Plant Kingdom Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. An example of colonial alga is—
- Volvox
- Ulothrix
- Spirogyra
- Chlorella
Answer: 1. Volvox
“plant kingdom MCQ with answers”
Question 2. The life cycles of Ectocarpus and Fucus respectively are—
- Diplontic, Haplodiplontic
- Haplodiplontic, Diplontic
- Haplodiplontic, Haplontic
- Haplontic, Diplontic
Answer: 2. Haplodiplontic, Diplontic
Read and Learn More WBCHSE Multiple Choice Question and Answers for Class 11 Biology
Question 3. Which of the following would appear as the pioneer organisms on bare rocks?
- Liverwort
- Mosses
- Green algae
- Lichens
Answer: 4. Lichens

Question 4. In bryophytes and pteridophytes, transport of male gametes requires—
- Insects
- Birds
- Water
- Wind
Answer: 3. Water
“multiple choice questions on plant kingdom for class 11”
Question 5. Select the correct statement
- Salvinia, Ginkgo and Pinus all are gymnosperms
- Sequoia is one of the tallest trees
- The leaves of gymnosperms are not well adapted to extremes of climate
- Gymnosperms are both homes prosperous and heterosporous
Answer: 2. Sequoia is one of the tallest trees
| Class 11 Biology | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Class 11 Physics |
| Class 11 Biology MCQs | Class 11 Physics MCQs |
| Class 11 Biology | Class 11 Physics Notes |
Question 6. The ovule of an angiosperm is technically equivalent to—
- Megasporangium
- Megasporophyll
- Megaspore mother cells
- Megaspore
Answer: 1. Megasporangium
Question 7. Which one of the following statements is wrong—
- Algae increase the level of dissolved oxygen in the immediate environment
- Algin is obtained from red algae and carrageenan from brown algae
- Agar-agar is obtained from Gelidium and gracilaria
- Laminaria and Sargassum are used as food
Answer: 2. Algin is obtained from red algae and carrageenan from brown algae
Question 8. Conifers are adapted to tolerate extreme environmental conditions because of
- Broad hardy leaves
- Superficial stomata
- Thick cuticle
- The presence of vessels
Answer: 3. Thick cuticle
Question 9. Which one is a wrong statement?
- Brown algae have chlorophyll a and c, and fucoxanthin
- Archegonia are found in Bryophyta, Pteridophyta and Gymnosperms
- Mucor has biflagellate zoospores
- The haploid endosperm is a typical feature of Gymnosperms
Answer: 3. Mucor has biflagellate zoospores
“plant kingdom MCQs for NEET preparation”
Question 10. An alga which can be employed as food for human beings is
- Ulothrix
- Chlorella
- Spirogyra
- Polysiphonia
Answer: 2. Chlorella
Question 11. Which one of the following living organisms completely lacks a cell wall?
- Cyanobacteria
- Sea-fan (Gorgonia)
- Saccharomyces
- Blue-green algae
Answer: 2. Sea-fan (Gorgonia)
Question 12. Which one of the following shows isogamy with non-flagellated gametes?
- Sargassum
- Ectocarpus
- Ulothrix
- Spirogyra
Answer: 4. Spirogyra
Question 13. Which one of the following is wrong about Chara?
- Upper oogonium and lower round antheridium
- Globule and nucule present on the same plant
- Upper antheridium and lower oogonium
- Globule is the male reproductive structure
Answer: 3. Upper antheridium and lower oogonium
“important MCQs on plant kingdom with explanations”
Question 14. Which of the following is responsible for peat formation?
- Marchantia
- Riccia
- Funaria
- Sphagnum
Answer: 4. Sphagnum
Question 15. Male gametophyte with least number of cells is present in—
- Pteris
- Funaria
- Lilium
- Pinus
Answer: 3. Lilium
Question 16. Choose the wrong statement
- Gymnosperms lack vessels in their xylem
- The cell wall of collenchyma is made up of cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin
- The first formed primary xylem elements are called protoxylem
- The cell wall of parenchyma is made up of pectin
- Gymnosperms have albuminous cells and sieve cells in their phloem
Answer: 2. The cell wall of collenchyma is made up of cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin
Question 17. Choose the correct statement—
- Bryophytes can live in soil but are dependent on water for sexual reproduction
- The sex organs in bryophytes are unicellular
- In bryophyte, the main plant body is a gametophyte which is differentiated into true root, stem and leaves
- A common example of liverwort is Polytrichum
- A common example of moss is Marchantia
Answer: 1. The sex organs in bryophytes are unicellular
Question 18. Which of the following groups of algae belongs to the class Rhodophyceae?
- Laminaria, Fucus, Porphyra, Volvox
- Gelidium, Porphyra, Dictyota, Fucus
- Gracilaria, Gelidium, Porphyra, Polysiphonia
- Volvox, Spirogyra, Ulothrix, Sargassum
- Sargassum, Laminaria, Fucus, Dictyota
Answer: 3. Gracilaria, Gelidium, Porphyra, Polysiphonia
Question 19. Match the following and choose the correct combination from the options given.
