Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers Population Stabilisation And Birth Control
Question 1. Study of the human population is known as ………… .
- Anthropology
- Demography
- Geography
- Ethnology
Answer: 2. Demography
- Demography is the study of statistics such as births, deaths, income or the incidence of diseases, which illustrate changing structure of the human population.
- Other options are explained as Anthropology is the study of human behaviour, biology and societies.
- Geography is the study of places and relationships between people and their environment.
- Ethnology is the study of the characteristics of different people, differences and relationships between them.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 2. 11th July is observed as
- World Population Day
- No Tobacco Day
- World Environment Day
- World Health Day
Answer: 1. World Population Day
- World Population Day is an annual event that is observed on 11th July every year. It seeks to raise awareness of global population issues.
- The event was established by the Governing Council of the United Nations Development Programme in 1989.
“neetprep reproductive health “
Question 3. Consider the following statements.
- India is the second largest populated country in world.
- China’s population is largest among all countries.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct as The countries with largest population are as follows
Country – Human population
China – 1341000000
India – 1210000000
USA – 311075000
Indonasia – 237556363
Brazi – 190732694
Thus, China is most populated country in world and India is the second largest country in terms of population count.
NEET Biology Population Stabilization MCQs with answers
Question 4. Given below is the count of world population in different years.
- 1900 – ~ 2 billion
- 2000 – ~ 6 billion
- 2011 – ~ 7.2 billion
Choose the option containing correctly matched pairs.
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2 and 3only
Answer: 3. 1, 2 and 3
All the given options represent correctly matched pairs. Thus, option (c) is correct.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers

Question 5. Assertion (A) Human population has doubled every 35 years in contrary to 200 years since 1600-1800. Reason (R) Rapid increase is due to the availability of better health facilities.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
“mcq reproductive health “
- Better medical or health facilities play a major role in increasing the population.
- Invention of vaccines for almost all dreadful diseases for infants and adults has led to the reduction in death rate.
So, the population has doubled every 35 years in contrary to 200 years since 1600-1800.
Question 6. What is meant by population explosion?
- Increased frequency of diseases in population
- Rapid increase in population number
- Rapid decrease in population number
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Rapid increase in population number
Rapid increase in population over a relatively short period is called population explosion. In 150 years, from 1700 AD human population has doubled from 0.6 billion to 1.2 billion. In contrast, it increased five times during the next 150 years. In 2011, it was 7 billion.
Important MCQs on Birth Control for NEET
Question 7. A reason for the occurrence of population explosion is
- Decline maternal mortality rate
- Decline rate of infant mortality
- Better medical services
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Few reasons for population explosion are as follows
- Decline death rate
- Decline Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR)
- Decline rate of infant mortality.
- Better medical services
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 8. Assertion (A) Overpopulation has become a serious problem in developing countries. Reason (R) It leads to exhaustion of natural resources, causes unemployment and increases pollution.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Overpopulation may exhaust natural resources, causes unemployment and increases pollution, especially in developing countries.
Question 9. Certain demographic features of developing countries are
- High fertility, low or rapidly falling mortality rate, rapid population growth and a very young age distribution
- High fertility, high density, rapidly rising mortality rate and a very young age distribution
- High infant mortality, low fertility, uneven population growth and a very young age distribution
- High mortality, high density, uneven population growth and a very old age distribution
Answer: 1. High fertility, low or rapidly falling mortality rate, rapid population growth and a very young age distribution
Some characteristic demographic features of developing countries are high fertility, low or rapidly falling mortality rate rapid population growth and a very young age distribution.
Question 10. The year 1927 saw a decline in population. The reason for this is
- First World War
- Flood
- Food scarcity
- Second World War
Answer: 3. Food scarcity
- The decline in population in 1927 occurred due to food scarcity.
- First World War took place within year 1916 to 1918 and second World War took place between 1940 to 1942.
Question 11. In India, human population is heavily weighted towards younger age groups as a result of
- Short lifespan of many individuals and low birth rate
- Long lifespan of many individuals and low birth rate
- Short lifespan of many individuals and high birth rate
- Long lifespan of many individuals and high birth rate
Answer: 3. Short lifespan of many individuals and high birth rate
In India, human population is heavily weighted towards the younger age group as a result of high birth rate and short lifespan of many individuals.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 12. Where we can find overstrained infrastructure due to population growth?
- In rural areas
- In forest areas
- In desert areas
- In urban areas
Answer: 4. In urban areas
- Due to overpopulation, growth facilities such as housing, transportation, healthcare and education become inadequate.
- The worst symptoms of congestion in every aspect of living conditions are manifested in the urban areas.
Question 13. In India, the Population Policy was announced in the year
- 1971
- 1976
- 1978
- 1981
Answer: 2. 1976
“questions about reproductive health “
In April 1976, India framed its first ‘National Population Policy’.
It was called for an increase in the legal minimum age of marriage from 15 to 18 for females and from 18 to 21 for males.
Question 14. Practice which does not help greatly in arresting population explosion is
- Use of contraceptives by the married couple
- Educating the masses about the benefits of planned family
- Vasectomy and tubectomy
- Early child marriage
Answer: 4. Early child marriage
- Early child marriage does not help in arresting population explosion.
- It contributes to higher total fertility as women marrying earlier tend to both have children earlier and bear more children over their lifetime than if, they had married later.
- Whereas use of contraceptives by married couples, vasectomy and tubectomy, educating the masses about the benefits of planned family helps in arresting population explosion.
NEET quiz on Population Stabilization and Birth Control with solutions
Question 15. What is the need to control the population growth in India?
- To improve the standard of living among existing people
- To utilise all the natural resources among the existing people
- To participate in war among neighbouring nations
- To increase the mortality rate in India
Answer: 1. To improve the standard of living among existing people
- The need for controlling population growth is urgent and pressing, so that the existing people may have an improved standard of living.
