Chapter 1 Motion Of The Earth Introduction
The Earth—our homeland is a planet. The earth appears to be stationary. But the earth is not stationary in the universe. The ancient people used to think that the earth was a static body and that the sun, stars, and other heavenly bodies revolved around it.
It was only in 476 A.D., the great Indian astronomer and philosopher, Aryabhatta came to know that the earth is a revolving body in space and it is revolving around the sun.
This idea of the great Indian scientist influenced the thoughts. of the scientists of the later ages all over the world.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Notes for Class 7 Middle Class Geography
It was after about one thousand years came learned Nicholas Copernicus in 1543 A.D., Galileo Galili in 1610, and Johans Capler in 1630 with the idea to ascertain the movement of planets and stars of the universe.
The earth has three basic movements, namely galactic movement, rotation, and revolution.
Galactic movement is the movement of the earth with the sun and the rest of the solar system in an orbit around the center of the milky way galaxy.
This movement has little effect on the changing environment of the earth and is the concern of astronomers rather than geographers.
“WBBSE class 7 geography chapter 1 notes”
The other two movements of the earth, rotation on its axis facing the sun and revolution around the ^un on an elliptical orbit cause the phenomena of day and night, variation in the length of day arid night, and the change of seasons.
The Earth undergoes both rotation and revolution simultaneously. Thus both these two motions are of vital interest to the geographer.
The Rotation of the Earth :
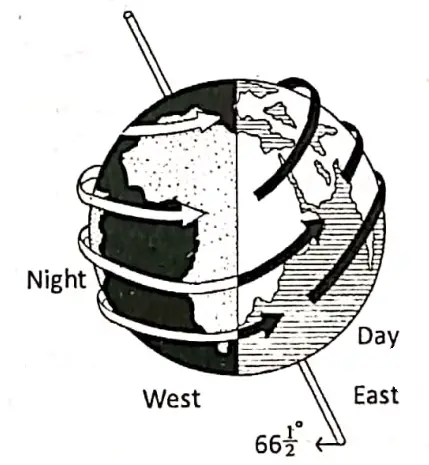
The spinning of the earth on its own axis from west to east causing day and night is called ‘rotation’.
The earth rotates on its axis once in 24 hours (23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds).
It is a solar day. The movement is also known as the ‘Diurnal Motion’ Or ‘the daily movement of the; earth’.
The Revolution Of The Earth :
While the earth rotates on its axis, it revolves around the sun, in an anticlockwise direction along an elliptical orbit in a little less than 365 days 6 hours is called the ‘Revolution of the earth.
The Period of Revolution :
The duration of one complete revolution is 365 days 5 hours48 minutes and 46 seconds.
This period is called the ‘solar year’. In the round figure, this is considered as 365 days i.e. one year.
So the revolution of the earth is also known as the ‘Annual Motion’ or the ‘yearly motion of the earth’.
“motions of the earth WBBSE class 7 geography”
Leap year :
The earth takes approximately 365 days 6 hours (actually 365 days 5 hours, 48 minutes 46 seconds) to complete one revolution around the sun.
We refer to this period as a year and consider it as 365 days.
The balance of 6 hours every year gets added and becomes (6 hours x 4 = 24 hours) or 1 day in four years.
Hence, once in four years, the length of the year is taken as 366 days by adding an extra day to the calendar in the month of February.
We call such a year a ‘Leap year’. In a leap year, the month of February gets 29 days and the year consists of 366 days.
All non-centurial years which are divisible by 4 and all centurial years (those ending ’00’) which are divisible only by 400, are made ‘Leap years’.
For example 1984, 1988, 1992, 1996, and 2000 years are leap years. But 1900 is not a leap year as it is not divisible by 400.

Chapter 1 Motion Of The Earth Features Related to the Earths Revolution
Earth’s Orbit And Orbital Plane:
The fixed elliptical path along which the Earth revolves around the sun is called the Earth’s orbit.
Circumference of the earth’s orbit is 960 million (96 crores) km.
The plane, on which the earth moves, is called the ‘plane of orbit’ or ‘orbital plane’, center of the earth and the sun lie on this plane.
