Chapter 8 Air Pollution Introduction
The Earth comprises three domains namely, the solid lithosphere (land), the liquid hydrosphere (water) and gaseous atmosphere (air). The land, water and air are the three basic amenities for living organisms.
So, the Earth is an ‘unique planet’ of the Solar system because of its environment favours the evolution and survival of various forms of life.
“WBBSE class 6 physical geography chapter 8 notes”
But now the environment is fulfilled with undesirable and harmful substances that make it unhealthy, unsafe and hazardous for living organisms. This phenomenon of harming the environment is called ‘pollution’.
Pollution
The fouling of the environment by man which makes it harmful for living organisms or reduces its amenity value is called pollution. Pollution changes the physical, chemical or biological balance of the environment that has adverse effects on the normal functioning of all lifeforms, including humans.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Notes For Class 6 Junior School Geography
Pollutants :
Pollutants are the substance which causes pollution. Pollutants may be solid, liquid or gaseous substances. Air pollution is caused by various types of pollutants released mainly from industries, thermal power plants, domestic appliances and automobiles.
“air pollution WBBSE class 6 geography notes”
Air Pollution
According to the Oxford Dictionary of Geography, the term ‘air pollution’ refers to the presence of contaminants released by human activities into the Earth’s atmosphere which has the potential to cause harm to property or the precious lives of plants, animals or humans.
Air pollution may be defined as an unwanted change in the quality of Earth’s atmosphere caused by the emission of gases due to the burning of fuels, and outpouring of volcanic ashes, pollen and organic compounds from vegetation.

Causes Of Air Pollution
Air pollution is caused by different types of poisonous gases like carbon dioxide, carbon-monoxide, sulphur-dioxide, nitrogen-oxide, chemical substances like lead, chloroform carbon; organic elements, smoke and dust particles.
Air pollution may be caused in two ways :
- Air pollution caused by nature and
- Air pollution caused by human activities.
Air Pollution caused by nature :
Air pollution may be caused by nature in the following ways :
| Class 6 History | Class 6 Social Science |
| Class 6 Geography | Class 6 Science |
| Class 6 Maths | Class 6 Science MCQs |
| Class 6 General Science | Class 6 Maths Solutions |
| Class 6 Geography | Class 6 Hindi |
Volcanic eruption :
During volcanic eruption carbon-monoxide, sulphides, and sulphur-dioxide gases come out along with ashes, cinders and pyroclastic materials from the crater and mix with air causing pollution.

Forest fire :
Forest fire caused due to friction of dry leaves release carbon- dioxide that mix with the air and pollute it.

Dust Storms :
Dust and sand particles from the dry desert areas can also make the air polluted.

Emission of gas :
The decomposition of swampy land and logs emits methane gas and thus pollutes air. Air is also polluted by pollen and organic compounds from vegetation.

Air Pollution Caused By Human Activities
Air pollution may be caused by human activities also. These are as follows :
1. Smoke from motor vehicles :
Smoke or fume discharged from motor vehicles is responsible for large-scale air pollution up to about 60%. In metropolitan cities like Mumbai, Delhi, Kolkata, Chennai etc. about 60% to 70% or air pollution is caused by automobiles alone.

Burning of fossil fuels :
Large-scale burning of fossil fuels such as coal, and petroleum (diesel, petrol etc.) produces several gas like carbon monoxide (CO), carbon- dioxide (C07), nitrogen oxide (N.O) and sulphur dioxide (SO_). These poisonous gases pollute the air.

Urbanisation
Population explosion has let to an increased number of people who need clear areas to build houses for settlement.

Due to urbanisation, trees are being cut constantly and for this reason, our atmosphere is lacking oxygen and the amount of carbon dioxide in the air is increasing alarmingly.
4. Deforestation :
Due to deforestation, our atmosphere is lacking oxygen and the amount of carbon dioxide in the air is increasing which also pollutes air.

5. Industrialisation :
Burning of coal in the industries produces a large amount of smoke, and dust particles which mixes with air and pollute it. Cement, glass and fertilizer industries release a large amount of oxide of silicon, calcium and aluminium into the air.

6. Uses of atomic fuels:
Burning and uses of atomic fuels In atomic plants emits gas and heat which also pollutes the air.

Smog :
Smog (a combination of smoke and fog) with dust particles and sulphur- dioxide also pollutes the air.

