India Location, Administrative Divisions True Or False Type:
Question 1. Sri Lanka is a neighboring country that shares a boundary with India.
Answer: False
Question 2. The largest union territory is Pondichery.
Answer: False
Question 3. Haryana attained statehood in 1966.
Answer: True
Read and learn all WBBSE Solutions For Class 10 Geography And Environment
Question 4. Goa, Daman, Diu became a part of India in 1961.
Answer: True
Question 5. State Reorganisation Committee was set up in 1953.
Answer: True
Question 6. Himachal Pradesh was made a full-fledged state in 1970.
Answer: True
“WBBSE Solutions for Class 10 Geography India Location and Administrative Divisions”
Question 7. Chandigarh is the capital of Punjab and Haryana.
Answer: True
Question 8. The largest state of India is Madhya Pradesh.
Answer: False
Question 9. The extreme southern point of India is Indira Point.
Answer: True
India Location, Administrative Divisions Fill In The Blanks Type:
Question 1. The total area of India is ______ sq. km.
Answer: 32,87,263 sq. km.
Question 2. The newest state of India is ______.
Answer: Telangana.
Question 3. India includes 29 states & ______ Union Territories.
Answer: 7.
Question 4. Meghalaya became a state in ______.
Answer: 1972.
Question 5. Manipur attained statehood in ______.
Answer: 1972.
Geography Class 10 West Bengal Board
Question 6. Mysore became Karnataka in ______.
Answer: 1973.
Question 7. State Reorganisation Act was passed in ______.
Answer: 1953.
“Class 10 Geography and Environment India Location solutions WBBSE”
Question 8. Arunachal became a state of India in ______.
Answer: 1987.
Question 9. Haryana became a state of India in ______.
Answer: 1966.
Question 10. The largest state of India is ______.
Answer: Rajasthan.
Question 11. The smallest state of India is ______.
Answer: Goa.

India Location, Administrative Divisions Very Short Answer Type:
Question 1. In which year India became the Sovereign Democratic Republic?
Answer: On 26th January 1950, India became the Sovereign Democratic Republic.
Question 2. How many states are there in India at present?
Answer: There are 29 states at present in India.
Question 3. How many union territories are there in India at present?
Answer: There are seven union territories in India at present.
Question 4. When was Mysore’s name changed to Karnataka and that of Laccadives, Minicoy, and Amindivi to Lakshadweep?
Answer: Both in 1973.
Question 5. What was the position of India in 1956?
Answer: There were 14 states and 6 union territories in India in 1956.
Question 6. When was the State Reorganisation Committee was set up?
Answer: In 1953, State Reorganisation Committee was set up.
“WBBSE Class 10 Geography Administrative Divisions solved questions”
Question 7. How many Union Territories are there in the Indian Union?
Answer: Seven.
Question 8. What was the main basis of state reorganization in India?
Answer: Language and Population.
Question 9. What is the area of India?
Answer: 32,87,263 sq. km.
Question 10. When did Meghalaya come into being as a state?
Answer: 1972 A.D.
Question 11. In which year Himachal Pradesh became a state?
Answer: 1971 A.D.
Question 12. In which year Andhra Pradesh became a state?
Answer: 1953 A.D.
Question 13. In which year Haryana became a state?
Answer: 1966 A.D.
Question 14. In which year Chhattisgarh came into being as the 26th state of India?
Answer: 1st November 2000 A.D.
Question 15. In which year Uttaranchal came into being as the 27th state of India?
Answer: 1st November 2000 A.D!
Question 16. In which year Chhattisgarh came into being as the 28th state of India?
Answer: On 15th November 2000 A.D.
Question 17. In which year Sikkim became a constituent state of India?
Answer: 26th April 1975 A.D.
Question 18. In which year Mizoram and Arunachal Pradesh became full-fledged states of India?
Answer: On 20th February 1987 A.D.
Question 19. Which is the smallest union territory of India?
Answer: Lakshadweep.
Question 20. Which is the most densely populated state in India?