- Overpopulation causes various ill effects on both humans and as well as on the environment.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 16. Which of the following parameter of the population can be negative?
- Birth rate
- Replacement level
- Growth rate
- All of the above
Answer: 3. Growth rate
Population growth rate is the annual average growth rate. It can be a negative parameter. Birth rate and replacement level can never be negative.
Question 17. The best way to control population is
- Educating people on the importance of small families
- Family planning
- Better living conditions
- Better healthcare
Answer: 2. Family planning
- Family planning is the best way to control population.
- It allows people to attain their desired number of children and determines the spacing of pregnancies.
Question 18. ‘Hum Do Hamare Do’ slogan encourages
- Family planning
- Immunisation
- Electronic growth
- Patriotism
Answer: 1. Family planning
“class 12 reproductive health “
‘Hum do Humare Do’ slogan encourages family planning.
Question 19. Assertion (A) Zero population growth should be achieved as early as possible to control human population. Reason (R) This demands a couple to have more than two children.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 3. A is true, but R is false
- A is true, but R is false because two children per couple holds good for zero population growth.
- But in large democratic countries like India, it will take many years for population growth to attain the zero level because couple need to have less than two children to obtain zero growth.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 20. The …………… forbids the practice of child marriages in India.
- The Children Act, 1960
- Dowry Prohibition Act, 1961
- Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006
- Commissions for the Protection of Child Rights
Answer: 3. Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006
- According to the Prohibition of Child Marriage Act (PCMA), 2006, child marriage is a marriage in which the boy is under the age of 21 years and the girl is lesser than 18 years of age.
- It came into effect from 1st November 2007, replacing the Child Marriage Restraint Act (CMRA) of 1929 or Sharda Act.
- This law was amended in 1978, wherein the legal age of marriage of girls was raised from 15 to 18 years and of boys from 18 to 21 years. The amended law was known as the Child Marriage Restraint Act, 1929.
Question 21. Age group in a population is classified on the basis of
- Reproduction rate
- Death rate
- Age of marriage
- Sex ratio
Answer: 1. Reproduction rate
Age groups in a population are classified on the basis of reproductive age. Three major age groups are as follows
- People aged 30-44-Post reproductive years
- People aged 15-29-Reproductive years
- People aged 0-14-Pre-reproductive years
Question 22. Increasing the minimum marriageable age of girls and boys
- Reduces the child bearing period of a married couple
- Increases the child bearing period
- First increases and then decreases the child bearing period
- No effect
Answer: 1. Reduces the child bearing period of a married couple
Raising the minimum age of marriage reduces the fertility (child bearing) period, thereby the chances of birth become less
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 23. Consider the following statements.
- Reproductive potential is maximum reproductive capacity of a population under optimal conditions.
- Pouplation shows highest fertility in botic potential.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 2. Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Statement I is incorrect, but II is correct because, Biotic potential I is the maximum reproductive capacity of a population under optimum environmental conditions.
- Whereas, reproductive potential is the relative capacity of a species to reproduce itself under optimum conditions.
Question 24. ‘Sex ratio’ simply refers to
- Number of males/1000 females
- Number of females/1000 males
- Both 1 and 2
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Number of females/1000 males
Sex ratio refers to the number of females /1000 males in the population. It is an important social indicator to measure the extent of prevailing equity between males and females in a society at a given point of time.
“reproductive health bank of biology “
Question 25. According to the census of 2011, the state to show poorest sex ratio is
- Kerala
- Gujarat
- West Bengal
- Haryana
Answer: 4. Haryana
According to the census, 2011, Haryana has the lowest sex ratio (877) in Indian states, while the union territory, Daman Diu has lowest sex ratio of 618.
Question 26. ………… is responsible for declining female:male ratio.
- Marriage
- Female foeticide
- Contraceptives
- Coitus interruptus
Answer: 2. Female foeticide
Female foeticide involves the process of finding out the sex of the foetus and then aborting it, if it is a girl. It is the major factor for declining female to male ratio.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 27. The vital index means
- Natality – Mortality
- Natality – Mortality/100
- Mortality – Natality
- Natality- Mortality × 100
Answer: 4. Natality- Mortality × 100
- Vital index is defined as the ratio of births to deaths within a population during a given time.
- Birth rate or natality rate is defined as number of births per 1000 individuals of a population per year.
- Death rate or mortality rate is generally expressed as number of deaths per 1000 individuals of a population per year. Therefore, the formula of vital index is Natality x 100 Mortality
Question 28. The best permanent measure to arrest overpopulation is
- Employing vasectomy and tubectomy on the deserving partners of the couple
- Use of condoms by the partners of the couple
- Coitus interruptus
- Safe period method
Answer: 1. Employing vasectomy and tubectomy on the deserving partners of the couple
The best (more or less) permanent measure to arrest overpopulation and birth control is option 1, while options 2, 3 and 4 have a limited advantage.
Question 29. The success of birth control programmes in controlling population growth is dependent on
- Use of contraceptives
- Tubectomy
- Vasectomy
- Acceptability of the above procedures by people
Answer: 4. Acceptability of the above procedures by people
The success of birth control programmes in controlling population growth is dependent on acceptability of the use of contraceptives, tubectomy and vasectomy by all people of society.
Question 30. Natural methods of contraception involve
- Increased spermicidal activity
- Preventing fertilisation
- Decreasing mortality
- Increasing mortality
Answer: 2. Preventing fertilisation
Natural methods of contraception are natural ways to prevent fertilisation. These methods do not employ the use of any device or medicine.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 31. Which of the following is abstinence method for birth control?
- Use of condom
- Use of diaphragm
- Tubectomy
- Avoiding intercourse
Answer: 4. Avoiding intercourse
Abstinence means avoiding intercourse when the chances of conception are the highest.
