Transport In Plants Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Which of the following facilitates the opening of the stomatal aperture?
- Decrease in turgidity of guard cells
- Radial orientation of cellulose microfibrils in the cell wall of guard cells
- Longitudinal orientation of cellulose microfibrils in the cell wall of guard cells
- Contraction of an outer wall of guard cells
Answer: 2. Radial orientation of cellulose microfibrils in the cell wall of guard cells
“transpiration and ascent of sap MCQs with answers”
Question 2. The water potential of pure water is
- Less than zero
- More than zero but less than one
- More than one
- Zero
Answer: 4. Zero
Read and Learn More WBCHSE Multiple Choice Question and Answers for Class 11 Biology
Question 3. Water vapor comes out from the plant leaf through the stomatal opening. Through the same stomatal opening, carbon dioxide diffuses into the plant during photosynthesis. Reason out the above statements using the following option.
- Both processes can happen together because the diffusion coefficient of water and C02 different
- The above processes happen only during nighttime
- One process occurs during day time and the other at night
- Both processes cannot happen simultaneously
Answer: 1. Both processes can happen together because the diffusion coefficient of water and CO2 different
“transport in plants MCQ with answers”
Question 4. Root pressure develops due to—
- Increase in transpiration
- Active absorption
- Low Osmotic potential in soil
- Passive absorption
Answer: 2. Active absorption
” transport in plants neetprep”

Question 5. A column of water within xylem vessels of tall trees does not break under its weight because of—
- Positive root pressure
- Dissolved sugars in water
- Tensile Strength Of Water
- Lignification of xylem vessels
Answer: 3. Tensile Strength Of Water
“transport in plants chapter-wise MCQ practice questions”
| Class 11 Biology | Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry | Class 11 Physics |
| Class 11 Biology MCQs | Class 11 Physics MCQs |
| Class 11 Biology | Class 11 Physics Notes |
Question 6. The osmotic expansion of a cell kept in water is chiefly regulated by
- Mitochondria
- Vacuoles
- Plastid
- Ribosomes
Answer: 2. Vacuoles
“multiple choice questions on transport in plants for class 11”
Question 7. In which of the following, expenditure of energy is required?
- Osmosis
- Diffusion
- Active transport
- Passive transport
Answer: 3. Active transport
neetprep transport in plants
Question 8. In a plant cell, the diffusion pressure deficit is zero when it is
- Plasmolyzed
- Turgid
- Flaccid
- Incipient
Answer: 2. Turgid
Question 9. Guttation occurs through
- Roots
- Hydathode
- Trichome
- Stomata
Answer: 2. Hydathode
Question 10. Choose the wrong statement.
- Cells swell in hypertonic solutions and shrink in hypotonic solutions
- Water potential is the kinetic energy of water which helps in the movement of water
- The absorption of water by seeds and dry woods takes place by a special type of diffusion called imbibition
- Solute potential or ψs is always negative
- Less than 1% of the water reaching the leaves is used in photosynthesis and plant growth
Answer: 1. Cells swell in hypertonic solutions and shrink in hypotonic solutions
“important MCQs on transport in plants for NEET”
Question 11. Which of these is/are not a property of facilitated Which of these is/are not a property of transport?
- Requires special membrane proteins
- Highly selective
- Uphill transport
Choose the correct option.
- [1] and [2]
- [3] and [4]
- [2] and [3]
- [2] and [4]
Answer: 2. [3] and [4]
Question 12. When water moves out of the plant cell and the cell membrane of a plant shrinks away from its cell, then this condition is known as
- Plasmolysis
- Exosmosis
- Hydrolysis
- Endosmosis
Answer: 1. Plasmolysis
Question 13. A special type of diffusion when water is absorbed by solids is called
- Osmosis
- Plasmolysis
- Both A And B
- Imbibition
Answer: 4. Imbibition
“water and mineral transport in plants quiz with answers”
Question 14. A layer of cells impervious to water because of a band suberised matrix is called the
- Endodermis
- Casparian strip
- Plasmodesmata
- None of these
Answer: 2. Casparian strip
Question 15. Study the following table showing the components of water potential of four cells of an actively transpiring plan Identify the four cells as root hair, cortical cell, endodermal cell (lacking Casparian strips), and pericycle respectively in the young root (assuming symplastic water flow through them).
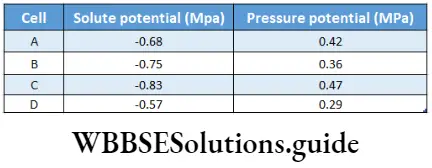
- B, D, C, A
- D, A, C, B
- A, D, C, B
- A, C, B, D
Answer: 3. A, D, C, B
Question 16. Flaccid cell means
- Cell turgidity
- Plasmolysed cell
- The Cell in which water flows in and out of the cell is in equilibrium
- The Cell kept in a hypotonic solution
Answer: 2. Plasmolysed cell
“MCQs on xylem and phloem transport with explanations”
Question 17. Cell A and cell B are adjacent plant cells. In cell A, ψs = -20 bars and ψs = 8 bars. In cell B, ψs = -12 bars and = 2 bars. Then.
- Water moves from cell B to cell A
- An equal amount of water is simultaneously exchanged between cell A and cell B
- Water moves from cell A to cell B
- There is no movement of water between cell A and cell B
Answer: 1. Water moves from cell B to cell A
Question 18. Cell A has an osmotic potential of -18 bars and a pressure potential of 8 bars, whereas, cell B has an osmotic potential of -14 bars and a pressure potential of 2 bars. The direction of flow of water will be—
- From cell B to cell A
- From cell A to cell B
- No flow of water
- In both directions
Answer: 2. From cell A to cell B
Question 19. The property of semi-permeability belongs to—
- Cell wall
- Plasma membrane
- Mitochondria only
- None of these
Answer: 2. Mitochondria only
“previous year transport in plants MCQs for competitive exams”
Question 20. Translocation of photosynthetic end products in sieve tubes is
- 305 mm/h
- 3-5 cm/h
- 1-15 cm/h
- 60-100 cm/h
Answer: 4. 60-100 cm/h
Question 21. Transpiration is measured by—
- Potometer
- Parameter
- Auxanometer
- Respirometer
Answer: 1. Potometer
Question 22. Which of the following theories gives the latest explanation for the closure of stomata?
- ABA theory
- Munch theory
- Starch glucose theory
- Active K+ transport theory
Answer: 4. Active K+ transport theory
“active and passive transport in plants MCQs with solutions”
Question 23. By which mechanism, the salt-resistant plants can get rid of excess Na+ ions to the outer side, through the roots?
- H+—ATPase uniport system
- Na+—ATPase uniport system
- H+—Cl–symport system
- Na+— H+ antiport system
Answer: 4. Na+— H+ antiport system
