Chapter 8 Soil Pollution
What Is Soil?
Soil is a fundamental natural resource. The loose inorganic and organic unconsolidated material that forms the uppermost layer of the earth’s crust is called soil. It consists of many minerals and organic particles, humus, bacteria, etc.
Soil is formed through the chemical and mechanical weathering of rock cover.
Soil Is The Host Of Life: ‘Soil is a valuable gift of nature. It is one of the most useful renewable resources. About one-third (30%) of the earth is landmass and soil covers, the upper level of it.
Mankind has lived and continues to live on the soil. Many human and economic activities depend upon soils.
All our food comes directly or indirectly from the soil. Livestock farming depends upon the raising of grass on different soils.
Read and Learn More WBBSE Notes for Class 7 Middle Class Geography
Soils form an important element for all living things. Soils have affected the march of civilizations. Ancient civilizations developed in fertile river valleys. Fertile soils attract human settlements.
The density of the population depends upon soil fertility and productivity. So it is called that “soil is the host of life”.
“WBBSE class 7 geography chapter 8 notes”
What Is Soil Pollution: A decrease in the quality or fertility of soil either due to anthropogenic sources or natural sources or both is called soil pollution.
When Soil Is Polluted?
Soil is polluted when it loses its quality or fertility because of the use of dangerous chemicals such as pesticides and fertilizers and the dumping of industrial wastes, garbage, plastic, and radioactive materials.

Soil Pollutants: The soil pollutants may be so chemical and organic or biological types. Some of the pollutants have been reported to be naturally present in harmful concentrations.
“soil contamination effects “
Naturally, present organic pollutants are solanine, gossypol, oxalic acid, and erucic acid. The potential chemical pollutants are fluoride, nitrate, pesticides, radioactive isotopes, and many trace elements, e.g. selenium, lead, mercury, chromium, tin, cadmium, etc.

Chapter 8 Soil Pollution Causes or Sources of Soil Pollution
Depletion of valuable land resources or soil is a serious problem almost in every corner of the world. There are numerous sources of soil pollution, but the most important among them are the following three.
- Indiscriminate discharge of industrial effluents on land and in water.
- Open defecation by animals and human beings especially in rural areas of the country.
- Unscientific disposal of solid wastes on land.
In developing countries like India, the major source of soil pollution is, of this type and is prevalent in both urban as well as rural regions.
“soil pollution WBBSE class 7 geography notes”
In the following table, the important causes/sources of soil pollution are mentioned and indicate how soil gets polluted.

