WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer In English
Chapter 5 Light MCQs
Question 1. The formation of the spectrum is due to:
- Reflection
- Refraction
- Dispersion of light
Answer: 3. Dispersion of light.
Question 2. A person uses the spectacle of power + 2D. He is suffering from:
- Presbyopia
- Astigmatism
- Long-sightedness of hypermetropia
- Short-sightedness of myopia
Answer: 3. Long-sightedness of hypermetropia.
Read And Learn More: WBBSE Solutions For Class 10 Physical Science And Environment
Question 3. A person cannot see objects clearly beyond 2m. The power of the lens required to correct his vision will be :
- + 2D
- -1D
- + ID
- 0.5D
Answer: 4. 0.5D.
Question 4. Myopia is due to:
- Older age
- Shorting of eyeball
- Irregular change in focal length
- Elongation of the eyeball.
Answer: 4. elongation of the eyeball.

Question 5. Rainbow is formed due to a combination of
- Refraction and absorption
- Refraction and scattering
- Dispersion and total internal reflection
- Dispersion and focussing
Answer: 3. Dispersion and total internal reflection.
“WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science and Environment Chapter 5 solutions, Light”
Question 6. Which of the prism is used to see the infrared spectrum of light?
- Rock salt
- Flint
- Nicol
- Crown
Answer: 1. Rock salt.
Question 7. Which of the following colours suffers maximum deviation in a prism?
- Yellow
- Green
- Blue
- Orange
Answer: 2. Blue.
Question 8. The splitting of white light into several colours on passing through a glass prism is due to:
- Reflection
- Diffraction
- Interference
- Refraction
Answer: 4. Refraction.
“Class 10 WBBSE Physical Science Chapter 5 solutions, Light study material”
Question 9. A convex lens will become less convergent in
- Oil
- Water
- Both
- None
Answer: 2. water.
Question 10. The source of ultraviolet light is :
- Electric bulb
- Carbon arc lamp
- Red hot iron bulb
- Sodium vapour lamp
Answer: 2. carbon arc lamp.
Question 11. Which of the following materials cannot be used to make a lens?
- Water
- Plastic
- Clay
- Glass
Answer: 2. Clay.
Question 12. No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be :
- Plane only
- Concave only
- Convex only
- Either plane or convex
Answer: 4. Either plane or convex.
Question 13. A ray of light suffers refraction through an equilateral prism. The deviation produced by the prism does not depend on the:
- Angle of incidence
- Size of the prism
- colour of light
- material of the prism
Answer: 3. size of the prism.
Question 14. A ray of light incident on a lens parallel to its principal axis, after refraction passes through or appears to come from:
- its second focus
- its optical centre
- its first focus
- the centre of curvature of its second surface
Answer: 1. its second focus
Question 15. What is the value of W1/f1+ W2/f2
- 2
- 3
- 5
- 0
Answer: 4. 0
Question 16. The terminal colours of the pure spectrum of white light are :
- Blue and violet
- Red and orange
- Red and violet
Answer: 3. Red and violet.
Question 17. Yellow colour is called :
- Primary
- Middle colour
- Secondary colour
- Top colour
Answer: 2. Secondary colour
“WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Chapter 5, Light solved examples”
Question 18. The___________ colours can be seen distinctly in pure spectrum.
- Six
- Eight
- Seven
- Nine
Answer: 3. Seven.
Question 19. The dispersion of white light was first observed by:
- Sir Issac Newton
- Boyle
- Max Well
Answer: 1. Sir Issac Newton.
Question 20. The arrangement of the seven colours of spectrum is:
- VIBGYOR
- RAINBOW
- VBIGOYR
Answer: 1. VIBGYOR.
Question 21. The object is placed in between ‘f’ and ‘2f’ in convex lens, the size of image will be
- Greater in size the object
- Equal in size of the object
- Greater in size the object.
- Smaller in size than the object
Answer: 1. Greater in size the object
Question 22. To for m virtual image on the same side of the object in case of a convex lens, the object should be placed :
- In between the lens and the focus
- In between ‘f’ and ‘2f’
- At ‘2f’ from the lens
- At a distance greater than ‘2f’ from the lens
Answer: 1. In between the lens and the focus.
