Class 10 Geography West Bengal Board India – Industries Of India True Or False Type:
Question 1. One of the forest-based industries of India is the paper industry.
Answer: True
Question 2. The Petrochemical Industry is called a “Modern Industrial Giant”.
Answer: True
Question 3. Ahmedabad is called the Manchester of India.
Answer: True
Read and learn all WBBSE Solutions For Class 10 Geography And Environment
Question 4. Salem Steel Plant is a steel industry.
Answer: True
Question 5. The Visveswaraiya Iron and Steel Ltd. gets iron ore from the Singbhum district of Jharkhand.
Answer: False
“WBBSE Solutions for Class 10 Geography Industries of India”
Question 6. Maruti Udyog Ltd. is situated in Gurgaon in Haryana.
Answer: True
Question 7. The IT industry employs about 1 million Indian population.
Answer: False
Question 8. Jamshedpur (Tata Iron and Steel Co.) is a Public Company.
Answer: False
Question 9. Bokaro Steel Plant is the largest steel plant in India.
Answer: False
Geography Class 10 West Bengal Board

Question 11. India is one of the leading nations in the world in cotton textile production.
Answer: True
Question 12. Manganese is one of the essential raw materials for manufacturing iron and steel.
Answer: True
Question 13. One of the problems of the Indian iron & steel industry is the availability of quality coking coal.
Answer: True
Question 14. Vadodara is noted for petrochemicals.
Answer: True
Question 15. The biggest petrochemical complex in India is situated at Haldia.
Answer: False
Question 16. Gurgaon is famous for its shipbuilding industry.
Answer: False
Question 17. Kayal in Gujrat is the largest oil refinery in India.
Answer: True
Question 18. A humid climate is favourable for the cotton textile industry.
Answer: True
“Class 10 Geography and Environment Industries of India solutions WBBSE”
Question 19. Heavy engineering industry centres have proximity to the iron and steel centres in India.
Answer: True
Question 20. Chennai is famous for its aircraft industry.
Answer: False
Question 21. Coimbatore is known as the Manchester of South India.
Answer: True
Question 22. The Kolkata port plays an important role in the development of the jute industry.
Answer: True
Question 23. Kayali is a noted oil refinery.
Answer: True
Question 25. Dalmia Puram has the first cement factory.
Answer: True
Question 26. Dalmianagar has the first paper mill.
Answer: True
Question 27. Maulhandar is noted for copper melting.
Answer: True
Question 28. Raniganj has paper mills.
Answer: True
Question 29. Durgapur is called the Ruhr of India.
Answer: True
Class 10 Geography West Bengal Board India – Industries Of India Fill In The Blanks Type:
Question 1. Jamnagar is famous for _______ industry.
Answer: Oil refining & Petrochemical
Question 2. _______ city is called as the “Manchester of South India”.
Answer: Coimbatore.
Question 3. Heavy Engineering Corporation is situated at _______.
Answer: Ranchi/Hatia.
Geography Class 10 West Bengal Board
Question 4. Bhopal is noted for ______ industry.
Answer: Heavy Electricals.
Question 5. Rourkela is noted for the industry.
Answer: lron and Steel.
Question 6. ______ is entrusted with the iron & steel industry.
Answer: SAIL.
Question 7. Bhadrawatiiron & steel plant in run by _______.
Answer: Charcoal.
Question 8. ______ is noted for Heavy Engineering Industry.
Answer: Ranchi.
Question 9. ______ in Orissa is noted for a new steel plant.
Answer: Paradeep.
“WBBSE Class 10 Geography Industries of India solved questions”
Question 10. Rupnagar is noted for ______ industry.
Answer: Aluminium.
Question 11. Rupnarayanpur is noted ______ industry.
Answer: Cable.
Question 12. Korput is noted for ______ industry.
Answer: Aircraft.
Question 13. Kanpur is noted for the industry.
Answer: Scooter.
Question 14. MAMC is situated at ______.
Answer: Durgapur.
Class 10 Geography West Bengal Board India – Industries Of India Very Short Answer Type:
Question 1. Where was the first cotton mill set up in India?
Answer: Ghusuri (West Bengal).
Question 2. Which city is called the Manchester of South India?
Answer: Coimbatore (Tamil Nadu).
Question 3. What is the full form of SAIL?
Answer: Steel Authority of India Ltd.
Question 4. Name the largest steel plant of India.
Answer: Bhilai (Chhattisgarh).
Geography Class 10 West Bengal Board
Question 5. Name the steel plant which is run by charcoal.
Answer: Bhadravati Iron and Steel Plant.
Question 6. Name the steel plant of Tamil Nadu.
Answer: Salem Iron and Steel Plant.
Question 7. Name one centre producing only diesel locomotives in India.
Answer: Marundi near Varanasi.
Question 8. Name one railway locomotive manufacturing unit of India under private management.
Answer: Telco, Jamshedpur. :
Question 9. Why is manganese used in the iron and steel industry?
Answer: Manganese is for hardening steel and for making ferromanganese.
Question 10. Which steel plant is run by charcoal?
Answer: Bhadarbati is the only iron and steel centre which is run by charcoal. It is in the state of Karnataka.
Question 11. Which industrial region is called the Ruhr of India?
Answer: Durgapur industrial region in West Bengal is called the Ruhr of India.
Question 12. Name the iron and steel plant at Bhadrabati.
Answer: Visweshwraya Iron and Steel Limited.
Question 13. Name one important centre of automobiles in India.
Answer: Gurgaon in Haryana (Maruti Udyog Ltd.).
Question 14. Name the Cottonopolis of India.
Answer: Mumbai.
Question 15. Name a major cotton textile centre in Gujarat.
Answer: Ahmedabad.
Question 16. Name-the most important centre of the cotton textile industry in Tamil Nadu.
Answer: Coimbatore.
Question 17. Name the biggest centre of the cotton textile industry of the U.P.
Answer: Kanpur.
Geography Class 10 West Bengal Board
Question 18. Name an iron and steel centre in Orissa.
Answer: Rourkela.
Question 19. Name the centre of the steel plant in Jharkhand set up in collaboration with the Soviet Union.
Answer: Bokaro.
Question 20. Name the centre of the steel plant in Chhattisgarh setup with the help of the Soviet Union.
Answer: Bhilai.
Question 21. Name a centre of steel plant in Tamil Nadu.
Answer: Salem.
Question 22. Name the oldest steel plant in India.
Answer: Jamshedpur.
Question 23. Name an Iron and Steel plant of India having a coastal location.
Answer: Vishakhapatnam.
Question 24. Which steel plant in India has been set up with the collaboration of the U.S.S.R?
Answer: Bhilai Steel Plant in Chattisgarh had been set up with the collaboration of U.S.S.R.
Question 25. Where is the biggest Iron and Steel factory of India located?
Answer: The biggest Iron and Steel Plant of India is located at Bhilai in Chhattisgarh.
Question 26. Which are the leading centres of the Cotton Textile Industry in India?
Answer: Ahmedabad in Gujarat/Mumbai in Maharashtra is the leading centre of the Cotton Textile Industry in India.
Class 10 Geography WBBSE India – Industries Of India 2 Marks Questions And Answers:
Question 1. What do you mean by “pure raw materials”?
Answer: An element that does not change its weight or mass when it is turned into the finished product. It contains no impurities that are burnt off or removed so the weight will remain the same.
Question 2. Name one agro-based and one forest-based industry of India.
Answer: Agro-based industries: Cotton textile, Jute textile, Sugar industry, Flour industry. Forest-based industries: Paper industry, Lumbering industry.
Question 3. What do you mean by information technology?
Answer: Information Technology is the application of computers and telecommunication equipment to store, retrieve, transmit and manipulate data in the context of a business or other enterprise. The term is now used as a synonym for computers and computer networks. Several other industries associated with Information Technology are —computer hardware, software, electronics, semiconductors, internet; telecom equipment, e-commerce and computer services.
Geography Class 10 West Bengal Board
Question 4. What is meant by the engineering industry?
Answer: The industry which uses iron and steel as its main raw material for the production of different types of machinery and other steel goods is called the engineering industry.
It can be divided into two categories:
1. Heavy Engineering and
2. Light Engineering.
“Industries of India Class 10 WBBSE solutions and answers”
Question 5. What are ancillary industries?
Answer:
Ancilliary Industries: Ancilliary industries are associated industries. They grow up when one major large-scale industry is set up.
Example: The engineering industry is an ancillary industry. It grows up depending on iron and steel produced by an iron-steel plant.
Question 6. Name one centre for each of the locomotive and petrochemical industries of India.
Answer:
Centre of Locomotive Industry: Mauradi (near Varanasi).
Centre of Petrochemical Industry: Ankleshwar (Gujarat).
Question 7. From where does the steel plant of Jamshedpur get the required minerals?
Answer: Jamshedpur is in Jharkhand. It gets an adequate supply of iron ores from the iron belt of Mayurbhanj and Singhbhum. Coal, Manganese, limestone, etc. are necessary for the growth of this industry. Coal is brought to Jamshedpur from Jharia coal fields, limestone is brought from neighbouring areas, and manganese from Madhya Pradesh.
Question 8. Why is Manganese required in the Iron and Steel industry?
Answer: Manganese is essential in steel making. A little manganese added to iron removes gases and acts as a ‘cleaner’ in the manufacture of steel. Further addition of manganese makes the steel tough and hard, and it does not rust easily.
Question 7. Name two agro-based industries except for the sugar industry. Why is the sugar industry now shifting from North India to South India?
Answer: Two agro-based industries are the cotton textiles industry and the jute industry. The sugar industry is now shifting from North to South because of the following reasons:
1. The sugar content in sugarcanes is 10.5% higher in southern states than in the north.
2. It is a seasonal industry and is suited to the cooperative sector which is better organised in the south.
Question 8. Name two centres where the petrochemical industry is located.
Answer: The petrochemical industry is located near Mumbai and Vadodara near the source of the raw material crude oil.