Whereas use of condom, diaphragm and tubectomy are measures for birth control.
Question 32. Periodic abstinence is avoiding intercourse during the …………… of menstrual cycle.
- Luteal phase
- Ovulatory phase
- Menstrual phase
- None of these
Answer: 2. Ovulatory phase
In periodic abstinence, intercourse is avoided by couple during the ovulatory phase of menstrual cycle.
Question 33. Risky period of conception’, here refers to ‘period’
- 3rd to7th day
- 7th to13th day
- 12th to14th day
- 17th to25th day
Answer: 3. 12th to14th day
- A female is most fertile at the time of ovulation, which usually occurs 12th to14th days before the next period starts.
- This is the time of the month when the female is most likely to get pregnant, i.e. it is the risky period of conception.
Question 34. ‘Safe period’ a means of birth control is based on
- Ovulation occurs on the 14th day of menstrual cycle
- Ovum survives for about 2 days
- Sperms remain alive for about 3 days
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
“reproductive health bank of biology “
- ‘Safe period’ refers to the days when a woman has minimal chances of getting pregnant.
- Ovulation occurs on the 14th day of menstrual cycle, ovum survives for about two days and if insemination takes place then sperms remains active for three days in female reproductive tract.
- During this period, chances of fertilisation are very high thus, one should abstain from coitus from day 10th to17th of menstrual cycle when ovulation could be expected.
- If one consider these parameters, they can calculate their safe period according to their menstrual cycle. Thus, option 4 is correct.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 35. The temporary method of birth control which involves withdrawal of the penis by male before ejaculation is
- Vasectomy
- Coitus interruptus
- Spermicides
- IUCD
Answer: 2. Coitus interruptus
Coitus interruptus, also known as withdrawal or the pull-out method, is a method of birth control in which the male partner, during sexual intercourse, withdraws his penis from a woman’s vagina prior to ejaculation.
Question 36. Identify the natural contraception methods.
- Implantation
- Lactational amenorrhea
- Condoms
- Vasectomy
- Tubectomy
- Sterilisation
Choose the correct option.
- 1 and 2
- 3 and 4
- 5 and 4
- Only 2
Answer: 4. Only 2
Among the listed methods, lactational amenorrhea is the natural contraception method to prevent unwanted pregnancies.
Question 37. Lactational amenorrhea is
- Absence of menses in adult age
- Late onset of menses
- Absence of menses during lactation
- No menses during pregnancy
Answer: 3. Absence of menses during lactation
Lactational amenorrhea refers to the absence of menstruation during intense lactation period. This method is effective only up to maximum period of six months after childbirth.
Question 38. Assertion (A) A woman rarely, conceives during lactation period. Reason (R) Ovulation does not occur during lactation in a postpartum woman.
- Both the A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- Lactational amenorrhea method is based on the fact that ovulation do not occur during the period of intense lactation following parturition.
- Therefore, as long as the mother breast feeds the child, chances of conception are almost nil.
Question 39. Match the following columns.
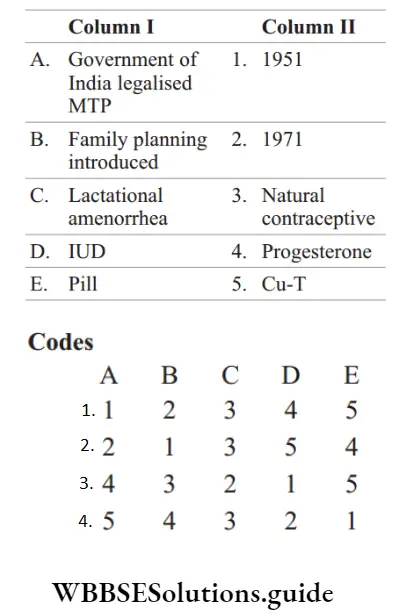
Answer: 2. A-2, B-1, C-3, D-5, E-4
Question 40. Ovulation does not occur in lactating mothers because of the release of
- Inhibin
- Prolactin
- Prostaglandin
- Oxytocin
Answer: 2. Prolactin
- In lactating mother, the release of prolactin helps in the production of milk.
- This hormone suppresses the release of Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH), so during intense lactation, ovulation does not occur.
Question 41. The use of contraceptive during lactation
- Decreases milk secretion
- Increases milk production
- Enhances the antibody production
- Both 2 and 3
Answer: 1. Decreases milk secretion
“reproductive health bank of biology “
According to WHO study, users of the combined and contraceptive pills experienced a 42% decline in milk volume after 18 weeks and they excrete small quantities of antibodies in their breast milk, which can have adverse effects on child.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 42. Birth control devices are mass produced and sold at nominal prices by government to
- Control price rise of articles
- Gain entry in the field of competition
- Control population explosion
- Compete with foreign countries
Answer: 3. Control population explosion
Birth control devices are mass produced and sold at nominal prices by government to control population explosion.
Question 43. A contraceptive is
- Condom, cervical cap or diaphragm
- Intrauterine device
- Pill
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Condom, cervical cap, IUD and pills (combined pills and minipills) are the contraceptives that are used as birth control measures. Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 44. An ideal contraceptive should have which of the following characteristics?
- User friendly
- Easily available
- Cheap and effective
- Interrupt coitus
- Expensive and effective
Choose the correct answer
- 1, 3 and 4
- 1, 4 and 5
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2, 4 and 5
Answer: 3. 1, 2 and 3
An ideal contraceptive should be user friendly, easily available, cheap, effective and reversible with least side effects.
It should not interfere with the sexual drive, desire and sexual act or coitus of the user.
