Biology Class 11 WBCHSE Photosynthesis In Higher Plants Some Important Questions And Answers
Question 1. What are the reasons for photosynthesis being an anabolic process?
Answer:
- It involves the conversion of simple compounds (CO2, H2O) into complex compounds (C6H1206).
- It results in an increase in dry weight.
- The solar energy trapped gets stored as chemical energy in glucose.

Question 2. Why is chloroplast referred to as a semi-autonomous organelle?
Answer: Although chloroplasts exist within cells, they (and mitochondria) are referred to as semi-autonomous organelles because they contain their own DNA and ribosomes of prokaryotic nature. They also contain other apparatus necessary for protein synthesis. They can reproduce and photosynthesise independently of the nucleus of the eukaryotic cell in which they are located.
Question 3. What is solarisation?
Answer: The process by which photosynthesis gets inhibited by the high intensity of light is called solarisation. Due to the high temperature, chlorophyll turns red in the presence of oxygen and the leaves get discoloured.
Read and Learn More WBCHSE Solutions For Class 11 Biology
Question 4. What is a green window?
Answer: When white light falls on a chlorophyll molecule, the green light with a wavelength between 480 and 550 nm is not absorbed, but is reflected. This is why chlorophyll-containing leaves and stems appear green. This non-absorbing region of the visible spectrum is called the “green window”.
Question 5. What is the difference in the chemical structure of a molecule of chlorophyll a and that of chlorophyll b?
Answer: In chlorophyll a molecule, a methyl (-CH3) group is present on C3 of the 2nd pyrrole ring of the porphyrin portion. On the other hand, in the case of chlorophyll b molecule, the above-mentioned position is occupied by an aldehyde (-CHO) group instead of a methyl group (CH3).
Question 6. How is photosynthesis a redox reaction?
Answer: In the case of photosynthesis, the electron donor (H2O) gets oxidised and a reducing agent (NADPH+ H+) is produced. Simultaneously, CO2 is reduced by the reducing agent, thereby producing glucose. Thus, both oxidation and reduction are taking place, hence it is a redox reaction.
Biology Class 11 WBCHSE
Question 7. What does Emerson’s enhancement effect prove?
Answer: Emerson’s enhancement effect proves that more than one photosystem is involved in photosynthesis. As the chloroplasts are illuminated by different wavelengths of light, the rate of photosynthesis increases. Each photosystem within the chloroplast gets excited by different wavelengths of light. This may lead to a fall, followed by a subsequent rise in the rate of photosynthesis.
Question 8. How the rate of Calvin cycle can be enhanced?
Answer: The rate of the Calvin cycle can be enhanced by increasing the concentration of its intermediates. It means that the cycle is autocatalytic in nature. The Calvin cycle can produce more substrate than is consumed.
Question 9. In which plant was it proved that PGA is the first stable product?
Answer: Chlorella was the plant in which PGA, a 3-carbon compound, was proved to be the first stable product.
Question 10. Why should we not stand below trees at night?
Answer: At night, photosynthesis cannot take place due to the absence of sunlight. Hence the production of O2 is also prevented at this time. On the other hand,_ respiration continues to take place, thereby releasing CO2 As CO2 is heavier than the rest of the components of the atmosphere, it settles down below the trees. If we stand below the trees, then this CO2 may enter our body, combine with the blood and cause breathing trouble. Hence, we must avoid standing below trees at night.
Question 11. What do you understand by the Warburg effect?
Answer: Scientist Warburg was the first to prove that the rate of photosynthesis decreases when the concentration of O2 is very high. This happens because, in a high concentration of O2, RuBP carboxylase functions as RuBP oxygenase and binds to O2. It forms phosphoglycolic acid instead of PGA. This further reduces the rate of photosynthesis. Since this effect was observed first by Warburg, this effect is known as the Warburg effect.
Question 12. How many molecules of ATP, C02 and NADPH are required to produce 1 molecule of glucose?
Answer: For producing every 1 molecule of CO2 in the Calvin cycle, 3 molecules of ATP and 2 molecules of NADPH are required. To produce 1 molecule of glucose, 6 Calvin cycles are required. Hence 6 molecules of CO2, 18 molecules of ATP and 12 molecules of NADPH are required to produce 1 molecule of glucose.
Question 13. Which plants show characteristic dimorphism of chloroplasts?