“what do you mean by natural environment for class 7 “
Shape Of The Earth’s Orbit :
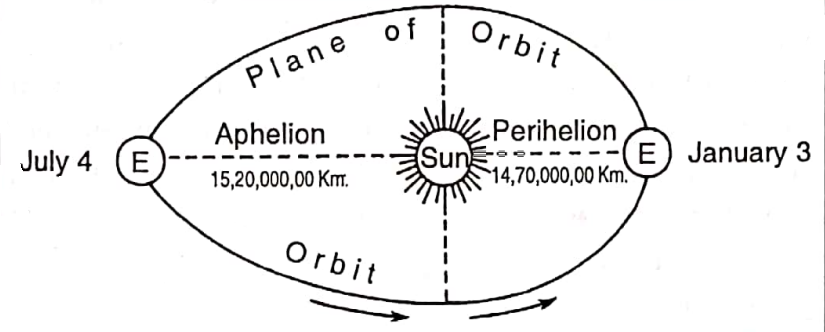
Earth’s orbit is called elliptical, for its shape is an ellipse. The sun is Located at the ‘Focus’ of this ellipse.
Position Of The Earth On Its Orbit :
Aphelion and perihelion: the distance between the earth and the sun is not constant. the orbit of the earth is not circular in shape within it. the distance between the sun and earth reduce to about 14 crores 70 lacks (147 million) km at perihelion (from Greek: peri, close or near to; helios, sun) on 3rd January.
The distance rises to about 15 crores 20 lacks (152 million) km at aphelion (from Greek: ap, away; helios, sun) on 4th July.
“exercise 1 solved questions on motions of the earth”
Effects Of Aphelion And Perihelion
- The average distance between the sun and the earth is 15 crore km. Considering the distance of the sun, this difference is nothing and so it does not really affect the temperature on the earth’s surface. However, summers and winters are slightly moderated in the northern hemisphere and intensified in the southern hemisphere owing to the coincidence of perihelion and aphelion.
- As the earth is slightly nearer in January than in July, the winter sun in the. Northern Hemisphere appears biggest because of perihelion.
- The speed of the1 earth is revolving around the sun is not uniform. The earth journeys more quickly in its orbit when it is at perihelion than it does when it is at aphelion. This causes less duration of winter in the northern hemisphere and summer in the southern hemisphere.
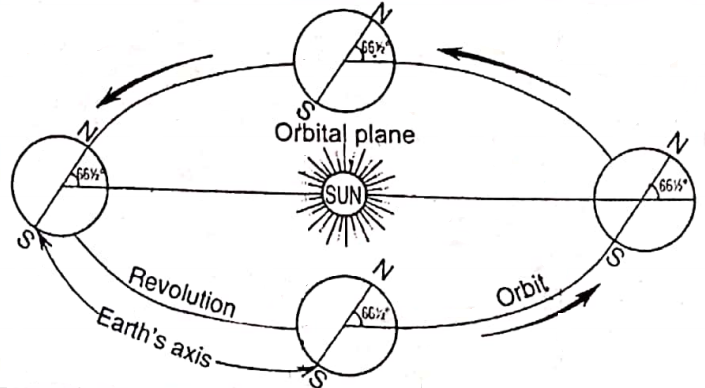
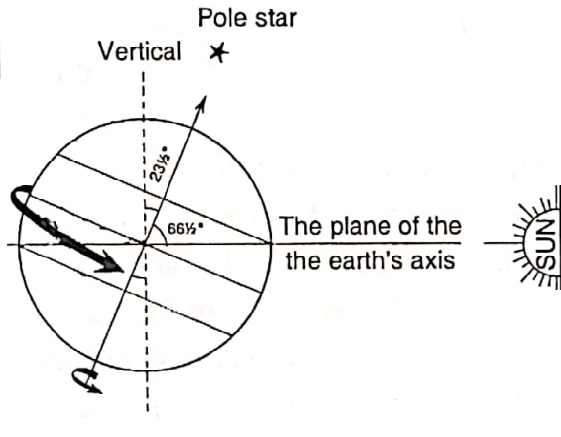
The Inclination And Parallelism Of The Earth’s Axis On The Plane Of Its Orbit And Its Result :
The axis of the earth is inclined at an angle of 661⁄2° on its orbital plane. It always points to the same direction i.e. to the polestar during the revolution of the earth and remains parallel in all positions on the orbit of the earth. The inclination of the earth’s axis is responsible for causing varying lengths of day and night and season changes during the year.
If the earth’s axis were vertical to the orbital plane, all places on the earth will have 12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of the night. There will be no seasonal changes also.
Velocity or speed of the Revolution :
The earth moves in an anticlockwise direction at a very high speed. The mean speed or velocity of the earth in its orbit is about 107000 km per hour. The speed comes to 29-72 km per second. The bullet from a gun moves at a speed of 9 km per second.
