WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer In English
Chapter 6 Current Electricity MCQs
Question 1. How many electrons constitute the current of IA?
- 6.25 x 109
- 6.25 x 105
- 6.25 × 1018
- 6.25 x 106
Answer: 3. 6.25 x 1018
Question 2. The material of a wire of a potentiometer is
- Copper
- Steel
- Magnani
- Aluminium
Answer: 3. Magnanin.
Read And Learn More: WBBSE Solutions For Class 10 Physical Science And Environment
Question 3. The vertical component of Earth’s magnetic field is zero at a place where the angle of dip is :
- 0°
- 60°
- 45°
- 90°
Answer: 1. 0°
Question 4. A magnetic needle suspended freely orients itself: in a definite direction upward
- In a definite direction
- In no direction
- Upward
- Downward
Answer: 2. In no direction.

Question 5. The unit of specific conductivity is.
- Ohm – cm-1
- Ohm – cm–2
- Ohm-1-cm-1
- Ohm-1 cm–2
Answer: 3. ohm-1 cm-1
“WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science and Environment Chapter 6 solutions, Current Electricity”
Question 6. The length of a wire is doubled. Its conductance will be
- Unchanged
- Halved
- Doubled
- Quadrupled
Answer: 2. Halved.
Question 7. The resistance of the discharge tube is:
- Ohmic
- Non – Ohmic
- Both
- None of these
Answer: 2. Non-ohmic.
Question 8. A wire of resistance 1 W is stretched to double its length. The resistance will be:
- 3V
- 9V
- 5V
- 15V
Answer: 2. 9V.
Question 9. The specific resistance of a wire depends upon
- Length
- Cross-sectional area
- Mass
- None of these.
Answer: 4. None of these
Question 10. The unit of specific resistivity is
- Ohm – cm-1
- Ohm – cm–2
- Ohm-cm
- Ohm-1 cm–2
Answer: 3. Ohm – cm
Question 11. The SI unit of electric charge is
- Coulomb
- Ampere
- Ohm
Answer: 1. Coulomb
“Class 10 WBBSE Physical Science Chapter 6 solutions, Current Electricity study material”
Question 12. The unit of potential difference is
- Joule
- Ohm
- Volt
- Ampere
Answer: 3. Volt.
WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Solutions
Question 13. The unit of electrical power is:
- Volt
- Ohm
- Watt
- Joule
Answer: 3. Watt
Question 14. What material an electric fuse made of?
- Copper
- Iron
- Silver
- Tin-lead alloy
Answer: 4. Tin-lead alloy.
Question 15. Unit of resistance is
- Ampere
- Ohm
- Coulomb
- Joule
Answer: 2. Ohm.
Question 16. Specific resistance of a conductor depends on
- Its length
- Its Cross-sectional
- It’s material
Answer: 3. It’s material.
Question 17. Which one is not the conductor of electricity
- Copper
- aluminu
- Gold
- Plastic
Answer: 4. Plastic
“WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Chapter 6, Current Electricity solved examples”
Question 18. The electric meter is a house record:
- Charge
- Current
- Energy
- Power
Answer: 3. Energy.
19. The main fuse is connected in:
- Live wire
- Neutral wire
- Both the live and earth wires
- Both earth and the neutral wire
Answer: 1. Live wire.
Question 20. In parallel combination of resistances
- P.d. is the same across each resistance
- Total resistance is increased
- Current is same in each resistance
- None of the above
Answer: 1. p.d. is the same across each resistance.
Question 21. For which of the following substances, resistance decreases with increase in temperature?
- Copper
- Mercury
- Carbon
Answer: 3. Carbon.
Question 22. Which of the following is an ohmic resistance?
- Carbon-arc lamp
- Diodevalve
- Nichrome
- Junction diode
Answer: 3. Nichrome.
Question 23. The amount of heat develops due to current can be known from
- Ampere law
- Ohm’s law
- Joules law
Answer: 3. Joule’s law.