Answer: West Bengal.
Question 21. Name the most densely populated union territory of India.
Answer: Delhi.
“WBBSE Geography and Environment India Location solutions PDF”
Question 22. In which year the State Reorganisation Act was passed?
Answer: in 1956.
Question 23. In which year Nagaland became a state?
Answer: In 1962.
Question 24. In which year Punjab was reorganized?
Answer: In 1966. It was made into two states: Punjab and Haryana.
Question 25. Which is the youngest state of India?
Answer: Telangana.
Question 26. Name a Cape in south India.
Answer: Cape Comorin.
India Location, Administrative Divisions 2 Marks Questions And Answers:
Question 1. When did Meghalaya come into being as a state? Who named it?
Answer:
Meghalaya was carved out of Assam in 1970 as a Union Territory. It became a full-fledged State in 1972. It like many other places such as Marusthali, Arunachal Pradesh, etc. was named by Prof. S.P. Chatterjee, the doyen (the most respected person) of geography in India.
Question 2. Name the largest and the smallest States in India in terms of their area.
Answer:
Rajasthan is the largest state in India and Sikkim is the smallest state in India.
Question 3. When were the following States formed:
(1)Andhra Pradesh, (2) Himachal Pradesh?
Answer:
(1) On 1st October 1953 out of Madras State.
(2) In 1954 Himachal Pradesh emerged as a centrally administered territory and in 1971 as a full-fledged State.
“India Location and Administrative Divisions Class 10 WBBSE solutions”
Question 4. When did Harayana and Chandigarh come into being?
Answer:
On November 1st, 1966, Punjab was divided into Punjab and Haryana as full-fledged States and Chandigarh as a Union Territory.
Question 5. Where is New Delhi situated?
Answer:
New Delhi, the capital of India, is within the Union Territory of Delhi-situated on the bank of the Yamuna River.
Question 6. When did (1) Dadra and Nagar Haveli and (2) Goa, Daman, and Diu become part of India?
Answer:
(1) August 1961, (2) December 1961.
Question 7. In which year did (1) Nagaland, and (2) Arunachal Pradesh come into being?
Answer:
(1) Nagaland became a Union Territory in December 1957 and a full-fledged state in December 1963.
(2) In 1957, North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) was carved out of Assam as a Union Territory. It was renamed Arunachal Pradesh in 1972.
“Class 10 WBBSE Geography India Location important questions”
Question 8. What was the position of India when she acquired independence in 1947?
Answer: At that time there were 15 states governed by governors, 5 states governed by chief commissioners and there were more than 600 princely states.
Question 9. What was the basis of the reorganization of the united states? In which year State Reorganisation Act was passed?
Answer: Language was the main basis of the state reorganization of India. The Act was passed in the year 1956.
Question 10. What was the main basis of state reorganisation in India and why?
Answer: Language was the main basis of state reorganisation in India because there was a widespread public demand for it.
Question 11. Name and locate the water bodies surrounding India.
Answer: India is surrounded by water bodies on three sides, i.e., the Bay of Bengal in the southeast, the Indian Ocean in the south, and the Arabian Sea in the southwest.
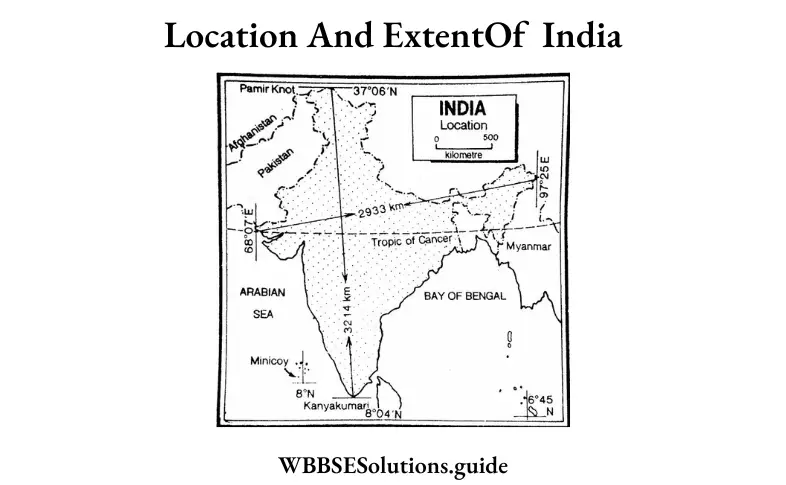
Question 12. Write the latitudinal & longitudinal extent of India.
