Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers Pregnancy and Embryonic Development
Question 1. After implantation, finger-like projections on the trophoblast are called …A… which are surrounded by …B… and maternal blood. Here, A and B refer to
- A–chorion, B–foetal cell
- A–chorionic villi, B–uterine tissue
- A–uterine tissue, B–chorionic villi
- A–foetal cell, B–chorion
Answer: 2. A–chorionic villi, B–uterine tissue
Question 2. The layer of uterus which becomes much eroded due to placental villi is known as
- Endothelium
- Endometrium
- Endoderm
- Trophoblast
Answer: 2. Endometrium
During the development of foetus, endometrium gets eroded due to placental villi.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 3. Chorionic villi are formed by the modification of
- Outer layer of trophoblast
- Inner layer of trophoblast
- Inner cell mass
- Blastocyst
Answer: 1. Outer layer of trophoblast
Chorionic villi are the modification of outer trophoblast layer of blastocyst, which get attached to the endometrium of uterus.
pregnancy and embryonic development class 12
Question 4. The number of foetal membranes in humans is
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 0
Answer: 3. 4
Humans possess four foetal membranes, viz. amnion, chorion, allantois and yolk sac.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
NEET Biology Pregnancy and Embryonic Development MCQs with answers
Question 5. Extraembryonic membranes are also called
- Foetal membranes
- Embryonic membranes
- Accessory membranes
- Placental membranes
Answer: 1. Foetal membranes
Extraembryonic membranes are also called foetal membranes.
Question 6. Foetal membranes provide
- Protection to embryo
- Nutrition to embryo
- Protection and nutrition to embryo
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Protection and nutrition to embryo
Extraembryonic membranes or foetal membranes are concerned with protection, respiration, excretion and nutrition of developing embryo.
Question 7. The first extraembryonic membrane to make its appearance in the mammals is
- Allantois
- Amnion
- Yolk sac
- Serosa
Answer: 3. Yolk sac
The yolk sac is first membranous sac attached to an embryo. It is formed by the cells of hypoblast adjacent to the embryonic disc. This is alternatively called the umbilical vesicle.
Question 8. Identify A, B, C and D in the figure given below.
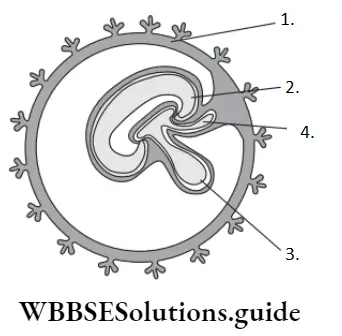
- A–Yolk sac, B–Amnion, C–Allantois, D–Chorion
- A–Chorion, B–Amnion, C–Yolk sac, D–Allantois
- A–Chorion, B–Amnion, C–Allantois, D–Yolk sac
- A–Chorion, B–Allantois, C–Amnion, D–Yolk sac
Answer: 2. A–Chorion, B–Amnion B–Yolk sac, D–Allantois
pregnancy and embryonic development class 12
Question 9. The yolk sac in mammals is
- Absent
- Secretory
- Active
- Present right after fertilisation then disappears
Answer: 3. Active
An active yolk sac is found in mammals. It serves as the first site of blood cell production in human ontogeny until about the 6th week, when the liver takes over this role.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 10. In an organism having amnion, the foetal membranes are
- Zona pellucida, vitelline membrane
- Allantois, chorion
- Choroid, vitelline membrane
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Allantois, chorion
Amnion, chorion, allantois and yolk sac are the foetal membranes or extraembryonic membranes of reptiles, birds and mammals.
Question 11. Which extraembryonic membrane in humans prevents desiccation of the embryo inside the uterus?
- Yolk sac
- Amnion
- Chorion
- Allantosis
Answer: 2. Amnion
Amnion surrounds the embryo and forms amniotic cavity that is filled with amniotic fluid. The amniotic fluid serves as a shock absorber for the foetus (protects the embryo from external injury), regulates foetal body temperature and prevents its desiccation.
Question 12. The amnion of mammalian embryo is derived from
- Ectoderm and mesoderm
- Ectoderm and endoderm
- Mesoderm and trophoblast
- Endoderm and mesoderm
Answer: 1. Ectoderm and mesoderm
Amnion in mammals is formed from mesoderm on outer side and ectoderm on inner side.