Question 24. An example of the conservation of electrical energy into mechanical energy is :
- Electric cell
- Electric lamp
- Electric motor
Answer: 3. Electric motor.
Question 25. Ammeter measure :
- Resistance
- Potential difference
- Current
Answer: 3. Current.
Question 26. If the cross-section of the conductor is kept unaltered and the length of the conductor is increased then its resistance :
- Increases
- Decrease
- Remains unaltered
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Increases.
Question 27. Potential difference is measured by
- Volt meter
- Voltmeter
- Galvano meter
Answer: 2. Volt meter.
Question 28. The action of electric current on magnet was first observed by
- Oersted
- Joule
- Barlow
- Newton
Answer: 1. Oersted
Question 29. Ohm’s law is related to:
- The current and potential difference
- Volume and pressure
- Temperature density.
Answer: 1. current and potential differences.
Question 30. Electric supply company measures the electricity consumed by the consumers in their household in terms of:
- Joule unit
- Watt-hour
- B.O. T units
Answer: 3.B.O. T units.
Question 31. The dimensional formula of electric density is :
- [MLT-2 A-1]
- [MLT–3 A-1]
- [ML2T–3-3A-1]
- [ML2T–3-A-2]
Answer: 2. [MLT–3 A-1]
Question 32. The physical quantity measured by kilowatt-hour :
- Electric power
- Electric energy
- Current
Answer: 2. Electric energy.
“WBBSE Class 10 Current Electricity solutions, Physical Science and Environment Chapter 6”
Question 33. The correct relation is:
- Watt= \(\frac{\text { Volt }}{\text { Ampere }}\)
- Watt = \(\frac{\text { Ampere }}{\text { Volt }}\)
- Watt=Volt x Ampere
Answer: 3. Watt Volt x Ampere
Question 34. Electric Flux at a point in an electric field is :
- Positive
- Zero
- Negative
Answer: 2. Zero
Question 35. What is the dimensional formula of electric charge?
- [M°L° TA]
- [M°L°T-1A]
- [M°L°TA-1]
- [M°L°T-1A-1]
Answer: 1. [M°L° TA]
Question 36. If six identical cells each having emf of 6V are connected in parallel the emf of the combination is :
- IV
- 1/6V
- 6V
- 36V
Answer: 3. 6V.
Question 37. What is the equivalent resistance of the resistances 3 ohm, 5 ohm and 12 ohm combined in series?
- 15 ohm
- 18 ohm
- 20 ohm
- 10 ohm
Answer: 3. 20 ohms.
Question 38. A wire of resistance 1 W is stretched to double its length. The resistance will become :
- \(\frac{1}{4}\)
- 1
- 2
- 4
Answer: 4. 4
Question 39. A soap bubble is charged to a potential of 16V. Its radius is doubled. The potential of the bubble now will be
- 16V
- 4V
- 8V
- 2V
Answer: 3. 8V.
Question 40. The resistance will be least in a wire with dimension :
- L|2, 2A
- 2L, A
- L, A
Answer: 1. L|2, 2A.
Class 10 Physical Science WBBSE Chapter 6 Current Electricity Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Define the unit of electric unit.
Answer: The unit of current is ampere. It is the one coulomb of charge flowing through a conductor in one second.
Question 2. What do you mean by the conductivity of a material? Give its SI unit.
Answer: It is the reciprocal of resistivity. Its SI unit is Ohom-‘.
Question 3. How does the drift velocity of electrons in a metallic conductor vary with temperature?
Answer: The drift velocity of a metal decreases with an increase in temperature.
Question 4. What is 1B.O.T?
Answer: The total electric energy expended in 1 hour at the rate of 1 kilowatt is known as 1 B.O.T. (Board of Trade unit.)
Question 5. State the cases in which Ohm’s law is not valid.
Answer: Ohm’s law is not valid for current flowing through gases under low pressure, electrolytes, and semi-conductors.