Answer: C4 plants show characteristic dimorphism of chloroplasts. This means that the chloroplasts are of two types. The chloroplasts of bundle sheath cells are large, centrally located, and contain starch granules. They do not contain grana. On the other hand, the chloroplasts of mesophyll cells are smaller and have a general structure of that of the chloroplasts.
Biology Class 11 WBCHSE
Question 14. What kind of photosynthesis is observed in each of the following organisms—Chromatium, Oscillatoria, Rhodospirillum and Chlorobium?
Answer:
Chromatium: It is a purple sulphur bacteria which shows non-oxygenic photosynthesis. Oscillatoria: It is a photosynthetic cyanobacterium which shows oxygenic photosynthesis.
Rhodospirillum and Chlorobium: They are purple sulphur bacteria and green sulphur bacteria respectively. Both these organisms show non-oxygenic photosynthesis.
Question 15. Which is the first stable compound in C3 photosynthesis?
Answer: The C3 cycle begins with RuBP (5C). 6 molecules of RuBP combine with CO2 to form 6 molecules of the 6C compound. This unstable compound reacts with water readily, to form 12 molecules of 3C compound, PGA. This is the first stable compound formed in the C3 cycle.
Question 16. What is meant by etiolation?
Answer: If plants are kept in the dark, all the chloroplasts as well as the chlorophyll molecules get destroyed. This phenomenon is known as etiolation.
Question 17. What is the significance of adding NaHC03 to the water in the experiment, where Chlorella is used to produce O2?
Answer: On adding NaHCO3 to the water, the availability of CO2 to the plant, Chlorella, increases. This increases the rate of photosynthesis and thereby the production of O2.
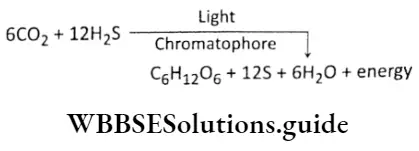
Question 18. Write the chemical equation for photosynthesis in green sulphur bacterium, Chlorobium sp.
Answer: The chemical equation for photosynthesis occurring in green sulphur bacterium is as follows—
Question 19. What is the ‘sieve effect’ with respect to the arrangement of chlorophyll in leaves?
Answer: The chlorophyll molecules are stored only within chloroplasts instead of being uniformly arranged throughout the mesophyll tissues. So light gets absorbed only in the chloroplast. Within the rest of the mesophyll tissue, light gets either reflected or refracted. Thus the mesophyll tissue seems to be acting like a ‘sieve’ allowing light to be absorbed only through a certain part of it.
Hence, this effect has been named as ‘sieve effect’ by the scientists. Due to this effect, the absorption of light within the leaves is lesser than the absorption by the same number of chlorophyll molecules in solution.
Biology Class 11 WBCHSE
Question 20. Is the ionisation of 1 molecule of water and dissociation of 1 molecule of water, the same?
Answer: Under normal conditions, some molecules of water remain hydrolysed into negatively charged OH– and positively charged H+ ions. This is the dissociation of water molecules. It occurs as a reversible reaction.
⇒ \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \rightleftharpoons \underset{\text { Hydroxylion }}{\mathrm{OH}^{-}}+\underset{\text { Hydrogen ion }}{\mathrm{H}^{+}}\)
During photosynthesis, the sun’s rays dissociate water molecules. This produces unstable OH radicals, hydrogen ions (protons) and excited electrons. This is the ionisation of water molecules. It does not occur under normal conditions and requires a large amount of energy. It is an irreversible reaction.
⇒ \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \stackrel{\text { Energy }}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{OH}+\underset{\begin{array}{l} \text { Unstable, } \\ \text { uncharged, } \\ \text { neutral radical } \end{array}}{\mathrm{H}^{+}}+\underset{\begin{array}{c} \text { Electron } \\ \text { (with free } \\ \text { energy) } \end{array}}{\mathrm{e}^{-}}\)
Question 21. What is the Z-scheme of photosynthesis?
Answer: In the light phase of photosynthesis, both PS 1 and PS 2 absorb light of different wavelengths and get excited. The electron transport pathway through PS 1 and PS 2, was discovered by Hill and Bendall, in 1960. They proved that on plotting the successive reactions of the electron transport chain, vertically, beginning with water and ending with NADP+, a Z–shaped pattern is observed. This is known as the Z-scheme of photosynthesis.
Question 22. What is known as protochlorophyll?