Important MCQs on Pregnancy and Embryonic Development for NEET
Question 14. Consider the following statements.
- Chorion is derived from trophoblast on outer side.
- The inner side of chorion is derived from endoderm.
Choose the correct option
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 1. Statement 1 is correct, but 1 is incorrect.
Chorion is formed from outer trophoblast and somatopleuronic mesoderm inside.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 15. Urinary bladder of the embryo is
- Yolk sac
- Allantois
- Amnion
- Both chorion and allantois
Answer: 2. Allantois
Allantois stores the metabolic waste of embryo and thus, acts as urinary bladder of the embryo
pregnancy and embryonic development class 12
Question 16. …A… is composed of endoderm inside and somatopleuric extraembryonic mesoderm outside. In humans, it is small and help in gaseous exchange.
- Allantois
- Chorion
- Amnion
- Placenta
Answer: 1. A–allantois
Question 17. …A… completely surrounds the embryo and protects it. It also takes part in the formation of …B…. . Here, A and B refer to
- A–Chorion, B–placenta
- A–Amnion, B–amniotic cavity
- A–Allantois, B–endoderm
- A–Yolk sac, B–endoderm
Answer: 1. A–Chorion, B–placenta
Question 18. Which of the foetal membrane is directly connected with blood?
- Allantois
- Amnion
- Chorion
- Yolk sac
Answer: 3. Chorion
The chorion membrane is a fibrous tissue layer containing the foetal blood vessels. Villi formed on the outer surface of the chorion, maximise the surface area for contact with maternal blood.
Question 19. Consider the following statements.
- The space between embryo and the amnion is called amniotic cavity which is filled with clear watery fluid secreted by both embryo and membrane.
- It protects the embryo from shock and desiccation.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements, 1 and 2 are correct.
Question 20. The placenta is fully developed
- In first week of pregnancy
- By the end of third month
- Immediately after implantation
- By the end of second week of pregnancy
Answer: 2. By the end of third month
In humans, placenta is fully developed by the end of third month of pregnancy and it lasts throughout the pregnancy.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 21. The placenta of human beings belongs to the category of
- Haemo-chorialis
- Syndesmo-chorialis
- Endothelio-chorialis
- Epithelio-chorialis
Answer: 1. Haemo-chorialis
The placenta of human beings belongs to the category of haemo-chorialis. In this, maternal blood baths foetal chorionic villi directly.
NEET quiz on Pregnancy and Embryonic Development with solutions
Question 22. The type of placenta found in human beings is
- Diffused
- Zonary
- Cotyledonary
- Metadiscoidal
Answer: 4. Metadiscoidal
Metadiscoidal type of placenta is present in human being. In it, the villi are restricted to one disc only. It is also called monodiscoidal condition.
Question 23. Placenta acts as an
- Endocrine gland
- Exocrine gland
- Apocrine gland
- Merocrine gland
Answer: 1. Endocrine gland
Placenta releases oestrogens, progesterone, HCG and relaxin. That is why, it is considered as an endocrine gland.
Question 24. Human placenta develops from
- Ectoderm
- Trophoblast
- Endoderm
- Mesoderm
Answer: 2. Trophoblast
Tropho-ectoderm (trophoblast) is the outermost layer of the cells of a blastocyst. It forms the foetal part of placenta and do not form any part of the embryo properly.
Question 25. The placenta lacks ……………
- Arteries
- Veins
- Smooth muscles
- Nerves
Answer: 4. Nerves
Nerves are not found in placenta. The placenta may be the only human organ that is uninnervated. Only the segment of umbilical cord, closest to the foetus contain nerve fibres.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 26. In humans, the placenta is
- Allanto-chorial
- Pseudo-cotyledon
- Haemochorial
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
The human placenta is allanto-chorial, i.e. the chorial placental circulation is connected with the foetal allantois. It is also haemochorial, metadiscoidal, pseudocotyledon (the villi are grouped and incompletely separated by walls that are between them). Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 27. As compared to the simplest type of placenta, how many barriers are lost in human placenta?
- One
- Two
- Three
- Four
Answer: 3. Three
The simplest type of placenta possesses six barriers. In humans, three barriers are lost. These include uterine epithelium, uterine connective tissue and endothelium of maternal blood vessel.