Chapter 8 Soil Pollution A few specific incidents of soil pollution
In 1984 at midnight, poisonous gas from the Union Carbide factory in Bhopal (Capital of M.P.), India mixed with air and soil. Many people died and since then many were disabled.
“exercise 8 solved questions on soil pollution class 7”
In 1986 an accident occurred in Chornobyl nuclear reactor in Ukraine and in 2011 an accident occurred in Fukushima Daichi nuclear reactor in Japan. Disastrous radio-active wastes spread on soil, water, and air in surrounding areas, and many people were affected.
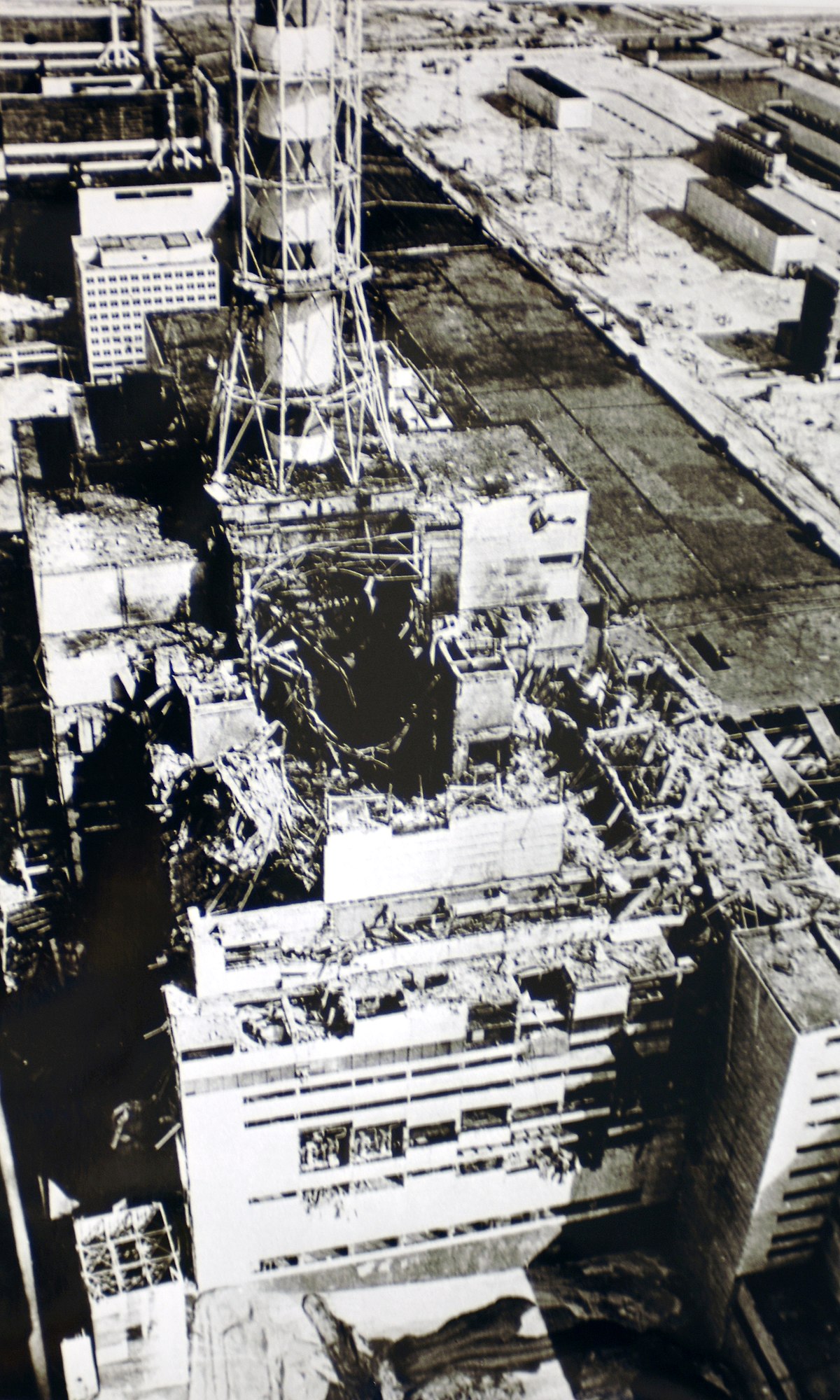
“effects of soil pollution on human health “
Effects Of Soil Pollution: Effects of soil pollution on human beings, animals, and plants are far-reaching. Since pollutants degrade the quality of the soil. This results in a substantial decrease in agricultural production.
Chemical pollutants in form of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and insecticides after reaching the soil eventually reach the human and animal bodies through food chains and cause various diseases and several deaths.
“types of soil pollutants WBBSE class 7 geography”
Chapter 8 Soil Pollution Prevention Of Soil Pollution
Much environmental damage has been done in the past – through ignorance or carelessness, and there are now increasingly strict controls to try to prevent further damage.
- Control and judicious use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and insecticides.
- Immediate reduction in the use of D.D.T.
- Proper land use and crop management.
- Proper disposal of industrial and urban waste.
- The garbage generated in India contains about 30% to 40% compostable mats from which good quality manure can be made which not only will lessen pollution but will help increase soil quality.
- Use of urban and industrial effluents for irrigation purposes after proper treatment.
- Waste disposal on land should be minimized.
- Education to farmers about the proper uses of fertilizers.
- People should be educated to generate less refusal.
- Composting plants should be built in all cities.
- The proper research regarding the adverse effects of soil pollutants
“definition and causes of soil pollution class 7”
In These Ways, We Can Control Soil/Land Pollution.

“WBBSE class 7 geography chapter 8 important questions”
What To Do:
- Throw waste of household and garbage in a certain place.
- Use of organic manure in agricultural farms instead of chemical fertilizers and pesticides. • Planting more trees in the home garden and roadside.
- Use paper or jute bags instead of plastic/polythene.
- There is still much to be learned about the harmful effects of chemicals used by farmers, as well as by industrialists…
- Making the awareness of the people around the school and home increase.
What Not To Do:
- Throwing waste and garbage here and there.
- Excessive use of pesticides and fertilizers.
- Felling trees and uprooted plants.
- Excessive use of polythene and plastic.
- Respond to nature’s call outside a proper latrine/toilet/lavatory.
