typical Mendelian dihybrid cross, what is the total number of plants obtained in the cross?
- 135
- 245
- 140
- 240
Answer: 4. 240
The phenotypic ratio of Mendelian dihybrid cross is 9 : 3 : 3: 1 in which 9 specifies yellow round, 3 specifies greeen round, 3 specifies yellow wrinkled and 1 specifies green wrinkled. Then the total number of plants obtained in the cross would be as follows
∴ 9 ×15 = 135
3 ×15 = 45
3 × 15 = 45
1 × 15 = 15
So, total number of plants obtained in the cross = 240.
Question 155. In cross between yellow round (YYRR) and green wrinkled (yyrr), find out the ratio between seeds, having yellow and green seed colour.
- 3: 2
- 3: 1
- 9: 7
- 7: 9
Answer: 2. 3: 1
3:1 ratio appeared as 9:3:3: 1 such ratio appeared for several characters that Mendel studied.
9/16= Yellow round
3/16 = Yellow wrinkled
3/16 = Green yellow
1/16 = Green wrinkled
Seed colour–Yellow (9 + 3 = 12) :
Green (3 + 1 = 4) or 3: 1
Seed texture–Round (9 + 3 = 12) :
Wrinkled (3 + 1 = 4) or 3: 1
Question 156. In a dihybrid cross AABB × aabb, F2 progeny of AABB, AABb, AaBB and AaBb occurs in the ratio of
- 1: 1: 1: 1
- 9: 3 : 3: 1
- 1: 2: 2: 1
- 1:2: 2: 4
Answer: 3. 1: 2: 2: 1
When a cross is made between AABB × aabb, in the F2 generation, the genotypic ratio is AABB-1, AABb-2, AaBB-2, AaBb-4, AAbb-1, Aabb-2, aaBB-1, aaBb-2, aabb-1. So, the correct option is (3).
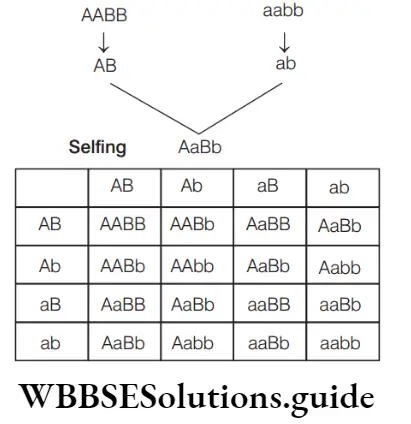
Question 157. In Mendel’s experiments with garden pea, round seed shape (RR) was dominant over wrinkled seeds (rr) and yellow cotyledon (YY) was dominant over green cotyledon (yy). What are the expected phenotypes in the F1 -generation of the cross RRYY × rryy?
- Only round seeds with yellow cotyledons
- Only wrinkled seeds with yellow cotyledons
- Only wrinkled seeds with green cotyledons
- Round seeds with yellow cotyledons and wrinkled seeds with yellow cotyledons
Answer: 1. Only round seeds with yellow cotyledons
When a cross (dihybrid) is made between plants bearing round yellow (RRYY) and wrinkled green (rryy) seeds, all the plants in F1 – generation would have only round seeds with yellow cotyledons because these are dominant traits.
Question 158. When red wheat kernel is crossed with white wheat kernel, the probability of getting darkest red plant is
- 1/16
- 4/16
- 6/16
- 2/16
Answer: 1. 1/16
When red wheat kernel is crossed with white wheat kernel, the probability of getting darkest red plant, i.e. AABB, is 1/16
Question 159. When yellow round heterozygous pea plants are self-fertilised, the frequency of occurrence of RrYY genotype among the offspring is
- 9/16
- 3/16
- 2/16
- 1/16
- 6/16
Answer: 3. 2/16
Yellow round heterozygous pea plant may be represented by genotype RrYy.On selfing such plants, total 16 genotypes will be obtained in the nextgeneration, out of which the frequency of occurrence of RrYY genotype is 2 or 2/16.
Question 160. In a dihybrid cross, where two parents differ in two pairs of contrasting traits like seed colour yellow (YY) and seed colour green (yy) with seed shape round (RR) and seed shape wrinkled (rr), the number of green coloured seeds (yy) among sixteen products of F2-generation will be
- 2
- 4
- 6
- 8
Answer: 2. 4
Since, round seed shape is dominant over wrinkled seed shape and yellow cotyledon is dominant over green cotyledon, so RRYY individual is round yellow and rryy is wrinkled green.
Question 161. The percentage of yr gametes in YyRr is
- 25%
- 50%
- 75%
- 100%
Answer: 1. 25%
The gametes produced by YyRr will be YR, Yr, yR and yr. Hence, the percentange of yr gametes would be 4/16 or 25%.