Question 45. An example of mechanical barrier in men that help in family planning is
- Condom
- Mala-D
- IUD
- Copper-T
Answer: 1. Condom
- Mechanical barriers are devices that provide a physical barrier between the sperm and the egg. Examples of mechanical barriers include the male condom, female condom, diaphragm, cervical cap and sponge.
- The condom is the only contraceptive method that helps to prevent Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs).
Question 46. How are condoms helpful?
- They decrease sperm motility
- They increase sperm motility
- They act as a barrier to prevent fusion of sperm and ova
- They increase phagocytosis
Answer: 3. They act as a barrier to prevent fusion of sperm and ova
- Condoms are the barriers madeup of thin rubber/latex sheath used to cover the penis in the male and vagina or cervix in female.
- They prevent the deposition of the ejaculated semen into the vagina of the female. Thus, they prevent the fusion of sperm and ova.
NEET expected MCQs on Birth Control 2025
Question 47. Assertion (A) Use of condoms safeguards a person against sexual diseases such as AIDS and also keep a check on unwanted pregnancy. Reason (R) Certain contraceptives are planted under the skin of the upper arm to prevent pregnancy.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 2. Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- AIDS can be prevented by using condoms that are a kind of barrier contraceptives.
- Contraceptive planted under the skin are called implant and these have synthetic steroid preparation. It works similar to the contraceptive pills.
Question 48. Female condoms are also known as
- Femidom
- Ring condom
- Caps
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Femidom
Femidom term is used for female condoms.
Question 49. …………. are counterparts of condom for females.
- IUCD
- Condom
- Diaphragm and cervical cap
- Copper-T
Answer: 3. Diaphragm and cervical cap
Diaphragm and cervical cap are counterparts of condom for females. Other options are explained as IUCD, is an Intrauterine Contraceptive Device, which is a small device made from plastic and copper. These are planted inside the uterus. It is also known as coil and copper-T is one of its example.
“reproductive health bank of biology “
Question 50. Which of the following is a mechanical barrier used in birth control?
- Loop
- Dalcon shield
- Copper-T
- Diaphragm
Answer: 4. Diaphragm
- The diaphragm is a shallow, dome-shaped cup with a flexible rim that fits securely in the vagina to cover the cervix.
- It blocks the semen from entering the cervix and thus, it is a mechanical barrier used in birth control. Loop, Dalcon shield and copper-T are intrauterine devices.
Question 51. The action of vaginal diaphragm is to
- Prevent the ova to come in the uterus
- Prevent the sperm to come in contact with ova
- Act as a spermicidal agent
- Prevent the implantation of a zygote
Answer: 2. Prevent the sperm to come in contact with ova
The diaphragm covers the cervix and physically prevents sperm from entering the uterus. The spring in the rim of the diaphragm forms a seal against the vaginal walls. These are inserted deep into the vagina and prevent the sperm to come in contact with ova.
Question 52. Diaphragms are contraceptive devices, used by females.
- They are introduced into the uterus.
- They are placed to cover the cervical region.
- They act as physical barriers for sperm entry.
- They act as spermicidal agents.
Choose the option containing correct statements for diaphragm.
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 3 and 4
Answer: 3. 2 and 3
- Statements 2 and 3 are correct for diaphragm whereas 1 and 4 are incorrect.
- These can be corrected as Diaphragm is placed in vagina and it acts as a mechanical barrier for contraception.
Question 53. Spermicidal cream used as the coating of condoms, diaphragms, cervical cap and vaults are meant
- For lubrication
- To prevent infection
- For increasing effectiveness
- To provide medication
Answer: 3. For increasing effectiveness
Spermicidal creams contain chemicals, which kill the sperms. If they are used along with the barrier contraceptives, the effectiveness of contraception increases.
Question 54. Jellies and cream
- Are spermicidal in nature
- Entangle the sperms
- Prevent the release of ova
- Enable the sperms to reach towards ovum rapidly
Answer: 1. Are spermicidal in nature
When spermicidal tablets, foam, jellies and cream are introduced into the vagina before sexual intercourse, it adheres to the mucous membrane and kills the sperm. Thus, these are spermicidal in nature.
Question 55. Which of the following is a method of birth control?
- IUDs
- ZIFT
- GIFT
- 4F-ET
Answer: 1. IUDs
Among the listed options, IUDs help in birth control. Other options represent assisted reproductive techniques which are explained as
- ZIFT is Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer
- GIFT is Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer
- IVF-ET is In Vitro Fertilisation and Embryo Transfer
Question 56. IUD refers to
- Intra Uterus Device
- Intra Uterine Device
- Inter Uterine Device
- Inter Ureter Device
Answer: 2. Intra Uterine Device
The full form of IUD is Intra Uterine Device.
“reproductive health bank of biology “
Question 57. Which one of the following is the most widely accepted method of contraception in India at present?
- Cervical caps
- Tubectomy
- Diaphragms
- IUDs
Answer: 4. IUDs
IUDs are ideal contraceptives for females who want to delay pregnancy. They are one of the widely accepted methods of contraception in India. On the other hand, cervical caps, tubectomy and diaphragms also act as contraceptives
Question 58. Intrauterine devices are used to prevent
- The sperm from reaching the egg
- The sperm from leaving the male reproductive system
- The sperm from surviving for many days in the female reproductive system
- All of the above
Answer: 1. All of the above
The Intra Uterine Device (IUD) causes a foreign body reaction in the uterus, thus leading to cellular and biochemical changes in the endometrium and uterine fluids. These changes impair the viability of the gamete and thus, prevent sperms from reaching the egg.
NEET Biology Birth Control MCQs with explanations
Question 59. Which of the following is a correct statement ?
- IUDs once inserted need not be replaced
- IUDs are generally inserted by the user herself
- IUDs increase phagocytosis of sperms in the uterus
- IUDs suppress gametogenesis
Answer: 3. IUDs increase phagocytosis of sperms in the uterus
Statement in option 3 is correct. Rest of the statements are incorrect and can be corrected as
- IUDs can be replaced as this is a reversible contraception method.