Question 23. Linear magnification is equal to :
- (Length of image)/(Length of the object).
- (Length of image) × (Length of the object).
- (Length of image) + (Length of the object).
- (Length of image) – (Length of the object).
Answer: 2. (Length of image)×(Length of the object)
Question 24. A mirror produces a magnified erect image of an object. The nature of the mirror is
- Convex
- Concave
- None of these
- Plane
Answer: 2. Concave.
Question 25. A plane mirror produces a magnification of:
- -1
- + 1
- Zero
- Between 0 and + a
Answer: 2. + 1.
“WBBSE Class 10 Light solutions, Physical Science and Environment Chapter 5”
Question 26. Focal length of a convex lens will be maximum for:
- Blue light
- Red light
- Greenlight
- Yellow light
Answer: 3. Red light.
Question 27. The number of images observable between two parallel plane mirror is:
- 2
- 4
- 11
- Infinite
Answer: 4. Infinite.
Question 28. When a mirror is rotated through an angle 0, the reflected ray from it turns through an angle of :
- θ
- θ/2
- 0
- 2θ
Answer: 4. 2θ
Question 29. A ray is incident at an angle 38° with a mirror. The angle between normal and deflected ray is :
- 90°
- 75
- 38°
- 52°
Answer: 4 52°
Question 30. The focal length f of a speherical mirror of radius of curvature R is :
- \(\frac{R}{2}\)
- R
- \(\frac{3}{2}\) R
- 2R
Answer: \(\frac{R}{2}\)
Question 31. A concave mirror of focal length f (in air) is immersed in water (μ = 3). The focal length of the mirror in water will be :
- \(\frac{4}{3}\) f
- \(\frac{9}{5}\) f
- \(\frac{3}{5}\) f
- f
Answer: 4. f
Question 32. A plane mirror is approaching a person at a speed of 5 cm S-1. At what speed will his image approach him?
- 10 cms-1
- 20 cm S-1
- 5cms-1
- 15cm S-1
Answer: 1. 10 cm S-1
Question 33. If an object is 30 cm away from a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm, the image will be :
- Erect
- Reflection of light
- Diminished
- Of same size
Answer: 4. Of the same size
Question 34. Mirage is a phenomenon due to:
- Reflection of light
- Refraction of light
- Diffraction of light
- Total internal reflection of light
Answer: 4. Total internal reflection of light.
Question 35. The principle behind optical fibres
- Total internal reflection
- Total external reflection
- Diffraction
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 1. Total internal deflection
Question 36. A convex lens is dipped in a liquid whose refractive index is euqal to the refractive index of the lens. Then its local length will:
- Become zero
- Become infinite
- Increase
- Reduce
Answer: 2. Become infinite.
Question 37. What is the value of the refractive index of a diamond?
- 2.47
- 3.47
- 1.47
- 0.47
Answer: 1/. 2.47.
Question 38. Write an example of an isotropic medium.
- Air
- Water
- Iron
- Fire
Answer: 1. Air.
Question 39. Write the value of speed of light.
- 3 x 106 m/s
- 3 x 108 m/s
- 3 x 107 m/s
- 3 x 109 m/s
Answer: 3. 3 x 108 m/s.
Question 40. What is the value of refractive index of alcohol?
- 1.37
- 2.37
- 4.37
- 0.37
Answer: 1. 1.37.
WB Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer Chapter 5 Light Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is the far point of a normal eye?
Answer: Infinity.
Question 2. Which colour of light travels faster in vacuum?
Answer: Light rays of all colour travel with same speed in vacuum.
Question 3. What is the least distance of distinct vision?
Answer: 25 cm.
Question 4. How is deviation produced in a prism related to the angle of the prism and angles of incident and emergency?
Answer: δ= i1+i2 – A
Question 5. Is dispersion of white light in a vacuum possible?
Answer: No.
Question 6. Define the power of a lens.