Question 9. What is the use of newsprint? Name two raw materials of the paper industry.
Answer: The paper required for newspapers is called a newsprint. The first newsprint plant was set up at Nepanagar in Madhya Pradesh. West Bengal, Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh are the leading states in the paper industry. Raw materials required for the paper industry are Bamboo and wood pulp.
Question 10. What are the most important raw materials of the iron and steel industry?
Answer: Iron ore, coal, water and refractories nature.
Question 11. Name the integrated steel plants of India.
Answer: Durgapur, Bhilai, Bokaro, Rourkela, Burnpur, Bhadrawati and Jamshedpur.
Question 12. Name five heavy engineering centres.
Answer: Bangalore, Hyderabad, Durgapur, Bhopal, Naini.
Question 13. Name the automobile centres of India.
Answer: Hindmotor (Kolkata), Premier Automobiles (Mumbai), Maruti Udyog (Gurgaon), DCM Toyota, Surajpur (Uttar Pradesh).
Question 14. Name the steel plants under SAIL.
Answer: Bokaro, Bhilai, Rourkela, Durgapur, VISL and Salem Steel Plant.
Question 15. Name the main centres of textile production in
1. Gujarat and
2. Maharashtra.
Answer:
1. Ahmedabad;
2. Bombay.
Question 16. Where have the four iron and steel plants of India been set up in the post-independence period?
Answer: Durgapur, Rourkela, Bhilai and Bokaro.
Question 17. Name 3 textile manufacturing centres in West Bengal.
Answer:
1. Belgharia.
2. Sleeper
3. Srirampur.
Question 18. Where are the three mini steel plants of India?
Answer: The mini steel plants are at Salem in Tamil Nadu, at Balacheravu in Andhra Pradesh, and at Vijaynagar in Karnataka.
Question 19. What are the uses of petrochemicals?
Answer: The derived petrochemicals are used in the manufacture of various articles such as:
1. Synthetic Fibres
2. Synthetic Rubber
3. Plastics
4. Dye-stuffs
5. Ferrous and Non-ferrous Metals
6. Insecticides
7. Drugs and Pharmaceuticals
8. Synthetic Detergents.
Question 20. What are the raw materials of the cotton textile industry?
Answer: The principal raw materials of the cotton textile industry are
1. Raw cotton.
2. Chemicals (caustic soda, chlorine, bleaching powder, dyes, etc.)
3. Freshwater
4. Electricity.
Question 21. What are the major products of the Bhilai steel plant?
Answer: The plant produces heavy rails, structurals, beams, billets and rolled wire. It produces plates for the shipbuilding industry. The plant also produces by-products like ammonium sulphate, benzol, coal tar and sulphate acid, etc.
Question 22. Define the petrochemical industry.
Answer: These industries are primarily involved in the production of petrochemicals which are derived from petroleum resources. These chemicals are used in the manufacturing of a large variety of articles, such as polymers, (polyethene, polypropylene, polystyrene), synthetic fibres, synthetic rubber, plastics, dye-stuffs, insecticides, drugs, pharmaceuticals and synthetic detergents.
Question 23. Why do most of the petrochemical industrial centres and industrial centres grow in proximity to ports in India?
Answer: The inputs of petrochemical industries are mostly imported & the output is mostly exported. Hence, the availability of the nearest port is a great advantage in the growth of petrochemical industries.
Class 10 Geography WBBSE India – Industries Of India Short notes:
Question 1. Petrochemical industrial complex.
Answer:
Petrochemical industrial complex:
A petrochemical industrial complex may be defined as an agglomeration of related industries based on the distillation of crude oil into its component chemicals.
Products: Industrial chemicals, explosives, fertilizers, plastics, pesticides, synthetic fibres, paints, medicines and, of course, petroleum products.
Positive effect: It has a positive effect on any economy because of its capital-intensive nature with a cascading interlink among its component units. The flourishing downstream industries bring an economic boom in the regional set-up.
Negative effects: They generate almost limitless gaseous pollutants based on mainly hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides, some of which are fatal for human life.
In 1984, Bhopal Gas Tragedy killed an estimated 23,000 people by an accidental release of toxic gas.
Examples: Trombay, Thane (Maharashtra), and Haldia (West Bengal).
Question 2. Food processing Industry.
Answer:
Food processing Industry:
The industry where agro-based raw materials are used to produce easily usable, attractive and long-lasting food items, is called the food-processing industry. The types of food-processing units found in India are
1. Rice mills,
2. Flout mills,
3. Fruit and vegetable processing units,
4. Soft drinks and aerated drinks,
5. Sugar mills, etc. Food processing is one of the modern concepts of industries in India and is prospering in leaps and bounds.
Class 10 Geography West Bengal Board India – Industries Of India 3 Marks Questions And Answers:
Question 1. What steps have been taken to overcome all the problems of the Indian cotton textile industries?
Answer:
Remedies: Through plans, India’s cotton textile industry is having altogether a new pattern of production.
1. Mills are encouraged to specialise in spinning.
2. Previously mills and handlooms were keenly competitive with each other. But ey are now becoming interdependent.
3. Farmers are encouraged the production of long-staple cotton and high prices are assured to them.
4. Labour problems are tackled with the help of the labour commission.
5. Variety of production to attract foreign markets.
“WBBSE Class 10 Geography Industries of India chapter answers”
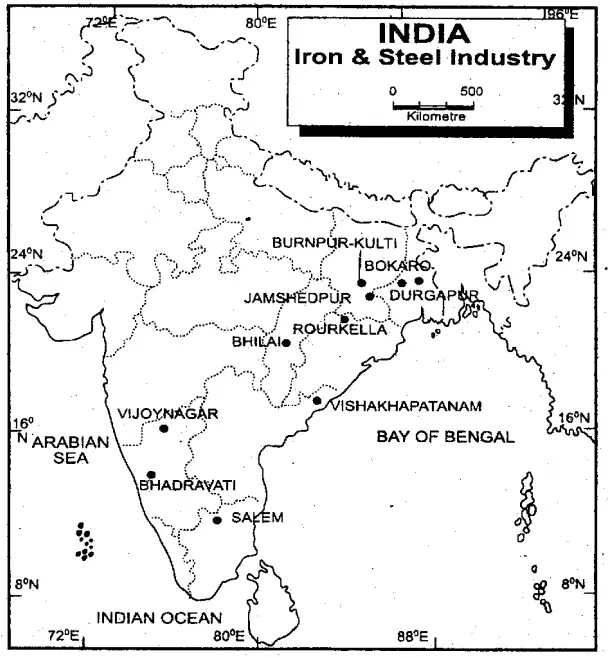
Question 2. Name the iron and steel centres of India.
Answer:
The mainiron and steelcentresofIndia are:
1. TISCO —Jamshedpur (Bihar),
2. Kulti, Burnpur (West Bengal),
3. Durgapur (West Bengal),
4. Rourkela (Orissa),
5. Bhilai (Chhattisgarh),
6. VISL — Bhadravati (Karnataka)
7. Vijaynagar Steel Plant (Karnataka),
8. Salem Steel Plant (Tamil Nadu),
9. Visakhapattanam (Andhra Pradesh)
10. Bokaro —Jharkhand
Besides these, there are 169 mini steel plants and they are producing 31.22 lakh tons of iron and steel.
Question 3. Name the automobile centres of India. Which is the largest one?
Answer:
Automobile Centres:
1. Hindusthan Motors (Hindmotor) (West Bengal).
2. The Premier Automobile Ltd. (Bombay).
3. Mahindra and Mahindra Ltd. (Bombay and Kolkata).
4. Ashok Leyland Ltd. (Madras).
5. Tata Engineering and Locomotive Co. Ltd. (Bombay and Jamshedpur).
6. Maruti Udyog (Gurgaon).
Hindusthan Motors of Kolkata is the largest automobile centre in India.
Question 4. Name the locomotive-producing centres of India. Which is the largest one?
Answer:
Locomotive Producing Centre:
1. Chittaranjan Locomotive Factory: Producing Diesel, Electric and Stream Engines.
2. Diesel Engine Works: Producing only Diesel Engines, Varanasi: Maruadi, U.P.
3. Tata Locomotives: Producing Narrow Guage Engines.
Chittaranjan is the largest locomotive-producing centre in India.
Question 5. What are the problems of the Iron and Steel industries?
Answer:
(1) Coke coal crisis: Steel plants require good quality coking coal containing 17% ash content. But CIL mines produce coal with 19.1 ash content.
(2) Low rate of capacity utilization: Basic causes for the low rate of capacity utilization include lack of proper maintenance, delay in replacing old parts, managerial problems, bad relations between owner and worker, etc.
(3) Sickness of the mini-steel industry: Storage of key raw materials such as scrap and graphite electrodes and highly inadequate availability of power is the main cause.
(4) Low demand in the International market: Japan produces the best quality steel in the world and India is far behind her. Naturally, Indian steel’s buyers are fewer, only the poor underdeveloped countries.
(5) Capital problem: India doesn’t have plenty of flow capital or finance to construct new Iron and Steel plants or repair and expand the old plants.
Question 6. What raw materials are needed for the cotton textile industry?
Answer:
The raw materials needed for the cotton textile industry are:
The principal raw materials for the cotton textile industry are:
- Raw cotton,
- Chemicals [caustic soda, chlorine, bleaching powder, dyes, etc.],
- Fresh water,
- Power resources [coal, electricity, hydel or thermal, etc.],
- Machineries,
- Moist climate.
Question 7. What is Engineering Industry? What are its divisions?
Answer:
Engineering Industry:
The industry which used iron and steel as its main raw material for the production of different types of machinery and other steel goods is called the engineering industry. It can be divided into two categories:
1. Heavy Engineering: These are those engineering industries that produce large and heavy machines for big industries like generators, tractors, and motor vehicles.
2. Light Engineering: The engineering industries that produce delicate machines or machine parts like cameras, radios, typewriters, watches, electrical fans, etc. are called the light Engineering Industry.