Answer: India lies between 8°4′ (Cape Comorin) and 37°6′ (the northern extreme of Jammu & Kashmir) north latitudes, and 68°7′ (the western end of Gujarat) and 97°25′ (the eastern end of Arunachal Pradesh) east longitudes.
Question 13. Name two islands that covered India.
Answer: (1) Andaman & Nicobar Islands, (2) Lakshadweep.
India Location, Administrative Divisions 3 Marks Questions And Answers:
Question 1. State how West Bengal attained its present shape since the partition of India in 1947.
Answer:
At the time of the partition of India, West Bengal was a truncated state northern and southern parts remained separated from each other. Cooch Behar became a part of West Bengal in 1948 and the French Chandanagar-Gourhati in 1954. In 1956 when the Purulia subdivision and parts of the Kishengunj subdivision of Bihar were added, the State attained its present shape.
Question 2. Name any three union territories of India along with their capitals.
Answer:
Three union territories of India are :
(1)Lakshadweep: Kavaratti
(2)Damanand Diu: Daman.
(3)Andaman and Nicobar Islands: Port Blair.
“WBBSE Class 10 Geography India Location chapter answers”
Question 3. State three basis of division of states after Independence.
Answer:
Basis of the division of states of India after Independence: After independence, the different states or provinces of India were demarcated on the basis of some criteria; namely, language, culture, administration skills, economic stability, and physical and geographical similarities.
1. Language: India is a land where people speak different languages in different parts of the country. Based on this, the states were demarcated in 1956, designating the region speaking a common language as one state. E.g. the region where most people speak Assamese was marked as Assam, and the region where most people speak Punjabi was marked as Punjab.
2. Administrative advantage arid skill: Although language was a criterion of demarcating states, only this could not work very well. E.g. Hindi is the main language spoken in Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, and Uttaranchal. But if all these states were kept united as one single state, it would have covered a huge area, causing difficulty in administration. Also, Bengali is spoken in West Bengal and also dominantly in Tripura. But due to physical distance, these two states could not be put together.
3. Culture: Even though the language spoken is the same, the local cultures and rituals followed in a particular region may differ. Hence, for administrative efficiency, these regions are frequented in different states. For E.g. Bjhar has been fragmented into Bihar and Jharkhand.
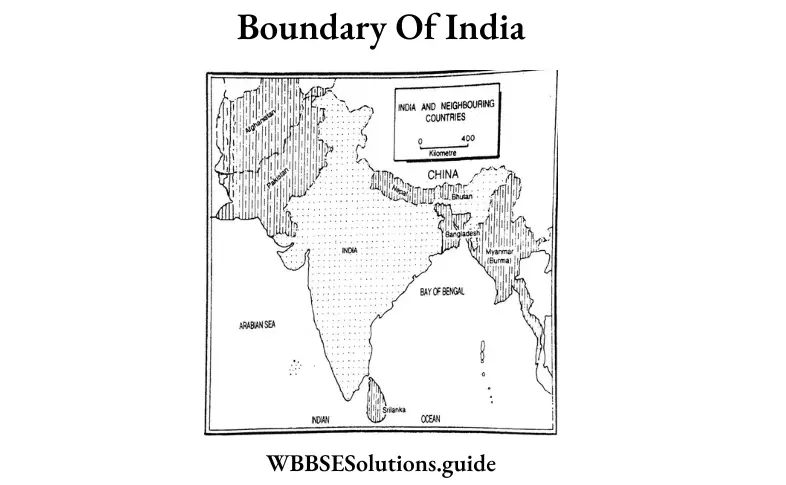
Question 4. Explain the boundary of India.