Question 28. The role of placenta is to
- Convey nerve impulses
- Act as storage organ
- Protect embryo from shocks
- Provide nutrition for developing embryo
Answer: 4. Provide nutrition for developing embryo
The placenta helps to provide oxygen and nutrients to the foetus, whilst removing carbon dioxide and other waste product. It metabolises a numbers of substances and can release metabolic products into maternal and foetal circulations.
pregnancy and embryonic development class 12
Question 29. Which of the following hormones is not secreted by placenta?
- Oestrogen
- Progesterone
- Prolactin
- HCG
Answer: 3. Prolactin
Prolactin is a hormone produced by the anterior pituitary gland and not by placenta.
Question 30. Which of the following substances move from foetal blood to maternal blood?
- Glucose
- Antibodies
- CO2 and urea
- Vitamins
Answer: 3. CO2 and urea
Foetal waste, such as CO2 and urea move from foetal to maternal blood. Glucose, antibodies and vitamins move from maternal blood to foetal blood.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 31. Which one of the following is not the function of placenta?
- Facilitates supply of oxygen and nutrients to embryo
- Secretes oestrogen
- Facilitates removal of carbon dioxide and waste material from embryo
- Secretes oxytocin during parturition
Answer: 4. Secretes oxytocin during parturition
Option 4 is not the function of placenta. Oxytocin is secreted by posterior pituitary gland and not by the placenta. Rest options represent the functions of placenta.
Question 32. Assertion (A) Placenta is connected to the foetus by an umbilical cord. Reason (R) Foetal components of the placenta are derived from the chondroblast.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 3. A is true, but R is false
A is true, but R is false. Reason can be corrected as The foetal component is composed of all placental portions which originate from the blastocyst, including the placental disc, the amniotic and chorionic membranes (often referred to as the foetal membranes) and the umbilical cord. The maternal component is termed decidua and is derived from the maternal endometrium.
NEET expected MCQs on Pregnancy and Embryonic Development 2025
Question 33. A deciduate placenta is one in which union of chorionic villi and uterine mucosa is extensive and complete. Identify which of the following is not a deciduate placenta.
- Zonary deciduate
- Discoidal deciduate
- Contra-deciduate
- Metadiscoidal deciduate
Answer: 3. Contra-deciduate
Contra-deciduate is not a deciduate placenta. In this type, foetal villi and uterine crypts are so intimately connected that most of foetal placenta is left behind at birth to be broken and absorbed by maternal leucocytes, e.g. mole.
Question 34. A placenta that takes part of uterine mucosa with it when it is expulsed is
- Decidua
- True placenta
- Omphaloidean placenta
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Decidua
Human placenta is deciduous type, i.e. at birth, variable amount of maternal uterine mucosa is pulled out with blood.
Question 35. Oxygenated blood flowing in umbilical cord of mammalian embryo is
- 50% maternal and 50% foetal
- 100% maternal
- 100% foetal
- 75% maternal and 25% foetal
Answer: 2. 100% maternal
Oxygenated blood flowing in umbilical cord of mammalian embryo is 100% maternal.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 36. In the given diagram, find out A, B and C.
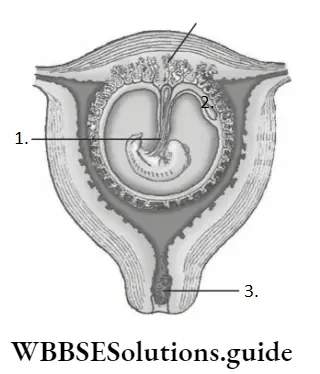
- A–Plug of mucous in cervix, B–Placental villi, C–Umbilical cord
- A–Umbilical cord, B–Placental villi, C–Plug of mucus in cervix
- A–Umbilical cord, B–Plug of mucus in cervix, C–Placental villi
- A–Placental villi, B–Plug of mucus in cervix, C–Umbilical cord
Answer: 2. A–Umbilical cord B–Placental villi C–Plug of mucus in cervix
pregnancy and embryonic development class 12
Question 37. Umbilical cord is formed from
- Yolk sac-amnion
- Yolk sac-allantois
- Yolk sac-chorion
- Chorion-allantois
Answer: 4. Chorion-allantois
Umbilical cord is formed from chorion-allantois. It begins to form by the end of third week of development and by the fifth week of development, its formation is completed.
