Types Of Organic Reactions
Substitution Reaction
The reactions in which an atom or a group in a molecule is replaced by another are called substitution reactions. The incoming group gets attached to the same carbon atom to which leaving group was attached. The substituting species may be a nucleophile, an electrophile, or a free radical.
Read And Learn More: NEET General Organic Chemistry Notes, Question And Answers
1. Nucleophilic substitution (SN) reactions: The substitution reactions which are brought about by the attack of nucleophiles are called nucleophilic substitution reactions.
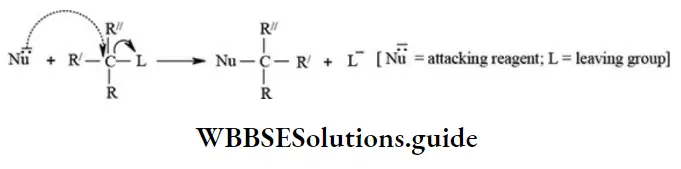
The common examples of reactions are as follows.
⇒ \(\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{X}+\mathrm{NaOH} \stackrel{\text { aqueous }}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{R}-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{OH}+\mathrm{X}^{-}\)
∴ \((\mathrm{X}=\mathrm{Cl}, \mathrm{Br}, \mathrm{I})\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{X}+\mathrm{KCN} \stackrel{\text { alcohol }}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{R}-\mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CN}+\mathrm{X}^{-}\)
⇒ \(\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{OH}+\mathrm{SOCl}_2 \longrightarrow \mathrm{R}-\mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{Cl}+\mathrm{HCl}+\mathrm{SO}_2\)
NEET organic chemistry types of organic reactions notes
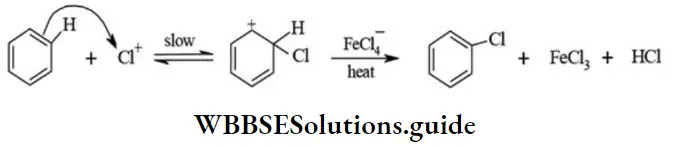
2. Electrophilic substitution (SE) reactions: The substitution reactions which are brought about by the attack of an electrophile are called electrophilic substitution reactions. The substitution reactions of aromatic compound such as chlorination, nitration of benzene are representatives of reactions.
Chlorination: \(\mathrm{Cl}_2+\mathrm{FeCl}_3 \rightarrow \mathrm{FeCl}+\mathrm{Cl}^{+}\)
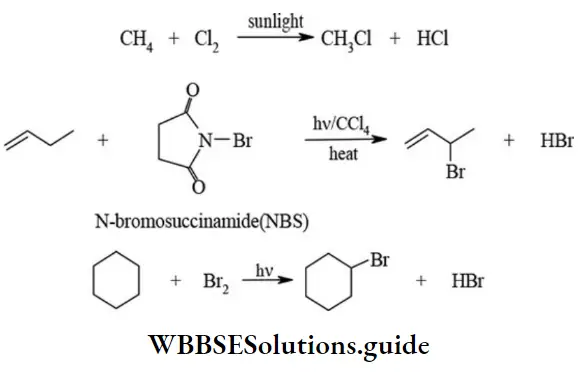
3. Free radical substitution The substitution reactions which are brought about by the attack of free radical are called free radical substitution reactions. The chlorination of aliphatic hydrocarbons in presence of diffused sunlight is common example of free radical substitution.
Different types of organic reactions for NEET with examples
Addition Reaction
“An addition reaction is defined as one in which an unsaturated molecule combines with reagent (addendum) to give a single saturated or nearly saturated compound”.

A few examples for different types of addition reactions are given below
1. Electrophilic addition reactions: The addition of common reagents like, HX, H2O, HOCl, etc. to alkenes and alkynes are common examples of electrophilic addition reactions. The addition of unsymmetrical molecules like HX, H2O, HOCl, etc. to unsymmetrical alkenes or alkynes takes place according to Markownikoffs’ rule.
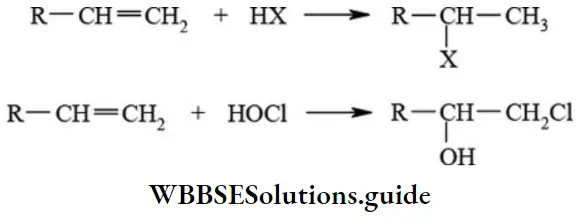
Organic reaction mechanisms and types NEET notes
2. Nucleophilic Addition Reactions: The electron-deficient carbonyl group of aldehydes or ketones is easily attacked by nucleophiles which can supply an electron pair. Thus the addition reactions of carbonyl compounds initiated by nucleophiles and known as nucleophilic addition reactions.