Answer: Boundary: India is bordered by the snowclad Himalayas in the north, the India Ocean in the south, the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh, and Myanmar (Burma) in the east, and the Arabian Sea and Pakistan in the west. The Himalayan Kingdom Nepal and Bhutan lie on the lap of the Himalayas in the north; China lies in the farther north. The three sides of the southern peninsula are washed by the Arabian Sea, the Bay of Bengal, and the Indian Ocean. India has a land frontier of 15,200 km and a coastline of 7,516 km. The Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal and Lakshadweep (island) in the Arabian Sea are part and parcel of the territory of India.
“Class 10 Geography India Administrative Divisions WBBSE notes”
Question 5. To what extent India is located? Explain.
Answer:
Extent: The mainland extends from the Himalayas in the north to the Cape Comorin (Kanyakumari, the southern-most tip of the mainland) in the south, measuring about 3,214 km from north to south and from the western end of Gujarat to the eastern end at Arunachal Pradesh, measuring about 2,933 km from west to east. India covers an area of 32,87,263 sq. km. In terms of area, India ranks seventh position among the countries of the world. Russia occupies the first position followed by Canada, China, the U.S.A., Brazil, and Australia.
Question 6. In 1950 how many states and union, territories were present in India? Explain.
Answer:
In the political map of 1950, we see that there were 28 states in India, they were classified into four groups stated as follows:
(1)9, ‘A’ States governed by Governors,
(2)8, ‘B’
(3)10, ‘C’ States governed by Chief Commissioners, and
(4)1, ‘D’ Union Territory.
WBBSE Class 10 Geography Chapter 5 Question Answer India Location, Administrative Divisions 5 Marks Questions And Answers:
Question 1. Give an account of the location, extent, and boundary of India.
Answer:
Location: India is located in the southern part of Asia, the largest continent of the world. The country lies towards the north of the equator, i.e., in the northern hemisphere. The mainland lies between 8°4 ‘(Cape Comorin) and 37°6 ‘(the northern extreme of Jammu & Kashmir) north latitudes, and 68°7 ‘(the western end of Gujarat) and 97°25′(the eastern end of Arunachal Pradesh) east-longitudes. The Tropic of Cancer passes almost through the middle of the country. The southernmost tip of the Nicobar Islands, i.e., the Indira Point touches the parallel of 6°45 ‘north latitude. India] States governed by the Princes,
occupies a strategic position in Asia, looking across the seas to Arabia and Africa on the west and to Myanmar, Malaysia, and the Indonesian Archipelago on the east. Geographically, the Himalayan Range in the north keeps India apart from the rest of Asia. India occupies a central position in south Asia. Of her unique geographical position, Indian civilization and culture spread over the countries of southeast and southwest Asia. India’s geographical location also influences the climate of the country. The presence of the lofty Himalayas in the north checks the inward flow of the southwest Monsoon to make rain. This is of immense importance for Indian agriculture.
“WBBSE Solutions for Geography Class 10 India Location MCQs and answers”
Extent: The mainland extends from the Himalayas in the north to the Cape Comorin (Kanyakumari, the southern-most tip of the mainland) in the south, measuring about 3,124 km from north to south and from the western end of Gujarat to the eastern end at Arunachal Pradesh, measuring about 2,933 km from west to east. India covers an area of 32,87,263 sq. km in terms of area. India ranks seventh position among the countries of the world. Russia occupies the first position followed by Canada, China, the U.S.A., Brazil, and Australia.
Boundary: India is bordered by the snowclad Himalayas in the north, the Indian Ocean in the south, the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh, and Myanmar (Burma) in the east, and the Arabian Sea and Pakistan in the west. The Himalayan Kingdom Nepal and Bhutan lie on the lap of the Himalayas in the north. The three sides of the southern peninsula are washed by the Arabian Sea, the Bay of Bengal, and the Indian Ocean. India has a land frontier of 15,200 km and a coastline of 7,516 km. The Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal and Lakshadweep (island) in the Arabian Sea are part and parcel of the territory of India.