Answer: The reciprocal of the focal length of the lens is called its power.
Question 7. What will be the focal length and power of a plane glass plate?
Answer: f = α; Power = 0
Question 8. Why is a night-angled prism a better reflector than a plane mirror?
Answer: As in the prism no part of the light refracted.
Question 9. Does a beam of light give a spectrum on passing through a hollow prism containing air, explain?
Answer: No, because all colours of light pass through vacuum or air same speed and there is no dispersion.
Question 10. What kind of lens one should use to correct myopic eye?
Answer: Concave lens.
Question 11. What kind of lens one should use to correct the astigmatic eye?
Answer: Cylindrical lens.
Question 12. What is monochromatic light?
Answer: The light which consists of only one colour is known as monochromatic light.
“Class 10 WBBSE Physical Science Chapter 5, Light easy explanation”
Question 13. What is a double convex lens?
Answer: If both the surfaces of a convex lens are convex then the lens is called a double convex lens. It is used in camera, telescopes etc.
Question 14. Will the focal length of a convex lens vary for refraction of light of different colours through it?
Answer: For different colours of light the convex lens will have different focal length.
Question 15. What is the edge of a prism?
Answer: The intersection of the refracting surfaces is called the edge of the prism.
Class 10 Physical Science Solution WBBSE
Question 16. An object is placed at the focus of a concave lens, where will be its image formed?
Answer:
u = f; f = – ve
So, \(\frac{1}{v}\)– \(\frac{1}{u}\) = \(\frac{1}{f}\) Or,
\(\frac{1}{v}\)= \(\frac{1}{f}\)+ \(\frac{1}{u}\) Or,
\(\frac{1}{v}\)= \(\frac{1}{f}\)+ \(\frac{1}{f}\)
= 0
∴ v= α
Question 17. Name the type of mirror which has focal length equal to infinity.
Answer: A plane mirror.
Question 18. What are the types of reflection of light?
Answer:
The types of reflection of light are:
- Regular reflection
- Irregular reflection
Question 19. Write the expression of Newton’s Equation.
Answer: The expression of Newton’s Equation xy = f2.
Question 20. What is the mathematical expression of linear magnification?
Answer: The mathematical expression of linear magnification is m=\(\frac{v}{u}\)
Question 21. Write two classifications of image.
Answer: The two classifications of image are real and virtual.
Question 22. Write an example of opaque substance.
Answer: An example of opaque substance is iron.
Question 23. What will be the nature of the lens for u-v graph.
Answer: The nature of the graph is rectangular hyperbola.
Class 10 Physical Science Solution WBBSE
Question 24. Write the expression of dispersive power of lens materil.
Answer:
W = \(\frac{δμ}{μ- 1}\)
Question 25. Write the mathematical expression of generalised snell’s law.
Answer: The mathematical expression of generalised snell’s law :
⇒ μ2= sin i1
= μ sin i 2
Question 26. Write a characteristic of the image formed by a plane mirror.
Answer: The image is erect but laterally inverted.
Question 27. What is the value of refractive index of Benzene?
Answer: The value of refractive index of Benzene is 1.501.
Question 28. What are the two types of lens?
Answer: The two types of lens are convex and concave.
Question 29. Write the mathematical expression of lens maker’s formula.
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{f}\)= (μ – 1) = (1/r1 – 1/r2)
Question 30. Write the mathematical expression of the refraction index.
Answer:
⇒ \(\frac{sin r}{sin i}\) = 2μ1
WBBSE Solutions Guide Class 10 Chapter 5 Light Fill In The Blanks
Question 1. The light which consists of only one colour is called_____ light.
Answer: Monochromatic.
Question 2. Yellow colour is a _______colour.
Answer: Secondary.
Question 3. A transparent body absorbs all the colours of white light except the light of colour of its_________
Answer: Own.
Question 4. The elementary colours of white light are arranged in order of _______
Answer: Wavelength.
Question 5. _______First observed the dispersion of white light.
Answer: Sir Issac Newton.
Question 6. Lenses are generally of two types, concave and _______
Answer: Convex.