Answer: During chlorophyll synthesis, a molecule called protochlorophyll is initially formed. In it, two H-atoms are absent in the 4th pyrrole ring due to the absence of light. In the presence of light, the two H-atoms bind with the 4th pyrrole ring to form chlorophyll.
Class 11 Biology WBCHSE Photosynthesis In Higher Plants Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Where are photosynthetic pigments located in chloroplast?
Answer: The photosynthetic pigments are located in the thylakoid membrane, attached to specific proteins.
Question 2. Where are the pigments found in photosynthetic bacteria?
Answer: In photosynthetic bacteria, the photosynthetic pigments remain associated with specific proteins in unorganized chromatophores.
Question 3. What is assimilatory power?
Answer: ATP and NADPH are collectively called Assimilatory power.
Question 4. What is phosphorylation?
Answer: Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphoryl group (PO32-) to a protein or any other organic molecule. The formation of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate by ATP synthase enzyme is an example of phosphorylation.
Question 5. Give one point of difference between chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b.
Answer: The side group at the 3rd carbon is the methyl (- CH3) group in the case of chlorophyll a and the aldehyde (-CHO) group in the case of chlorophyll b.
Question 6. Name one accessory and one essential photosynthetic pigment of photosynthetic plants.
Answer: The accessory photosynthetic pigment is 3-carotene and the essential photosynthetic pigment is chlorophyll a.
Question 7. What would happen to the rate of photosynthesis in C3 plants if the CO2 concentration almost doubles from its present concentration in the atmosphere?
Answer: The photosynthetic rate will be increased
Question 8. Who proposed the Z-scheme and suggested that photosystems operate in series?
Answer: Hill and Bendall (1960) proposed the so-called “Z-scheme” Govindjee et al. (2010) published the current versions of the Z-scheme and suggested that photosystems operate in series.
Question 9. What are the actual sites of light reaction and dark reaction inside the chloroplasts?
Answer: The site of light reaction and dark reaction in photosynthesis are the thylakoid membrane (grana) and stroma within the chloroplast, respectively.
Class 11 Biology WBCHSE
Question 10. What is the difference between a quantum and a photon?
Answer: A quantum of energy is just a small, indivisible, discrete piece of it. Light can be thought of as particles. These particles are known as photons. A photon is a quantum of light.
Question 11. What is the quantum requirement?
Answer: The quantum requirement of photosynthesis (<P) is the number of photons absorbed per mole of CO2 fixed or per mole of O2 evolved
Question 12. Which one is the most important limiting factor in photosynthesis?
Answer: Carbon dioxide is the most important limiting factor in photosynthesis.
Question 13. What is the basis of naming of C3 and C4 pathways?
Answer: The first stable product obtained during CO2 fixation in C3 plants is 3-PGA, a 3C compound and in C4 plants is oxaloacetate, a 4C compound. This is the basis of naming of the pathways
Question 14. Which products formed during the light reaction of photosynthesis are used to drive the dark reaction?
Answer: ATP and NADPH are the products of light reaction, used to drive the dark reaction.
Question 15. How many types of photosynthetic pigments are available according to solubility?
Answer: On the basis of solubility, photosynthetic pigments are of two types
- Chlorophylls and carotenoids, which are fat-soluble and water-insoluble,
- Phycobillins (phycocyanin and phycoerythrin), which are water-soluble.
Class 11 Biology WBCHSE
Question 16. 2H2O → 2H++O2+ 4e– Based on this equation, answer the following questions:
- Where does this reaction take place in plants?
- What is the significance of this reaction?
Answer:
- The reaction takes place in the thylakoid lumen.
- The energy-rich electrons extracted from water are used to generate the assimilatory power
Question 17. Which is the first product obtained during carbon assimilation in C4 photosynthesis?
Answer: The first product obtained during carbon assimilation is 3-phosphoglyceric acid (PGA) in C4 plants.
Question 18. Does moonlight support photosynthesis? Find out.
Answer: The intensity of moonlight is 1/50,000 times that of sunlight, so it is not strong enough to enable plants to photosynthesize. In a full moon, the light is normally too weak for photosynthesis to occur at a high rate but it may take place at a much reduced rate.
19. Which range of wavelength (in nm) is photosynthetically active radiation (PAR)?
Answer: Photosynthetically active radiation designates the solar radiation from 400 to 700 nm, approximately
Question 20. Name the enzyme which is not found in C3 plants.
Answer: Pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase and PEPcarboxylase are not found in C3 plants.