- IUDs are inserted by doctors or expert nurses in the uterus through vagina.
- IUDs do not affect gametogenesis.
Question 60. The material used in manufacturing IUDs is
- Plastic only
- Metal only
- Plastic or metal
- Latex sheaths
Answer: 3. Plastic or metal
IUDs are manufactured using plastics or metal objects
Question 61. Disadvantages of IUD include
- Haemorrhage
- Chances of infection
- Spontaneous expulsion of IUD
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
- Disadvantages of IUD includes haemorrhage, chances of infection and spontaneous expulsion of IUD. Menstruation flow may become heavier, longer or more painful, though this may improve after a few months.
- It does not protect against STD, so the user may need to use condoms as well. If the user get an infection through fitted IUD, it could lead to a pelvic infection, if not treated. Most women stop using an IUD because of vaginal bleeding and pain, although these side effects are uncommon. Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 62. An example of non-medicated IUD is
- Cu-T
- Cu-7
- Multiload-375
- Lippes loop
Answer: 4. Lippes loop
Lippes loop is a non-medicated IUD. It is a flexible polyethylene plastic loop of appropriate size for the uterine cavity. On the other hand, Cu-T, Cu-7, Multiload 375 are medicated intrauterine devices.
Question 63. Who discovered Lippes loop?
- Jack Lippes
- Daniel Lippes
- R L Lippes
- None of these
Answer: 1. Jack Lippes
In 1960, Jack Lippes made the first model of his ‘Double-S’ intrauterine contraceptive device, Lippes loop.
Question 64. Which IUD increases the phagocytosis of the sperms within the uterus?
- Non-medicated IUD
- Copper releasing IUD
- Both 1 and 2
- Hormone releasing IUD
Answer: 3. Both 1 and 2
- Both IUDs in option 1 and 2, increase phagocytosis of sperms within the uterus.
- They are available in the form of non-medicated IUDs, copper releasing IUDs and the hormone-releasing IUDs. Thus, option 3 is correct.
Question 65. Among the following methods of contraception, which can be regarded as the most cost effective reversible contraceptive?
- Copper-T
- Oral pills
- Tubectomy
- Vasectomy
Answer: 1. Copper-T
Among the given options, copper-‘T’ is the most effective method of reversible contraception.
Question 66. An example of copper releasing IUD is
- Cu-T
- Cu-7
- Multiload-375
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Copper releasing IUDs that are frequently used include Cu-T, Cu-7 and Multiload-375. Thus, option (d) is correct.
“reproductive health bank of biology “
Question 67. Cu-T prevents pregnancy by preventing
- Fertilisation
- Ovulation
- Implantation of fertilised egg
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Fertilisation
- Cu- T is an intrauterine copper releasing IUD. This device is inserted by doctors in the uterus through vagina.
- Cu ions that are released in the uterus suppress sperm motility and the fertilising capacity of the sperms. Thus, it prevents pregnancy by preventing fertilisation.
Question 68. The function of copper ions in copper releasing IUDs is
- They suppress sperm motility and fertilising capacity of sperms
- They inhibit gametogenesis
- They make uterus unsuitable for implantation
- They inhibit ovulation
Answer: 1. They suppress sperm motility and fertilising capacity of sperms
Cu2+obstructs sperm motility in the female genital tract and thus, supresses fertilising capacity of sperms.
Question 69. Select the hormone releasing intrauterine devices.
- Vaults, LNG-20
- Multiload-375, Progestasert
- Progestasert, LNG-20
- Lippes loop, Multiload-375
Answer: 3. Progestasert, LNG-20
- Progestasert and LNG-20 are hormone releasing IUDs, which make the uterus unsuitable for implantation and the cervix hostile to sperms.
- In contrast, vaults are mechanical contraceptives, Multiload-375 and Lippes loop are non-hormonal IUDs for preventing pregnancy.
Question 70. Progestogens alone or in combination with oestrogens can be used as a contraceptive in the form of Reason (R) These hormones inhibit ovulation.
- Only implants
- Only injections
- pills, injections and implants
- Only pills
Answer: 3. pills, injections and implants
- Progestogens alone or in combination with oestrogens can be used as a contraceptive in the form of pills, injections and implants under the skin.
- They inhibit ovulation and implantation of the zygote as well as alter the quality of cervical mucus to prevent/retard entry of sperm.
Question 71. Which is the hormonal method of birth control?
- Pill
- IUD
- Vasectomy
- Femidom
Answer: 1. Pill
- Use of oral contraceptive pills is the hormonal method of birth control. Pills have to be taken daily for the period of 21 days starting preferably within the first five days of menstrual cycle.
- After a gap of 7 days (during which menstruation occurs), it has to be repeated in the same pattern till female desires to prevent conception.
Question 72. Which of the following contraceptive methods do involve a role of hormone?
- Lactational amenorrhea, pills, emergency contraceptives
- Barrier method, lactational amenorrhea, pills
- Cu-T, pills, emergency contraceptives
- Pills, emergency contraceptives, barrier methods
Answer: 1. Lactational amenorrhea, pills, emergency contraceptives
- In lactational amenorrhea, due to high prolactin level, gonadotropin level decreases. Oral pills are either progestogens or progestogen-oestrogen combinations used by the females.
- Emergency contraceptives include the administration of progestogens or progestogen-oestrogen combination or IUDs within 72 hours of coitus. So, lactational amenorrhea, oral pills and emergency contraceptives involve a role of hormone.
Question 73. Assertion (A) There is no male contraceptive oral pill available as yet. Reason (R) Male spermatogenic cycles are erratic.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 3. A is true, but R is false.