Question 8. Why are there so many petrochemical industries in Gujarat?
Answer:
The reasons behind the development of the petrochemical industry in Gujarat are:
1. Availability of crude oil: Gujarat ranks second in the country in the production of crude oil. The main areas of crude oil are the Cambay region, Ankleshwar region, Ahmedabad region, etc.
2. Demand: There is great demand for the products of the petrochemical industry in India and abroad.
3. Development of transport: Gujarat is well-connected with road and railway networks. Gujarat has 40 ports, of which Kandla is a major one.
4. Development of downstream industries: A number of chemical industries and other industries based on the petrochemical industry have come up, which has led to an increase in demand.
Question 9. Not a single jute mill can be found in this region, Ahmedabad Why?
Answer:
Not a single jute mill can be found in this region, Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad region is providing with all other facilities mainly required for the development of the jute industry except raw materials. Raw jute is not produced as the climatic condition is not all suitable for the production of jute.
Jute raw material for the jute industry can be brought from West Bengal by means of Railways and Roadways but the cost of production will go high. So jute industry is not developed here but the cotton textile industry is developed here because of the availability of raw cotton.
Question 10. State the important raw materials of the Petrochemical industry and their occurrence.
Answer:
1. Natural Gas: It is mainly composed of methane, ethane, propane, butane, pentane, hexane and higher hydrocarbons. Natural Gas is found associated with crude oil or non-associated.
“Class 10 Geography Industries of India WBBSE notes”
2. Gas from Refinery Operations: Some gas is also produced at various stages in the refinery operations mainly from
(1)The Straight Distillation Units and
(2)Thermal and Catalytic Cracking and Reforming processes.
3. Naptha: It is the most potential raw material for petrochemicals. Naptha is obtained from fertilizer. pants. It is used for the production of
(1)Aromatics: benzene, toluene, zylene and
(2)Synthetic Fibres.
Natural Gas is found in Naharkatiya and Roran oil fields in Assam and Ankleshwar, Kalol and Cambay (Khambat) oilfields in Gujarat. Naptha occurs in the fertiliser plants of Trombay, Gorakhpur, Kota, Chennai, Goa, Kochi, Durgapur, Tuticorin, Mangalore and Barauni.
Question 11. What do you mean by pure and impure raw materials?
Answer:
Pure Raw Materials: Pure raw materials are those whose weight does not reduce in the process of production. E.g-100 kg of raw cotton will yield 100 kg of cotton cloth.
Impure Raw materials: Impure raw materials are those whose weight reduces to a great extent in the process of production. E.g-100 kg of iron ore will not yield 100 kg of pure iron. It will depend on the percentage of iron content in the ore.
Question 12. Give an account of the Salem steel plant in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
1. Location: This plant is located in Salem in Tamil Nadu. It was commissioned in 1983.
2. Raw Materials: Salem area is rich in iron ore and has easy access to various raw materials. It gets iron ore from the nearby mines of Karnataka and lignite coal from Neyveli.
3. Power & Water Supply: The plant enjoys the facilities of cheap power, charcoal and a vast market.
4. Products: It produces stainless steel, electrical steel and other special types of steel.
Question 13. What are the advantages of petrochemical products?
Answer:
Advantages of Petrochemical Products: Petrochemicals are cost-effective, economically stable, and cheaper as produced on a mass scale. Its. the raw material is easily available, and not dependent on agricultural raw material as in the case of jute. Therefore, traditionally raw materials like wood, glass and metals are being replaced by petrochemical products. For example:
Natural Material Petrochemical Product
1. Leather footwear Plastic chappals and Synthetic footwear.
2. Natural rubber Synthetic rubber.
3. Jute fibre Synthetic fibre.
4. Steel pipes PVC.
5. Steel utensils Plasticware/containers.
6. Cloth and jute bags Polythene bags.
Class 10 Geography West Bengal Board
Question 14. State some causes of the concentration of cotton textile industry in southern India.
Answer:
In the southern zone, cotton mills are located in Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Karnataka and Goa. The causes for their development are :
1. Cotton is easily available in this region.
2. The moist climate favours spinning and weaving.
3. The ports of Chennai, Kochi, New Mangalore, Murmagaon and Tuticorin provide port facilities.
4. People need light cotton clothing.
5. The other favourable factors are:
(1) Cheap hydro-electric power (of Pykara, Mettur and Papnasam),
(2) Local cheap labour and
(3) Facilities for export.
Class 10 Geography West Bengal Board India – Industries Of India 5 Marks Questions And Answers:
Question 1. Explain the major factors responsible for the development of the Iron and Steel industry in Eastern and Central India.
Answer:
Factors responsible for the development of the Iron and Steel Industry: Most of the iron and steel plants of India, such as Jamshedpur, Burnpur, Durgapur, Rourkela, Bhilai and Bokaro are located in Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha and Chattisgarh. The causes for the concentration of iron and steel plants in eastern India are:
1. Iron ore: About 80% of India’s iron ore is available in this region. The major mines are
(1) Noamundi, Guwa, Budaburu, Pansiraburu of Singhbhum district, Jharkhand,
(2) Gurumahishani, Badampahar, Sulaipat and Bonai of Mayurbhanj district and Bagiyaburu of Keonijhar district, Odisha.
2. Coal: About 97% of India’s coal is mined in this region. The steel plants of Kulti, Burnpur, and Durgapur get their coal from the mines in Raniganj and Asansol. The steel plants of Jamshedpur, Bokaro and Rourkela get their coal from Jharia, Bokaro, Ramgarh and Giridih in Jharkhand.
3. Other raw materials: Limestone, dolomite, manganese, etc. are collected from Kalahandi, Gangapur and Kara put of Odisha. Other raw materials like chromium, tungsten, nickel, etc. are easily collected from the Chotanagpur plateau.
4. Water: The rivers Damodar, Mahanandi, Subarnarekha, etc. supply ample water required in the steel plants.
5. Transport: The network of roadways and railways in eastern India help in trade and commerce. The ports at Kolkata, Haldia and Paradweep help in international trade.
6. Power Supply: Thermal power is acquired from Bokaro and Durgapur thermal power plants. Hydel power is acquired from power projects at Hirakud, Myth, Panchet and Tilaiya.
Question 2. Mention the geographical factors responsible for the growth of iron and steel industry in West Bengal.
Answer:
The geographical factors responsible for the growth of iron and steel industry in West Bengal are:
1. Durgapur Steel Plant and Indian Iron & Steel Company, Kulti-Burnpur are very close to the coking coal mines at Raniganj, Asansol and Jharia.
2. iron-ore is brought from Bonai, Keonjhar, and Sulaipat to the steel plants, which are not very far away from these plants.
3. Ferro-alloys like manganese can be brought from Orissa by means of railway wagons in lieu of sending coal there which is minimising the carrying cost.
4. Availability of clear water and cheap hydel and thermal power from Damodar Valley Corporation.
5. Closeness to the vast market of Kolkata and its surrounding is another factor.
6. Nearest port facility is another factor.
7. Availability of cheap labour is another factor. The state is densely populated, so there is a steady supply of cheap labour.
Question 3. Name the raw materials mainly required for the development of iron and steel industry.
Answer:
Raw materials needed for iron and steel industry are:
1. Iron ore is the most important and basic raw material for the iron and steel industry.
2. Fuels: The important fuels are coal and coke. Modern blast furnaces use coke. Many iron and steel plants even today use charcoal (Bhadrawati).
3. Flux (Limestone & Dolomite): Flux is used in the blast furnace to draw impurities out. Limestone and dolomite are mixed with the extracted impurities to form slag.
4. Refractories: Both blast and steel furnaces are lined with refractories. Refractories are used for lining furnaces for smelting iron ore. It is also used for the lining of the furnaces of locomotives, and boilers and for making fire bricks.
5. Silica or sand is used in the iron and steel plant for moulding. A huge quantity of sand is needed for moulding purposes.
6. Water: Water is an important raw material for the iron and steel industry. It is mainly used for quenching coke, cooling blast furnaces, making steam, cooling furnace doors, operating hydraulic machinery and to have sewage disposal.
7. Air: Air is an important item for the iron and steel industry. Near about 4 tonnes of air are needed to make one tonne of steel.
8. Ferro-Alloys: For the production of steel of different grades, various non-ferrous metals like aluminium, chromium, cobalt, copper, lead, etc. are used. Among the ferroalloys, manganese is widely used in the industry.
9. Electricity: Cheap electricity is required for the iron and steel industry. Hydel, thermal and atomic powers are needed for the production of iron and steel.
Question 4. Why is Ahmedabad called the Manchester of India?
Answer:
Ahmedabad is known as the Manchester of India because it has many similarities with Manchester in the development of the cotton textile Industry. Manchester, situated on the bank of river Marshey behind the port Liverpool, is the largest textile centre in the U.K.
Favourable factors for the development of the textile industry in Manchester:
(1) It imports long-staple cotton from Egypt and other countries.
(2) Temperate climate is suitable for spinning fibre thread.
(3) Coal is obtained from the Pennine range nearby.
(4) Water of the river Marshey is good for dying thread.
(5) Textile machinery is locally manufactured.
(6) The products have a worldwide market.
Like Manchester, Ahmedabad is situated on the bank of river Sabarmati near the Kandla port.
Favourable factors of the development of textile industries in Ahmedabad:
(1) The black soil is suitable for the production of long-staple cotton. It is also imported from foreign countries through the ports of Kandla and Mumbai.
(2) Cotton textile machinery are locally produced and can be easily imported.
(3) The water of Sabarmati is good for dying thread.
(4) The temperate climate is also good for spinning fine thread.
(5) The products have a huge demand inside and outside India.
(6) Cheap labour is obtained from the neighbouring areas.
All these factors have made this centre as the greatest textile centre of India.
Question 5. What are the factors responsible for the concentration of the Iron and Steel industry in eastern and central India?