Question 38. In the foetus, the blood vessel connecting the pulmonary artery to the aorta is the ductus
- Caroticus
- Thoracicus
- Venosus
- Botalli
Answer: 3. Venosus
In foetus, ductus venosus connects the pulmonary artery to the aorta.
Question 39. Consider the following statements.
- The outer surface of chorion develops chorionic villi.
- Human placenta is also called chorionic placenta.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct.
The outer surface of the chorion in humans develops a number of finger-like projection called chorionic villi. Because the chorion takes part in the formation of placenta, the human placenta is chorionic placenta.
Question 40. Which of the following statements about maternal and foetal blood in placenta is incorrect?
- The maternal and foetal blood is not in direct contact
- There is always compatibility between maternal and foetal blood
- The pressure of the maternal blood is far too high for the foetal blood vessels
- Oxygen from the maternal blood passes into the foetal blood
Answer: 2. There is always compatibility between maternal and foetal blood
tatement in option is incorrect and can be corrected as Maternal and foetal blood are not always compatible, e.g. Rh incompatibility. Rest options are correct about maternal and foetal blood in placenta.
Question 41. Which hormone plays an important role during pregnancy?
- HCG
- FSH
- LH
- Progesterone
Answer: 1. HCG
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) is secreted by trophoblastic cells whose properties are similar to that of Luteinizing Hormone (LH). If pregnancy is confirmed, hCG maintains the corpus luteum and stimulates progesterone secretion. So, hCG hormone plays an important role during pregnancy.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 42. Assertion In a woman, hCG is excreted with urine during pregnancy. Reason (R) Presence of hCG in urine is the basis for pregnancy test.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
During pregnancy, hCG is secreted in greater amount by placenta and thus, it is excreted in urine. It forms the basis of pregnancy test.
Question 43. In the event of pregnancy, the corpus luteum persists under the influence of
- LH
- FSH
- Chorionic gonadotropin
- Progesterone
Answer: 3. Chorionic gonadotropin
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) is a peptide hormone produced during pregnancy. Its role is to prevent the disintegration of the corpus luteum of the ovary and thereby, maintain progesterone production that is critical for pregnancy in humans.
NEET Biology Pregnancy and Embryonic Development MCQs with explanations
Question 44. Hormones secreted by the placenta to maintain pregnancy are
- HCG, hPL, progestogens, prolactin
- HCG, progestogens, oestrogens, glucocorticoids
- HCG, hPL, progestogens, oestrogens
- HCG, hPL, oestrogens, relaxin, oxytocin
Answer: 3. HCG, hPL, progestogens, oestrogens
- Placenta releases human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) hormone which stimulates the corpus luteum during pregnancy to release oestrogen and progesterone and also rescues corpus luteum from regression.
- Human Placental Lactogen (hPL) is involved in growth of body of mother and breast. Progesterone maintains pregnancy and prevent uterine contractions by increasing uterine threshold to contractile stimuli.
pregnancy and embryonic development class 12
Question 45. The function of hPL is/are
- Stimulate breast growth and development
- Increase resistance of mother’s tissue to insulin
- Promote breakdown of maternal fats
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
All the listed functions are attributed to hPL. Thus, option is correct.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 46. Select the correct option describing gonadotropin activity in a normal pregnant female.
- High level of FSH and LH stimulates the thickening of endometrium
- High level of FSH and LH facilitates implantation of the embryo
- High level of hCG stimulates the synthesis of oestrogen and progesterone
- High level of hCG stimulates the thickening of endometrium
Answer: 3. High level of hCG stimulates the synthesis of oestrogen and progesterone
Option is correctly describing the gonadotropin activity in a normal pregnant female. hCG is released by placenta which helps in sustaining the level of sex hormones like oestrogen and progesterone to support pregnancy.
Rest options are not correct and can be corrected as High level of progesterone stimulates thickening of endometrium and facilitates implantation of embryo.
Question 47. Identify the correct statement.
- HCG, hPL and relaxin are produced in women only during pregnancy
- During pregnancy, the level of hormones like oestrogens, progestogens, cortisol, prolactin, thyroxine, etc., are increased several folds in the maternal blood
- Increased production of hCG, hPL, progesterone, etc., is essential for supporting the foetal growth, metabolic changes in the mother and maintenance of pregnancy
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
All given statements are correct. hCG, hPG and relaxin are produced during pregnancy. Also, the levels of other hormones like oestrogen, progesterone, cortisol, prolactin, thyroxine, etc., increased several folds in maternal blood.