Although, there is ongoing research into a male contraceptive pill, but these are not available yet. To develop one such pill, male spermatogenic cycle is required to be studied in details. Like mentioned, it is not erratic, but occur in a sequential manner.
Question 74. Given below are the four methods and their modes of action in achieving contraception. Choose the correct mode of action in Column I for the methods in Column 2.

Answer: 3. A-3, B-1, C-4, D-2
Mock test on Birth Control for NEET preparation
Question 75. Administration of progesterone, progestogen-oestrogen combination and IUDs are effective in
- 72 hrs
- 48 hrs
- 24 hrs
- 96 hrs
- Answer: 1. 72 hrs
Administration of oral contraceptives is effective in 72 hours. Oral contraceptive pills increase the risk ofintravascular clotting. Therefore, they are not recommended for women with a history of disorders of blood clotting.
Question 77. One of the following is not a method of contraception. Which one?
- Condoms
- Pills of a combination of oxytocin and vasopressin
- Lippes loop
- Tubectomy
Answer: 2. Pills of a combination of oxytocin and vasopressin
- Oxytocin is a birth hormone that induces foetal ejection reflex and milk ejection following parturition.
- Vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone) reabsorbs water from the renal tubules to conserve water in the body. They have no role in contraception.
Question 78. Consider the following statements and choose the right ones.
- MTP is safe in 2nd trimester.
- Generally, chances of conception are nil until mother breast feed the child for two years.
- Intrauterine devices like copper-T are effective contraceptive.
- Contraceptive pills may be taken up to one week after coitus to prevent conception.
Choose the correct answer
- 3 and 4
- 1 and 3
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
Answer: 1. 3 and 4
- Statements 3 and 4 are correct whereas I and II are incorrect. These can be corrected as
- MTP (Medical Termination of Pregnancy) is safe until the first trimester (12 weeks) and chances of conception are nil until the mother breast feed child, up to six months only.
“reproductive health bank of biology “
Question 79. Pills have to be taken daily for period of … A… day preferably, starting within first five days of menstrual cycle.
It has to be restarted in the same pattern after a gap of …B… days.
- A–27, B–1
- A–21, B–7
- A–22, B–5
- A–24, B–4
Answer: 2. A–21, B–7
- Oral contraceptive pills (oral pills) are used in the form of tablets therefore, they are called ‘pills’.
- Pills have to be taken daily for the period of 21 (A) days, starting within the first five days of menstrual cycle. After a gap of 7 (B) days, it has to be repeated.
Question 80. What role do contraceptive pills carry out?
- They inhibit ovulation and implantation.
- They alter the quality of cervical mucus to prevent or retard the entry of sperms.
- They prevent the ejaculated semen from entering the female vagina.
- They inhibit spermatogenesis.
Choose the correct option.
- 1, 2 and 4
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 2
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: 3. 1 and 2
Oral pills inhibit ovulation and implantation. They alter the quality of cervical mucus to prevent or retard the entry of sperm. But they have no role in preventing spermatogenesis and insemination. Thus, option 3 is correct.
Question 81. Assertion (A) Ovulation is controlled by the hormone oestrogen. Reason (R) Contraceptives are therefore, made up of both oestrogen and progesterone.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- A is false, but R is true
Answer: 4. A is false, but R is true.
Assertion can be corrected as The process of ovulation is controlled by the hypothalamus of the brain and through the release of hormones, Luteinizing Hormone (LH) and Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH).
secreted by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland.
Question 82. Which of the following contraceptive devices makes uterus unsuitable for implantation?
- Progestasert
- Cu-T
- Lippes loop
- Multiload
Answer: 1. Progestasert
Progestasert is a hormone releasing IUD, which makes the uterus unsuitable for implantation and cervix hostile to the sperms.
Question 83. Which hormone of the female body is suppressed by the oral contraceptive pills?
- FSH
- Oestrogen
- Progesterone
- Testosterone
Answer: 1. FSH
- Contraceptive pills contain progestogens and oestrogen hormones.
- These hormones suppresses the FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) which stimulates follicle growth and ovulation.
Question 84. An example of daily oral contraceptive pill is
- Saheli
- Mala-D
- I-pill
- All of these
Answer: 2. Mala-D
- Regular dose oral contraceptive pill can be used as post-coital pill in prescribed dose. Currently available daily oral pills are Mala-D and Mala-N. Mala-N or combined oral contraceptives use two hormones (oestrogen and progestin) to prevent pregnancy.
- Other options are explained as Saheli, the new oral contraceptive for the females contains a non-steroidal preparation.
- It is a once a week pill with very few side effects and high contraceptive value.
- I-pill is used as an emergency contraceptive tablet to prevent unwanted pregnancy in case of unprotected sex or contraception faliure.
Question 85. Use of the pill is associated with an increased risk of
- Stroke
- Endometrial cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Stroke
- Oral contraceptive pills have been associated with increased risk for myocardial infarction, stroke and venous thromboembolism.
- Studies have been published recently that suggest that these risks are minimal in appropriately chosen low risk women.
NEET practice test on Population Stabilization
Question 86. Which among the following is regarded as an absolute contraindication of oral contraceptive pill ?
- Eczema/Dermatitis
- Lactating mother
- Carcinoma breast
- Epilepsy
Answer: 3. Carcinoma breast
Absolute contraindications of oral contraceptive pills include thrombophlebitis or thromboembolic disorders, cerebrovascular or coronary artery disease, carcinoma of the breast or other oestrogen- dependent neoplasia, undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding, known or suspected pregnancy, benign or malignant liver tumour.
Question 87. The difference of oral contraceptives and hormonal implants.
- Differ in sites of implantation
- Differ in duration of action
- Both 1 and 2
- Differ in constituents
Answer: 3. Both 1 and 2
Hormonal implants and oral contraceptives have the combination of oestrogen and progestogen hormones.