Answer:
The factors responsible for the concentration of Iron and Steel industry in eastern and central India are as follows:
1. Availability of Iron ore: High-graded iron ores are available in Singbhum district of Jharkhand, Mayurbhanj, Bonai and Sundargarh district of Orissa, and Dhalli-Rajhara of Durg district, Bailadila of Bastar district of Chhattisgarh. It determines the location of Iron and Steel plants in East and Central India.
2. Availability of Coal: Like iron ores, coal is essential for Iron and Steel plants. Jharia coal field of Jnarkand supplies high-quality coal. Coal fields are also located in the East-Central parts of India such as Raniganj, Bokaro, Giridih, Korba, Talcher, etc. It is one of the most important factors causing this concentration.
3. Concentration of the other raw materials: Other raw materials for Iron and Steel plants are manganese, limestone, dolomite, water and others. They are also available in the Eastern-Central parts of the country. It also encourages its development.
4. Port facilities: The ports of Kolkata, Vishakhapatnam, etc. provide port facilities for importing machinery for the industries and exporting finished products.
5. Ready market: The central and western parts of India provide a ready market for the iron and steel produced. The dense population and the industrial belts of the Hooghly Industrial Region, Asansol-Durgapur Industrial Region, and Jamshedpur-Muri Industrial Regions have a high demand for iron and steel.
6. Other factors for the development of this industry are
(1) Availability of water from rivers,
(2) Transport facilities of roadways and network of railways,
(3) availability of cheap industrial labour.
Question 6. Justify the concentration of the cotton textile industry in the black soil region of Western India.
Answer:
The reasons for the concentration of the cotton textile industry are as follows:
1. Raw materials: Lava region is situated near Mumbai. This region is famous for black cotton soil and by rail and road transport cotton is collected at the industrial units. Ahmedabad is situated in the heart of the cotton-growing area of Gujarat.
2. Rail: road transport system is highly developed through Thalghat and Bhorghat (for Mumbai) for the transportation of raw materials as well as finished products.
3. Mumbai has excellent harbour facilities for importing long-staple cotton and machinery for the mills and exporting the finished products.
4. Cheap hydel power is available in Mumbai while the Sabarmati river supplies soft water for dyeing and bleaching, etc.
5. Humid climate is favourable for spinning and weaving in both regions.
6. Bombay & Ahmedabad both are connected by roads and railways with every part of the country.
7. There are good markets both home and foreign for the yarn and fabrics.
8. There is a supply of skilled and unskilled workers in large numbers.
9. Chemical industries are well-developed in Mumbai, Ahmedabad and Pune regions.
“WBBSE Solutions for Geography Class 10 Industries of India MCQs and answers”
Question 7. Analyse the locational advantages of any one Iron and Steel industrial centre of India under the public sector.
Answer:
The steel plant is situated in the district of Burdwan in West Bengal. It was set up in the second five-year plan period with the collaboration of ISCON (a British firm). It started production in 1962.
1. Iron ore is obtained from Singhbhum (Jharkhand) and Keonjhar (Orissa).
2. Coking coal is obtained from Ranigunj, Jharia and Barakar.
3. Manganese from Barbil, Jamdar and Bonai (Orissa).
4. Limestone and Dolomite from Birmitrapur (Orissa) and Hathibari.
5. Situated on the bank of the Damodar river, it gets water from the river of adjoining state.
6. Cheap and skilled labour is available from the agricultural and mining regions of adjoining states.
7. Calcutta, at a distance of (175 km) provides market-cum-port facilities.
8. The centre is situated on the Eastern Railway and National Highway No 2. Hence the transport facility is available.
9. Hydel power from D.V.C. and thermal power from Santhaldih and Bokaro are easily available.
Question 8. Explain why Durgapur, Rourkela and Bhilai have been selected as centres of the iron and steel industry.
Answer:
Durgapur: Durgapur has been selected as a centre of iron and steel manufacturing for the following reasons:
1. The coal mines of Raniganj, Asansol, etc. are close by.
2. Iron ore, limestone & manganese can be brought by empty wagons coming from Bihar and Orissa to carry coal there.
3. Availability of water and power from D.C.
4. Labour is available in plenty.
5. It is connected with the market. and port of Kolkata by rail and road, the distance is only 160 km.
Rourkela: Rourkela is situated on the left bank of the Brahmani river in Orissa. It has been selected as a centre of iron and steel industry for the following reasons:
1. A large supply of iron ore is available within a distance of 50 km in the state of Orissa.
2. The coal belt of Bihar and West Bengal are close by. The wagons which carry iron ore from Orissa to Burnpur and Durgapur return to Rourkela with coking coal from Jharia.
3. Cheap labour is available.
4. It is connected by railways with important ports like Kolkata, Madras, Visakhapatnam and Paradeep.
Bhilai: Bhilai is situated in Chhattisgarh. It has been selected as an iron and steel manufacturing centre for the following reasons:
1. Iron ore is available from the Dalli-Rajhara mines (32 km) in Madhya Pradesh.
2. Cialis are available here at Korba and more can be easily brought from the state of Bihar also.
3. Cheap labour is available.
4. Manganese and limestone are available in large quantities.
5. It is connected with important cities of central India and also Kolkata and Mumbai by railways.
Question 9. What are the prospects of the Indian Iron and Steel Industry?
Answer:
The prospects of the Indian Iron and Steel Industry
India possesses a large potential for the development of the Iron and Steel Industry. India enjoys a substantial comparative cost advantage even with respect to the steel industries of advanced countries like Japan and Germany.
1. Basic raw materials like iron ore, coal (coke), limestone, dolomite, manganese ore and other ferroalloys, and refractory materials are available in India. India has a large human resource of scientists and engineers. Labour cost is also one of the lowest in the world.
2. The industry has acquired a high degree of technological self-reliance. Considerable expertise in planning, detailed engineering, machine-making, etc. has been built up in institutions like the Metallurgical and Engineering Consultants (India) Limited (MECON). A research and development unit has been set up under SAIL. These measures will help the steel industry to reduce production. cost and improve the quality of production in near future.
3. Industrialisation programmes in the second and subsequent plans and the consequent industrial revolution through the growth of capital goods industry, capital consumer goods industry and consumer goods industry have created a ready domestic
the market for iron and steel.
4. The strength of the Indian steel industry is to be judged by its export success which is already commendable.
5. The functional autonomy granted to SAIL is a good move for achieving a high degree of capacity utilisation in all plants in the public sector. In TISCO, technological updating has been taken up as a continuous process which is really the secret of Tata Steel’s remarkable success.
6. Today electrical furnace units and the mini steel plants, as they are called, are providing 30% of the total steel supply. There are 169 mini-steel plants already in operation.
7. Certain measures like the privatisation of industries have been taken to improve the operational efficiency of the steel plants.
Question 10. Give an account of the growth and development of the Cotton Textile Industry in India.
Answer:
Growth of Cotton Textile Industry in India: The foundation of modern industry in India was laid with the development of the cotton textile industry in the second half of the 19th century. Even today the cotton textile industry is the backbone of our economy. About 9.5 lakh workers or about 2.6 per cent of industrial labour in India is engaged in the cotton textile industry. It is the main foreign exchange earning industry. It also supports a number of other industries – dyes, chemicals, mills, stores, packing material and the handloom industry.
The growth of the Indian cotton industry took place in two stages. In the first stage, mills were largely concentrated in Bombay and in the nearby areas. A Parsee industrialist started the cotton factory at Bombay in 1851. From that time up to the First World War (1914), the cotton textile industry rapidly developed around Bombay.
The main factor for the development of the industry was located around a natural port. This helped to export the yarn to the huge markets of China and Japan, and also import machinery and coal from Britain and South Africa. The nearby cotton growing areas supplied the raw material. Progress was so rapid that in about 50 years’ time about 80 cotton mills were located in Bombay and in its nearby areas. In the second stage of growth of the textile industry, factories were located interior of the country and away from the cotton growing areas. This was because:
(1) At the beginning of this century, Japan also developed her industry very rapidly. She started competing with India. India not only lost her market in China and Japan, but Japanese goods started flooding the Indian market. To capture the local market, therefore, _ industry shifted to the interior, especially in the northern and eastern parts of the country.
(2) Development of railways also helped the industry to shift to the interior, especially near the cotton growing areas. Ahmedabad, Nagpur, Baroda, Sholapur, and Broach developed the industry.
(3) Development of hydro-electricity in South India, Punjab and western parts of Uttar Pradesh also helped in the rapid development of
the industry.
(4) High labour wages, more taxes, high-cost maintenance around Bombay also forced the industry to move towards different areas where cheap labour, low rent of land, power and coal, etc. offered many facilities for industry
(5) During the Second World War there was a considerable rise in military demand
(6) Also the impact of the Swadeshi movement had also a stimulating effect on the development of the textile industry in the country.
By the end of 1974, there were 691 mills (403 spinning and 288 composites) spread in different parts of the country in about 75 towns. However, more than 374 of the mills are distributed in four zones
(1) The Western zone,
(2) The Southern zone,
(3) The Eastern zone and
(4) The Northern Zone.
India’s cotton Textile Production
| Year | Production | Year | Production |
| 1951 | 4210 | 1971 | 7602 |
| 1961 | 6738 | 1981 | 8368 |
Question 11. Describe the cotton textile mills of the Eastern Zone and the Northern Zone in India.
Answer:
The Eastern Zone: The industry is mostly developed in the Hooghly basin. Demand for cotton cloth is the main factor for the development of the industry. Cotton is mostly imported from Egypt and Sudan. Coal is available from Raniganj.
Calcutta is already an industrial and very densely populated city. Skilled and cheap labour is, therefore, easily available. A network of excellent roads, railways and many rivers connects the industry with the nearby towns, villages and cities which provide a ready market. The cotton industry here specialises in the production of coarse, grey and bleached cloth.
