Chapter 7 World Of Microbes Diversity Of Microbes
If you look around you will see a large variety of living organisms. It may be plants, animals, fungi, etc. But there are also several organisms that you cannot see with your naked eyes yet these organisms are around you.
Those organisms which are not visible with the naked eye and are viewed under a microscope only are called Microbes. If you increase the area of observation, the range and variety of organisms that you see would increase. This is the biodiversity of organisms.
“WBBSE Class 8 General Science Chapter 7 notes, World of Microbes”
Biodiversity :
(Bios = life, diversity = forms) Biodiversity in short is the number and types of organisms present on earth.
Microbes :
The word microbe (microorganism) is used to describe an organism that is small and normally it cannot be seen without the aid of a microscope example viruses, bacteria, fungi, Protista, etc.
Read and Learn more WBBSE Notes For Class 8 General Science And Environment
Activity :
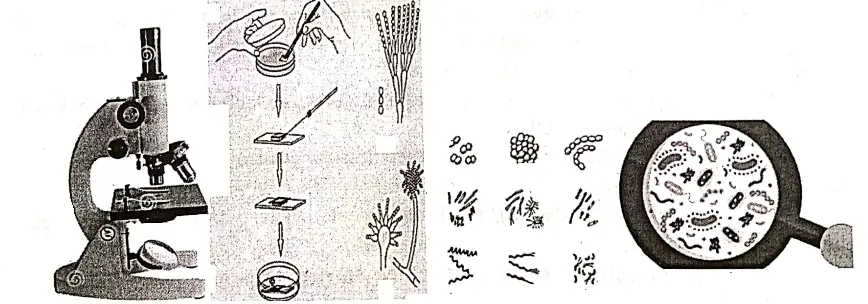
- Collect some water from different places—drains, ponds, or other water bodies.
- Collect some fresh water—wash a leaf and collect the water again.
- Collect some wet soil and mix it with some water into a beaker, and collect the water from the upper surface.
See all the water samples under the microscope separately. You will find different types and numbers of microorganisms or microbes. - Virtually Microbes are found everywhere.

Chapter 7 World Of Microbes Microbes
Microbes or microorganisms are many large, extremely diverse groups of organisms. They cannot be seen without the use of a microscope.
“Class 8 WBBSE General Science Chapter 7 notes, World of Microbes study material”
Microbiology—Scientific study of microbes.
Microbes are the most primitive organisms that have existed from the beginning of life to Earth till now. The first existence of microbes (cyanobacteria) has been recorded 3-5 billion (350 crores) years back. Microbes include—viruses, bacteria, fungi, archaea, and Protista.

- About 60% of the mass of all living organisms are microbes.
- Nearly half (50%) of the oxygen inhaled by us comes into the atmosphere from microbes.
- Nearly 10 lakh types of microbes in the soil.
- About 100 crore microbes may be present in 1 gram of soil sample.
Chapter 7 World Of Microbes Characteristics Of Microbes :
Characteristics Of Microbes
- Microbes are microscopic organisms that can only be seen under the microscope and are not visible to the naked eye because they have a size of 0.1 mm or less.
- They are found almost everywhere—land, water, and air in animals, plants, food products, dead wood, and clothes virtually everywhere. They are found also in extremely cold conditions (poles) to extremely hot conditions (deserts).
- Microbes are also found inside or outside the body. They are found in the human alimentary canal as well as in termites (insects).
- Microbes generally do not have complex multicellular structures. Microbes belong to diverse groups of organisms.
- Bacteria, archaea (prokaryotes), fungi, microscopic plants, viruses, and viroids are also included among microbes.
- The majority of microbes use oxygen for their survival few can live in low oxygen concentrations but few can survive without oxygen.
- Moist (damp), dark or less lighted areas are preferable for microbes’ growth and survival.
- Direct sunlight destroys some microbes.
- Some microbes collect their food from dead and decaying organic substances. Some take shelter to other plants or animals and collect their food from these organisms (host) and
- Live as a parasite. Algae and some microbes are able to synthesize their own food (autophytic)10. Microbes can survive at places where no other organisms can live. For example microbes in hot springs and hydrothermal vents with temperatures of 100°C (Thermophilic bacteria-heat loving) and several meters under thick snow several degrees below 0°C. Microbes can also live in a highly saline or extremely acidic environment. Usually, microbes can grow better between 25°C—38°C.
| Class 8 General Science | Class 8 Maths |
| Class 8 History | Class 8 Science LAQs |
| Class 8 Geography | Class 8 Science SAQs |
| Class 8 Maths | Class 8 Geography |
| Class 8 History MCQs | Class 8 History |
Staining :
Microbes are. microscopic organisms. Before observing microbes under the microscope these organisms are colored by different substances, these coloring substances are known as stains and the process is known as staining.