Their mode of working is same but the site of implantation and the duration of action is different. Thus, option 3 is correct.
“reproductive health bank of biology “
Question 88. The oral contraceptive developed at CDRI was
- Saheli
- Mala-D
- Both 1 and 2
- None of these
Answer: 3. Both 1 and 2
The contraceptive pill called Saheli was developed by CDRI, Lucknow whereas Mala-D was developed by CDRI, Dehradun. Thus, option 3 is correct.
Question 89. Facts about ‘Saheli’ are
- Developed at CDRI, Lucknow.
- Contains a steroidal preparation.
- ‘Once-a-week’ pill.
- Many side effects.
- High contraceptive value.
- Very few side effects.
Choose the correct answer
- 1, 2, 3, 6 and 5
- 1, 3, 5 and 6
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
- 1, 3, 4 and 5
Answer: 2. 1, 3, 5 and 6
Facts listed in 1, 3, 5 and 6 are correct. Facts 2 and 4 are incorrect and can be corrected as Saheli is non-steroidal pill and it has least side effects.
Question 90. Assertion (A) Saheli is most desirable female oral contraceptive. Reason (R) It is the only non-steroidal contraceptive without any side effects.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Being non-steroidal, Saheli has least side effects. Therefore, it is highly desirable female oral contraceptive.
Question 91. The contraceptive ‘Saheli’
- Blocks oestrogen receptors in the uterus, preventing eggs from getting implanted
- Is a post-coital contraceptive
- Is an IUD
- Increases the concentration of oestrogen and prevents ovulation in females.
Answer: 1. Blocks oestrogen receptors in the uterus, preventing eggs from getting implanted
- The contraceptive ‘Saheli’ blocks oestrogen receptors in the uterus, thus prevent eggs from getting implanted.
- It contains the molecule centchroman which instead of using oestrogen to prevent pregnancy, blocks the oestrogen to do the same.
Question 92. Match the following columns.
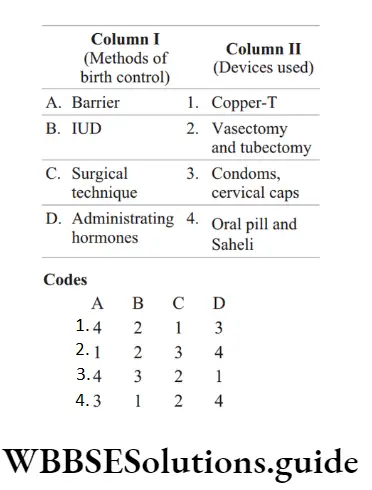
Answer: 4. A-3, B-1, C-2, D-4
Question 93. Which of the following methods is not available for males?
- Surgical
- Hormonal
- Contraceptive
- Abstinence
Answer: 2. Hormonal
Hormonal pills for females are available to prevent unwanted pregnancies, e.g. Mala-D, Saheli, etc. Such hormonal pills are not available for males.
Question 94. Progesterone or progestogen-oestrogen combination injections and implants are used by the females under the
- Skin of the inner arm above elbow
- Vagina
- Stomach’s upper skin
- Cervix
Answer: 1. Skin of the inner arm above elbow
To achieve contraception, six matchstick-sized capsules containing steroids are inserted under the skin of female’s inner arm above the elbow. These steroid capsules slowly release the synthetic progesterone for about five years.
Question 95. Consider the following statements.
- Birth control pills do not cause cardiovascular problem.
- A woman who substitutes the biological mother to nurse the embryo is called surrogate mother.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 2. Statement I is incorrect, but II is correct.
- Incorrect statement can be corrected as Oral contraceptive pills increase the risk of intra vascular clotting.
- Therefore, they are not recommended for women with a history of disorders of blood clotting, blood vessel damage, hypertension, liver malfunction, heart disease or cancer of the breast or reproductive system.
Question 96. Which of the following technique is safest?
- Rhythm method
- Use of physical barriers
- Termination of unwanted pregnancy
- Sterilisation techniques
Answer: 4. Sterilisation techniques
The success rate of the sterilisation method is very high as compared to the other techniques and the number of complications are also very less. So, sterilisation technique is the safest and best
Question 97. The term ‘sterilisation’ refers to
- Tubectomy
- Vasectomy
- Hysterectomy
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Sterilisation refers to any process that eliminates, removes or kills all forms of life. In humans, it is achieved by tubectomy, vasectomy, hysterectomy, etc. Thus, option 4 is correct.
“reproductive health bank of biology “
Question 98. What does surgical method of contraception result in?
- Preventing gamete motility
- Preventing gamete formation
- Gametogenesis promotion
- Facilitates implantation
Answer: 1. Preventing gamete motility
In surgical method of contraception, vas deferens in males and Fallopian tubes in female are cut due to which the motility of gametes is inhibited.
Question 99. Surgical removal of a segment of vas deferens and ligation cut ends is known as
- Tubectomy
- Vasectomy
- Gonadectomy
- Castration
Answer: 2. Vasectomy
Surgical removal and then ligation of vas deferens or sperm duct in males is called vasectomy.
Question 100. Surgical removal of testes is known as
- Testectomy
- Gonadectomy
- Castration
- None of these
Answer: 3. Castration
- Castration is any surgical, chemical or otherwise action, by which an testicles loses its function.
- Surgical castration is bilateral orchidectomy and chemical castration uses pharmaceutical drugs to impair the testes. Thus, surgical removal of testes is known as castration
Question 101. Which of the following is incorrect regarding vasectomy?
- No sperm occurs in seminal fluid
- No sperm occurs in epididymis
- Vasa deferentia is cut and tied
- Irreversible sterility
Answer: 2. No sperm occurs in epididymis
Option 2 is incorrect and can be corrected as Following vasectomy, sperms are formed in testis but they cannot move out of reproductive tract. The option (b), stating that no sperm occurs in epididymis is wrong because, it is a part of testis only. Thus, sperms are found in epididymis even after vasectomy. Rest options are correct regarding vasectomy.
