Biology MCQs with answers for NEET Regulation Of Gene Expression
Question 1. The term ‘regulation’ refers to the control over the working of
- A gene
- Rrna
- Trna
- Mrna
Answer: 1. A gene
The term regulation refers to the control over the working of a gene. Regulation of gene expression refers to a very broad term that may occur at various levels. Considering gene expression results in the formation of a polypeptide, it can be regulated at several levels.
In eukaryotes, regulation could be exerted at
“molecular basis of inheritance “
The transcriptional level (formation of primary transcript) Processing level (regulation of splicing) transport of mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm Translational level
Question 2. Operon is
- A set of closely linked genes, regulating a metabolic pathway in prokaryotes
- The sequence of three nitrogen bases determining a single amino acid
- The sequence of nitrogen bases in mRNA, which codes for a single amino acid
- A gene responsible for switching on or off other genes
- A segment of dna, specifying one polypeptide chain in protein synthesis
Answer: 1. A set of closely linked genes, regulating a metabolic pathway in prokaryotes
Operon is a set of closely linked genes that regulate a metabolic pathway in prokaryotes.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 3. Who gave the first operon system?
- Frederick sanger
- Jacob and Monod
- Both 1 and 2
- Bateson
Answer: 2. Jacob and Monod
The first operon, lac operon was discovered by Jacob and Monod (1961).
They found out that the genetic material possesses a regulated gene a unit called an operon.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
NEET Biology regulation of gene expression MCQs with answers
Question 4. Which type of regulation takes place in lac operon?
- Positive regulation
- Neutral regulation
- Negative regulation
- Both 1 and 3
Answer: 4. Both 1 and 3
Regulation of lac operon by the repressor is referred to as negative regulation. Lac operon is under the control of positive regulation as well, by CAP (Catabolic Activator Protein).
It exerts a positive control in the lac operon because, in its absence, RNA polymerase is unable to recognize the promoter gene and switch off the lac operon. So, positive and negative types of regulations take place in the lac operon
Question 5. Jacob and Monod studied lactose metabolism in e. Coli and proposed operon concept, which is applicable for
- Prokaryotes
- Eukaryotes
- Protozoans
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Prokaryotes
The Operon model was given by Jacob and Monod (1961) for the regulation of protein synthesis in prokaryotes (bacteria)
Question 6. In the lactose operon of Escherichia coli, what is the function of the promoter?
- Binding of gyrase enzyme
- Binding of RNA polymerase
- Codes for RNA polymerase
- Processing of messenger RNA
Answer: 2. Binding of RNA polymerase
In the lactose operon of E.coli, promoter gene (P) is the actual site of the start of transcription and it is the site where RNA polymerase binds to the DNA prior to the beginning of transcription.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 7. All of the following are part of an operon except
- An operator
- A promoter
- An enhancer
- Structural genes
Answer: 3. An enhancer
All of the following are part of an operon except an enhancer
Regulation of gene expression multiple choice questions for NEET
Question 8. In the regulation of gene expression in prokaryotes,
- Lactose acts as a suppressor for the gene expression.
- Tryptophan acts as an inducer for the gene expression.
- The regulatory gene is the one that produces the repressor molecule.
“molecular biology mcq “
Choose the options containing correct statements.
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Only 3
- 1 And 2
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer: 3. Only 3
Statement 3 is correct for the regulation of gene expression in prokaryotes whereas 1 and 2 are not correct and can be corrected as Lactose acts as an inducer for the gene expression in the lac operon. Tryptophan acts as a repressor for gene expression in the trp operon
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 9. The region of the lac operon must be free (unbound) for the structural gene transcription to occur in
- Operator
- Promoter
- A gene
- Regulator
Answer: 1. Operator
The operator is a DNA sequence present between the promoter region and the first coding gene.
A regulator gene regulates the expression of structural genes by its protein product which is mostly transcription factors. This regulatory protein binds to the operator region and hence, prevents the binding and transcription.
Thus, the operator region serves as a repressor protein binding site and it must be free (unbound) for the structural gene transcription to occur.
NEET MCQs on gene expression and regulation with solutions
Question 10. The functioning of structural genes is controlled by
- Operator
- Promoter
- Ligase
- Regulatory gene
Answer: 1. Operator
The operator gene allows the functioning of the operon. Operator genes are a region of DNA sequence capable of interacting with a specific repressor molecule and thus, it affects the activity of other genes downstream to it.
Question 11. In lac operon, a repressor comprises
- Dna
- Rna
- Protein
- Lactose
Answer: 3. Protein
The repressor is a regulatory protein, which is synthesized all the time by the regulator gene.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 12. Lactose operon is considered to be glucose sensitive due to
- Catabolite induction
- Allosteric inhibition
- Anabolic inhibition
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Catabolite induction
Glucose is a positive regulator of lactose operon. It responds to levels of glucose through catabolite induction which requires Catabolite Activator Protein (CAP) and cyclic AMP.
The binding of the CAP-cAMP complex to a promoter is required for the transcription of the lac operon.
