Cubes
Today Sundy and Firoz are making many colourful boxes.
Measuring we see that the length of the box is 1 cm, breadth is 1 cm and height is 1 cm, i.e., each of these boxes is cubical.
Length of each side of this cubical box is 1 cm.
But to make a cubical box of side 3 cm in length,27 small boxes are required.
What shall we call such numbers like 1, 8, 27,?
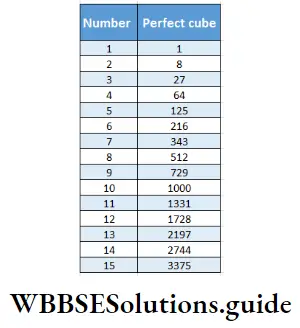
1,8, 27 are called perfect cube numbers because 1 = (1)3, 8
= (2)3, 27 = 33, 8 = 23, 64 = 43, 125 = 53, .
| Class 8 General Science | Class 8 Maths |
| Class 8 History | Class 8 Science LAQs |
| Class 8 Geography | Class 8 Science SAQs |
| Class 8 Maths | Class 8 Geography |
| Class 8 History MCQs | Class 8 History |
i.e., cubes of 1,2, 3, 4, 5, are respectively 1, 8, 27, 64, 125,…
I try to make a cube with 32 cubes of same size:
32 = 2×2×2×2×2
= (2 × 2) x (2 × 2) × 2
= 4×4×4, i.e., 32 ≠ (any integer)3
Read and Learn More WBBSE Solutions For Class 8 Maths
We see, it not possible to make a bic, cube with 32 small cubes. But it is possible to make a big cube with 32×2=64 small cubes. So, 64 is a perfect cube number, i.e., 32 is not a perfect cube number but we get a perfect cube number by multiplying 32 with the smallest positive integer 2 because 64 = 43
Let’s see whether Tatai can make a big cube with 54 small cubes of the same size as above.
54 = 2×3×3×3
We see 54 is a not-perfect cube number (Perfect cube no. / not perfect cube number.)
∴ Is 54? If we divide by the smallest positive integer then we will get perfect cube number. So, 54÷2 = 27 a not perfect cube number Because 27 = 33.
Cubes Exercise
Question 1. Let’s find perfect cube from the following numbers: 125, 500, 64, 73, 729, 968.
Solution:
Given
125, 500, 64, 73, 729, 968.
125 = 53, 64 = 44, 73, 729 = 93
Let’s write perfect cubes in the chart below, making cube from 1 to 20.
See the term from the above chart 9 = 13 + 23, 280= 43+ 63, 1729 = 103+ 103(Let’s make another).
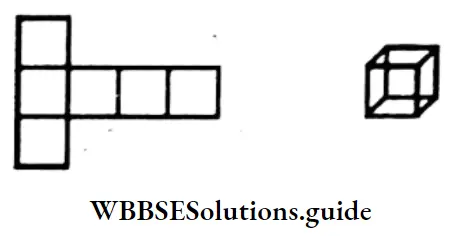
Firoz made many big cubes attaching these small cubes. Suhana and I are measuring the length of each side of cube.
There are 27 small cubes in this big cube.
See, the length of each side of big cube beside the picture is 3 cm. I got differently 27 = 33
What can be termed 3 of 27?
Cubing 3, we get 27.
So the cube root of 27 is 3.
125= 5×5×5=53
“WBBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 5 solutions, Cubes”
∴ \(\sqrt[3]{125}\) = 5
729 = 3×3×3×3×3×3
= 33+33
∴ \(\sqrt[3]{729}\) = 3×3=9
Cubes Exercise
Question 1. Let’s form two cubes with sides of length 5 cm and 1 cm. Let us calculate the number of small cubes to form the big cube.
Solution:
Given
Sides of length 5 cm and 1 cm.
Number of small cubes required to make this big cube = (5)3 = 5 × 5 × 5 = 125
Question 2. Sumanta has made many cubes of 1 cm length. Manami is trying to make big cubes attaching these small cubes. Let’s see in which of the cube given below Manami will be able to make big cubes.
1. 100
Solution:
Given
100 = 2 × 2 × 5 × 5 = 22 × 52
2. 1000
Solution:
Given
1000 = 10 × 10 × 10 = (10)3
∴ \(\sqrt[3]{1000}\) = 10
“Class 8 WBBSE Maths Chapter 5 solutions, Cubes study material”
3. 1331
Solution:
Given
1331 = 11×11×11= (11)3
∴ \(\sqrt[3]{1331}\)=11
4. 324
Solution:
Given
324 = 2×2×3×3×3×3 = (2)2 × (3)2 × (3)2
5. 3375.