Increased production of these hormones is essential for supporting the foetal growth, metabolic changes in the mother and maintenance of pregnancy. Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 48. hCS (human Chorionic Somatomammotropin) was previously called
- Human Placental Lactogen (hPL)
- Chorionic thyrotropin
- Chorionic corticotropin
- Relaxin
Answer: 1. Human Placental Lactogen (hPL)
Human Placental Lactogen (hPL) was previously called human Chorionic Somatomammotropin (hCS).
Question 49. ……….. secretes the hormone relaxin.
- Placenta
- Ovary
- Anterior lobe of pituitary
- Posterior lobe of pituitary
Answer: 2. Ovary
Relaxin is secreted by ovary. It increases the flexibility of the pubic symphysis and ligaments of the sarcoiliac and sacrococcygeal joints that help to dilate the uterine cervix during labour pain.
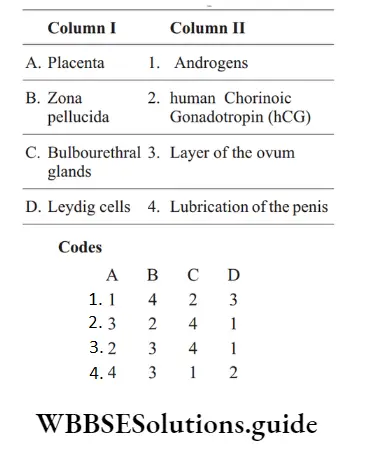
Question 50. Match Column I with Column II and select the correct option using the codes given below

Answer: 2. A-3, B-4, C-1, D-2
Question 51. The main function of trophoectoderm in mammalian embryo is
- Protection of the developing cells
- Drawing food for the developing cells
- Formation of yolk sac
- Formation of body of developing embryo
Answer: 2. Drawing food for the developing cells
rophoectoderm forms placenta which helps to draw food or nutrition for the developing cells.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 52. Which of the following is not derived from ectoderm?
- Inner ear
- Middle ear
- Optic nerve
- Skin
Answer: 2. Middle ear
- External ear, outer layer of tympanic membrane, membranous labyrinth (internal ear) are the derivative of ectoderm.
- Epithelium of Eustachain tube, middle ear, inner layer of tympanic membrane are derived from endoderm. So, middle ear is not derived from ectoderm.
pregnancy and embryonic development class 12
Question 53. Bones of our body are derived from the mesoderm except
- Facial
- Femur
- Radula
- Occipital
Answer: 1. Facial
All bones are derived from the mesoderm, but only facial bones are derived from the ectoderm.
Question 54. In human body, ectoderm produces
- Nervous system
- Sweat gland
- lens of eye
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
All given options derived from ectoderm in human body. In human body, ectoderm produces nervous system, sweat gland, eye lens, etc.Thus, option is correct.
Question 55. Eye develops from
- Ectoderm
- Mesoderm
- Endoderm
- Ecto-endoderm
Answer: 1. Ectoderm
Eye (retina, lens and cornea) develops from embryonic ectoderm.
Question 56. Salivary glands are derived from
- Ectoderm
- Mesoderm
- Endoderm
- All of these
Answer: 1. Ectoderm
Salivary glands are ectodermal in origin.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 57. Ectodermal origin is seen in
- Spleen
- Hypothalamus
- Pituitary gland
- Both 2 and 3
Answer: 4. Both 2 and 3
Hypothalamus and pituitary gland are derived from embryonic ectoderm. Thus, option is correct.
Mock test on Pregnancy and Embryonic Development for NEET preparation
Question 58. Which option contain mesodermal structures only?
- Kidney, urinary and genital ducts
- Nasal epithelium, coelomic epithelium
- Urinary bladder, pancreas
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Kidney, urinary and genital ducts
Kidney, urinary and genital ducts are mesodermal in origin.