It means that the Earth moves in its orbit around the sun with a speed three times that of a bullet. It is the greatest at perihelion and the least at aphelion.
“WBBSE class 7 geography chapter 1 important questions”
Escape Velocity :
We know that if we throw any object upward, it will go up to a certain distance and then fall down due to the gravitational force of the earth. But always it is not true. If an object is thrown up at a very high speed can travel past the gravitation attraction of the Earth and escape to space.
Any object thrown at a speed or velocity of 11-2 km per second, will go past the zone influenced by gravity and will start revolving around the Earth. This velocity is called ‘Escape velocity’. Artificial satellites are launched into their orbits at escape velocity.
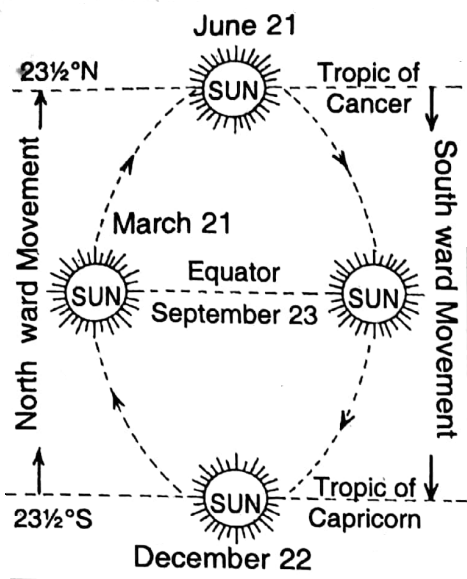
Apparent Annual Movement of the Sun
While the earth revolves around the sun over the course of a year, the sun seems to move between 23½° N and 23½° S latitudes. As the sun does not actually move, this migration of the sun is known as its apparent annual movement.
This apparent movement of the sun’s perpendicular position from the Tropic of Cancer (23½° N latitudes) to the Tropic of Capricorn (23½° S latitudes).
southward and again from the Tropic of Capricorn (23½° S latitudes) to the Tropic of Cancer (23½° N latitude) northward continuously holds on round the year without any break.
So once a year the sun shines directly over each tropic and twice a year over all the places lying between the tropics (Tropic means ‘turning place’).
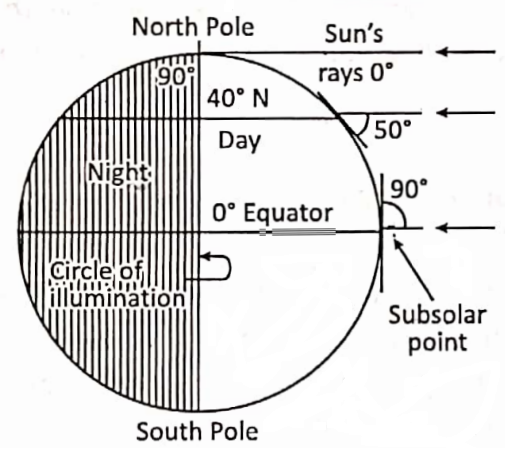
Sub-solar point :
The point at which the sun remains perpendicular to the earth is called the sub-solar point. The sub-solar point moves a 47° latitude range between the Tropic of Cancer (23½° N) and the Tropic of Capricorn (23½° S) crossing the Equator (0° latitude) twice annually.
Proofs or Evidence of the Earth’s Revolution :
The following facts prove that the earth revolves around the sun.
- The more frequent occurrence of meteors during fixed periods of the year.
- We do not see the same set of stars at the same time, during different seasons.
- The duration of the days and nights are not equal throughout the year.
- The change of seasons proves that the earth revolves around the sun.
- The other planets are revolving around the sun. The earth is also a planet and it is expected that it also should move around the sun.
Effects of Revolution
The revolution of the earth results in-
1. Idea of a year formed: One complete revolution gives us the length of the year. It is the major unit of time.
2. Determination of latitudes: The revolution of the earth helps us to determine latitudes. In the summer season, the places on the earth which have vertical sun are all situated at 23½º N. For example, the sun is vertical at 23½° N (Tropic of Cancer) on June 21 and at. 23½° S (Tropic of Capricorn) on December 22, Equator (0°) is situated in between the two positions.
3. Shifting of wind belts: Due to the various inclination of sun rays on the earth from the Equator to the poles, the temperature is different. In fact, various pressure belts are formed. Due to the apparent movement of the sun, the pressure belts are shifted due to the inclination of sun- rays.