Solution:
Given
3375 = 15×15×15 = (15)3
∴ \(\sqrt[3]{3375}\) = 15
6. 1372
Solution:
Given
1372 = 2×2×7×7×7 = 22×73
Question 2. Manami can make a big cube by attaching the following number of small cubes :
Solution:
- 1000,
- 1331
- 3375
Question 3. Let us write number which is not a perfect cube in the numbers given below :
1. 216
Solution:
Given
216 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 x 3
= 23 x 33
= 63
216 = 63
2. 343
Solution:
Given
343 = 7 x 7 x 7
= 73
343 = 73
3. 1024
Solution:
Given
1024 =2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2
= 23×23×23×2
= 83×2
1024 = 83×2
4. 324
Solution:
Given
324 = 2×2×3×3×3×3
= 23 × 33 × 3
324 = 23 × 33 × 3
“WBBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 5, Cubes solved examples”
5. 1744
Solution:
Given
1744 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 109
= 23×2 ×109
1744 = 23×2 ×109
6. 1372
Solution:
Given
1372 = 2 × 2 × 7 × 7 × 7
= 22 × 73
1372 = 22 × 73
The following aren’t perfect cube numbers :
- 1024,
- 324,
- 1744 and
- 1372
Question 4. Dabnath has made a cuboid whose length, breadth, and height are respectively 4 cm, 3 cm, and 3 cm. Let’s see how many cuboids of this type will form a cube.
Solution:
Given
Dabnath has made a cuboid whose length, breadth, and height are respectively 4 cm, 3 cm, and 3 cm.
Length of the cuboid = 4 cm
Breadth = 3 cm.
Height = 3 cm
∴ Number of cuboids required to make the cube = 4×3×3 = 36
Question 5. Let us calculate with which positive smallest number should be multiplied by the numbers below so that the product will be a perfect cube.
1. 675
Solution:
Given
675 = 3 ×3 × 3 × 5 × 5 = 33 × 52
∴ 675 is not a perfect cube number.
But, 33 ×52 × 5 = 33 × 53 = (15)3
= 3375
Multiplying 675 by the smallest positive number 5, the product 3375 will be a perfect cube number.
2. 200
Solution:
Given
200 = 2×2×2×5×5 = 23×52
∴ 200 is not a perfect cube number.
But, 23×52×5 = 23×53=(10)3 = 1000
Multiplying 200 by the smallest positive number 5, the product 1000, will be a perfect cube number.
3.108
Solution:
Given
108 = 3 × 3 × 3 × 2 × 2 = 33 × 22
∴ 108 is not a perfect cube number.
But, 33 × 22×2
= 33 × 23
= (6)3
= 216
∴ Multiplying 108 by the smallest positive number 2, the product 216 will be a perfect cube number.
“WBBSE Class 8 Cubes solutions, Maths Chapter 5”
4. 121.
Solution:
Given
121 = 11 ×11 = (11)2
∴ 121 is not a perfect cube number
But, (11)2 × 11 = (11)3 = 1331
∴ Multiplying 121 by the smallest positive number 11, the product 1331 will be & perfect cube number.
5. 1225
Solution:
Given
1225 = 5×5×7×7 = 52×72
∴ 1225 is not a perfect cube number
But, 52 × 72 × 5 × 7
= 53 × 73
= (35)3
= 42875
∴ Multiplying 1225 by the smallest positive number 35, the product 42875 will be a perfect cube number.
Question 6. Let us calculate with which positive smallest number should the number be divided so that the quotient will be a perfect cube.
1. 7000
Solution:
Given
7000 = 7 × 10 × 10 × 10 = 7 × (10)3
∴ Dividing 7000 by the smallest positive number 7, the quotient will be a perfect cube number.
∴ Required number = 7
2. 2662
Solution:
Given
2662 = 2×11 × 11 × 11 = 2 × (11)3
∴ Dividing 2662 by the smallest positive number 2, the quotient will be a perfect cube number.
∴ Required number = 2
3. 4394
Solution:
Given
4394 = 2 × 13 × 13 × 13 = 2 × (13)3
Dividing 4394 by the smallest positive number 2, the quotient will be a perfect cube number.
Required number = 2
4. 6750
Solution:
Given
6750 = 2 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 5 × 5 × 5 = 2 × 33 × 53
Dividing 6750 by the smallest positive number 2, the quotient will be a perfect cube number.