Question 7. The _________colours can be seen distinctly in pure spectrum.
Answer: Seven.
Question 8. A convex lens is called a _______lens.
Answer: Converging.
Question 9. The middle colour is _______
Answer: Yellow.
Question 10. Red flower appears _______green light.
Answer: Black.
Question 11. Yellow and blue colours are _________colours colours of each other.
Answer: Complementary.
Question 12. A beam of rays of light parallel to the principal axis of a convex lens, will passe through the______focus after refraction.
Answer: Principal.
“WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Chapter 5 solutions, Light PDF”
Question 13. Magenta colour is made by mixing red and ______colour.
Answer: Blue.
Question 14. During dispersion of light, light is splitting up into________ colours
Answer: Seven.
Question 15. A ________ lens is used as a magnifying glass.
Answer: Convex.
Question 16. The arrangement of seven colours of the spectrum is ________
Answer: VIBGYOR.
Question 17. A plane mirror produces a magnification of ________
Answer: +1.
Question 18. The focal length f of a spherical mirror of radius of curvature R is.
Answer:
⇒ \(\frac{R}{2}\)
Question 19. Mirage is a phenomenon due to ________.
Answer: Total internal reflection of light
Question 20. The band of different colours obtained due to dispersion of white light is called the________.
Answer: Spectrum
Question 21. The lens which is thinner at the centre and wider at the two edges is known as a ________ lens.
Answer: Convex
WB Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer
Question 22. If a ray be incident on a convex lens parallel to its principal axis, then the refracted ray through the lens passes through the ________ of the lens.
Answer: Focus
Question 23. The straight line that joins the centres of the spherical surfaces forming the lens is called the _______ axis of the lens.
Answer: Principal
Question 24. The distance of the principal focus from the optical centre of a lens is called its principal _______ length.
Answer: Focal
Question 25. An object place perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens will have its image _______ to the principal axis.
Answer: Perpendicular
Question 26. The focal length of a convex lens will be maximum for _______
Answer: Red light
Question 27. The number of images observable between two parallel plane mirror is_______
Answer: Infinite
Question 28. The formation of the spectrum is due to _______
Answer: Dispersion
Question 29. The terminal colours of pure spectrum of white light are
Answer: Red and violet
Question 30. _________of the prism is used to see infrared spectrum of light.
Answer: Rocksalt.
WB Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer Chapter 5 Light Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is a centre of curvature of a lens?
Answer:
Centre of curvature: The spherical surface of a lens is a part of sphere. The centre of this sphere is known as centre of curvature of the surface of lens.
Question 2. What is Focal plane?
Answer:
Focal plane: The plane passing through the principal focus of a lens and perpendicular to the principal axis of the lens is known as the focal plane of the lens.
Question 3. What is Radius of curvature?
Answer:
The radius of curvature: The radius of curvature of a lens is the radius of the glass sphere from which the surfaces of the lens are cut.
Question 4. What is Focal length?
Answer:
Focal length: The distance between the optical centre and the focus is known as focal length.
Question 5. What do you mean by the principal axis of a convex lens?
Answer:
Principal axis of a convex lens
Principal axis of a convex lens joining the centres of curvature of the two spherical surfaces of a convex lens is called its principal axis.
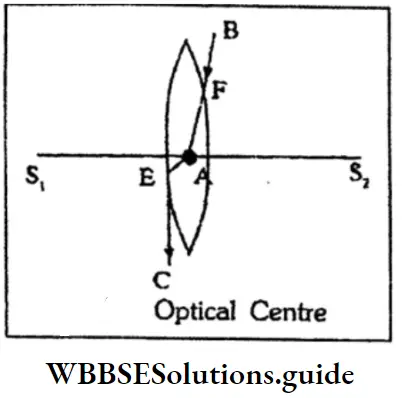
Question 6. What is optical centre?
Answer:
Optical centre: If a ray of light strikes the surface of a lens in such a way that the emergent ray from the other surface is parallel to it then the corresponding refracted ray passes through a definite point on the principal axis. This point (A) is the optical centre of the lens.