The Northern Zone: Some factories are also developed at various places in Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana and Delhi. Important centres here are Kanpur (17 mills), Lucknow, Agra, Aligarh, Bareilly, Meerut, Ludhiana and Amritsar. The dense population also provides necessary markets and cheap labour and irrigated areas in Uttar Pradesh and Punjab provide cotton. Local, as well as imported cotton, is used.
Kanpur with 17 mills is the main cotton textile centre in the north. It is located on the bank of the river Ganges which provides water for washing, bleaching and dyeing. The cotton is available from nearby irrigated areas. Imported cotton is also used. Coal comes from the nearby state of Bihar (Jharia coal fields). Kanpur specialises in khaki cloth and cloth for tents.
“Industries of India WBBSE Class 10 question answers PDF”
Question 12. Explain the pattern of distribution of engineering industries in India.
Answer:
The pattern of Distribution of Engineering Industries in India: The growth of the engineering industry in India is noted mostly after independence. This industry is developed mainly to change the basis of the economy from agriculture to industry and also to be free from importing machinery from outside.
Various factories are set up to design, build and fabricate a wide variety of machines and equipment from light to heavy engineering goods. India at present manufactures industrial, electrical and agricultural equipment. The various factories are controlled by both private and public sectors.
On the whole, the location of engineering industries is influenced by various factors- power, skilled labour – fitters, turners, engineers, etc. and entrepreneurship rather than raw materials. The industry. gains considerably from agglomeration economies and hence various units-+;e clustered near one another. More concentration of factories and foundries noticed in the iron and steel industry near coal mines and hydel-power sites and big urban centres where skilled hours ud other factors are available.
The main public sector units, however, give the idea of the foot-loose nature of the industry. To bring about balanced growth of industrial units in various areas is the main concern of public engineering units. Heavy Engineering factories are located at Ranchi, Naini (Allahabad), Tungabhadra (Karnataka) and Visakhapatnam. Thus various plants manufacture complex steel structures: building structures, power-transmission towers, pressure vessels, cranes, ropeways, and equipment for petrochemicals, heavy chemicals and allied industries.
Light Mechanical industries are located near the main industrial centres of India-Hooghly basin, Bombay-Pune region, Delhi-Gaziabad region, Bangalore – Hyderabad region, Vadodra, etc. Various items like bicycles, ball and roller bearings, alarm timepieces, agricultural implements, tractors, etc. are manufactured here.
Heavy electrical industry centres are located at Bhopal [Heavy Electrical (India) Ltd.], Haridwar [Heavy Electrical Equipment Plant], Tiruchirapalli (Heavy Power Equipment Plant), Rama Chandrapuram (Hyderabad), Rupnarayanpur in West Bengal. The above units manufacture large AC and DC motors and Switchgear, generators, Power transformers, water and steam turbines and power cables (Rupnarayanpur).
The various precision instruments, survey instruments Factory, Calcutta, Ophthalmic blanks and lenses are made at the Ophthalmic Glass project at Durgapur. X-ray and electro-medical instruments are manufactured at Bharat Electronics Ltd., Jallhalli (Bangalore). Production of scientific surveying, optical and mathematical instruments went up from Rs. 2.3 crores in 1971 to Rs. 3.3 crores in 1974.
Progress made by the engineering industry is remarkable. Thus the output of light and medium industries increased from Rs. 50 crores in 1950-51 to Rs. 3600 crores is 1974-75. Export of engineering goods in 1974-75 touched an all-time record of Rs. 312 crores as against only 6 crores in 1950-51. The very important and encouraging feature of our exports is that various engineering goods are not only in demand in the developing countries but there is noticed a very rapid increase in demand even in the most developed countries like the U.K., France, U.S.And Germany.
Question 13. Why is Durgapur called the Ruhr of India?
Answer:
Durgapur is called the Ruhr of India because of the following reasons: The plant is situated on the bank of the river Damodar 15 km away from the Kolkata Delhi Railway route.
It gets raw materials:
1. iron ore is obtained from the Bonani mines of Orissa.
2. Coal from Jharia and Barakar fields.
3. Limestone is obtained from Birmitrapur and Hathibari areas.
4. Water is obtained from the Damodar river.
5. Manganese from Jamdar of Bonai.
6. Electricity from DV.C., Santalidh, Bokaro thermal and hydel power stations.
7. Kolkata port is only 175 km away from this region which can be easily reached by national highway and railways—South-eastern and Eastern.
8. Cheap and skilled labour is obtained from the densely populated mining and agriculture belt.
9. Wide market of West Bengal and its adjoining states.
10. Well-developed transport and communication by means of roadways, railways and waterways. All these factors have favoured the growth of an iron and steel centre in al Durgapur, along with other allied industries. Durgapur Iron and Steel Centre has a similarity with the Ruhr region of West Romanies.
Ruth valley is also developed in the field of iron and steel and allied industries. Coal from the neighbouring region, iron-ore from Sweden, water from the “er Ruhr, a well-suited climate for hard-working, labour’s wide market, Rhine-Ruhr Waterway along with roadways and railways, wide market inside and outside the Country. Humberg port facility labourers, etc. have favoured the growth of iron and Steel industries along with other allied industries. As it has a similarity with Durgapur Gf India, Durgapur is called the Ruhr of India.
Question 14. Give a short account of the Bhadrabati Steel plant.
Answer:
Bhadrabati Steel Plant: The Steel Plant at Bhadrabati has changed its name from Mysore Iron and Steel Company (MISC) to Visweshwarya Iron and Steel Limited (VISL). It is situated on the Bhadra river in Karnataka. It derives:
1. Iron ore supply from Kemangunidi mines on the Bababudan hills to the south.
2. Charcoal (as coal is not available nearby) from the Shimoga Kadur forests to the east.
3. Cheap and abundant hydel power from Jog Falls to the northwest.
4. Plenty of water from the Bhadra reservoir to the southwest.
5. Manganese from Shimoga and Chitradurga districts and Limestone from Bhandigunda district to the northwest.
With the depletion of forests, the plant no longer depends on Charcoal. Instead, it brings coking coal from Korba and uses cheap hydel power to produce special types of high-value steel.
Question 15. What are the raw materials needed for the iron and steel industry? What are the geographical factors responsible for the growth of this industry in West Bengal Where is the biggest iron and steel factory in India located?
Answer: The chief raw materials for manufacturing pig blast furnaces are iron ore, coke and limestone. A modern blast furnace requires more than 1 lakh ft. of air to produce only 1 ton of iron. Steel is made by reheating pig iron in converters to remove the impurities and adding carbon and various ferro-alloys such as manganese, vanadium, chromium, cobalt, nickel, tungsten, etc.
The geographical factors responsible for the growth of the iron and steel industry in West Bengal are:
1. The plants of Durgapur, Burnpur, and Kulti are very close to the coking coal mines at Raniganj, Asansol and Jharia.
2. Iron ore, limestone, manganese and other ferro-alloys can be brought very cheaply by railway wagons coming from Bihar and Orissa to carry coal there, which otherwise would have returned empty.
3. Availability of plenty of water and power of D.V.C.
4. Closeness (about 160 km) to the vast market of Kolkata and to the port.
5. Availability of cheap labour.
The biggest iron and steel factory of India is being set up at Bokaro, Bihar.
Question 16. What are the problems faced by the cotton textile industries in India?
Answer:
The cotton textile industry suffers from the following problems:
1. Shortage of Raw Material: There is a shortage of raw material, particularly of long-staple cotton, which is imported from Pakistan, Kenya, Uganda, Sudan, Egypt, the USA and Peru.
2. Sick Industrial Units: The cotton industry faces the constant threat of sickness and consequent closure, because of
(1) Uncertainty of raw material.
(2) low productivity of machines and labour.
(3) Increasing competition from the power loom sector.
(4) Lack of modernisation and
(5) management problems. These sick units require heavy financial investments for replacement and modernisation purposes. Many of these
sick units have been taken over by the government.
3. Loss of Foreign Markets: The Indian cotton textile industry has lost some of the foreign markets due to production and the development of the cotton textile industry a number of Asian countries like China and Japan and African countries. The Indian cotton textile goods face stiff competition in foreign markets from Taiwan, South Korea and Japan whose goods are cheaper and better in quality. i
4. Inadequate Production: The cotton textile industry faces inadequate production because of the lack of adequate and unfailing power supply and also because of competition with the decentralised sector. Thus she has to face stiff competition! On from other Asian countries.
5. Shortage of Power: The cotton textile mills are facing an acute shortage of power. Supplies of coal are difficult to obtain and frequent cuts in electricity and load-shedding affect the industry badly. This leads to loss of man hours, low production and loss in the mills.
6. Obsolete Machinery: In India, most of the cotton textile mills are working with old and obsolete machinery. According to an estimate, in India over 60 per cent of the spindles are more than 30 years old. The automatic looms account for only 18 per cent of the total number of looms in the country against the world average of 62 per cent and 100 per cent in the United States. Obsolete machinery results in low output and poor quality of goods as a result of which Indian textile goods are not able to face competition in the international market.
Question 17. Give an account of the major IT sector in India.
Answer: India is the world’s largest outsourcing destination for the IT industry. The industry employs about 10 million Indians and contributes significantly to the social and economic transformation in the country. It energises the higher education sector, especially in engineering and computer science. The Indian IT industry is divided into four major segments
1. IT services,
2. Business process management,
3. Software products and engineering services,
4. Hardware. Indian IT’s core competencies and strengths have placed it on the international canvas, attracting investments from major countries.
E.g: The software and hardware industry attracted $ 13,788.56 million between April 2000 and December 2014. The main centres of IT in India are — Bangalore, Hyderabad, Chennai, Kolkata, Mumbai, Delhi, etc. Bangalore and its surrounding region is known as silicon valley due to the presence of numerous IT centres.
Question 18. State the factors for the growth of IT sector in India.
Answer:
Factors for the Growth of It sector in India: This industry has flourished in India because of certain factors:
1. The Government of India has started the ‘Digital India’ project which has given IT a secured position inside and outside India.