Required number = 2
“Class 8 WBBSE Maths Chapter 5, Cubes easy explanation”
5. 675
Solution:
Given
675 = 3×3×3×5×5 = 33×52
Dividing 675 by the smallest positive number 25, the quotient will be a perfect cube number.
Required number = 25
Question 7. Let us write the number below as product of prime factors and write the cube roots of the numbers.
1. 512
Solution:
Given
512 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2
The cube root of 512
= 23 × 23 × 23 = 83
∴ \(\sqrt[3]{512}\) = 8
The cube root of 512 = 8
2. 1728
Solution:
Given
1728 = 2×2×2×2×2×2×3×3×3
= 23×23×33
=(12)3
∴ \(\sqrt[3]{1728}\)= 12
The cube root of 1728 = 12
3. 5832
Solution:
Given
5832 = 2×2×2×3×3×3×3×3×3
= 23× 33×33=(18)3
∴ \(\sqrt[3]{5832}\)= 18
The cube root of 5832 = 18
4. 15625
Solution:
Given
15625 = 5×5×5×5×5×5
= 53×53 = (25)3
∴ \(\sqrt[3]{15625}\) = 25
The cube root of 15625 = 25
5. 10648
Solution:
Given
10648 = 2×2×2×11×11×11
= 23× 113= (22)3
∴ \(\sqrt[3]{10648}\) = 2
After measuring we see that the length of a side of this cubical box is 12 cm. ‘
∴ Volume = 123 cc. = 1728 cc.
Question 8. If the length of a side of the cubical box was x cm, then the volume was = (x cm)3 = x3 cc. If the length of a side of the cubical box was (x + 2) cm, then the volume of the box was = (x + 2)3 cm.
Solution:
Given
If the length of a side of the cubical box was x cm, then the volume was = (x cm)3 = x3 cc. If the length of a side of the cubical box was (x + 2) cm, then the volume of the box was = (x + 2)3 cm
Let us see what we get after expanding (x + 2)3.
(x + 2)3 = (x + 2) x (x + 2)2
= (x + 2) {x2 + 4x + 4} [with the help of identity (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2]
= (x + 2) x2 + (x + 2) 4x + (x + 2) 4 [with the help of Distributive Law]
= x3+ 2x2 + 4×2+ 8x + 4x + 8 [with the help of associative] law]
= x3+ 6x2 + 12x + 8
Titli wrote the length of a side of this cube as (a + b) cm.
∴ The volume of this cube is (a + b)3 cc.
= (a + b)3 = (a + b) (a + b)2
= (a + b) × a2 + 2ab + b2
= (a + b) x a2 + (a + b) 2ab + (a + b) b2 [Distributive Law]
= a3 + b2a + 2a2b + 2ab2 + ab2 + b3 [Distributive Law]
= a3 + ab2 + 2a2b + 2ab2 + ab2 + b3 [b2a = ab2, by commutative Law of Multiplication.]
= a3 + 3a2b + 3ab2 + b3
We get (a + b)3 = a3 + 3a2b + 3ab2 + b3
(a + b)3 = a3 + 3a2b + 3ab2 + b3
= a3 + 3ab (a + b) + b3
We got with the help of commutative & distributive laws (a + b)3 = a3+ b3 + 3ab (a + b)
1. (2y + 3)3 (Let’s expand).
Solution:
Given (2y + 3)3
= (2y)3 + 3 (2y)3 3 + 3.2y. (3)3 + (3)3 there a =2y b = 3
(2y + 3)3 = (2y)3 + 3 (2y)3 3 + 3.2y. (3)3 + (3)3
2. (15)3
Solution:
Given (15)3
= (10+5)3
= 3375
(15)3 = 3375
3. (101)3
Solution:
Given (101)3
= (100+1)
= (100+1)
= 1030301
(101)3 = 1030301
“WBBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 5 solutions, Cubes PDF”
4. (210)
Solution:
Given (210)
= (200+10)3
= 9261000
(210) = 9261000
5. If the length of one side of the cube is = (a – b) cm, we get,
Solution:
The volume of the cube = (a – b)3 cc
(a – b)3 Let’s see by expanding
(a – b)3 = {a + (- b)}3 = a3 + 3 (a2) (-b) + 3a (-b)2 + (-b)3
(a – b)3 = a3 – 3a3b + 3ab2 – b3
With the help of identity no.3, I expand
6. (99)3 and find the value of it.