Fertilizers :
When chemical fertilizers are used on the crop Fields, a part of them mixes with air due to evaporation causing air pollution.

Pesticides and insecticides :
Pesticides and insecticides are complex organic compounds using toxic elements like arsenic, chlorine, bromine etc. for killing pests and insects. When these compounds are sprayed on the crops, a part of them mixes with the air and causes air pollution.

Burning of firewood, coal etc :
In the rural areas firewood, coal, cow dung cakes etc. are used for cooking purposes. Due to the burning of these materials, harmful gases mix with the air and the air gets polluted.

Smoke from incense sticks, mosquito coils and oil :
In cities and towns and even in villages also incense sticks are used for worshipping and mosquito coils and oil are used to fly away them. Smoke from these are also pollutes the air

Domestic and industrial wastes :
Dry leaves, and domestic, industrial and farm wastes are burnt in order to dispose of them. These produce carbon-monoxide gas which mixes with air and pollutes it.

13. Smoking bidis, cigarettes, cigars etc. :
Smoking of bidis, cigarettes and cigars etc. produces carbon-monoxide gas due to incomplete combustion of tobacco leaves. This also pollutes the air.
14. Artificial building materials and chemicals :
Artificial building materials like plywood and chemical like paints, varnishes etc. can cause indoor pollution. Poor ventilation in homes can worsen the situation.
“summary of class 6 physical geography chapter 8 WBBSE”
15. Explosion :
Explosion in the nuclear power plant also pollutes the air. In 2011, there was an explosion in the nuclear plant at Fukushima in Japan. As a result, a huge amount of radioactive materials contaminated the air causing pollution.
Effects Of Air Pollution
The detrimental effects of air pollution are noticed both in the natural and man-made environment. If the air gets excessively polluted, the survival of the living being would then become more difficult or Impossible.
The harmful effects of air pollution are as follows :
Rising atmospheric temperature :
If air is polluted, it would result in the rise of temperature of the ground surface and lower atmosphere. This would cause
- Depletion of the ozone layer, global warming, acid rain, melting of continental glaciers, rise in sea level etc.
Depletion of the Ozone layer :
A zone with n the atmosphere generally between 20 and 40 km where ozone terms In Its greatest concentration it caMed the Ozonosphere or Ozone layer’ Recently the researchers have shown that there is a gradual depletion of ozone gas in the atmosphere.
The mam culprit of ozone depletion are chloroflurocarbons (CFC from refrigerators, air conditioners and deodorants are slowly destroying the ozone layer.
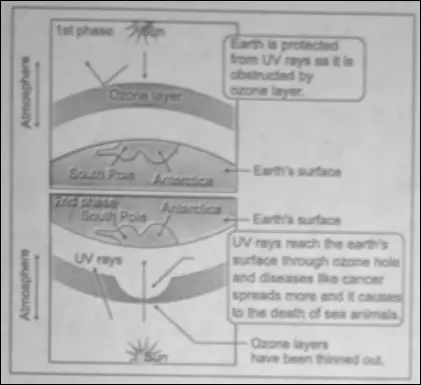
NiTrogen-Oxides emitted from supersonic jets (faster than ‘sound), nuclear explosions are causing harm to the ozone layer. As the ozone layer is getting thinner day by day, ultraviolet rays are reaching the Earth.
“important questions from air pollution class 6”
As a result of skin cancer to white-skinned people and optical diseases are increasing Agricultural production is decreasing as chlorophyll in t’ee leaves are being damaged Many plants and animals are facing extinction as a result of these and the whole ecosystem of the biosphere d disturbed.
Acid rain :
The oxides of sulphur and nitrogen emitted from vehicles and factories are carried thousands of kilometres away from their source of origin, and due to prolonged existence in the atmosphere, they are oxidised into sulphuric and nitric acids respectively.
When these acids fall on the Earth’s surface it is called add rain’. Acid ram enhances soil acidity. So, animals as well as plants living on land and in water are equally badly affected.