Wind belts are also shifted towards the north in summer and towards the south in winter. It has tremendous economic and psychological importance.
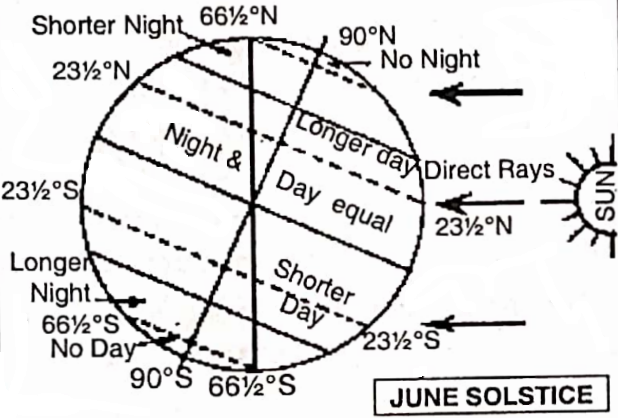
4. Variation in the length of days and nights: The earth is tilted at 66½° angle on its orbital plane during revolution around the sun. So there is variation in the length of day and night on the earth’s surface i.e., days are longer than nights at some places; while nights are longer than days in others.
“types of earth’s motions rotation and revolution”
Days and nights are equal only twice in a year-21st March and 23rd September on all the places of the earth
stored at place. If the storing heat is continued for several days the place becomes hot. Again if the nights are larger than the days, the heat is fully released at night and the place becomes cold within a few days.
5. Change Of Seasons :
Seasons: Seasons refer to those periods of the year which have some peculiar weather and climatic conditions.
Causes of Seasons: Seasons are caused by-
- The revolution of the earth around the sun.
- The spherical shape of the earth.
- The inclination of the earth’s axis at an angle of 66½º to the plane of orbit.
- The elliptical shape of the earth’s orbit and
- The parallelism of the earth’s axis throughout its all positions along the plane of its orbit.
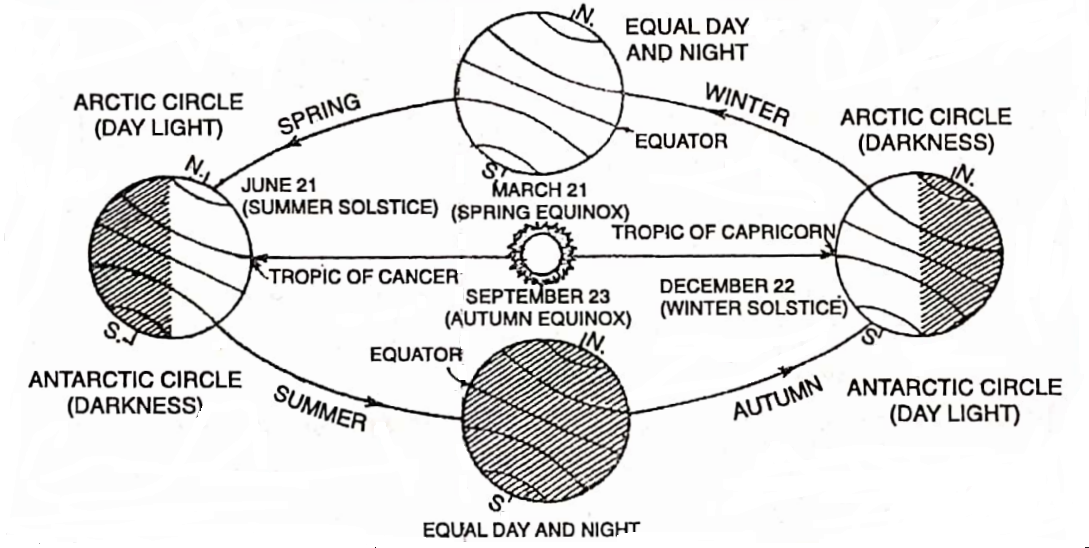
Change of Seasons
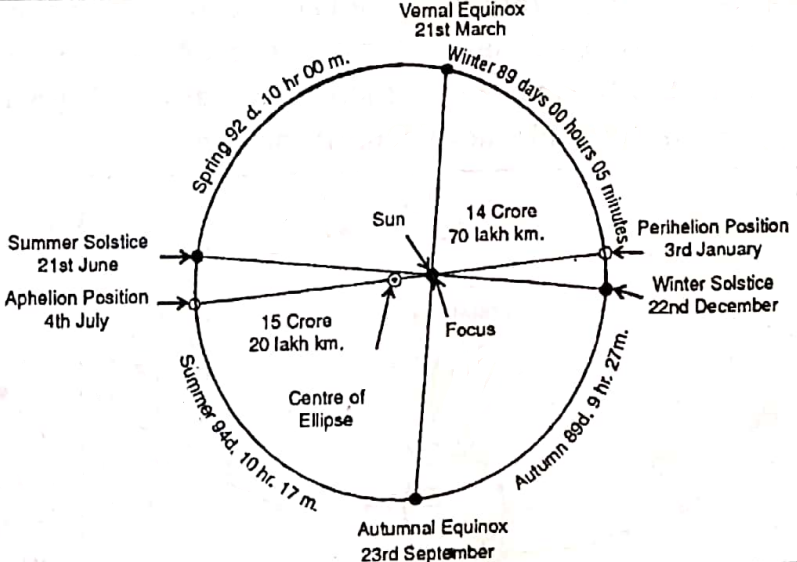
From the point of view of the earth’s inclination, there are four positions of solstices and equinoxes. Hence there are the following four seasons according to the positions of the earth in one complete revolution of the earth around the sun.