Solution:
Given (99)3
= (100 – 1)3
= (100)3 – 3 (100)2 x 1 + 3 x 100 x (1 )2 – (1 )3
= 970299
(99)3 = 970299
Question 9. If x – \(\frac{1}{9 x}\)= 1 then find the value of 27×3 – \(\frac{1}{27 x^3}\)
Solution:
= \(x-\frac{1}{9 x}=1\)
or, \(3\left(x-\frac{1}{9 x}\right)\) = 1×3(Multiplying both sides by 3)
or,\(3 x-\frac{1}{3 x}\) = 3
or,\(\left(3 x-\frac{1}{3 x}\right)^3\) = 3 (Cubing both sides)
or,\(27 x^3-\frac{1}{27 x^3}-3 \times 3 x \times \frac{1}{3 x}\left(3 x-\frac{1}{3 x}\right)\) = 27
or,\(27 x^3-\frac{1}{27 y^3}-3 \times 3\) = 27
∴ \(27 x^3-\frac{1}{27 x^3}\) = 36
Question 10. Let us solve the questions below with the help of identities from I to IV.
1. If x – y = 2 then find the value of x3 – y3 – 6xy.
Solution:
Given x – y = 2
x3 – y3 – 6xy = x3 – y3 – 3xy.2 = x3 – y3 – 3xy (x – y)
= (x – y)3.
= (2)3
= 8
The value of x3 – y3 – 6xy = 8
2. If a + b = – -then prove that a3+ b3 – ab = \((a+b)^3-3 a b(a+b)-a b\)
Solution:
Given a3+ b3 – ab = \((a+b)^3-3 a b(a+b)-a b\)
L.H.S. = a3 + b3 – ab .
= (a + b)3 – 3ab (a + b) – ab
a3+ b3 – ab = (a + b)3 – 3ab (a + b) – ab
= R.H.S. Proved
3. If x + y = 2 and \(\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{y}=2\) then find the value of x3 + y3.
Solution:
Given
x + y = 2 and \(\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{y}=2\)
= \(\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{y}=2\)
= \(\frac{y+x}{x y}\) =2
= \(\frac{x+y}{x y}\) = 2
or, \(\frac{2}{x y}\)= 2
or, xy = 1
= x3 + y3
= (x + y)3 – 3xy (x + y)
= (2)3 – 3×1 x 2
= 8-6
= 2
The value of x3 + y3 = 2
4. If \(\frac{x^2-1}{x}\) = 2 then find the value of \(\frac{x^6-1}{x^3}\)
Solution:
Given
\(\frac{x^2-1}{x}\) = 2
= \(\frac{x^2-1}{x}=2\)
or, \(\frac{x^2}{x}-\frac{1}{x}=2\)
or,\(x-\frac{1}{x}=2\)
∴ \(\frac{x^6-1}{x^3}\)
= \(\frac{x^6}{x^3}-\frac{1}{x^3}\)
= \(x^3-\frac{1}{x^3}\)
= \((x)^3-\left(\frac{1}{x}\right)^3\)
= \(\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)^3+3 \cdot x \cdot \frac{1}{x}\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)\)
= (2)3 + 3x2
= 8 + 6
= 14
The value of \(\frac{x^6-1}{x^3}\) = 14
“WBBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 5, Cubes important questions”
5. If x + \(\frac{1}{x}\) = 5 then find the value of x³ + \(\frac{1}{x^3}\)
Solution:
Given
x + \(\frac{1}{x}\) = 5
= \(x+\frac{1}{x}=5\)
= \(x^3+\frac{1}{x^3}\)
= \((x)^3+\left(\frac{1}{x}\right)^3\)
= \(\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)^3-3 \cdot x \cdot \frac{1}{x}\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\)
= (5)3-3×5
= 125-15
=110
The value of x³ + \(\frac{1}{x^3}\) =110
6. If x = y + z then find the value of x3– y3– 3xyz.
Solution:
Given
x = y + z
= x – y = z
= (x – y)3 = (z)3 (Cubing both sides)
= x3– y3– 3xy (x – y) = z3
= x3– y3 – 3xy.z = z3 (∴x – y = z)
= x3– y3 – 3xy.z=0
The value of x3– y3– 3xyz =0
“Class 8 Maths Cubes solutions, WBBSE syllabus”
7. If xy ( x + y) = m then prove that x3+ y3+ 3m =\(\frac{m^3}{x^3 y^3}\)
Solution:
Given xy ( x + y) = m
xy ( x + y) = m
= x + y=\(\frac{m}{x y}[latex]
= [latex](x+y)^3=\left(\frac{m}{x y}\right)^3\)
= \(x^3+y^3+3 x y(x+y)=\frac{m^3}{x^3 y^3}\)
= \(x^3+y^3+3 x y \cdot \frac{m}{x y}=\frac{m^3}{x^3 y^3}\)
= \(x^3+y^3+3 m=\frac{m^3}{x^3 y^3}\)
Proved.