The presence of glucose in a cell decreases cAMP concentration which in turn decreases the amount of CAP-cAMP complex.
Due to this, the promoter gets inactivated and the lac operon is turned off. Thus, due to catabolite induction, the lac operon is considered glucose sensitive.
“rna polymerase diagram “
Question 13. Repressor proteins of lac operon bind to
- Exons
- Introns
- Operator
- Structural genes
Answer: 3. Operator
Regulatory genes or i-gene produce mRNA, which makes repressor proteins that in turn, bind to the operator.
Due to the binding of the repressor to the operator, RNA polymerase cannot bind with the promoter. As a result, the working of the operon stops.
Question 14. In the lac operon model, all time or constitutively working gene is
- Operator
- Promoter
- Regulator
- Structural
Answer: 3. Regulator
In the lac operon, the regulatory gene or i-gene keeps on synthesizing the inhibitor. Thus, it is a constitutively working gene. It is the inducer (lactose) that inhibits the inhibitor by binding to its specific sites.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 15. Positively regulated proteins are called
- Activator
- Repressors
- Necessary proteins
- Codons
Answer: 1. Activator
The operon is regulated in both negative and positive ways. Negative control The product of the regulatory genes (repressor) shuts off the expression of genes under its control.
Positive control The product of the regulatory genes (activator) activates the expression of genes under its control. Thus, the positively regulated proteins are called activators.
Question 16. Genes that are responsible for the synthesis of a polypeptide chain are called
- Structural gene
- Operator gene
- Promoter gene
- Regulator gene
Answer: 1. Structural gene
Structural genes are the genes that are responsible for the synthesis of the polypeptide chain.
They transcribe to give mRNA which contains codons for amino acids
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 17. Match the components of ‘lac operon’. Coli is given under column 1 with their functions listed in column 2. Choose the option from the codes given below.
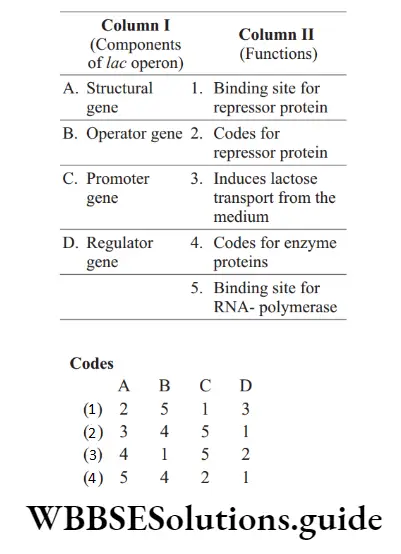
Answer: 3. 1–4, 2–1, 3–5, 4–2
Important gene regulation questions for NEET exam
Question 18. The sequence of the structural genes in the lac operon concept is
- Lac a, lac y, lac z
- Lac a, lac z, lac y
- Lac y, lac z, lac a
- Lac z, lac y, lac a
Answer: 4. Lac z, lac y, lac a
Lac operon (lactose operon) is a genetic system of E. coli, which is responsible for the uptake and initial catabolism of lactose. The lac operon consists of three structural genes in a sequence of lac Z, lac Y, lac A
Question 19. Lactose is transported into cells through
- Β-galactosidase
- Permease
- Transacetylase
- Transferase
Answer: 2. Permease
Lactose is transported into the cells by the enzyme permease. Permease enzyme is produced by the structural gene Y
“which one of the following is not applicable to rna “
Question 20. Consider the following statements.
Structural genes produce mRNA when the operator gene is turned on by an inducer.
The promoter gene base sequence determines which strand of dna acts as a template.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 21. The lac operon is turned on when allolactose molecules bind to
- Promoter site
- Operator site
- Mrna
- Repressor protein
Answer: 4. Repressor protein
The repressor protein binds to the operator region of the operon and prevents RNA polymerase from transcribing the operon.
In the presence of an inducer, such as lactose or allolactose, the repressor is inactivated by interaction with the inducer. This allows RNA polymerase access to the promoter and transcription proceeds. Thus, the lac operon is turned on when allolactose molecules bind to the repressor protein
Solved MCQs on gene expression and regulation for NEET Biology
Question 22. In the lac operon, the structural genes are switched off when
- The repressor binds to the operator
- Repressor binds to the promoter
- Repressor binds to regular
- Repressor binds to inducer
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Repressor binds to the operator
The structural genes remain switched off and do not proceed with transcription till the repressor remains bound to the operator
Question 23. The lactose (lac) operon is regulated by
- Lac repressor only
- Lac repressor and cap-cgmp complex
- Lac repressor and cap-camp complex
- Cap-camp and cap-cgmp complex
Answer: 3. Lac repressor and cap-camp complex
Two regulators turn the operon on and off in response to lactose and glucose levels, the lac repressor, and the CAP–cAMP complex.
The lac repressor acts as a lactose sensor. It normally blocks transcription of the operon but stops acting as a repressor when lactose is present.
Glucose is a positive regulator of lactose operon. It responds to levels of glucose through catabolite induction which requires Catabolite Activator Protein (CAP) and cyclic AMP.