Question 59. Notochord, skeletal system and dermis of the skin are the derivatives of
- Mesoderm
- All the three layers
- Ectoderm
- Endoderm
Answer: 1. Mesoderm
Notochord, skeletal system and dermis of the skin are mesodermal in origin.
pregnancy and embryonic development class 12
Question 60. In humans, visceral peritoneum, circulatory system and muscles are derived from
- Mesoderm
- Ectoderm
- Endoderm
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 1. Mesoderm
Visceral peritoneum, circulatory system and muscles are derived from mesoderm in humans.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 61. The lateral mesoderm splits to form visceral and parietal layer which encloses the
- Proctodaeum
- Stomodaeum
- Splanchnocoel
- None of these
Answer: 3. Splanchnocoel
Splanchnocoel in vertebrates embryo is a pair of temporary coelomic cavities located on either side of the body below the gut. Lateral mesoderm splits to form visceral and parietal layer which encloses the splanchnocoel.
Question 62. After gastrulation, the roof of archenteron is formed by
- Neural plate
- Mesoderm
- Ectoderm
- Chordamesoderm
Answer: 4. Chordamesoderm
Chordamesoderm is a type of mesoderm that lies along the central axis under the neural tube. It gives rise to notochord. It forms the roof of archenteron after gastrulation process.
Question 63. Which of the following system is not mesodermal in origin?
- Circulatory system
- Muscular system
- Nervous system
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Nervous system
Nervous system is derived from the ectoderm (not mesoderm) layers. The other three structures are mesodermal in origin.
Question 64. All the following structures are ectodermal except one which is mesodermal in origin.
- Epithelium of retina
- Optic nerve
- Eye lens
- Outer eye layers
Answer: 4. Outer eye layers
Outer eye layers are mesodermal (not ectodermal) in origin.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 65. Which of the following is correct?
- Mesoderm produces brain
- Ectoderm produces liver
- Mesoderm produces skeleton
- Endoderm produces heart
Answer: 3. Mesoderm produces skeleton
Option is correct.Connective tissue, bone (skeleton) and cartilage, heart, blood, muscles and gonads are formed from mesoderm. Rest options are incorrect.
Question 66. Spleen develops from
- Ectoderm
- Mesoderm
- Endoderm
- None of these
Answer: 2. Ectoderm
Spleen is mesodermal in origin.
Question 67. Gonads are derived from embryonic
- Mesoderm
- Endoderm
- Ectoderm
- Mesoderm and endoderm
Answer: 1. Mesoderm
Gonads are derived from embryonic mesoderm.
NEET practice test on Pregnancy and Embryonic Development
Question 68. The only human system that is derived from all the three germ layers is
- Digestive system
- Excretory system
- Respiratory system
- Nervous system
Answer: 1. Digestive system
The human digestive system is derived from all the three germ layers, e.g. mouth is ectodermal, mesentron or midgut is endodermal and walls of gut are mesodermal in origin.
Question 69. Which layer develops first during embryonic development?
- Ectoderm
- Mesoderm
- Endoderm
- Both 2 and 3
Answer: 3. Endoderm
Endodermal cells are formed first during gastrulation (embryonic development). They first cover the free surface of the embryonal knob. Then, they rapidly multiply, spread out in all directions.
pregnancy and embryonic development class 12
Question 70. Ontogenetically the liver is …………… in origin.
- Ectodermal
- Endodermal
- Epidermal
- Mesodermal
Answer: 2. Endodermal
Ontogenetically, the liver is derived from endoderm.
Question 71. After the formation of endoderm, the embryonic knob becomes columnar to form
- Amniotic cavity
- Embryonic disc
- Embryonic coelom
- Chorion
Answer: 2. Embryonic disc
The floor of the amniotic cavity is formed by the embryonic disc. It is composed of a layer of prismatic cells called the embryonic ectoderm. These are derived from the inner cell mass and lie in apposition with the endoderm.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 72. Human tongue is derived from
- Ectoderm
- Mesoderm
- Endoderm
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 3. Endoderm
Human tongue is derived from endoderm.
Question 73. An endodermal structure is
- Intestinal glands
- Salivary glands
- Ciliary muscles
- Both 1 and 3
Answer: 1. Intestinal glands
Intestinal glands are endodermal in origin.
Question 74. Archenteron is lined with
- Ectoderm
- Mesoderm
- Endoderm
- Mesoderm and endoderm
Answer: 3. Endoderm
Archenteron is lined with the endoderm.