Types Of Microbes :
Microbes are mainly belong to 4-major groups.
- Bacteria (Monera—kingdom).
- Protozoa (Protista—kingdom)
- Fungi (Fungi—kingdom)
- Algae (Plantae—kingdom)
Viruses though acellular are also treated as microbes, Virus can be seen only by an electron microscope.
Chapter 7 World Of Microbes Bacteria
Bacteria
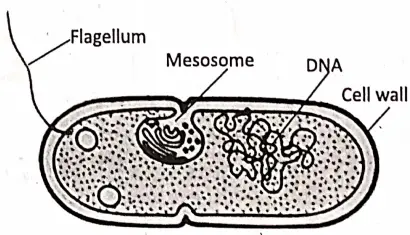
- Bacteria are simple, small, single-cell (unicellular) prokaryotes.
- Bacteria are of various shapes—rounded, coma, rod or spiral-shaped.
- They have some similarities with plant cells. They have an outer cell wall but its composition is not like that of the plant cell wall.
Plant cell wall—have cellulose (Complex carbohydrate)
Bacteria—cell walls have sugar and amino acid (peptidoglycan) - True nucleus is absent (Prokayotic) cell contain circular or spiral DNA as genetic material (true chromosome absent)
- Cells have no membrane-bounded organelles like Golgi bodies, mitochondria, lysosomes, plastids etc but have membrane-less organelle ribosomes (the 70s) in the cytoplasm.
In many cases have a sac-like structure, (outgrowth from plasma membrane) mesosome, helps in respiration.
- Antony Von Leeuwenhoek, 1674 first time reported the existence of bacteria, observing under his own made microscope. –
- Ehrenberg, 1828, used the term bacteria for the first time.
- Bacteria have been placed in the kingdom Monera.
- Robert Koch: discovered two important human Pathogen—Cholera and Tubercu
Protozoa :
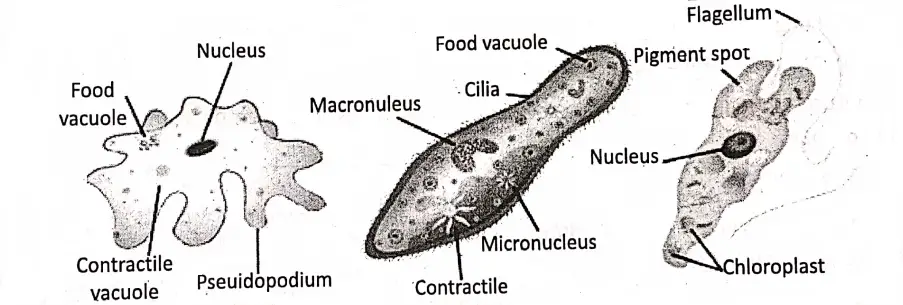
- Unicellular, have one or more nuclei in the cell,
- Protozoa were placed under Protista.
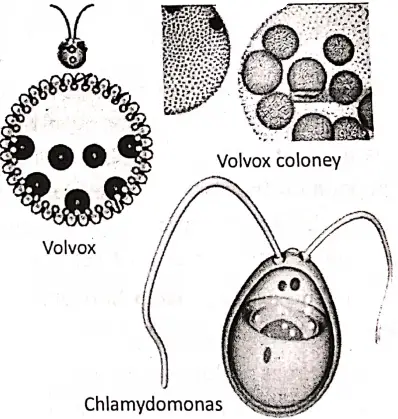
- They are variously shaped— such as rounded, oval, elongated or flat. Some form a colony. (e:g. volvox). Some are parasitic (live and collect food from host body).
- They have different types of locomotory organs such as Cilia (hair-like) flagella (whip-like) pseudopodia (a finger-like outgrowth of cytoplasm), which are the main locomotory organs.
Some protozoa have pigments that can produce food in their body such as Euglena.