“Class 10 WBBSE Physical Science Chapter 6, Current Electricity easy explanation”
Question 6. How does the resistance of a conductor depend on the cross-section of the conduction?
Answer: Resistance of the conductor decreases with the increase of cross-section.
Question 7. What is the SI unit of resistance?
Answer: The SI unit of resistance of Ohm.
Question 8. How is the heat generated due to electric current through a resistor related to the strength of the current?
Answer: Heat is directly proportional to square of the current.
Question 9. How is the heat generated due to electric current in a resistor related to the resistance of the resistor?
Answer: Heat is directly proportional to resistance.
Question 10. What is the usual color of a live wire?
Answer: The usual color of a live wire is red.
Question 11. What is the usual color of the earthing wise?
Answer: The usual color of the earthing wire is green
Question 12. What is the emf of a cell?
Answer: The potential difference between the electrodes of a cell in open circuit is called emf. (electromotive force)
Question 13. What is the SI unit of current strength?
Answer: The SI unit of current strength is ampere.
Question 14. What do you mean by relaxation time or mean free time?
Answer: It is the average time interval between the two successive collisions between electron and ion in a conductor.
“WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Chapter 6 solutions, Current Electricity PDF”
Question 15. What is current density?
Answer: It is the current flowing per unit area of a conductor.
Question 16. Illustrate a condition in which the electric field is not zero but the potential is zero.
Answer: The electric field on the equatorial line of an electrical dipole is not zero but the potential is zero.
Question 17. What is meant by the steady current?
Answer: A current whose magnitude does not change with time.
Question 18. What is meant by varying current?
Answer: A current whose magnitude changes with time.
Question 19. What is the emf of a simple voltaic cell?
Answer: The emf of a simple voltaic cell is 1.08 volt.
Question 20. Which effect of electric current is demonstrated in an electro-magnet?
Answer: Magnetic effect.
WB Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer Chapter 6 Current Electricity Fill In The Blanks :
Question 1. Coulomb =____________ × second.
Answer: Ampere.
Question 2. The equivalent resistance is smaller than the ____________ resistance in a parallel combination of resistances.
Answer: Smallest.
Question 3. Power potential difference x ____________
Answer: Current.
Question 4. I2rt is some electrical
Answer: Work.
Question 5. Resistance of a wire is ____________ proportional to the length of the wire.
Answer: Directly.
Question 6. The watt-hour is the practical unit of ____________energy.
Answer: Electrical.
“WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Chapter 6, Current Electricity important questions”
Question 7. Number of B.O.T. unit =\(\frac{\text { ampere } \times \text { volt }}{1000}\) × ____________
Answer: Hour
Question 8. The SI unit of current is ____________
Answer: Ampere
Question 9. When electric current does not change the direction it is called ____________
Answer: Direct current
Question 10. Watt= Volt x ____________
Answer: Ampere
Question 11. The electromagnets are made using the current.
Answer: Magnetic
Question 12. Usually the resistance of a conductor ____________ with the rise in temperature
Answer: Increases effect of electricity with the rise in temperature.
Question 13. In Ohm’s law, the constant ____________ and other physical conditions are remaining
Answer: Temperature
Question 14. The temperature remaining constant, the resistance between two opposite forces of a unit cube of a conductor is called its ____________
Answer: Specific resistance
Question 15. Ohm’s law is related to ____________
Answer: Current and potential difference
Question 16. Specific resistance of a conductor depends on____________
Answer: It’s material
Question 17. The unit of electrical power is ____________
Answer: Watt
Question 18. A ____________ is used to measure the potential difference between two points in a section of an electrical circuit.
Answer: Voltmeter
Question 19. An ammeter is used to measure the ____________ flowing through an electric circuit where the ammeter is connected in series.
Answer: Current
Question 20. A short circuit occurs due to accidental direct contact of the life and the ____________ wires.
Answer: Neutral
“Class 10 Physical Science and Environment Current Electricity solutions, WBBSE syllabus”
Question 21. The total resistance of a number of resistors in series is equal to the ____________ of the resistances of the component resistors.