The binding of the CAP-cAMP complex to a promoter is required for the transcription of the lac operon.
The presence of glucose in a cell decreases cAMP concentration which in turn decreases the amount of CAP-cAMP complex.
Due to this, the promoter gets inactivated and the lac operon is turned off. Thus, due to catabolite induction, the lac operon is considered glucose sensitive.
“which of the following is an initiation codon “
Question 24. Match the following columns.
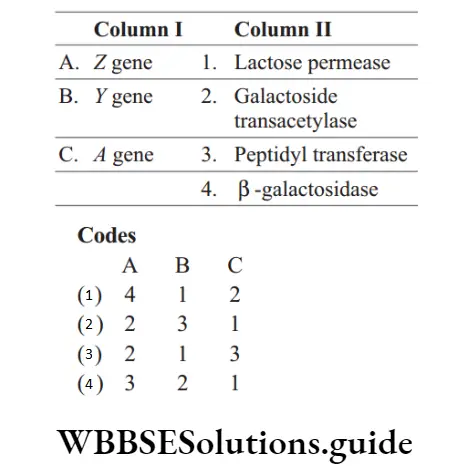
NEET Biology Mcq
Answer: 1. A-4, B-1, C-2
Question 25. In eukaryotes, the genes are regulated by
- Promoters
- Operator
- Repressors
- Enhancers
Answer: 4. Enhancers
Enhancers are positive DNA regulatory sequences that control tissue-specific gene expression.
These elements act independently of their orientation and distance relative to the promoters of target genes. So, the genes are regulated by enhancers in eukaryotes.
Best MCQs on gene regulation for NEET preparation
Question 26. Negatively regulatory proteins are known as
- Repressor
- Accessory proteins
- Catalytic proteins
- Both 1 and 3
Answer: 1. Repressor
The repressor is a negative regulatory protein, which is synthesized all the time by the regulator gene. It is meant to block the operator gene so that the structural genes cannot form mRNA.
Question 27. In the lac operon model, feedback repression is
- When the end product starts the process
- When the end product does not form
- When the end product halts the process
- When the start product stops the process
Answer: 3. When the end product halts the process
The end product is often utilized in some reactions so, it rarely accumulates. However, in the lac operon, it accumulates and stops the operon system. It is called feedback inhibition or repression.
Question 28. When tryptophan is present, what happens in the trp operon?
- Repressor becomes inactive
- The repressor is unable to bind to the operator
- Transcription of structural genes occur
- The repressor is able to bind to the operator
Answer: 4. Repressor is able to bind to the operator
When tryptophan is present in the cell, two tryptophan molecules bind to the trp repressor, which changes shape to bind to the trp operator.
The binding of the tryptophan-repressor complex at the operator physically prevents the RNA polymerase from binding and transcribing the downstream genes.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 29. E. Coli cells with a mutated z-gene of the lac operon cannot grow in a medium containing only lactose as the source of energy because
- In the presence of glucose, E. coli cells do not utilize lactose
- They cannot transport lactose from the medium into the cell
- The lac operon is constitutively active in these cells
- They cannot synthesize functional beta-galactosidase
Answer: 4. They cannot synthesize functional beta-galactosidase
Lac Z (3063 bp) codes for the enzyme β-galactosidase which breaks lactose into glucose and galactose to be utilized in the cell.
Therefore, E. coli cells with mutated Z-genes cannot grow in a medium containing only lactose as the source of energy because they cannot synthesize functional β-galactosidase
Question 30. Why cannot glucose and galactose act as an inducer for lac operon?
- Because they cannot bind with the repressor
- Because they can bind with the repressor
- Because they can bind with the operator
- Because they can bind with the regulator
Answer: 1. Because they cannot bind with the repressor
An inducer binds with the repressor protein and prevents the repressor protein from binding with the operator.
Glucose and galactose cannot act as an inducer because they do not have the binding sites for attaching to the repressor protein
Gene expression NEET practice questions and answers
Question 31. Given below are statements regarding lac operon. Identify the correct statements.
- Glucose or galactose may bind with the repressor and inactivate it.
- In the absence of lactose, the repressor binds with the operator region.
- The z-gene codes for permease.
- This was elucidated by Francois Jacob and Jacques Monod.
Choose the option containing the correct statements.
- 2 And 3
- 1 And 3
- 2 And 4
- 1 And 2
Answer: 3. The z-gene codes for permease.
Statements 2 and 4 are correct, but 1 and 3 are incorrect regarding the lac operon.
Incorrect statements can be corrected as Lactose or allolactose binds with the repressor and induces the lac operon system. The Z-gene codes for β-galactosidase.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 32. The gene not expressing any protein is known as
- Epistatic gene
- Hypostatic gene
- Pseudogene
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Pseudogene
Pseudogenes are inheritable genetic elements that are similar to functional genes but are non-functional as they do not encode proteins.
Their biogenesis results from the duplication of a parental gene or the retrotransposition of an mRNA sequence into different genomic loci.