Chapter 7 World Of Microbes Fungi
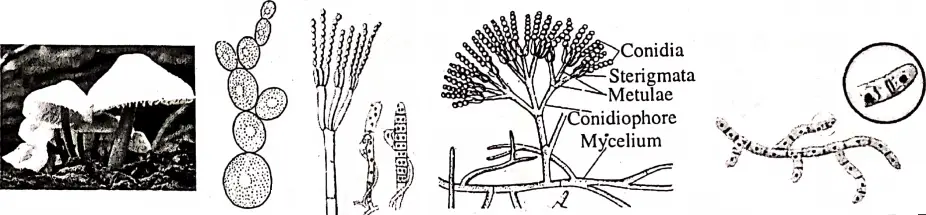
Fungi
- Their body cannot be differentiated into root, stem, and leaves.
- They have no photosynthetic pigment. Therefore, they are not able to produce their own food in their body. They collect food from decaying substances.
- They may be unicellular (yeast), or multicellular (Penicillium). Cells of the body connect each other and form a (filamentous) ribbon-like structure, hyphae. Often hyphae divide in branches, Hyphae combine to form a structure called mycelium (for example Penicillium, Mucor).
- Fungi have rigid cell-wall having chitin. (a nitrogenous compound) and glycan in it. They have no plastid in their cells! So they are unable to produce food.
- They are eukaryotic and have true nuclei.
- Fungi can be found in wetlands and dark and damp places.
Algae :
- Algae are unicellular or multicellular or sometimes cells join together and form a colony.
Unicellular algae—Chlamydomonas.
Multicellular—(Ribbon-like)— Spirogyro.
Colony forming (Ball like structure)—Volvox. - The body of algae like fungi cannot differentiate into root, stem, and leaves..(thallus-like- body) . Algae possess chlorophyll (green pigment) containing chloroplast as well as some have other types of pigments, such as (red, yellow, etc). As they have chlorophyll in their body they can produce their own food with the help of sunlight, C02, and water.
- The cells of algae are eukaryotic type and have true nuclei and other cell organelles including chloroplast.
- Algae are mainly aquatic (freshwater or marine) though it also grows in wet and moist places.
Chapter 7 World Of Microbes Virus :
Virus
The virus has not a typical cell. Viruses are called acellular because they have no protoplasm and they only behave like living organisms when they come in contact with a living organism.
Viruses can only be seen by electron microscope. Their possible existence was first noticed by Edward Jenner during his research with smallpox victims in Europe in 1796. But until the discovery of the Electron microscope, their detailed study could not be done. The term Virus’ means ‘poison’ (the Latin word)
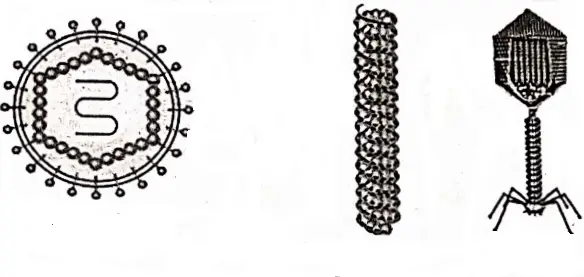
- Viruses may be rounded, tadpole like, or maybe of I different form.
- They have either DNA or RNA (nucleic acid) and a protein coat outside (capsid) the nucleic acid (DNA or RNA).
- They are parasitic in nature, they can grow and multiply within living organisms. Outside the host body, they are inert particles.
- Viruses are one of the main disease-causing agents.
Interrelationship With Living World—Symbiosis And Saprophytism
Some disease-causing microbes enter Into a particular part of the body or a particular type of cell (such as malarial parasite inter RBC, liver cells). Their growth and reproduction depend on the host cell.
They collect food and get shelter in particular cells or organs. These microbes later hamper the normal functioning of the host cell and system. The interrelationship between the host and parasite is called parasitism.
“WBBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 7, World of Microbes study guide”
Microbes influence man in many ways. Microbes are known to cause various diseases in man and other organisms and for Deteriorating food, .clothing, furniture, etc. But some of their activities are useful for us. Such activities include medicine (antibiotic production. Production of dairy products and fermented beverages, sewage treatment, etc.