Answer: Sum
Question 22. Electromotive force is some ____________ not a force.
Answer: Energy.
WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer
Question 23. In current electricity, the potential difference between two points is measured by the work done when unit ____________ flows from one point to the other.
Answer: Change
Question 24. If an electrical instrument of power 1 watt works for 1 hour, the electrical energy expended is known as 1 ____________
Answer: Watt-hour
Question 25. Potential difference between two points one ____________ when work is done to carry one coulomb charge between the points is 1 Joule.
Answer: Volt
Question 26. Resistance is the natural property of every material body by virtue of which the body ____________ flow of electric charge through it.
Answer: Opposes
Question 27. The current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference between its ends when ____________ and other physical conditionsof the conductor remain unaltered.
Answer: Temperature
Question 28. Ohm’s law is not valid for current flowing through ____________ under low pressure, electrolytes and semiconductors.
Answer: Gases
Question 29. The unit for specific resistivity is ____________
Answer: Ohm-cm
Question 30. Electric flux at a point in an electric field is ____________
Answer: Zero
Question 31. The material of a wire of a potentiometer is ____________
Answer: Magnanin
Question 32. Ammeter measures is ____________
Answer: Current
WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer Chapter 6 Current Electricity Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What is the definition of ohm?
Answer:
Ohm: If one-ampere current flowing through a conductor establishes 1-volt potential difference between the two ends of the conductor, the resistance of the conductor is one ohm.
Question 2. What do you mean by potential difference?
Answer:
Potential difference: It is the electrical condition of a point in an electric field or on a current-carrying conductor that indicates whether electrons will flow from it or it from another connected point.
Question 3. What is the definition of resistance from Ohm’s law?
Answer:
Definition of resistance from Ohm’s law : The resistance of a conductor is a ratio of the potential difference between its ends to the current flowing through it.
Question 4. What is the definition of a coulomb?
Answer:
Coulomb:
Coulomb It is the quantity of electric charge that passes through silver nitrate solution deposits 0.00 1118g silver at the cathode.
Question 5. What do you mean by a combination of resistance?
Answer:
Combination of resistance: In different electrical circuits more than resistance are connected together. This is known as a combination of resistance.
“WBBSE Class 10 Chapter 6 Physical Science, Current Electricity step-by-step solutions”
Question 6. What is a voltmeter?
Answer:
Voltmeter: A voltmeter is used to measure the potential difference between two points in a section of an electrical circuit; the voltmeter is connected parallel to the section.
Question 7. Why resistivity is also called specific resistance?
Answer:
Explanation: Resistivity is also called specific resistance as the resistivity of a material is the resistance offered by the material of specified dimensions unit length unit cross-sectional area.
Question 8. What is the internal resistance of a cell?
Answer:
Internal resistance: The small resistance offered by the electrolyte of a cell to the electric charges flowing through it from the negative to the positive plate is known as to the internal resistance of the cell.
Question 9. State ohm’s law.
Answer:
Ohm’s law (1826): The temperature and other physical conditions remaining constant the current flowing between any two points of a conductor is proportional to the potential difference between them.
Question 10. The specific resistance of copper 20°C is 1.6×10-6 ohm-cm, what do you mean by it?
Answer:
Specific resistance: The specific resistance of copper at 20°C is 1.6×10-6 ohm-cm, it means: Resistance across the opposite faces of a copper cube of 1 cm side, at 20°C is 1.6×10 ohm.
Question 11. What is an ammeter? What do you mean by 1-ampere electric charge?
Answer:
Ammetre: The current is measured by an instrument called an ammeter. When I coulomb of charge flows through any cross-section of a conductor in 1 second, the electric current flowing through it is said to be 1 ampere.
Question 12. What do you mean by potential difference?
Answer:
Potential difference: The potential difference between two points in an electric circuit is defined as the amount of work done moving a unit charge from one point to the other point.