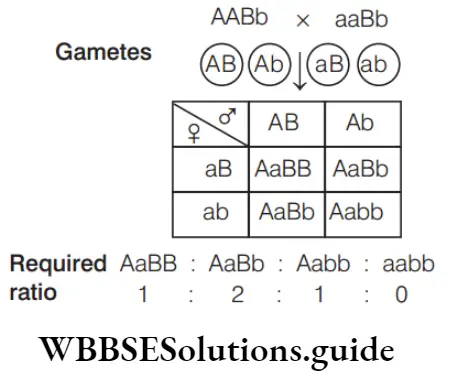
Question 162. From a cross AABb × aaBb, the genotypes AaBB : AaBb : Aabb : aabb will be obtained in which of the following ratio?
- 0: 3: 1: 0
- 1 : 2: 1 : 0
- 1: 1: 1: 1
- 1 : 1: 1 : 0
Answer: 2. 1: 2: 1 : 0
In the cross AABb × aaBb, the genotypes obtained are AaBB, AaBb and Aabb in a ratio of 1:2:1, whereas genotype aabb is not obtained. So, the correct answer is 1:2:1:0.
Question 163. In a plant species, flower colour yellow is dominant over white and fruit shape round is dominant over elongated. Crossing was performed between two purelines, one having yellow flower and round fruit and another with white flower and elongated fruit. About 20 plants survived in F1 progeny. Plants of F1 were allowed to self-fertilise and about 960 plants survived in F2. If the traits follow Mendelian inheritance, the number of plants would have yellow flower and round fruit in F1 and F2 are respectively,
- 20, 960
- 20, 540
- 10, 180
- 10, 600
Answer: 2. 20, 540
- In F1 -generation, all the 20 plants would be heterozygous for the trait and thus, would possess yellow flower and round fruit.
- When heterozygous plant of F1 -generation undergo selfing, F2progeny gives 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 phenotypic ratio, where out of 16 plants, 9 will have yellow flower with round fruit. Thus, in the given case, yellow flower with round fruit in F2 are= × =960 9 16 540 Thus, option (2) is correct.
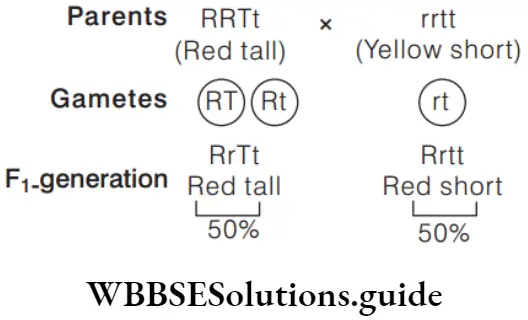
Question 164. In a plant, red fruit (R) is dominant over yellow fruit (r) and tallness (T) is dominant over shortness (t). If a plant with RRTt genotype is crossed with a plant that is rrtt
- 25% will be tall with red fruit
- 50% will be tall with red fruit
- 75% will be tall with red fruit
- All the offspring will be tall with red fruit
Answer: 2. 50% will be tall with red fruit
Since, red fruit colour is dominant over yellow fruit colour and tallness is dominant over shortness, 50% offspring will be tall with red fruit.
Question 165. A red and tall dominant character hybrid plant is crossed with recessive white dwarf plant (RrTt × rrtt). What will be the ratio of respective four combinations : red tall, red dwarf, white tall and white dwarf plants in the next generation?
- 9:3:3:1
- 15:1:0:0
- 9 : 3 : 4: 0
- 4: 4: 4: 4
Answer: 4. 4: 4: 4: 4
The dihybrid plant with genotype RrTt produces four types of gametes (RT, Rt, rT and rt). The double recessive white dwarf plant produces only single type of gametes (rt). Since, the ratio 4:4:4:4 is equal to the 1:1:1:1 ratio, the correct option is (4).
Question 166. Due to the cross between TTRr × ttrr the resultant progenies show what percent of tall, red flowered plants?
- 50%
- 75%
- 25%
- 100%
Answer: 1. 50%
The cross can be represented as
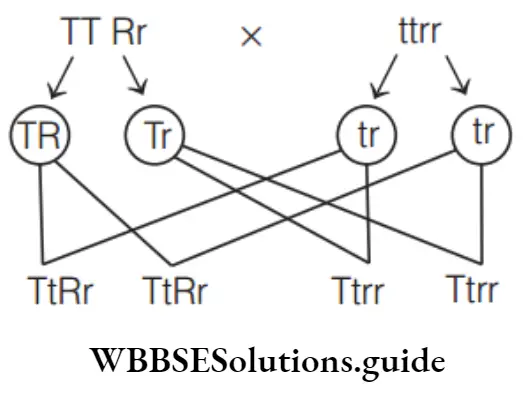
Tall red: TtRr- 50%
Tall white: Ttrr – 50%
Thus, 50% progeny would have tall, red-flowered plants.