2. The IT sector in India is generating 2.5 million direct employment. So, India has become one of the biggest IT capitals of the modern world.
3. Bengaluru is considered to be the Silicon Valley of India because it is the leading IT exporter. Exports dominate the industry and constitute about 77% of total industry revenue.
4. India provides a large domestic market for this industry.
5. The top 5 Indian IT Service Providers are Tata Consultancy Services, Infosys, Cognizant, Wipro and HCL Technologies.
6. The Software Technology Parks of India (STPI) is owned by the government. These parks in different cities provide satellite links to be used by firms.
7. The government also allowed individual companies to have their own dedicated links which allowed work done in India to be transmitted abroad directly.
8. A number of cities in India are developing IT infrastructure and are taking part in software exports.
9. Indian Institute of Information Technology is set up to create a pool of technically literate individuals for its growing industry.
10. High concentration of IT companies and quality research and development institutions throughout India also contribute to its growth.
Question 19. Give an account of Union Carbide India Ltd.
Answer:
Union Carbide India Ltd. (UCIL): This petrochemical plant was founded at Trombay (near Mumbai) in Maharashtra under the organisation of a multinational company. UCIL has a capacity of 60,000 tonnes of Naptha crackers.
Petrochemical Products: Under full capacity, UCIL can produce 11,000 tonnes of products—Polythelene, Butyl alcohol, Acetic acid, Ethyl acetate, Ethyl hexanal and Dioctyl phthalate.
Some Important End-Products of UCIL:
1. Films for Packaging,
2. Bags as hold-all,
3. Squeeze Bottles of various sizes and shapes,
4. Carboys for industrial chemicals and other industrial containers,
5. Insulation for electric wires and cables,
6. Pipes for carrying drinking water,
7. Tarpaulins,
8. Godown covers,
9. Films,
10. Canal lining,
11. PVC, etc.
Facilities for Plant Location of UCIL:
1. Raw materials are easily available from the local oil refineries at Trombay and Mumbai (erstwhile Bombay)
2. Products are quickly ported from the plant through Pipelines, Roadways and Railways.
3. Huge financing from multinational companies has enhanced the introduction of Modern Technology in the plant complex of UCIL;
4. Heavy demand of petrochemical products in the industrial units of the Mumbai-Pune Industrial Belt.
5. Hydel power supply from the projects of the Western Ghat region.
Question 20. Give an account of Haldia Petrochemicals Ltd.
Answer:
Haldia Petrochemicals Limited (HPL): HPL is a Joint Venture, promoted by West Bengal Industrial Development Corporation (WBIDC), Chatterjee Petrochem (Mauritius) Company of Chatterjee Group and ‘Tatas’ represented by TELCO and Tata Electric Companies. The groundbreaking, to commence construction of the Units under the HPL complex, took place in April 1997. This project of worth Rs. 5170 crores was inaugurated on 2 April, 2000.
The Rs. 1,6000 crores Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation promoted the purified terephthalic acid (PTA) project in Haldia was inaugurated on 11 April 2000, nine days after the commissioning of HPL. The locational advantages in and around Haldia are immense at the present time.
1. Haldia Dock Complex will be of unique help for the rapid progress in HPL performance.
2. HPL is situated within the Haldia Industrial Belt.
3. This Industrial town is devoid of infrastructural hazards.
4. The refinery at Haldia will always be assisting with necessary raw materials in abundance to its in-door petrochemical complex.
5. Transport network through railways, roadways, inland waterways and offshore sea routes is now well-knit with the HPL’s industrial point.
6. Power for this will be an uninterrupted energiser for HPL.
“Class 10 WBBSE Geography Industries of India important questions”
Question 21. Discuss the automobile industry in India and the reasons for its growth.
Answer:
Automobile Industry: Before independence, there was, in fact, no automobile industry in India; only assembly works were done from imported parts. The real beginning started with the establishment of Premier Automobiles Ltd. at Kurla (Mumbai) in 1947 and Hindustan Motors Ltd. at Uttarpara (Kolkata) in 1948.
Today, the automobile industry is a rapidly growing industry in India. Mumbai, Chennai, Jamshedpur, Jabalpur and Kolkata are the major centres for producing automobiles. All sorts of vehicles are produced in these centres. Maruti Udyog Ltd. (MUL) of Gurgaon in Haryana started the production of passenger cars in 1983.
It manufactures about 77 per cent of such vehicles are produced in India. Various types of automobiles, scooters, jeeps and vehicles are also manufactured at several places in the country, such as, Lucknow, Pune, Mumbai, Kanpur, Ennore, Chennai, Faridabad, Hyderabad, Kolhapur, Tirupati, New Delhi and Alwar (Rajasthan).
The causes of the development of this industry are as follows:
1. Steel is the basic raw material for this industry ancillary industries have developed near places producing tyres, tubes, storage batteries, etc.
2. Port cities like Mumbai, Chennai, etc. offer import and export of finished goods.
3. The industry in recent years has become market-oriented.
4. Capital investment in large amounts is easily obtained from Metropolitan cities like Mumbai, Chennai, Delhi and Kolkata.
Question 22. Give an account of the petrochemical industry in India.
Answer:
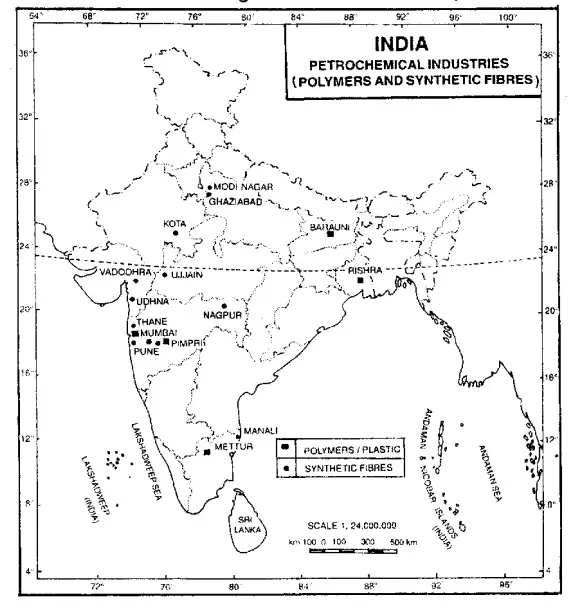
Petrochemical Industry: Petrochemicals are essentially chemicals and compounds derived from petroleum resources. These chemicals are used in the manufacture of a wide variety of articles, such as synthetic fibres, plastic, ferrous and non-ferrous metals, synthetic rubber, dye-stuffs, insecticides, drugs and pharmaceuticals and synthetic detergents.
The products from the petrochemical industry have entered every aspect of human activity. In India, the petrochemical industry is of recent growth The demand for products from the petrochemical industry has been rising rapidly in the country. The industry, therefore, has to expand its capacity to meet the growing demand. The important raw materials necessary for the petrochemical industry are Naptha, natural gas and refinery gas.
The first petrochemical complex was established by Union Carbide India Ltd. at Trombay in 1966. National Organic Chemical Industries Ltd. was set up in 1968 at Thane. The Index Plant at Kayali Refinery for the production of benzene and toluene was commissioned in 1969. IPCL’s mega petrochemical complex at Vadodara (largest government petrochemical industry in India) was commissioned in 1973 and the
Olefin complex was ae in IPCL has an up = Olefin complex at Nagothane in Maharashtra. The third such complex has been set up at Gandhar in
Gujarat. Jamnagar of Gujarat is the largest private petrochemical industry. Petrofils Corporation Ltd. (PCL) is a joint sector company of the Govt. of India and Weavers’ Co-operative Societies.
“WBBSE Geography and Environment Industries of India solutions PDF”
It manufactures polyester filament yarn and nylon filament yarn at its three units located at Vadodara and Naldhari in Gujarat. The Bongaigaon Petrochemicals Ltd. is set up at Bongaigaon as an adjunct to the Bongaigaon refinery. This complex manufactures polyester fibre and ortho-xylene.
There has been a steady increase in the consumption of major petrochemical products in India in recent years. To meet the growing demand, the Government has sanctioned several petrochemical complexes in the public and private sectors. As a result, petrochemical projects are being implemented at Hazira, Jamnagar and Bharuch in Gujarat, Chennai in Tamil Nadu, Mangalore in Karnataka, Vishakhapatnam in Andhra Pradesh, Haldia in West Bengal and Auraiya in Uttar Pradesh.
In 2000-2001, India produced 3441 thousand tonnes of polymers, 1,567 thousand tonnes of synthetic fibres, 55,000 tonnes of synthetic rubber and 359 thousand tonnes of synthetic detergents. The petrochemical industry now contributes 14% of the production of the entire manufacturing sector and its share in export is also 14%.
Question 23. Explain the distribution of cotton textile industries in India.
Answer:
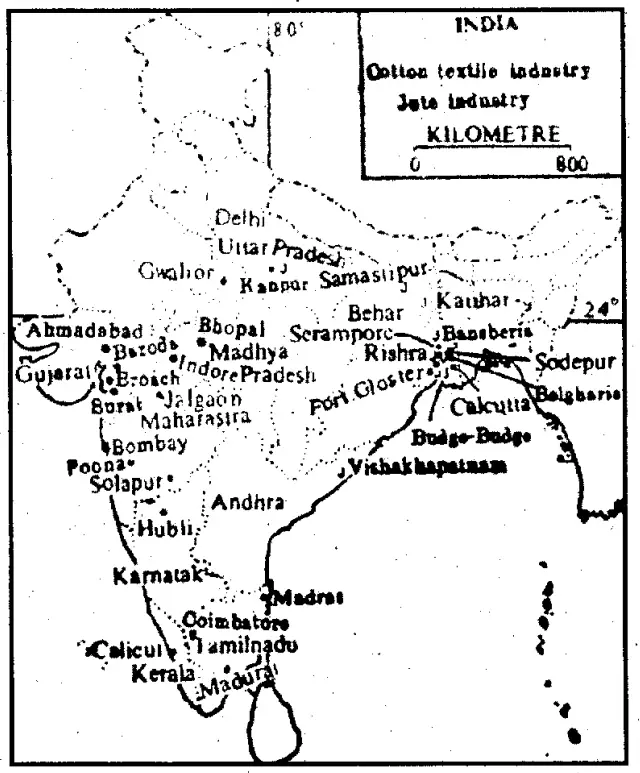
Distribution of Cotton Textile Industries in India: Indian monopoly in the manufacturing of cotton textiles is very old. The first modern cotton mill was set up at Ghushuri (Fort Glaster) near Kolkata. But that mill stopped functioning within a short period for want of raw cotton supply. The first successful modern cotton textile mill was established in Mumbai in 1854.