Chapter 7 World Of Microbes Harmful Effect Of Microbes
Harmful Effect Of Microbes
Many diseases of humans, plants, and other animals are caused by microbes. Microbes can enter inside the human body through air, water, food, blood, and also sometimes by a simple touch.
| Disease causing agents | Diseases |
| (1) Bacteria (Bacterial diseases) | (1) Tuberculosis, a certain type of Diarrhoea Cholera, Typhoid, Diptheria, Tetanus, whooping cough, Pneumonia, etc. |
| (2) Virus (viral diseases) | (2) Influenza, Pox, Polio, Measles, Hydrophobia Dengue, AIDS, etc. |
| (3) Fungi (Fungal diseases) | (3) Ringworm, Allergy diseases of the throat and lung, food poisoning sometime Diarrhoea, Aspergillosis |
| (4) Protozoa (Protozoal diseases) | (4) Amoebiasis, Giardiasis, Malaria, Kala-azar, Sleeping sickness, etc. |
Activity Work :
Make a list of ways of the entrance of microbes In the body and cause diseases.
- Through drinking water—Amoebiosis, Giadiarsis, Diarrhoea,…..
- Through cough, and sneezing—Tuberculosis, …..
- Through food—Amoebiasis, Diarrhoea, ……
- Through blood—Hepatitis, AIDS,…..
- Through carrier (vector)—Malaria, Dengue, Kalazar,……
Microbes help in human welfare :
Nitrogen is an essential element (Macro element) which is important for plant body formation. (Protein formation) and growth. Plants collect their nitrogen from the soil. Some Microbes (N2-fixing—bacteria) fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil. Some free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria present in soil are Azotobacter and Clostridium.

Few species of mushrooms are poisonous. Many of these deadly fungi bear an unfortunate resemblance to edible species, for example, Amanita (Deata cap, colorful)
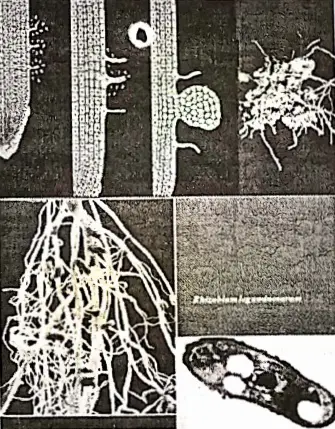
Chapter 7 World Of Microbes Symbiotic N2 Fixing Bacteria
Some nitrogen-fixing bacteria form a mutually beneficial association with the plant. This association is called symbiosis and these bacteria are called symbiotic bacteria: The most important of the symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria is Rhizobium. They live in the nodules of leguminous plants root such as peas, grams, beans, etc.
Rhizobium produces Nitrogenous compounds for the plant and shares it to plant, on the other hand, plants give them shelter.E.coli and some other symbiotic bacteria present in the intestine of human beings (getting food and shelter they’re) help in the production of Vitamin B12 which helps in the production of hemoglobin of RBC.
Leguminous plants before the preparation of cultivating fields are mixed with soil to increase soil nitrogen. Sometimes more than one organisms live together and share its nutritional product.
For example Lichen – an association in between algae and fungi. The fungus partner supplies water and minerals to the algae partner and the algae prepares food for itself and share it with the partner. partner.
“WBBSE Class 8 World of Microbes notes, General Science Chapter 7”
Many fungi and bacteria take part in the decaying process,, or decomposition. The process of collecting nutrients from dead decaying organic body and completing of the nutrition of their own is known as saprophytism.
Saprophytisms :
Many Microbes grow on dead animals and plants and help in the decay of organic matter. They break down complex organic matter into simple forms by the secreting enzymes. They also consume some nutrients after breaking down the complex organic forms Role of microbes in Environment.
Agriculture :
Free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria (microbes) fix nitrogen in the soil such as Azotobacter, Clostridium, and Plants collect it from the soil. Symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria Rhizobium forming nodules in the root of leguminous plants. (Pea, Gram, Pulse).
Plants take Nitrogen (N2 ) from the atmosphere and form nodules after the decomposition of the nodules nitrogen content of soil increases. During the preparation of green manure many leguminous and nonleguminous crops are grown in the field and plowed back into the soil when they are still young and green.
This practice helps to enrich soil nitrogen, phosphorus, calcium, sulfur, and other minerals. Nitrogen-fixing Cyanobacteria (blue-green algae)symbiotic association with several plants, for example, Azolla (fern). Most of plants, use soil, Nitrogen when it is in the form of Nitrate (N03 ) or NH4+.
Chapter 7 World Of Microbes Azolla :
Anabaena is Of great importance to agriculture. Anabaena (Azolla) resides in the leaf cavities of the fern Azolla and it fixes nitrogen. The decaying fern plants used in the field, before cultivation, as green manure. They decompose and, enrich the field for the next crop.