Question 13. What is the resistance of a conductor? What do you mean by the 1 ohm resistance of the conductor’?
Answer:
Resistance of conductor: The resistance of a conductor is the ratio of the potential difference across the ends of a conductor to the current flowing through the conductor. The resistance of a conductor is 1 ohm if a potential difference of Ivolt across the end of the conductor makes a current of 1 ampere pass through it.
Question 14. What do you mean by 1-volt potential difference’?
Answer:
Potential difference: The potential difference between two points in an electric circuit is defined as the amount of work done moving a unit charge from one point to the other point.
“WBBSE Class 10 Current Electricity, Physical Science Chapter 6 key concepts”
Question 15. Write the properties of electric charges. The properties of electric changes
Answer: Electric charges:
Properties of Electric changes:
- Like charges repel each other and unlike charges attract each other.
- Electric charge is always conserved.
Question 16. Define-electric current what is the S.I. unit of potential difference? Answer:
Electric current:
- The electric is the flow of electric charges in a conductor such as a metal wine.
- The S.I. unit of potential difference is volt.
Question 17 What do you mean by electric charge? Is electric charge a scalar quantity? Write S.I. unit of electric charge.
Answer:
Electric charge:
- Electric charge is the physical property of a matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field.
- Yes, the electric charge is a scalar quantity.
- The S.I. unit of electric charge is coulomb
Question 18. The define-terminal voltage of the cell. What is the e.m.f of a cell?
Answer: Terminal And E.M.f of a cell
- Terminal voltage of the cell: When the current is drawn from a cell, the cell is in a closed circuit, The potential difference between the electrodes of the cell is called the terminal voltage of the cell.
- E.m.f of a cell: The e.m.f. of a cell is the energy spent our work done per unit charge is taking a unit positive charge around the complete circuit containing the cell, when the circuit is open.
Question 19. What is meant by “The potential at a point is 1 volt”?
Answer:
The potential at a point: The potential at a point is one volt if one joule of work is done in moving one colomb of charge from infinity to that point in an electric field.
Question 20. Define the electromotive force of the cell electromotive force of cell :
Answer:
The electromotive force of cell:
- The work done in carrying a unit positive charge once through a complete circuit is called the electromotive force of the cell.
- The mathematical expression of the electromotive force of the cell: E = V + v.
Question 21. What is the electromotive force?
Answer:
Electromotive force:
- In a cell, the chemical action creates a difference in the concentration of electrons between the electrodes of the cell, which results in to the potential difference between the electrodes called electromotive force.
- When no current is drawn from a cell, the cell is in the open. circuit, the potential difference between the terminals of the cell is the electromotive force of the cell.
Question 22. Define the resistivity of a conductor.
Answer:
The resistivity of a conductor: The resistivity of a conductor is the resistance of the conductor of unit length and unit area of cross-section at a constant pressure.
Question 23. Short Note-Insulator.
Answer:
Insulator: There are substances that are very poor conductors of electricity having very low values of resistivity are called insulators.
Example: Wood, Glass.
Insulators are used to protect us from electric shocks.
Question 24. What is an electromagnet?
Answer:
Electromagnet: If soft iron is kept in a current-carrying solenoid, then that soft iron behaves like a magnet so long as the current passes. This magnet is known as an electromagnet.
Question 25. What is an electric motor?
Answer:
Electric motor:
- The device or machine which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy is known as an electric motor.
- An insulated copper coil, wound over a suitable frame rotates in a magnetic field when electric current passes through the coil.
Question 26. Deduce the mathematical form of Ohm’s law.
Answer:
The mathematical form of Ohm’s law:
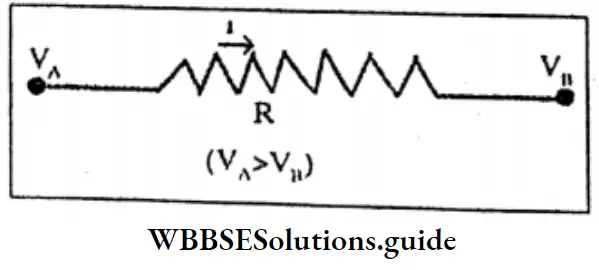
Let VA and VB be the potentials at the ends A and B of the conductor AB respectively.