Question 2. Give an account of the existing provinces and Union Territories of India.
Answer:
Existing provinces and Union Territories of India: India at present is a federal union of states comprising 29 states and 7 union territories. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and further into smaller administrative divisions.
Amongst the states of India, Rajasthan is the largest and Goa is the smallest state in terms of area. According to the size of population, Uttar Pradesh ranks the first and Sikkim the last position.
The highest density of population prevails in West Bengal (1029 per sq km), while the lowest density of population is recorded in Arunachal Pradesh (17 per sq km).
However, if we consider the population of the states and the union territories together, the highest density of population prevails at Delhi (11,279 per sq km) and the lowest at Arunachal Pradesh.
“India Location and Administrative Divisions WBBSE Class 10 question answers PDF”
A table is given below to show the details of the states and union territories:
WBBSE Class 10 Geography Chapter 5 Question Answer
| State | capital | Area in (sq. km) |
Population (in thousands) |
The density of Population(perqs. km.) |
| 1. Andhra Pradesh | Hyderabad | 160.205 | 49.386 | 308 |
| 2. Arunachal Pradesh | Itanagar | 83743 | 1,382 | 17 |
| 3. Assam (Asom) | Dispur | 78,438 | 31,169 | 397 |
| 4. Bihar | Patna | 94,163 | 103.804 | 1,102 |
| 5. Chhatisgarh | Raipur | 136,034 | 25,540 | 189 |
| 6. Goa | Panaji | 3,702 | 1,457 | 394 |
| 7. Gujarat | Gandhinagar | 195,024 | 60,383 | 308 |
| 8. Haryana | Chandigarh | 44,212 | 25,353 | 573 |
| 9. Himachal Pradesh | Shimla | 55,673 | 6,856 | 123 |
| 10 Jammu & Kashmir | Srinagar | 2,22,236 | 12,548 | 124 |
| 11. Jharkhand | Ranch | 79,714 | 32,965 | 414 |
| 12. Karnataka | Bengaluru | 191,791 | 61,130 | 319 |
| 13. Keraia | Thiruvanthapuram | 38,863 | 33,387 | 859 |
| 14. Madhya Pradesh | Bhopal | 308,000 | 72,597 | 236 |
| 15 Maharashtra | Mumbai | 307,713 | 112,372 | 365 |
| 16. Manipur | Imphal | 22,327 | 2,721 | 122 |
| 17 Meghalaya | Shillong | 22,429 | 2,964 | 132 |
| 18. Mizoram | Aizawl | 21,081 | 1,091 | 52 |
| 19. Nagaland | Kohima | 16,579 | 1,980 | 119 |
| 20. Odisha | Bhubaneshwar | 155,707 | 41,947 | 269 |
| 21. Punjab | Chandigarh | 50,362 | 27,704 | 550 |
| 22. Rajasthan | Jaipur | 3,42,239 | 68,621 | 201 |
| 23. Sikkim | Gangtok | 7,095 | 607 | 86 |
| 24. Tamil Nadu | Chennai | 1,30,058 | 72,138 | 555 |
| 25. Telangana | Hyderabad | 114,840 | 35,193 | 310 |
| 26. Tripura | Agartala | 10,491 | 3,671 | 350 |
| 27. Uttarkhand | Dehradun | 53,484 | 10,116 | 189 |
| 28. Uttar Pradesh | Lucknow | 240,928 | 199,581 | 828 |
| 29 West Bengal | Kolkata | 33.752 | 51 347 | 1,029 |
| Union Territories | ||||
| 1. Andaman & Nicobar | 3ort Blair | 8,249 | 379 | 46 |
| ?. Chandigarh | Chandigarh | 114 | 1.054 | 9,252 |
| 3. Dadrs 8 \agar Have | Silvassa | 491 | 342 | 698 |
| 4. Daman & Diu | Daman | 112 | 242 | 2,169 |
| 5. Delhi | Delhi | 1,483 | 16.753 | 11,297 |
| 6. Lakshadweep | Kavaratti | 32 | 64 | 2,0i3 |
| 7. Pondicherry | Pondicherry | 479 | 1,244 | 2.593 |
| India | New Delhi | 3,287,263 | 1,21,01,93,422 | 382 |
Question 3. Write in brief about the history of the demarcation of provinces of India after independence.