Question 7. What does the term ‘thin’ signify when it is related to a convex lens? Do all rays of light suffer deviation while crossing through a thin convex lens?
Answer:
A thin convex lens is one, the thickness at the middle of which is extremely small compared to the radii of curvature of its surfaces. Rays directed towards the optical centre do not suffer deviation while crossing through a convex lens.
“WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Chapter 5, Light important questions“
Question 8. What is a spectrum?
Answer:
Spectrum: The band of different colours obtained due to dispersion of white light is known as a spectrum.
Question 9. A concave mirror of a small aperture forms a sharper image why?
Answer:
A concave mirror of a small aperture forms a sharper image
It is because such a mirror is free from the defect due to spherical aberration.
Question 10. What are luminous and non-luminous object?
Answer:
Luminous object
Bodies which emit light of themselves are luminous sources.
Non-luminous object
Bodies which cannot emit light of themselves are non-luminous sources.
Question 11. State the principle of reversibility of light path.
Answer:
Reversibility of light path
If a ray starting from a point reaches a second point after suffering any number of reflections and refractions and then be reversed in direction, it will retrace its path and reach the first point provided that all other conditions under which reflections and refractions took place remain unaltered.
Question 12. Define real image.
Answer:
Real image
If reflected or refracted rays actually converge to a point, the point is called a real image.
Question 13. Define virtual image.
Answer:
Virtual image
If the reflected or refracted rays only appear to diverge from a point, the point is called a virtual image.
Question 14. Write the differences between real and virtual image.
Answer:
Differences between real and virtual image
- A real image is formed when a reflected or refracted ray actually converges to it, but in case of a virtual image, the reflected or refracted ray appear to diverge from it.
- A real image can be seen directly with eye. It can also be cast on a screen. But a virtual image can only be seen with eye but it cannot be cast on a screen.
Question 15. Define image.
Answer:
Image
It the rays diverging from a paint undergo changes in direction by reflection, refraction of by both, ultimately they either converge to a point or appear to diverge from a point.
Question 16. What is incident ray and reflected ray?
Answer:
Incident ray and reflected ray
- The light ray striking a reflecting surface is called the incident ray.
- The light ray obtained after reflection from the surface, in the same medium in which the incident ray is travelling, is called the reflected ray.
Question 17. What is plane of incidence and reflection?
Answer:
The plane containing the reflected ray and normal, is called the plane of reflection. The plane containing the reflected ray and the normal, is called the plane of reflection.
“Class 10 Physical Science and Environment Light solutions, WBBSE syllabus”
Question 18. Difine Lateral inversion.
Answer:
Lateral inversion
The interchange of the left and right sides in the image of an object in a plane mirror is called the lateral inversion.
19. Write two uses of plane mirror.
Answer:
Uses of plane mirror
- In a kaleidoscope, three plane mirrors inched with each other at 60° are used.
- In the solar heating devices such as solar cooker, etc plane mirror is used to reflect the light rays incident from sun. The substance to be heated.
Question 20. What is the principle of simple periscope.
Answer:
The principle of simple periscope
This instrument is used for looking over an obstacle which blocks the path of light from an object to the eyes of an observer.
Question 21. Define
- Centre of curvature
- Redius of curvature
- Principle axis
Answer:
- The centre of curvature of a mirror is the centre of the sphere of which the mirror is a apart.
- The radius of the sphere of which the spherical mirror is a part, is called the radius of curvature of the mirror.
- It is the straight line joining the pole of the mirror to its centre of curvature.
Question 22. Define
- Pole
- Aperture.
Answer:
- The geometric centre of the spherical surface of the mirror is called the pole of the mirror.
- The part of the mirror which is exposed to the incident light is called the aperture of the mirror. Thus it is the surface of the mirror from which reflection occurs.
Question 23. Define focus and focal length.
Answer:
Focus and focal length
- Focus-The focus of a concave mirror is a point on the principle axis through which the light rays incident parallel to the principal axis pass after reflection from the mirror.
- The focus of a convex mirror is a point on the principal axis at which the light rays incident parallel to the principal axis, appear to meet after reflection from the mirror.