So, the potential difference between the points is VA – VB = V (say) Now, if current I flows through the conductor,
Then following Ohm’s law, να I or,
V = RI (R = constant, the resistance of conductor)
Or, \(\frac{\mathrm{V}}{\mathrm{I}}\) = R
Question 27. On what factors does the resistance of a conductor depend? Answer:
Factors upon which the resistance of a conductor depends:
1. Effect of length: Temperature, material, and area of cross-sector remaining constant, the resistance (R) of a conductor is proportional to its length
∴ Rα I (When temperature, material, and cross-section are constant)
2. Effect of cross-section: Temperature, material, and length are constant.)
Question 28. Define equivalent resistance.
Answer:
Equivalent resistance: The single resistance, instead of multiple resistance in a circuit, keeps the voltage and current unchanged, which is called the equivalent resistance of those resistances.
Question 29. What is specific resistance?
Answer:
Specific resistance: We know, R α I when A is constant
R α \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{~A}}\) when 1 am constant
When both the length and the area of the cross-section of a conductor very then from the law of joint variation, we can write,
R α \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{~A}}\)
R= ρ \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{~A}}\) (ρ)(rho) is the constant is proportionality and is known as the specific of resistivity]
Now, if 1 = 1 and A = 1, then R = ρ
Specific resistance Definition:
The specific resistance or resistivity of a material is numerically equal to the resistance of a conductor of the material of length 1 meter and area of cross- section 1 m2.
Question 30. Define 1 kilowatt-hour?
Answer:
1 kilowatt-hour
If a machine of 1 kilo-hour operates for one hour the amount of energy spent is known as kilo-watt hour. This amount of energy is also known as the Board of Trade unit (B.O.T. units).
1 K.W.H = \(\frac{1 \text { B.O.T (watt } \times \text { hour })}{1000}\)
= \(\frac{\text { volt } \times \text { ampere } \times \text { hour }}{1000}\)
Question 31. What is watt-hours? Whose unit is it?
Answer:
Watt-hour: If an electrical machine of power one watt operates for one hour then one watt-hour amount of energy is said to be spent.
1 watt-hour = 1 watt x 1 hour = 1 watt x 3600 sec. = 3600 J
The unit of electrical energy is watt-hour.
Question 32. What do you mean by the statement? ‘Potential difference between two points in an electric field is 5 volts’?
Answer:
‘Potential difference between two points in an electric field is 5 volts’
Explanation: ‘Potential difference between two points in an electric field is 5 volts’-this statement means an external agent has to do 5 joules work to carry 1-coulomb positive charge from a point at the lower potential to a point at the higher potential in the electric field.
Question 33. How can the strength of the motor be increased?
Answer:
The strength of an electric motor can be increased by :
- Increasing the current in the armature.
- Increasing the strength of the magnetic field.
- Increasing the number of turns in the armature.
Question 35. What do you mean by series combination?
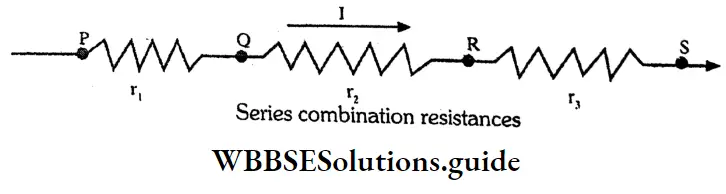
Answer:
Series combination: In this combination, resistances are so connected that extreme end of one resistance is joined to the beginning end of the next resistance soon. In this connection same current. flows through all the resistances.
If three resistors r1, r2, and r3, are connected in series, the same current I passes through each then their equivalent resistance R will be.
R = r1+ r2+ r3
Question 36. What do you mean by parallel combination?