Question 102. Vasectomy
- Prevents the production of sperm in the testes
- Prevents the production of semen
- Prevents the movement of sperm into the urethra
- Prevents a man from having an erection
Answer: 3. Prevents the movement of sperm into the urethra
Following vasectomy, sperm would not be found in female genital tract, e.g. urethra.
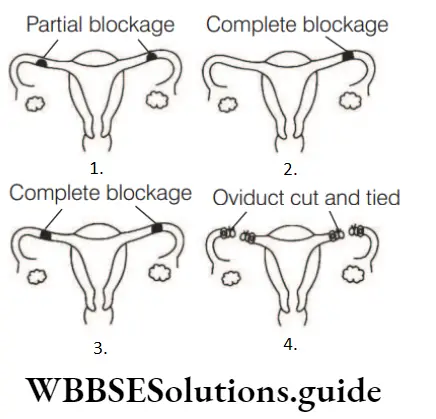
Question 103. From the images given below identify, in which condition of the uterus is fertilisation impossible?
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 3 and 4
- 1and 4
Answer: 3. 3 and 4
Fertilisation is not possible in situations C and D because ova would not be able to reach fertilisation site due to blocked or cutted Fallopian tubes.
Question 104. Which of the following approaches does not give the defined action of contraceptive?
- Barrier methods – Prevent fertilisation
- Intrauterine devices – Increase phagocytosis of sperms, suppress sperm motility and fertilising capacity of sperms
- Hormonal contraceptives – Prevent retarded entry of sperms, prevent ovulation and fertilisation
- Vasectomy – Prevents spermato genesis
Answer: 4. Vasectomy – Prevents spermato genesis
Option 4 does not give the defined action of contraceptive and can be corrected as Vasectomy causes sterilisation by preventing transfer of sperms.
It does not prevent spermatogenesis. Rest options give the defined action of contraceptive.
Question 105. If the vasa deferentia of man is surgically removed then
- Semen will be without sperms
- Spermatogenesis will not take place
- Sperms in semen will be non-motile
- Sperms will be enucleated
Answer: 1. Semen will be without sperms
Function of vasa deferentia is the conduction of sperms from testes to external genitilia. If it is disconnected, semen will be without sperms.
Question 106. Match the contraceptive methods given under Column 1 with their examples given under Column 2. Select the correct option from those given below.
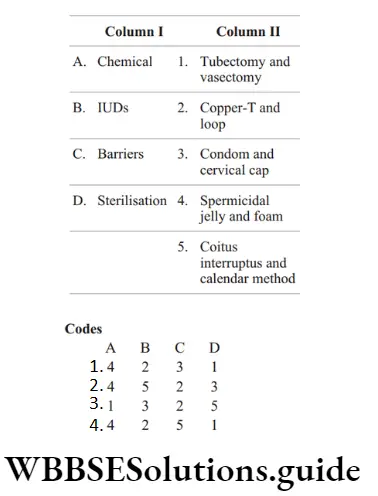
Answer: 1. A-4, B-2, C-3, D-1
107. Surgical removal of uterus is called
- Vasectomy
- Tubectomy
- Hysterectomy
- Anatomy
Answer: 3. Hysterectomy
A hysterectomy is an operation to remove a woman’s uterus. A woman may have a hysterectomy for different reasons, including uterine fibroids that cause pain, bleeding or other problems.
Question 108. The instrument used in tubal ligation
- Laryngoscope
- Proctoscope
- Laparoscope
- None of these
Answer: 3. Laparoscope
Tubal ligation is blocking of Fallopian tube. This procedure is performed using an instrument called laparoscope.
Question 109. Tubectomy, a method of sterilisation involves
- Small part of the Fallopian tube is removed or tied up
- Ovaries are removed surgically
- Small part of vas deferens is removed or tied up
- Uterus is removed surgically
Answer: 1. Small part of the Fallopian tube is removed or tied up
Tubectomy is a method of female sterilisation. A small part of the Fallopian tube is removed or tied up through a small incision in the abdomen or through vagina.
Question 110. Match the following figures with their respective identity.
- Tubectomy
- Vasectomy
- Implants
- Condoms
- Copper-T
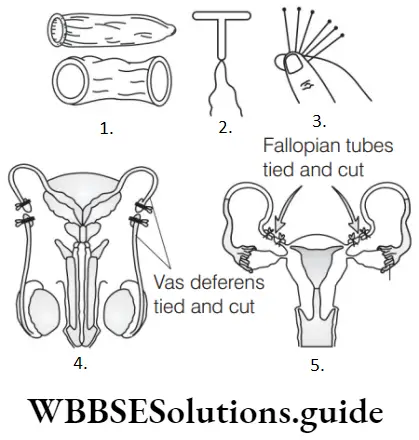
- A-4, B-5, C-3, D-2, E-1
- A-4, B-5, C-2, D-1, E-3
- A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4, E-V
- A-3, B-4, C-V, D-1, E-2
Answer: 1. A-IV, B-V, C-III, D-II, E-I
- Question 111. Identify the incorrect statement regarding the techniques of contraception.
- Tubectomy prevents oogenesis in females.
- Purpose of tubectomy is to prevent formation of ova.
- The most important component of the oral contraceptive pills is progestogens.
- Contraceptive oral pills help in birth control by preventing ovulation.
Choose the correct answer
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 2
- 3, 4 and 2
- 2 and 1
Answer: 2. 1 and 2
- Statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
- These can be corrected as The purpose of tubectomy is to block the passage of ova and it does not interfere with oogenesis. Rest statements are true regarding the techniques of contraception.