- Focal length-The distance of focus from the pole of the mirror is called the focal of the mirror.
Question 24. Write the differences between convex mirror and concave mirror.
Answer:
Concave mirror And Convex mirror:
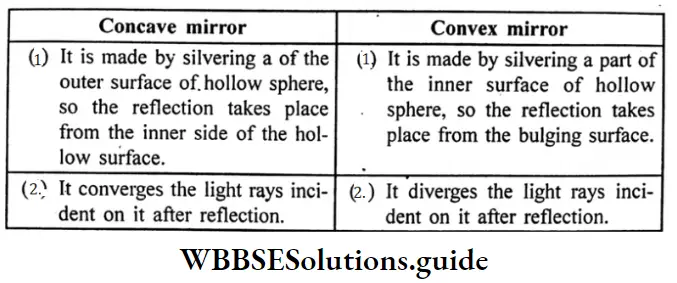
Question 25. Write two characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror.
Answer:
Characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror
- The dista nces of the object and its image is measured from the mirror are equal.
- The line joining the object and its image intersects the mirror perpendicularly.
Question 26. Define
- First principal focus.
- Second principal focus
Answer:
- Rays either diverging from or directed through the first principal focus of a spherical surface, after refraction at the surface becoms parallel.
- Rays moving parallel to the principal axis after refraction at a spherical surface either coverge to or appear to diverge from a point on the principal axis, known as second principal focus of the surface.
Question 27. What is Myopia?
Answer:
Myopia: The defect where for point is less than infinity is known as myopia. The defect is also called short Sightedness.
Question 28. How does the ray passes through the prism in the minimum deviation position?
Answer: In the minimum deviation position, the ray passes symmetrically through the prism i.e. the incident ray and emergent ray are equally inclined to the respective faces of prism.
Question 29. On what factors does the angular dispersion depend?
Answer:
The angular dispersion depends on :
- Refraction angle of the prism
- Nature of the material of the prism
- Wavelength of the incident light
Question 30. Why does a convex lens of glass = 1.5 behave as a diverging lens when immersed in a liquid of “μ = 1.65?
Answer:
The refractive index of glass with respect to the liquid [/latex]\frac{1.5}{1.65}[/latex]) is less than 1.
Question 31. Why does a diamond sparkle with great brilliance?
Answer: Multiple total internal reflections of light occur within the diamond. Diamond cutter uses this fact.
Question 32. What type of mirror would you use as shaving mirror?
Answer: A concave mirror of larger focal length is used for shaving purpose. Because it produces a magnified erect image of the face when placed within the focus of the mirror.
Question 33. The refractive index of diamond is much greater than the ordinary glass. Is this fact of some use to a diamond-cutter?
Answer: A critical angle [sin-1(\(\frac{1}{μ}\))] reflection takes place easily. of a diamond is much smaller and total internal
Question 34. How would you determine whether a mirror is plane, concave or convex?
Answer:
A plane mirror produces an erect image of the same size as that of the object. A concave mirror produces an erect and magnified image of an object when placed within its focus. A convex mirror produces always an erect and diminished image of an object.
“WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Chapter 5, Light summary”
Question 35. What is a Linear magnification of lens.
Answer: Linear magnification of lens: The ratio of the length of the image and that of the object is called the linear magnification.

Question 36. What is Focus of a convex lens?
Answer:
Focus of a convex lens: If a beam of parallel rays, travelling parallel to the principal axis of a convex lens are refracted by the lens, the rays become converg- ing and intersect each other at a particular point on the axis. The point is known as the focus of the convex lens.
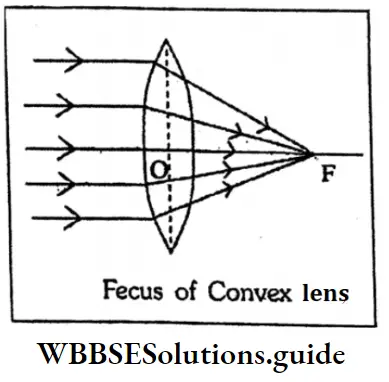
Question 37. Which rays should be considered n drawing ray diagrams for images formed by a convex lens?