Addition of hydrogen cyanide
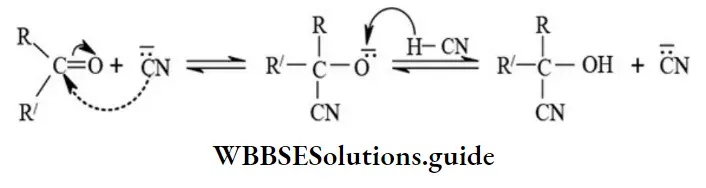
R′=H or alkyl (–CH3, –CH2CH3, etc.) or aryl (C6H5–) or aralkyl (C6H5CH2–)
Addition to Grignard reagent
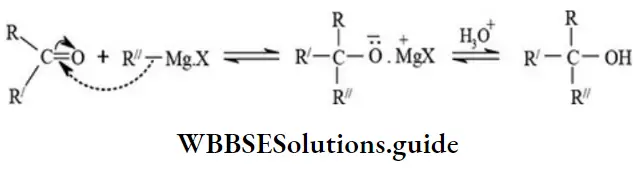
Addition of sodium bisulphite
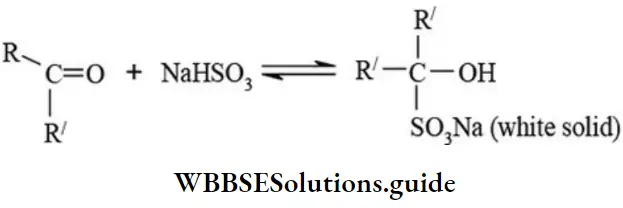
NEET chemistry important organic reactions with mechanisms
Elimination Reactions
An elimination reaction is one in which a molecule loses two atoms or groups without being replaced by other atoms or groups. The elimination reactions are two types, β-elimination reactions and α-elimination reactions
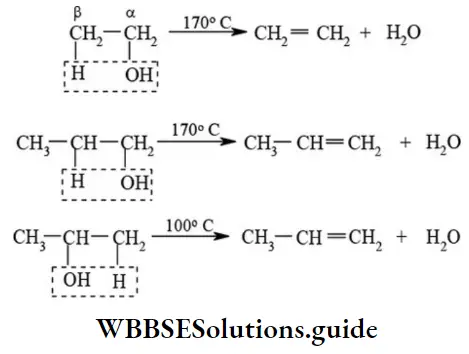
β-elimination reactions: This type of reaction involves the loss of two atoms or groups from vicinal (adjacent) carbon atoms resulting in the formation of a π bond. Thus, it is the reverse of addition reactions. The most familiar example of (β-elimination reactions are dehydrohalogenation reactions of alkyl halides, dehalogenation of haloalkanes, dehydration of alcohols, pyrolysis of esters, Hofmann elimination of quaternary ammonium hydroxide.
Dehydrohalogenation: When alkylhalides are treated with alcoholic potassium hydroxide solution or sodamide the corresponding alkenes are formed with the elimination of hydrogen halide.
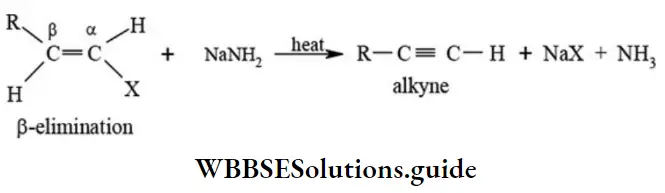
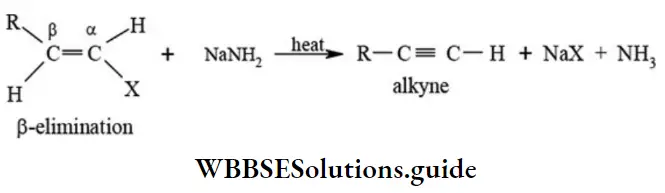
Classification of organic reactions NEET study material
- Sodamide (NaNH2) is a stronger dehydrohalogenating agent.
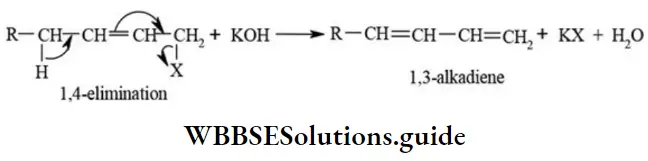
- An example of 1,4-elimination (δ-elimination) is
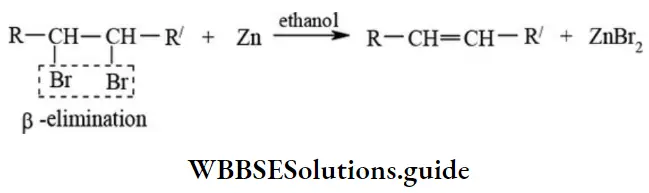
Dehalogenation: Dehalogenation involves the removal of halogen molecule (X2) from vicinal dihalide by heating with zinc dust in the alcoholic medium.
Dehydration of alcohols: When alcohols are heated with dehydrating agent like concentrated sulphuric acid, the corresponding alkenes are formed with the elimination of water (β-elimination). The reaction is called dehydration of alcohols.
NEET important organic reactions chart with mechanisms
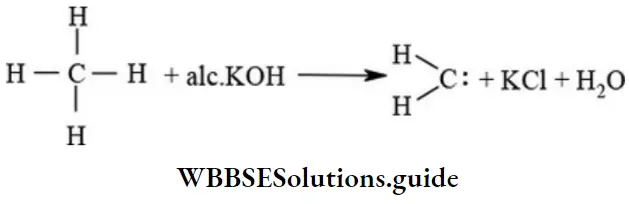
α-elimination: It involves loss of two atoms from same atom resulting in the formation of reaction intermediates like carbine
NEET chemistry solved questions on organic reaction types
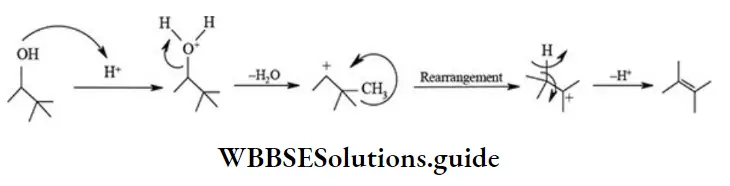
Rearrangement Reactions
The reactions which proceed by a rearrangement or reshuffling of atoms or groups in the molecule to produce a structural isomer of the original substance are called rearrangement reactions.