Today cotton textile is the largest industry of India. It gives employment to over 15% of all factory labour. It supports a large number of industries like chemicals, packaging materials and engineering works. Textile exports account for over 1/10th of the total value of export from the country. The cotton textile industry in India is divided into two sectors — the mill sector and the decentralised sector (power loom and handloom). Today 93% of the cotton cloth is produced in the decentralised sector.
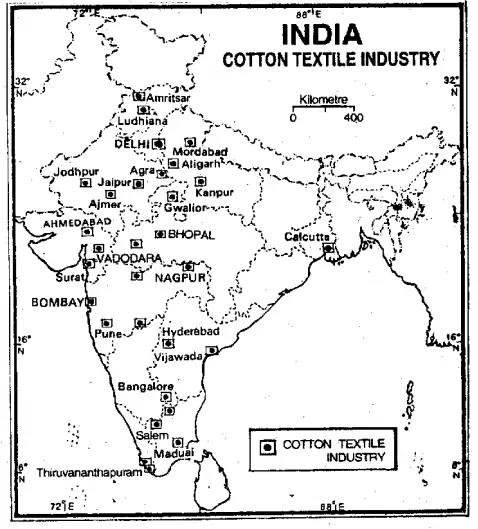
In the early years of the cotton textile industry, most of the mills were located in Maharashtra and Gujarat. Availability of raw cotton, market, humid climate, cheap labour and transport facilities in these areas contributed towards its localisation. Today, the cotton textile mills are spread over 80 towns and cities of India, but most of them are concentrated in Maharashtra, Gujarat, West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
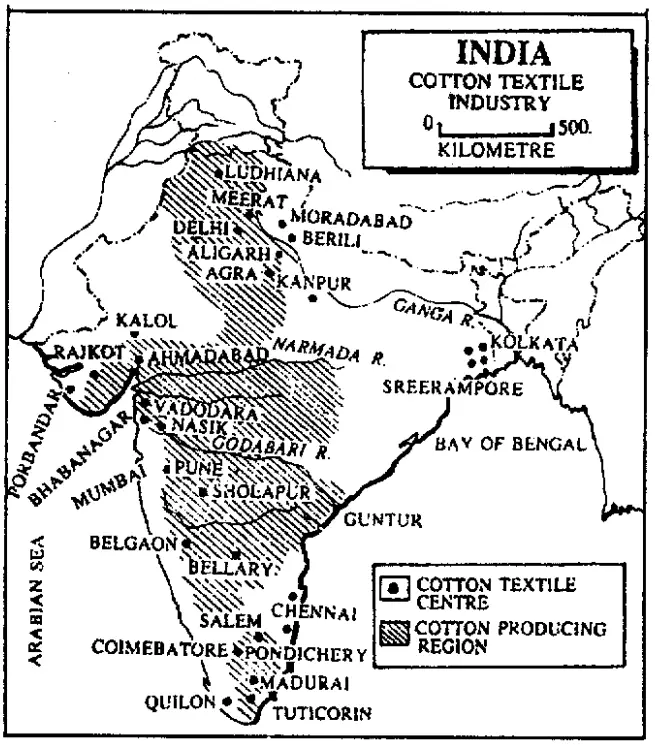
Maharashtra is the largest producer of cotton textiles. Mumbai is the largest centre with 63 mills out of Maharashtra’s total of 122 mills. Mumbai is called the cotton polos of India. Other important centres of Maharashtra are Solapur, Pune, Kolhapur, Satara, Wardha, Nagpur, Aurangabad, Amravati and Jalgaon.
Gujarat has 125 cotton mills. Ahmedabad is the largest centre where 73 out of 118 mills of Gujarat are located. The city is called the Manchester of India. Other important centres of a cotton mills in this state are Vadodara, Surat, Rajkot, Porbandar, Maurvi, Bhavnagar, etc.
In Madhya Pradesh cotton is grown and coal provides the necessary energy. Abundant cheap labour is available. Gwalior, Ujjain, Indore, Jabalpur, Bhopal, etc. are important centres. Among the southern states Tamil Nadu is the most important cotton textile producer. Coimbatore is the most important centre and is known as the Manchester of South India. Other important centres are Chennai, Madurai, Tirunelveli, Salem, Perambur, Tuticorin, etc. Other important centres of a cotton mill in the southern zone are Bangalore, Hubli, and Mysore in Karnataka, Thiruvananthapuram, Alleppey and Trichur in Kerala, Hyderabad, Vijaywada, Guntur in Andhra Pradesh, Pondicherry and Goa.
In the Eastern zone, some cotton mills are found in West Bengal, Jharkhand, Orissa and Bihar. In the Northern zone, some cotton mills are developed in Uttar Pradesh (Kanpur, Lucknow, Aligarh, Agra, Bareilly, Meerut), Punjab (Amritsar Ludhiana, Phagwara), Haryana (Bhiwani, Hissar, Rohtak), Rajasthan (Pali, Bhilwara, Udaipur, Jaipur, Ajmer) and Delhi.
Class 10 Geography West Bengal Board
Question 24. Describe the factors that influence the location of industries.
Answer:
Industries concentrate in certain areas which become centres of industrial activity.
The infrastructure of an industry depends on the following:
Geographical factors: These include raw materials, power supply, water, transport, labour, market, site and climate.
Commercial factors: These include capital, bank and credit facilities, Government policies and organisational efficiency.
Geographical Factors:
1. Raw Materials: The decision regarding the location of a particular industrial activity is guided by the availability of raw materials in a particular area. The earliest industries in India developed near the sources of raw material. For example, the textile mills of Mumbai received the supply of cotton from Gujarat and the jute mills of the Hooghly region got raw material from the deltaic region of the Ganga. Similarly, the iron and steel industry is located in the region where iron ore, limestone, manganese and coal are available.
The availability of raw materials nearby reduces the cost of transportation. The nature of raw materials also decides the location of industries. For example, perishable raw materials have to be processed without loss of time before manufacturing. That is why sugar mills are located in areas of sugarcane production.
2. Water Supply: Water is required for the development of industries as it is needed in the process of manufacturing, cleaning, cooling, washing, etc. All industries depend heavily on the availability of water for one purpose or the other. These include iron and steel (for cooling), textiles (for bleaching and washing), paper and pulp, chemicals, food processing, jute, leather, nuclear power, etc. Therefore, these industrial units are located at places where water is easily available.
3. Energy: Energy is required to process raw materials into manufactured goods. That is why the iron and steel industry is usually located near the coal resources, as it uses coking coal for fuel. Similarly, the electro-metallurgical and electro-chemical industries which require power are located where electricity is easily available. In the coal-deficient peninsular region, industries could develop by using hydel power instead of thermal power. Thus, the availability of energy in one form or the other is an important factor in deciding the location of a particular industry.
4. Transport: Transport is an essential pre-requisite for industrial development as transport facilities are required to carry raw materials to manufacturing units and finished products to the market. The availability of transport facilities has led to the development of industries near the port towns that are linked with rail and road to the hinterland.
5. Labour: The availability of both skilled and unskilled manpower is an important factor in the location of industries. The mobility of labour is also a significant factor. It is because of the mobility of cheap labour from the surrounding areas to Delhi and Mumbai, that a large number of industries are located in these metropolitan cities. Some of the small-scale industries, traditionally associated with labour are glasswork (Ferozabad), brasswork (Moradabad), utensils (Yamunanagar in Haryana), silk sarees (Varanasi), carpets (Mirzapur), etc.
6. Market: The existence of a market is the ultimate requirement of every industry because whatever is produced needs to be sold. High demand and satisfactory purchasing power provide impetus to industrial development. For example, heavy: chemical industries or machine industries are located in industrial areas because their products are required by other industries of the region. Similarly, petroleum refineries are established near markets as the transport of crude oil is easier. However, refineries using imported crude oil are located near ports.
School Geography Class 10 WBBSE
7. Climate: It plays a significant factor in the location of industries, especially agro-based industries. For instance, the cotton textile industry is located in Maharashtra which has a favourable climate and soil for the growth of cotton. An extreme type of climate, i.e., either located at Jamshedpur in Jharkhand. It was set up in 1951 and it started production of steam locomotives in 1951. Since 1970 the production of steam locomotives has been stopped.
Bharat Heavy Electricals Ltd (BHEL) has developed capabilities to manufacture electric locomotives for the Indian railways. Diesel Component works has been set up by the Indian Railways at Patiala for manufacturing and repairing of diesel loco components.
Question 25. State the factors favourable for the development of TISCO.
Answer: Tata Iron and Steel Company (TISCO) is one of the largest manufacturing plants in Asia. It is situated at Sakshi (now called Jamshedpur). It is the oldest steel plant in the country. The following factors were responsible for the plant being located at Jamshedpur:
1. Location: The TISCO plant is situated at Jamshedpur about 240 km northwest of Kolkata on the Kolkata-Nagpur rail line in the Singhbhum district. Jamshedpur is most ideally located with respect to iron ore, fuel and flux supplies which are obtained from within 175 km of it. Rivers Kharkai and Subarnarekha supply water.