Question 75. From one egg in gastrula if all endodermal cells are removed the organism will lack
- Eyes
- Heart
- Brain
- Visceral organs
Answer: 4. Visceral organs
If the endodermal cells are removed at gastrula stage of the development, the organisms will lack the visceral organs.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 76. The endodermal derivatives include
- Thyroid
- Pineal gland
- Spleen
- Pituitary
Answer: 1. Thyroid
Thyroid gland is endodermal derivatives.
Question 77. Choose the odd one out.
- Prostate gland
- Vaginal lining
- Sclerotic coat of eye
- Thymus
Answer: 3. Sclerotic coat of eye
Option is odd one out because Sclerotic coat of eye is mesodermal in origin, whereas the other three structures are endodermal in origin.
pregnancy and embryonic development class 12
Question 78. Identify the correctly matched pair/pairs of the germ layers and their derivatives.
- Ectoderm – Epidermis
- Endoderm – Dermis
- Mesoderm – Muscles
- Mesoderm – Notochord
- Endoderm – Enamel of teeth
Choose the correct answer
- 1 and 4 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
Answer: 3. 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 are correctly matched pairs of the germ layers and their der4at4es. Ectoderm – Epidermis, Mesoderm – Muscles Mesoderm – Notochord.
- Rest options (2 and 5) are not correctly matched pairs of the germ layers and their der4at4es. These can be corrected as Mesoderm-Dermis Ectoderm-Enamel of teeth.
Question 79. Stem cell can give rise to/the
- Any types of cells
- Heart cells
- Special tissue
- Special organs only
Answer: 1. Any types of cells
Stem cells are cells that can differentiate into any types of cell. They are also called totipotent cells. Stem cells are found abundantly in plants and animals.
Question 80. Inner cell mass contains certain cells known as ………….., which have the potency to g4e rise to all types tissues and organs.
- Stem cell
- Germ cell
- Mesodermal cell
- Special cell
Answer: 1. Stem cells are the specialised cell found in inner cell mass. They can transform or differentiated into any kind of cells.
Question 81. The term, ‘metaplasia’ refers to the process by which
- Differentiated cell is able to become transformed into a differentiated cell of another type
- Cell becomes differentiated
- Cell grows abnormally fast
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Differentiated cell is able to become transformed into a differentiated cell of another type
Metaplasia is the transformation of one differentiated cell type to another differentiated cell type. The change from one type of cell to another may be part of a normal maturation process or
caused by some sort of abnormal stimulus.
Question 82. The life history of an organism completed in the egg or in womb of the mother is called
- Post-natal development
- Pre-natal development
- Antogenetic development
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Pre-natal development
Pre-natal development refers to the process in which baby develops from a single cell called zygote into an embryo and later into a foetus inside the mother’s body.
Question 83. In human beings, at the end of 12 weeks during first trimester of pregnancy the following is observed
- Eyelids and eyelashes are formed
- Most of the major organ systems are formed
- The head is covered with fine hair
- Movement of the foetus
Answer: 2. Most of the major organ systems are formed
In human beings at the end of 12 weeks or first trimesters, most of the major organ systems are formed, e.g. the limbs and external genital organs are well-developed.
Question 84. Consider the following statements.
- During second trimester, hCG level increases.
- Placenta produces progesterone during second trimester.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 2. Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
pregnancy and embryonic development class 12
Statement I is incorrect, but 2 is correct. Incorrect statement can be corrected as In 2nd trimester of pregnancy, hCG level declines and corpus luteum deteriorates and the placenta completely takes over the production of progesterone which maintains the pregnancy.
Question 85. Embryologist can draw the fate maps of future organ of embryo in ………… stage.
- Blastula
- Morula
- Early gastrula
- late gastrula
Answer: 1. Blastula
Fate map is the map of future organs of the embryo and it is decided in blastula stage of embryo. Hence, fate map is drawn in blastula stage.
Question 86. During embryonic development, the establishment of polarity along anterior/posterior, dorsal/ventral or medial/lateral axis is called
- Organiser phenomenon
- Axis formation
- Anamorphosis
- Pattern formation
Answer: 2. Axis formation
- All vertebrate eggs are strongly polar structures. The two opposite poles are differentiated as animal pole and vegetal pole. The imaginary axis passing through these two poles is called polar axis or animal-vegetal axis. It is the main axis of egg.