Crop productivity dwindles and the health of all living animals, including humans, deteriorates. The ecosystem loses its balance as many bacteria and blue green algae are destroyed by acidification.
Greenhouse Effect
The warming up of the atmosphere as some of the gases trap solar radiation and the heat given out by the earth is called Green House Effect. It is a process of counter-radiation which makes the earth’s atmosphere too hot.
It is described more by anthropogenic tmHstom (emissions in the atmosphere caused by man) than any other natural causes. To facilitate identification these gates are alto called greenhouse gases.
“causes of air pollution class 6 geography notes”
Carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, methane, CFC, water vapours and o/one arc are also chief greenhouse gases it is said that as a result of human activities the volume of these gases in the atmosphere are rising. This is called ‘Global Warming’.
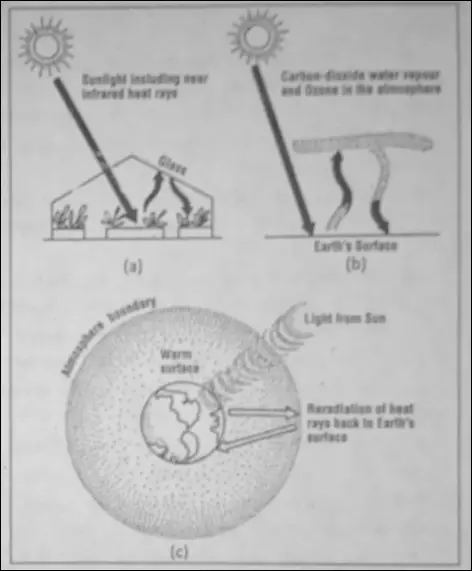
In other words, the abnormal increases of atmospheric temperature throughout the world is known as ‘Global Warming It affects the ecological balance of the Earth adversely.
Global warming can cause a normal reduction of rainfall, and melting of polar ice caps thereby rise in the sea level and submerging low lying areas together with some great cities of the world.
Effect of Mist, Fog and Smog (Smoke + Fog) :
Mist, fog and smog i e the mixture of fog, smoke dust and sulphur-dioxide gas causing thick black layer In the lower atmosphere near the Earth’s surface.
A form of ‘fog’ that occurs in areas where the air contains a large amount of ‘smoke’ is called ‘Smog’ (Smoke + Fog) In industrial towns and cities this ‘smog’ results in poor visibility on the roads The smooth movement of rail, road and air traffic gets disrupted.
“WBBSE class 6 geography chapter 8 key points”
A thick layer of smog can destroy plants and affect crop yield People suffer from diseases like asthma, bronchitis and heart problems. Throat infections and eye problems are also common disc1 is among people.
Measures for reducing Air Pollution :
Pollution can be reduced or controlled by taking some measures.
These are as follows :
- Use of public transport like trains, buses etc. should be encouraged instead of private car and transport.
- Emission of poisonous gases by trucks, buses, motor cars and other vehicles can be controlled by refining the petroleum products (petrol, diesel etc.) used as fuels.
- Use of fossil fuels like coal, petroleum, gasoline etc. should be controlled. Alternative sources of fuel like L.P.G. (Liquid Petroleum gas) and C.N.G. (Compressed Natural Gas) may be used as fuel for public transport and for domestic use.
- Newer engines with improved vehicular technology should be accepted replacing the cars with an old engines.
- Non-conventional sources of energy like solar energy, bio-gas, wind energy, tidal energy etc. may be used as substitutes of conventional energy like coal, petroleum etc.
- Deforestation (clearing of forest area by the felling of trees) should be prohibited by law and afforestation or planting of trees should be encouraged.
- The power plants should be located far away from residential areas. The factories and industrial plants should be located far away from residential areas.
- For checking industrial air pollution it is necessary to remove particulate matter and gaseous pollutants from the industrial waste.
- The waste material produced from industries needs to be treated.
- Clearing of the forested area by the felling of trees should be prohibited by law.
- Strict laws should be enforced and persons violating the provisions of air pollution control should be penalised.
- Mass social awareness campaigns should be indicated regarding the nature and effect of air pollution and remedial measures on a continuing basis.
WBBSE Notes for Class 6 Junior School Geography
- Chapter 1 The Universe and Solar System
- Chapter 2 Shape of The Earth: Is The Earth Around?
- Chapter 3 Location of a Place on The Earth’ Surface: Where You Are
- Chapter 4 The Earth’s Motion: The Earth Rotation
- Chapter 5 Water – Land – Air
- Chapter 6 The Ice Capped Continent: Antartica
- Chapter 7 Weather And Climate
- Chapter 8 Air Pollution
- Chapter 9 Noise Pollution
- Chapter 10 India
- Chapter 11 – Maps