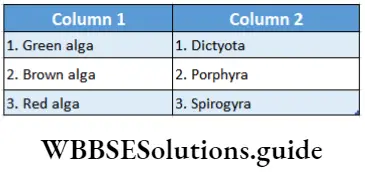
- 1-3, 2-2, 3-1
- 1-3, 2-1, 3-2
- 1-2, 2-3, 3-1
- 1-1, 2-2, 3-3
- 1-1, 2-2, 3-2
Answer: 2. 1-3, 2-1, 3-2
“plant kingdom quiz with multiple choice questions and answers”
Question 20 Which of the following are heterosporous pteridophytes?
- Lycopodium
- Selaginella
- Equisetum
- Salvinia
Answer: 4. Salvinia
Question 21. Marchantia is considered as a heterothallic plant because it is
- Heterogametic
- Bisexual
- Monoecious
- Dioecious
Answer: 4. Dioecious
Question 22. Mosses and liverworts are members of—
- Gametophytes
- Chlorophytes
- Bryophytes
- Pteridophytes
Answer: 3. Bryophytes
Question 23. The life cycle of algae such as Spirogyra is—
- Haplontic
- Diplontic
- Haplo-diplontic
- Diplo-haplontic
Answer: 1. Haplontic
Question 24. Which one of the following is the first group of vascular plants?
- Thallophyta
- Bryophyta
- Pteridophyta
- Spermatophyta
Answer: 3. Pteridophyta
“plant kingdom objective questions for competitive exams”
Question 25. The presence of pyrenoid is a characteristic feature of class
- Phaeophyceae
- Chlorophyceae
- Rhodophyceae
- Poaceae
Answer: 2. Chlorophyceae
Question 26. Food is stored in the form of mannitol in the class of algae—
- Rhodophyceae
- Phaeophyceae
- Chlorophyceae
- Poaceae
Answer: 2. Phaeophyceae
Question 27. Ectocarpus shows—
- Haplontic life cycle
- Diplontic life cycle
- Haplo-diplontic life cycle
- Diplontic-haplontic life cycle
Answer: 3. Haplo-diplontic life cycle
Question 28. Elaters are absent in—
- Funaria
- Marchantia
- Pellia
- Psilotum
Answer: 1. Funaria
Question 29. Besides paddy fields, cyanobacteria are also found inside the vegetative part of—
- Pinus
- Cycas
- Equisetum
- Psilotum
Answer: 2. Cycas
Question 30. Select the wrong statement—
- Isogametes are similar in structure, function behaviour
- Anisogametes differ in structure, function behaviour
- In monogamous, the female gamete is smaller and motile while the male gamete is larger and non-motile
- Chlamydomonas exhibits both isogamy and anisogamy and Fucus shows oogamy
Answer: 3. In oogamous, the female gamete is smaller and motile while the male gamete is larger and non-motile
Question 31. Isogamous condition with non-flagellated gametes found in
- Chlamydomonas
- Spirogyra
- Volvox
- Focus
Answer: 2. Spirogyra
“plant kingdom classification MCQs with solutions”
Question 32. Monoecious plant of Chara shows the occurrence of—
- Antheridiophore and archegoniophore on the same plant
- Stamen and Carpel on the same plant
- Upper antheridium and lower oogonium on the same plant
- Upper oogonium and lower antheridium on the same plant
Answer: 4. Upper oogonium and lower antheridium on the same plant
Question 33. Fruits are not found in gymnosperms because—
- They are seedless
- They are not pollinated
- They have no ovary
- Fertilisation does not take place
Answer: 3. They have no ovary
Question 34. Vegetative reproduction in Funaria takes place by—
- Primary protonema
- Gemmule
- Secondary protonema
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
“plant kingdom previous year MCQs for NEET and board exams”
Question 35. Alginic acid is found in the cell wall of—
- Gigartina
- Laminaria
- Gelidium
- Scytonema
Answer: 2. Laminaria
Question 36. Pinus belongs to the class—
- Gnetopsida
- Cycadopsida
- Coniferopsida
- Sphenopsida
Answer: 3. Coniferopsida
Question 37. Which one of the following is an example of chlorophyllous thallophyte?
- Volvariella
- Spirogyra
- Nephrolepis
- Gnetum
Answer: 2. Spirogyra
“plant kingdom chapter-wise MCQ practice questions”
Question 38. Algae, which form motile colonies, is—
- Volvox
- Nostoc
- Spirogyra
- Chlamydomonas
Answer: 1. Volvox
Question 39. Non-motile, greatly thickened, asexual spore in Chlamydomonas is
- Carpospores
- Aplanospores
- Akinetes
- Hypnospores
Answer: 4. Hypnospores
“plant kingdom solved MCQs PDF download”
Question 40. Identify the wrong combination—
- Dryopteris — Rhizome
- Cycas — Coralloid roots
- Volvox — Colonial form
- Marchantia — Pseudoelaters
Answer: 4. Marchantia — Pseudoelaters