1. Summer Solstices – On June 21; the northern hemisphere is inclined towards the sun while the southern hemisphere is inclined away from the sun. The sun’s rays fall vertically on the Tropic of Cancer (23½° N), so at this time of the year, the northern hemisphere has summer with longer days and shorter nights.
while the southern hemisphere, receiving slanting rays, has winter with shorter days and longer nights. This position is called summer solstice as the sun seems to stand still (solstitial-sun standing still).
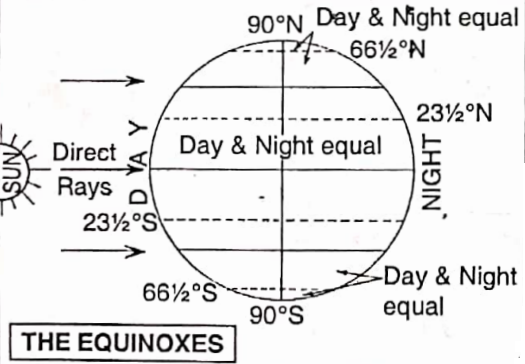
2. Autumnal Eqxuino – On September 23, the northern and southern hemispheres are equally inclined towards the sun. The sun’s rays are vertical at the Equator. As a result, the season is neither cold nor hot.
It is a situation between summer and winter. It is called the autumn season in the northern hemisphere and the southern hemisphere has sprung. This position is called the autumnal equinox (equinox-equal night).
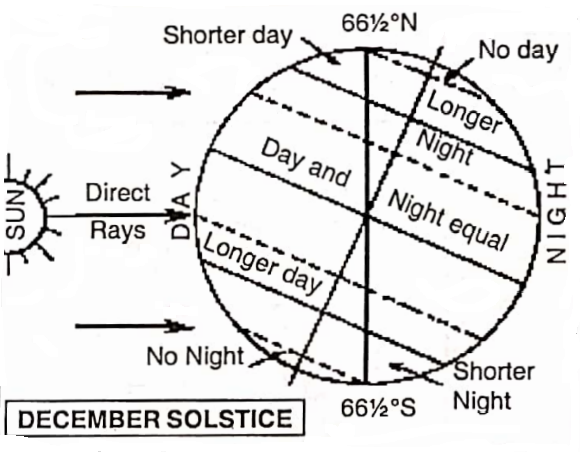
3. Winter Solstice -On December 22, the southern hemisphere leans most towards the sun, and the sun’s rays fall vertically on the Tropic of Capricorn (23½° S).
“effects of earth’s rotation day and night cycle”
As a result at this time of the year the southern hemisphere has summer with longer days and shorter nights, while the northern hemisphere has winter with shorter days and longer nights.
This position is called 90°N Day & Night equals the winter solstice.
4. Vernal or Spring Equinox -On March 21, the northern and southern hemispheres are equally inclined towards the sun. The sun’s rays again fall vertically on the Equator. So the days and nights are equal like Day & Night September 23, it is neither too hot nor too cold.
Now it is autumn in the southern hemisphere and spring in the northern hemisphere. This position is called the vernal or spring equinox.