Answer:
Parallel combination:
A number of resistors are said to be connected in parallel when they are placed side by side and their corresponding ends joined together so that the main current is distributed among them. If the individual resistances is parallel combination are r1+ r2+ r3 then their equivalent resistance R is given by
\(\frac{1}{R}=\frac{1}{r_1}+\frac{1}{r_2}+\frac{1}{r_3}\)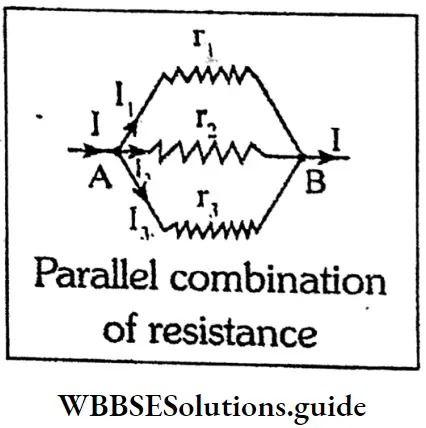
So, to create a low resistance out of a few respectively high resistances, those needed to be connected to a parallel combination. Equiva- lent resistance in parallel combination is lesser than the lowest of the individual resistances.
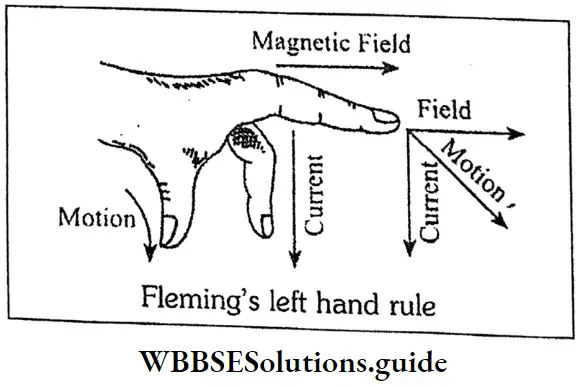
Question 37. State Fleming’s left-hand rule.
Answer:
Fleming’s left-hand rule:
If the thumb, the first finger, and the middle finger of the left hand be held mutually perpendicular to each other in such a way that the first finger points in the direction of the magnetic field and the second finger to that of the current, then the thumb will indicate the direction at motion of the conductor.
Question 38. State Ampere’s swimming rule.
Answer:
Ampere’s swimming rule: If a man is imagined to be swimming along a current carrying wire in the direction of the current (south or north) with his face turned towards a freely rotating magnetic needle, then the north pole of the needle will be deflected towards his left hand.
Question 39. Prove that, I =\(\frac{Q}{t}\)
Answer:
If Q amount of charge blows through a cross-section of a conductor in time t, then the current I is given by
I = \(\frac{Q}{t}\)
Question 40. Prove, VA– VB = \(\frac{W}{q}\)
Answer:
If W be the work done in moving a charge q from point B to point A then the potential difference (VA– VB) between the two points (VA– VB) = \(\frac{W}{q}\)

Question 41. Draw the graph between the current (I) VS potential difference.
Answer:
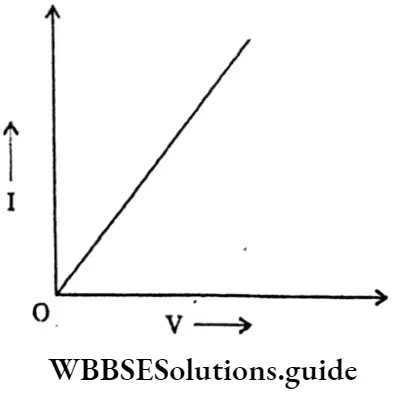
Question 42. What do you mean by conductors?
Answer:
Conductors: The substances which allow an electric current to flow easily through them are called conductors.
- The conductors have low resistance and resistivity. Resistances of conductors increase with the increase of temperature.
- Metals are good conductors of electricity having low volume of resistivity.