Answer:
The history of the demarcation of provinces of India after independence
India, a union of states, is a Sovereign Socialist Secular Democratic Republic. It became a Republic on 26th January 1950. In the political map of1950, we see that there were 28 states in India; they were classified into four groups stated as follows: 9, ‘A’ States governed by the Governors, 8, ‘B’ States governed by the Princes, 10, ‘C1 States governed by Chief commissioners and 1, ‘D’ Union Territory.
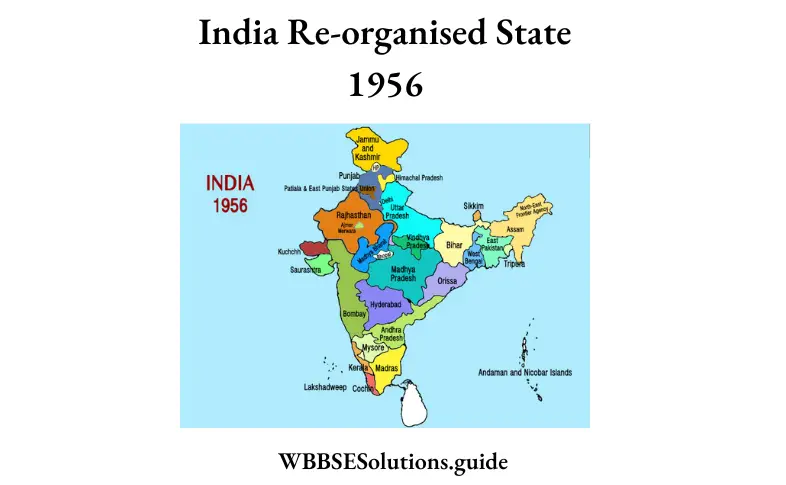
The State Reorganisation Commission was set up in 1953. According to the recommendation of the commission, the entire political setup of the country was reorganized on a linguistic basis. The classification of the States into ‘A’, ‘B1, and ‘C’ categories was abolished. Only two types of political divisions, namely ‘states’ and ‘union territory’ were recognised. The process of reorganization of states continued since 1st November 1956 and the political map of India went on changing.
A short account of this is given below:
1. The years between 1957 and 1987 saw the divisions of the former Assam and the birth of full-fledged states, such as, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Meghalaya and Mizoram.
2. On 1st May 1960 Bombay was bifurcated into Maharashtra and Gujarat states.
3. In 1961 India occupied the Portuguese enclaves of Goa, Daman, and Diu.
4. On 1st December 1963 Nagaland became a full-fledged state of the Indian Union.
5. On 1st November 1966 former Punjab of the Indian Union was divided again and the present Haryana and Punjab came into being.
6. In 1971 Himachal Pradesh and in 1972 Manipur, Meghalaya, and Tripura became full-fledged States.
7. On 26th April 1975 the Himalayan Kingdom Sikkim joined the Indian Union as its 22nd state.
8. On 20th February, 1987 Mizoram and Arunachal Pradesh, and on 30th May, 1987 Goa became the 2.3rd, the 24th and the 25th states of the Indian Union respectively.
9. On 1st November 2000 Chhattisgarh (Capital: Raipur), on 8th November 2000 Uttaranchal now known as Uttarakhand (Capital: Dehra Dun) and on 15th November 2000 Jharkhand (Capital: Ranchi) became the 26th, 27th and 28th States of India respectively.
10. On 2nd June 2014Telengana carved out from the north-western region of Andhra Pradesh, appeared as the 29th State of India with the city of Hyderabad as its capital.