- Thus, during embryonic development, the establishment of polarity along anterior/posterior, dorsal/ventral or media/lateral axis is called axis formation.
Question 87. The embryo is designated as foetus
- When heart starts beating
- After the second month
- After the completion of seventh month
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 2. After the second month
After the completion of second month, the embryo is called foetus.
Question 88. The early stage human embryo distinctly possesses
- Gills
- Gill slits
- External ear (pinna)
- Eyebrows
Answer: 2. Gill slits
Early human embryo possesses a dorsal hollow nerve cord, a well developed notochord and a series of gill slits, which represent the fundamental chordate characters.
Question 89. The branch of embryology which concerns with the study of abnormal embryonic development is termed as
- Gerantology
- Teratology
- Embryology
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Teratology
Teratology is the study of foetal malformations (i.e. abnormal embryonic development).
Question 90. Women who consume the drug thalidomide for relief from vomiting during early months of pregnancy gave birth to children with
- No spleen
- Harelip
- Extra fingers and toes
- Underdeveloped limbs
Answer: 4. Underdeveloped limbs
Thalidomide is a well-known synthetic teratogen drug which is often consumed by pregnant lady during early months of pregnancy to gain relief from vomiting. Use of this drug causes multiple defects in the growing embryo, out of which underdeveloped limbs in foetus is very common.
Question 91. From which embryonic structure does vertebral column develop?
- Notochord
- Nerve cord
- Coelom
- Atrium
Answer: 1. Notochord
- Notochord is a flexible rod-like structure of mesodermal cells that is the principal longitudinal structural element of chordates and of the early embryo of vertebrates.
- It plays an organisational role in nervous system development. In later vertebrate development, it becomes a part of the vertebral column.
Question 92. The process by which one part of a developing embryo influences the differentiation of other parts is known as
- Transduction
- Induction
- Metamorphosis
- None of these
Answer: 2. Induction
Induction is the process by which one part of a developing embryo influences the differentiation of other parts. It directs the development of various tissues and organs in most animal embryos.
Question 93. Heart is formed in embryo during …………… month of development.
- Fourth
- First
- Fifth
- Second
Answer: 2. First
In human embryo, the heart is formed during the first month of development.
Question 94. Interauricular septum in the embryonic stages has
- Fenestra ovalis
- Fossa ovalis
- Fenestra rotunda
- Foramen ovalis
Answer: 4. Foramen ovalis
The fossa ovalis is an oval depression in the interior part of the interauricular septum. It represents the foramen ovale of the foetus. The floor of the foramen ovale represents the fused wall of the septum primum of the foetus.
pregnancy and embryonic development class 12
Question 95. Limbs and digits of the foetus develop in ………… of development.
- 2nd month
- 3rd month
- 4th month
- 5th month
Answer: 1. 2nd month
The limbs and digits of the foetus develop by the 2nd month of pregnancy.
Question 96. Most of the organs of foetus are formed during ………… of development.
- 1st month
- 2nd month
- 3rd month
- 4th month
Answer: 3. 3rd month
Most of the organs of foetus are formed during the 3rd months of development.
Question 97. External genitalia develop in the ……………… of development.
- 2nd month
- 5th month
- 3rd month
- 1st month
Answer: 3. 3rd month
External genitalia develop in the the third month of development of the embryo.
Question 98. Appearance of hair on head is observed during ……………… of development.
- 2nd month
- 3rd month
- 4th month
- 5th month
Answer: 4. 5th month
The first movements of the foetus and appearance of hair on its head are usually observed during the 5th month of pregnancy.
Question 99. Baby moves vigorously, responds to the touch and loud noises, swallows amniotic fluid and urinates during ………. of development.
- 20 weeks
- 24 weeks
- 26 weeks
- 28 weeks
Answer: 4. 28 weeks
After 28 weeks of development, foetus move vigorously, responds to the touch and loud noises, swallows amniotic fluid and urinates.
Question 100. Body covered with fine hair, eyelid separates and eyelashes are formed during of development.
- 3rd month
- 4th month
- 5th month
- 6th month
Answer: 4. 6th month
In human embryo, during 6th month of development, the body is covered with fine hair, eyelid separates and eyelashes are formed.
Question 101. Match the following columns
Answer: 3. A–2, B–3, C–4, D–1