- Example: Silver, Copper
Question 43. Draw the graph of the resistivity of the conductor with an increase in temperature in the case of conductors.
Answer:
Graph of the resistivity of the conductor:
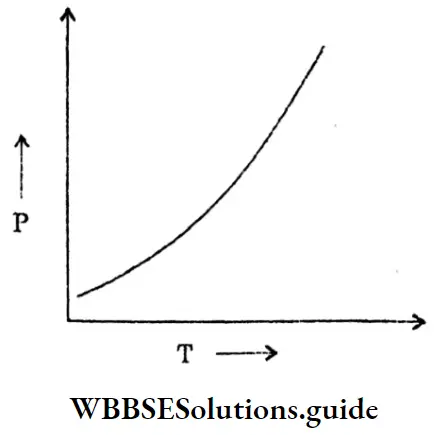
P = Resistivity of the conductor.
T = Temperature.
Question 44.
- Define-electrical power.
- What do you mean by one kilowatt-hour of electrical energy?
Answer:
- Electrical power: Electric power is the amount of electric energy consumed in a circuit per unit of time.
- One kilowatt: One-kilowatt hour is the amount of electric energy consumed by a 1000W electric device when it operates for one hour.
Question 45. What will the resistance of the bulb of 220V-100W?
Answer:
The power rating of (220V-100W) electric bulb means that the resistance of
Its filament while glowing is
R= \(\frac{\mathrm{V}^2}{\mathrm{P}}\)
R= \(\frac{(220)^2}{100}\)
R= 484 Ω
“WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Chapter 6 Current Electricity, definitions and examples”
Question 46. What is meant by earthing?
Answer:
Earthing
Earthing By earthing we mean that the metal body of the appliance is connected to a thick copper wire, which is buried deep in the earth, and its other end is connected to a copper plate surrounded by a mixture of charcoal and common salt.
Question 47. Electric cell as the source of EMF’-Explain.
Answer:
EMF:
- A source of electricity without the presence of active machinery parts is called an electric cell.
- By the transformation of chemical energy to electric energy, an electric cell generates a steady electric current in a current.
Question 48. 1 kilo watt hour = 3.6 x 106 Joule; Prove it.
Answer:
1 kilowatt-hour 1000 watt-hour.
1 watt = 1 Js-1
1 hour (60 × 60) second = 3600 second.
1 kilo watt-hour = 1000 Js–1× 3600 second = 3600000 J.
1 kilo watt-hour = 3.6 x 106 .
Question 49.
- State Lenz’s law.
- Explain Lenz’s law as a consequence of the principle of conservation of energy.
Answer:
Lenz’s law:
- The direction of induced emf in a circuit is such that it always arrases the very cause for which it is due.
- Lenz’s law is a consequence of the principle of conversation of energy. Lenz’s law is a form of the how of conservation of energy i.e., Lenz’s law can be derived from the principle of conservation of energy.
“WBBSE Class 10 Physical Science Chapter 6, Current Electricity summary”
Question 50. Draw the graph between resistivity vs increase in temperature in case on semiconductor.
Answer:
The temperature in case of semiconductors:
![]()
- Presistivity of the conductor
- T= Temperature
Question 51. Draw the graph between the resistivity and temperature in the case of a superconductor.
Answer:
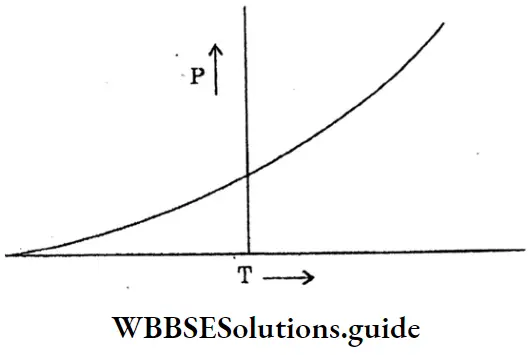
P = Resistivity of the conductor
T = Temperature