Some microbes present in soil also break the organic nitrogenous compounds and release NH3 (ammonia) the process is called ammonification and again ammonia converted into nitrite and then nitrite (N03) by some nitrifying bacteria.
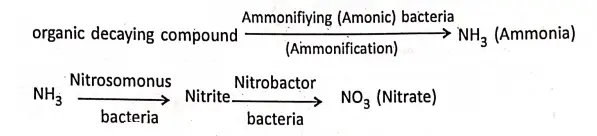
This process of (Nitrate) N03– formation from Ammonia (NH3) is called nitrification. There are some other microbes (bacteria) that break nitrogen compounds and free nitrogen from compounds; this process is known as denitrification.
You may have noticed that after cutting Jute stem have been submerged in water for few days.
- Jute fibers separated from Jute stem, decomposing the pectin (complex carbohydrate) present in the cell wall by microbes.
Food processing—by microbes.
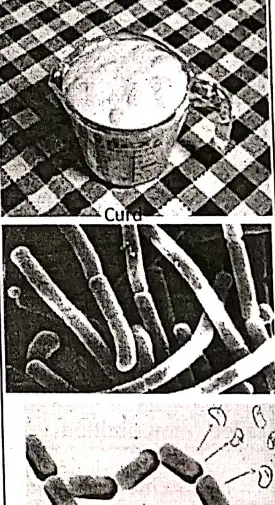
Curd, cheese, and other food substance production. - Curd—When Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) Lactobacillus are added to milk (hot milk at 37°C) it converts the lactose sugar of milk into lactic acid. Lactic acid causes the coagulation of milk protein (casein). Milk is changed into curd. Different microbes also help to produce yogurt and cheese.
- Using the fermentative activity of microbes we can prepare a number of products, such as Alcohol, Idli, Dosha, Cake Vinegar, etc.
Production of medicine
Many life-saving drugs, Antibiotic medicine are produced from microbes mainly fungi and bacteria. Some organic compounds produced by these microbes can arrest the growth of other bacteria, for example, Streptomycin, Ampicillin, Chloromycetin, etc. Antibiotics are chemical substances the secreted by some microorganisms which inhibit the growth and development of other microbes (pathogens).
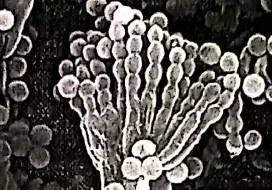
Alexander Flemming the father of antibiotics, first discover penicillin from the fungus Penicillium notatum. This was the first antibiotic which inhibit the growth of bacteria. This saves the life of millions and millions of people all over the world.

Chapter 7 World Of Microbes Vaccine
Vaccine
After the entry of some microbes like viruses, bacteria, protozoa, and fungi, they produce some toxic substances inside the body. These harmful agents (proteins) which enter into the body is called an antigen.
“Class 8 WBBSE General Science Chapter 7, World of Microbes easy explanation”
To prevent this antigen body produces some proteinous substance that prevents the entry and harmful activity of antigen called Antibody. Antibody attack and destroy the antigens. The natural system of body protection is called immunity.

To prevent some diseases some dead or weak microbes (viruses, bacteria) have been introduced in the body, which tiger body produces antibodies to fight against these antigens. The natural system of body protection is called immunity.
To Prevent some diseases some dead or Weak microbes (viruses, bacteria) have been introduced in the body. which tiger body produces antibodies to fight against these antigens. This process is called vaccination.
By this process, body is able to protect these diseases such as, polio, typhoid, cholera, diphtheria, etc. The process of improvement of body immunity is called immunization.
Vaccine and Vaccination :
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides immunity (active acquired immunity) to a particular disease and the process by which immunity can grow by using a vaccine is called vaccination.
“WBBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 7 notes, World of Microbes PDF”
Immunization :
Immunization is the process by which a person or animal becomes protected from disease.
Treatment Of ‘Waste Product’
If human feces, urine, food residue, and decaying substance are not treated properly some infections may happen. These are risks for human health. Some microbes (bacteria) live in less oxygenated conditions can break these compounds. into utilizable and harm less products.
- Microbes also help in biogas production. Biogas is a methane-rich fuel gas produced by
- Break down of biomass with the help of methanogenic bacteria (anaerobic) Some algae (microbes) are used in space centers and space shuttles to clean air.
- Microbes are also used in the biological control of pests.