Question 167. When a tall and red flowered individual is crossed with a dwarf and white flowered individual, phenotype in the progeny is dwarf and white. What will be the genotype of tall and red flowered individual?
- TTRR
- TtRR
- TtRr
- TTRr
Answer: 3. TtRr
Recessive allele in a zygote appears only if both of its parents have this allele, i.e. they are
heterozygotes. Thus, individual would have TtRr genotype.
Question 168. An individual heterozygous for two alleles (WWTt) produce two million sperms. How many of the sperms will have both the recessive alleles (in millions)?
- 1
- 2
- 0.5
- 0.25
Answer: 3. 0.5
- The given heterozygous individual will produce sperms having following genotype WT, Wt, wT, wt in the ratio 1:1:1:1.
- Thus, out of 2 million sperms, sperms having both the recessive alleles are 0.25 × 2 million = 0.5 million sperms. So, the correct answer is option (3).
Question 169. When a tall plant with round seeds (TTRR) crossed with a dwarf plant with wrinkled seeds (ttrr), the F1 -generation consists of tall plants with round seeds. What would be the proportion of dwarf plant with wrinkled seeds in F2 -generation?
- 1:4
- 1:16
- 0
- 1:2
Answer: 2. 1:16
In F1 -generation, there are no dwarf plants with wrinkled seeds. This is Mendel’s dihybrid cross in which ratio of dwarf plants with wrinkled seeds to total genotypes in F2 -generation is 1:16.
Question 170. Independent assortment means
- Separation of characters of one parent
- Non-separation of characters of one parent
- Combination of parental characters
- Separation of parental characters
Answer: 1. Separation of characters of one parent
According to law of independent assortment, the two factors of each character assort or separate independent of the factors of other characters at the time of gamete formation. They get randomly re-arranged in the offspring,producing both parental and new combinations of traits.
Question 171. If two genes experience independent assortment, which assumption is most likely true?
- They are located in close proximity on the same chromosome
- Crossing over between the genes does not occur
- The genes are located on different chromosomes or are far apart on the same chromosome
- The expression of one gene does not affect the expression of the other
Answer: 3. The genes are located on different chromosomes or are far apart on the same chromosome
Option (3) is most likely to be true as genes on different chromosomes split up independently during gamete formation.
These genes are mostly located on different chromosomes or far apart from each other when present on same chromosome.
Question 172. Which of the following statements is true?
- Segregation occurs at the time of fertilisation
- Segregation occurs at time of mitosis
- Independent assortment of alleles occurs during the formation of gametes by dihybrid cross
- Segregation occurs only in monohybrids
Answer: 3. Independent assortment of alleles occurs during the formation of gametes by dihybrid cross
Statement in option is true as Independent assortment of alleles occurs during the formation of gametes by dihybrid cross. Rest statements are false.
Question 173. How many different types of phenotypes would be produced in F1 progeny of AABBCC × aabbcc that obeys Mendel’s law of independent assortment?
- 8
- 32
- 16
- 1
Answer: 4. 1
In a cross between AABBCC and aabbcc, the gametes are ABC and abc respectively, hence the F1 -generation will have genotype as AaBbCc, i.e. only one type of phenotype.
Question 174.
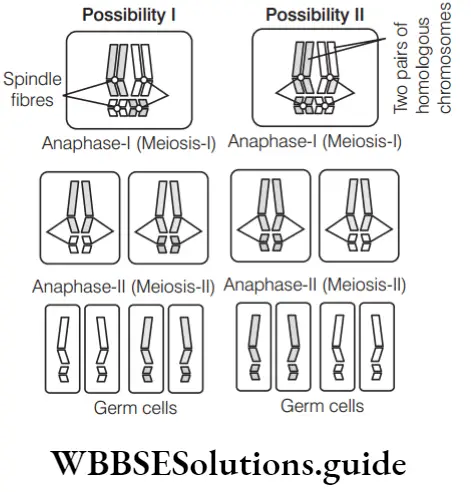
The figure depicts
- Linkage
- Independent assortment
- Law of dominance
- Equational division
Answer: 2. Independent assortment
- The process of gametogenesis or meiosis cell division is shown in the diagram given in question. This clearly indicates towards the Mendel’s law of independent assortment.
- The two factors of each character assort or separate independent of the factors of other characters at the time of gamete formation (gametogenesis) and get randomly re-arranged in the offspring producing both parental and new combination of traits.