2. Availability of Raw Materials: The plant obtains its requirements of iron ore from the Gurumahisani mines in the Mayurbhanj district of Orissa and from the Noamundi mines in the Singhbhum district of Jharkhand. These ore deposits are rich, containing over 60 per centurion in the ore. It receives manganese from Joda in the Keonjhar district, and limestone, dolomite and fire clay from the Sundergarh district of Orissa. Coal is obtained from the Jharia and Bokaro coal fields.
3. Power Supply: Coal is the main source of power for this plant. The supply of coal comes from Jharia and Bokaro coal fields located at a distance of about 177 km.
4. Water Supply: The two rivers Kharkai and Subarnarekha, which never run dry throughout the year, supply a continuous stream of water for cooling purposes.
5. Labour Force: The labour force for the plant is recruited from the densely populated valley of Ganga, mostly from the States of Bihar, West Bengal, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and Uttar Pradesh.
6. Market: The plant is located at a distance of 240 km from Kolkata which is not only an important market for the consumption of iron and steel goods but also has facilities for the export of finished goods.
School Geography Class 10 WBBSE
7. Transport Facilities: Jamshedpur is well-connected with roads and railways to the other parts of the country. The movement of raw materials and finished products is facilitated by the Eastern Railways. It is also connected with the Kolkata port for exporting of finished steel.
Question 26. Give an account of the Bokaro Steel plant.
Answer:
Bokaro Steel Plant: Bokaro steel plant was established in collaboration with the erstwhile USSR in 1964 (production started in 1972).
1. Location: The plant is located in the coal-rich and densely populated region of the Damodar valley near the confluence of the Bokaro and the Damodar rivers in the Hazaribagh district of Jharkhand.
2. Raw Materials: The plant obtains coal from Bokaro and Jharia coal fields; iron ore from the Kiriburu mines in Keonjhar district (Orissa); limestone from Bhabantpur and dolomite from Palamau (Jharkhand).
3. Power Supply: Power is supplied by Damodar Valley Corporation (DVC).
4. Water Supply: Water is obtained from a reservoir across the river Damodar.
Products: The plant has hot and cold rolling mills as its chief production units. They produce pig iron, crude steel and saleable steel. Its sludge and slag are used in making fertilizers at Sindhri.
Question 27. What are the reasons for the growth of the Durgapur Steel plant? State its major products.
Answer:
Reasons for the growth of the Durgapur Steel plant
Durgapur Steel Plant: This plant was set up during the Second Plan period at Durgapur in West Bengal with financial and technical assistance from the UK.
1. Location: It is situated along the Damodar river in the Burdwan district of West Bengal, about 160 km northwest of Kolkata on the Kolkata-Asansol rail line.
2. Raw Materials: The plant obtains iron ore from Singbhum (Jharkhand) and Keonjhar (Orissa). It gets coal from Jharia (Jharkhand) and Raniganj (W.B.); manganese from Keonjhar (Orissa) and limestone from Sundargarh district (Orissa).
3. Power Supply: Coal for the plant is obtained from the Jharia coal fields. Damodar Valley Corporation (DVC) has set up a 1,50,000 KW thermal station which supplies power to the plant. Besides this, 15,000 KW of power is generated within the plant.
4. Water Supply: Water is supplied from the Damodar river through a channel.
5. Transport Facilities: This plant is located on the Kolkata-Delhi rail line. In this way, it is connected with the major markets. It is also connected to the Kolkata port and, through a navigation canal, to the Hoogly River.
6. Labour Force: The labour force for the plant is recruited from Orissa, Bihar and Jharkhand.
Products: The plant specialises in the manufacture of alloy steel and railway items like wheels, axles and sleepers, ‘etc. It produces by-products like crude coal tar, ammonium sulphate, crude benzol, etc.
Question 28. Discuss the factors responsible for the growth of the Bhilai Iron & Steel plant.
Answer:
Bhilai Steel Plant was established in collaboration with the (then) USSR Government at Bhilai in 1953.
1. Location: It is located 720 km west of Kolkata in the Durg district of Chhattisgarh.
2. Availability of Raw Materials: The plant gets its raw material from the following sources: Large iron ore deposits are supplied from Dhali Rajhara mines, about 80 km away from the plant. Limestone is drawn from the quarries developed in Nandini, 19 km from Bhilai. Manganese is obtained from the neighbouring district of Balaghat.
School Geography Class 10 WBBSE
3. Power Supply: Coal is obtained from Bokaro, Kargati and Jharia fields in Jharkhand and Korba in Chhattisgarh. The main source of power is the thermal power station at Korba.
4. Water Supply: The plant gets water from a system of reservoirs at Tendula.
5. Transport Facility: The Bhilai Steel Plant lies on the Mumbai-Nagpur-Kolkata rail line which links the plant to the major markets.
6. Labour Force: The labour for the plant is recruited from the nearby states of Bihar, Jharkhand and Madhya Pradesh.
Question 29. Discuss the factors responsible for the growth of IISCO.
Answer:
Factors responsible for the growth of IISCO
It was established in 1981 at Burnpur in West Bengal. It had three separate plants, one at Hirapur, another at Kulti and the third at Burnpur. All these have been integrated into one unit. The management of IISCO was taken over by the Government of India in July 1972.
1. Location: The Lisco plants are situated at Bunpur, Hirapur and Kulti near Asansol about 227 km northwest of Kolkata.
2. Raw Materials: Iron ore is obtained from Singbhum (Jharkhand) and Mayurbhanj (Orissa), limestone from Sundergarh, and manganese from Jharkhand.
3. Power Supply: The supply of coal is obtained from the Jharia coalfield. Cheap hydroelectricity is provided by Damodar Valley Corporation.
4. Water Supply: Water is obtained from large reservoirs within the plant into which water is pumped from the Damodar river two miles away.
5. Labour: West Bengal, Jharkhand and Bihar provide labour to this plant.
6. Transport: Road and railways join the plant with Kolkata and other marketing centres. Kolkata provides port facilities for the movement of finished products.
Question 30. Briefly describe the Vijaynagar steel plant and the Vishakapatnam steel plant.
Answer:
Vijayanagar Steel Plant:
1. Location: Vijaynagar Steel Plant has been set up at Torangal near Hospet in the Bellary district of Karnataka.
2. Raw Materials: The plant gets iron ore from the Hospet region; good quality of limestone and dolomite from a distance of 200 km.
3. Power Supply: It gets coal from the Kanhan valley (Chhattisgarh) and Singareni (Andhra Pradesh) coal fields.
4. Water Supply: It gets water from the Tungabhadra reservoir (36 km from the plant site) and cheap hydel power from the Tungabhadra project.
Products: The plant specialises in ingot steel.
Vishakhapatnam Steel Plant:
1. Location: It is the first shore-based steel plant in India located at the port city of Visakhapatnam in Andhra Pradesh.
2. Raw Materials: The plant obtains iron ore from Bailadila in Chhattisgarh. It gets limestone, dolomite and manganese from the mines of Andhra Pradesh and Orissa.
3. Power Supply: It is well-connected with the coal fields of the Damodar Valley.
Question 31. What are the favourable factors for the Rourkela steel plant? State its major products.
Answer:
Rourkela Steel Plant: The Rourkela Steel Plant was built with technical cooperation from the German firm Krupps and Demang, in 1959.
1. Location: The plant is located at a distance of about 412 km from Kolkata at the confluence of two rivers, the Sankha and the Koel (Brahmani) in the Sundergarh district of Orissa.
2. Raw Materials: The plant is situated within 80 km of the high-grade iron ore reserves of the Sundergarh and Keonjhar districts in Orissa. Manganese is obtained from Barajmda, limestone from Bhirmitrapur and dolomite from Baradwar, all situated within a short distance from the plant.
3. Power Supply: Coal is obtained from Jharia, Talcher and Korba fields and electricity is from Hirakud Project.
4. Water Supply: Water is obtained from the Mandira dam across the Sankha river and also from Mahanadi.
5. Transport Facilities: Rourkela is situated on the Kolkata-Nagpur rail line. This provides easy access to raw material-producing areas and also to the markets.
6. Labour Force: It is recruited from Bihar, West Bengal, Jharkhand and Orissa.
Products: Its major products include hot-rolled sheets and strips, cold-rolled sheets, galvanised sheets and electrical steel plates. It also produces a large quantity of nitrogen as a by-product which is used for the manufacture of fertilisers and various chemicals.
Question 32. Describe the major units of the petrochemical industry in India.
Answer:
Production Units:
1. Union Carbide India Ltd: It is the first petrochemical complex and one of the biggest units. which was established in 1966 at Trombay in Maharashtra by Union Carbide. It manufactures films for packaging, bags, tarpaulins, godown covers, films, canal lining, industrial containers, insulation for electrical wires and cables, and pipes for carrying drinking water.
2. Herdillia Chemicals Ltd: It was set up in Chennai in collaboration with the Distillers Co. Ltd. of the UK and Hercules Power Co. of the USA. It manufactures a number of heavy organic chemicals like phenol, acetone, diacetone alcohol, and their derivatives, by-products, co-products and compounds.
3. National Organic Chemicals Industries Ltd: It is the biggest unit in India which was sponsored by Mafatlals in the Thana-Belapur area near Mumbai. It is also the first integrated plant in India which is based on the latest technology in the petrochemical field. The plant produces naphtha to produce ethylene, benzene, PVC, etc.
4. Petrofils Cooperative Limited (PCL): It is a joint venture of the Government of India and Weavers’ Cooperative Societies. It has three plants located at Vadodara and Naldhari in Gujarat. It manufactures yarn used for making swimsuits, undergarments, polyester filament yarn and nylon chips.
5. Indian Petrochemical Corporation Ltd: It is located at Jawaharnagar near Vadodara. It manufactures a number of petrochemicals like polymers, synthetic organic chemicals and fibres.
6. Bongaigaon Petrochemicals Ltd: It is located at Bongaigaon in Assam. It draws its raw materials from the Bongaigaon and Noonmati refineries.
7. The Reliance Industries: It is located at Hazira in Gujarat.