Aurora Borealis And Aurora Australis
During the long night extending over months together in polar regions peculiar lights in different colors and different forms flash into the sky at intervals. This polar light is known as aurora.
These spectacular colored lights, probably electromagnetic in origin in the ionosphere, are seen near the horizon in the night sky in high latitudes.
The light phenomenon seen in the sky at night in the northern hemisphere mainly in higher latitudes is known as ‘Aurora Borealis’ or ‘Northern Lights’.The light phenomenon seen in the sky at night in the southern hemisphere is known as ‘Aurora Australis’ or ‘Southern Lights’.
“how earth’s revolution causes seasons class 7”
Named for the Roman goddess of dawn, an aurora is a colorful night light display in or near the Arctic and Antarctic circles.
Midnight Sun :
On 21st June the position of the earth is so located on the orbit that the north pole leans towards the Sun. The vertical rays of the sun fall directly on the Tropic of Cancer.
Every part of the northern hemisphere remains in sunlight for more than 12 hours. All places within the Arctic Circle receive sunlight for the whole 24 hours.
In the region beyond the Arctic Circle, the Sun is visible in the sky at midnight. It is called ‘Midnight Sun’. Hammerfest (Norway) situated at 700N latitude, the region beyond the Arctic Circle, has continuous daylight from May 13 to July, 29. It is therefore popularly known as the ‘Land of Midnight Sun’.
“tilt of the earth’s axis and its impact WBBSE”
Cycle Of Seasons
There are many seasons like summer, winter, etc. in a year. The seasons have a close relationship with the annual movement of the sun’s rays on the earth’s surface.
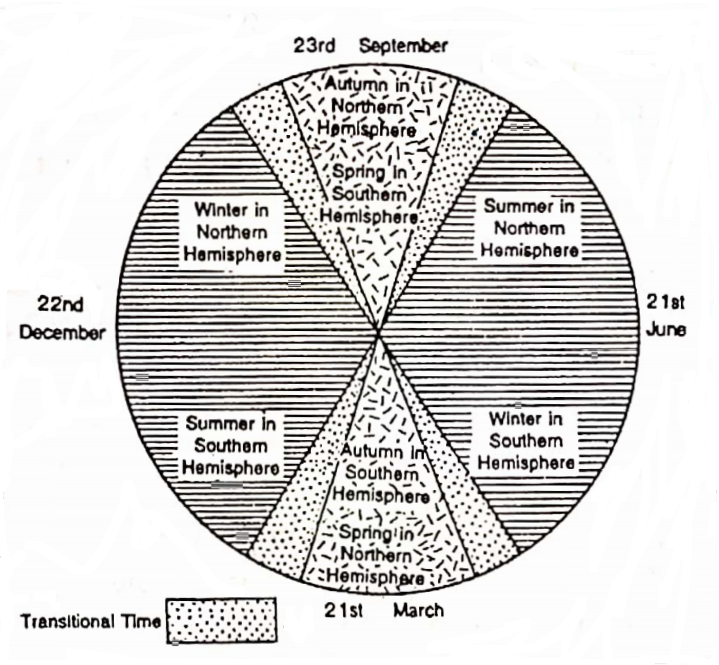
Cycle Of Seasons
| Northern Hemisphere | Southern Hemisphere | Duration (in Montly) |
| Summer season | Winter season | May-July |
| Autumn Season | Spring season | August-October |
| Winter Season | Summer Season | November-January |
| Spring Season | Autumn season | February-April |
Exceptions In The Change Of Seasons :
- There is no change of seasons-only winter occurs at the poles, as the polar regions receive inclined sun rays throughout the year.
- There is no change of seasons-only one hot and humid summer occurs over the Equator as the days and nights are equal throughout the year.
- India also experiences like other parts of the world, four seasons-summer, autumn, winter, and spring. But in West Bengal, early winter is called Dewi season (Hementa), and late summer, when heavy rainfall occurs, is called the rainy season.
“difference between rotation and revolution class 7”
The Influence Of The Earth’s Revolution On Living Beings:
- It is due to the revolution of the earth a suitable climate and natural environment are formed which is favorable for living beings.
- For the revolution of the earth variation of temperature is found in different places of the earth and it encourages the growth of a wide variety of plants, animals, and living beings at different parts of the earth.
- It is due to the revolution of the earth, people get different environmental conditions in their ways of living and livelihood is different. Types of food, clothing, shelter, and customs may be different.
- It is for the revolution of the earth people get different natural environments in which they follow different economic, social, and cultural activities.