Answer:
The following points should be considered :
- A beam of rays parallel to the principal axis after refraction through the lens pass through the principal focus.
- A beam of rays passing through principal focus emerge parallel to the principal axis, after refraction through the lens.
- A beam of rays through the optical centre pass out undeviated.
Question 38. What is a pure spectrum?
Answer:
Pure spectrum: The spectrum in which the constituent colours do not overlap on each other and are seperated distinctly into elementary colours is known as a pure spectrum.
Question 39. What is an impure spectrum?
Answer:
Impure spectrum: The spectrum in which the constituent colours partially superpose on each other and are not seperated distinctly into elementary colours is known as an impure spectrum.
40. Is dispersion possible without refraction?
Answer:
Question Explanation: Dispersion without refraction is not possible. In an optical medium different colours travel with different speed and so deviate with different magnitudes. Thus, the constituent colours of a poly chromatic light deviate by different amounts i.e. they are dispersed after refraction.
“WBBSE Class 10 Chapter 5 Physical Science, Light step-by-step solutions”
Question 41. Why blue is used after washing white shirts?
Answer:
Explanation Blue: Whitens yellow or orange colour. So, white shirts after washing may have some yellow or orange stain. To convert such stains to white, blue is used.
Question 42. What is the optical plane?
Answer:
Optical plane: It is an imaginary vertical plane that cuts the principal axis perpendicularly and passes through the optical centre of a lens.
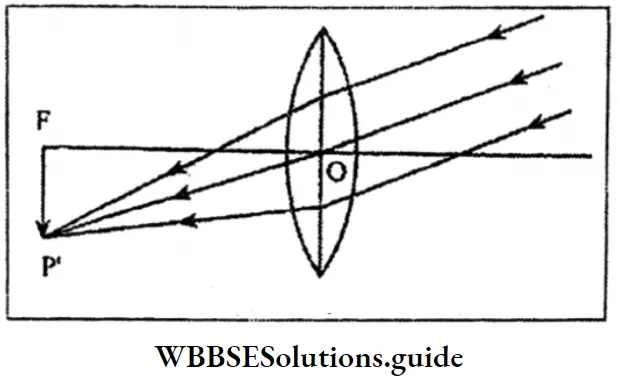
Question 43. Draw a neat diagram of the formation of image of an object at infinity by a convex lens.
Answer:
Formation of the image of an object at infinity by a convex lens :
- Distance of object: At infinity.
- The image formed: On the focal plane.
- Nature of image: Real and inverted.
- Size of image: Very much smaller than the object.
Question 44. The critical angle for a material c is 30°. Find its refractive index.
Answer:
The critical angle for a material c is 30°
⇒ μ=1/ sinc=1/sin 30% = 2.0
Refractive index = 2.0
“WBBSE Class 10 Light, Physical Science Chapter 5 key concepts”
Question 45. What is the focal length of a concave mirror of radius of curvature of 16.0 cm?
Answer:
The radius of curvature = 16cm. Focal length.
= ½ × Radius of curvature
= (\(\frac{1}{2}\) x 6) cm
= 8 cm.
Focal length of a concave mirror = 8 cm.
Question 46. A lens has a power of -2.5D. What is the focal length and the nature of the lens?
Answer:
P = – 2.5 D
Focal length =\(\frac{1}{P}\)
= \(\frac{1}{-2.5}\)
= -0.4m
= 40 sin.
Question 47. A lens has a focal length of -25cm. What is the power of the lens and what is the nature?
Answer:
Power = P = \(\frac{1}{f in m}\)
= \(\frac{1}{-0.25}\)
= – 4D.
Question 48. If the refractive index of glass in 1.5 and Zi=55, find the angle of refraction of glass.
Answer:
μ= \(\frac{sini}{sin r}\)
sin r = \(\frac{sin i}{μ}\)
=\(\frac{sin 55°}{1.5}\)
= 33.6°.