Question 175. A women with albinic father marries an albinic man. The proportion of her progeny is
- 2 normal:1 albinic
- All normal
- All albinic
- 1 normal :1 albinic
Answer: 4. 1 normal :1 albinic
The women is heterozygous as albinic condition is recessive hence when she marries an albinic man, the offspring are 50% normal and 50% albinic. So, the proportion of her progeny is 1 normal: 1 albinic.
Question 176. BB for black colour alleles. bb for brown colour alleles. If a black mouse is crossed with a brown mouse and their offspring is then interbreed then find out the percentage of black coat in them.
- 75%
- 50%
- Cross is not possible as black and brown mouse are different species
- 100%
Answer: 1. 75%
Black colour (B) is dominant over the recessive brown so by cross, it is easily inferred that 75% of the offspring are black and 25% are brown.
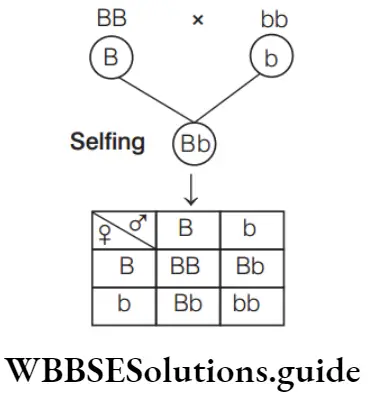
Thus, interbreeding of black offspring would generate 75% black coat and 25% brown coat.
Question 177. A human male produces sperms with the genotypes AB, Ab, aB and ab pertaining to two diallelic characters in equal proportions. What is the corresponding genotype of this person?
- AaBB
- AABb
- AABB
- AaBb
Answer: 4. AaBb
A person producing four type of gametes must have two heterozygote alleles. Only option represents such condition.
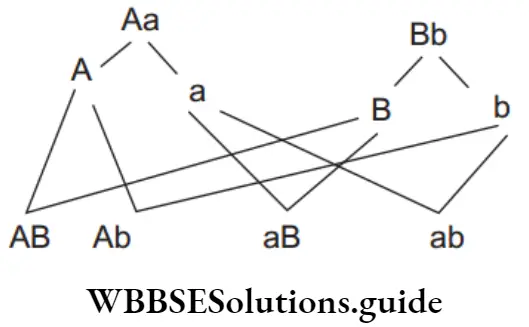
So, the corresponding genotype will be AaBb.
Question 178. How many different types of gametes can be formed by F1 progeny, resulting from the following cross AABBCC × aabbcc
- 3
- 8
- 27
- 64
Answer: 2. 8
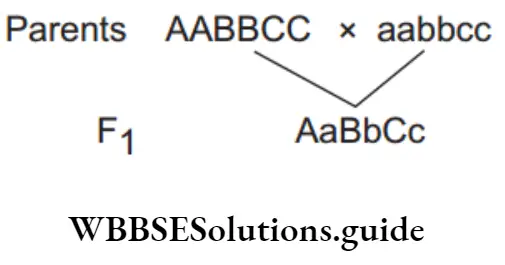
8 gametes will be formed by F1 progeny. Number of heterozygotes is 3. Number of gametes will be 2n or 23 = 8.
Question 179. An individual with genotype SsTtUu will produce …………… gametes.
- 4 types
- All same
- 8 different types
- 4 of one type and rest of one type
Answer: 3. 8 different types
Gametes are calculated by the formula 2n , where n = number of heterozygous alleles in genotype. Here, n =3. Thus, the number of combinations = 23= 8. The possible combinations are: STU, STu, StU, Stu, sTU, stU, sTu and stu.
Question 180. A tobacco plant heterozygous for albinism (a recessive character) is self-pollinated and 1200 seeds are subsequently germinated. How many seedlings would have the parental genotype?
- 1250
- 600
- 300
- 2250
Answer: 2. 600
- Suppose heterozygous for albinism is represented by Aa. If heterozygous for albinism tobacco plant is self- pollinated, 1200 seeds are germinated.
- The genotypic ratio is 1AA: 2Aa: 1aa. This shows that 50% seedlings have the parental genotype. Thus, out of 1200 seeds, 50% or 600 seedlings would have the parental genotype.
Question 181. In rabbits, the gene for grey fur (G) is dominant over that for black fur (g). In a litter, if 50% rabbits are grey, then the possible parental cross combination is
- GG × Gg
- GG × GG
- gg × gg
- Gg × gg
Answer: 4. Gg × gg
When heterozygous grey individuals (Gg) are crossed with homozygous black individuals (gg), then grey and black individuals will be obtained in equal ratio. It is a type of test cross and can be illustrated as
Question 182. A cell is heterozygous at four gene loci. How many different type of gametes can it form?
- 2
- 3
- 6
- 16
Answer: 4. 16
Number of gametes = 2n
n = 4 (given)
24 = 2× 2× 2 ×2 = 16