8. If 2x + \(\frac{1}{3 x}\) = 4 then prove that 27x3 + \(\frac{1}{8 x^3}\) = 189.
Solution:
Given
2x + \(\frac{1}{3 x}\) = 4
= \(2 x+\frac{1}{3 x}=4\)
= \(\frac{3}{2}\left(2 x+\frac{1}{3 x}\right)=\frac{3}{2} \times 4\)(Multiplying sides by \(\frac{3}{2}\)
= \(3 x+\frac{1}{2 x}=6\)
= \(\left(3 x+\frac{1}{2 x}\right)^3=(6)^3\)(Cubing both sides)
= \((3 x)^3+\left(\frac{1}{2 x}\right)^3+3.3 x \frac{1}{2 x}\left(3 x+\frac{1}{2 x}\right)=216\)
= \(27 x^3 \frac{1}{8 x^3}+\frac{9}{2} x 6=216\)
= \(27 x^3+\frac{1}{8 x^3}=216-27\)
= \(27 x^3+\frac{1}{8 x^3}=189\)
Proved.
9. If 2a-\(\frac{2}{a}\)+1=0 then find the value of \(a^3-\frac{1}{a^3}+2\)
Solution:
Given
2a-\(\frac{2}{a}\)+1=0
= \(2 a-\frac{2}{a}+1=0\)
or, \(2\left(a-\frac{1}{a}\right)=-1\)
or, \(a-\frac{1}{a}=-\frac{1}{2}\)
∴ \(a^3-\frac{1}{a^3}+2\)
= \((a)^3-\left(\frac{1}{a}\right)^3+2\)
= \(\left(a-\frac{1}{a}\right)^3+3 \cdot a \cdot \frac{1}{a}\left(a-\frac{1}{a}\right)+2\)
= \(\left(-\frac{1}{2}\right)^3+3\left(-\frac{1}{2}\right)+2\)
= \(\left(-\frac{1}{2}\right)^3+3\left(-\frac{1}{2}\right)+2\)
= \(-\frac{1}{8}-\frac{3}{2}+2\)
= \(\frac{-1-12+16}{8}\)
= \(\frac{3}{8}\)
The value of \(a^3-\frac{1}{a^3}+2\) = \(\frac{3}{8}\)
10. a3+b3+c3 = 3abc then find the value of (a+b+c). Given (a≠b≠c).
Solution:
Given a3+b3+c3 = 3abc
or, (a+b)3-3ab(a+b)+c3=3abc
or, (a+b)3+c3-3ab(a+b)-3abc=0
or, (a+b+c){(a+b)2-(a+b)c+(c)2}=0
or, (a+b+c) (a2+2ab+b2-ac-bc+c2-3ab)=0
or, (a+b+c) (a2+b2+c2-ab-ac-ac)=0
∵ The product of both expressions is zero.
∵ At least one of the expressions is zero.
∵ Here a≠b≠c
∵ a+b+c=0
The value of (a+b+c) =0
11. If m+n=5 and mn=6 then find the value of (m2+n2)(m3+n3).
Solution:
Given m+n=5 and mn= 6
(m2+n2) (m3+n3)
= {(m+n)-2mn}{(m+n)3-3mn(m+n)}
= {(5)2-2×6}{(5)3-3×6×5}
= (25-12) (125-90)
= 13×35
= 455
The value of (m2+n2)(m3+n3) = 455
Question 11. Let’s multiply with the help of identity no.5
1. (7 + 3x) (49 – 21 x + 9x2)
Solution:
Given (7 + 3x) (49 – 21 x + 9x2)
= (7 + 3x) (49 – 21 x + 9x2)
= (7 + 3x) {(7)2 – 7 x 3x + (3x)2}
= (7)3 + (3x)3
= 343 + 27x3
(7 + 3x) (49 – 21 x + 9x2) = 343 + 27x3
2. (x2 + y²) (x4 – x2y2 + y4)
Solution:
Given (x2 + y2) (x4 – x2y2 + y4)
(x2+y2){(x2)2-x2y2+(y2)2}
= (x2)3+(y2)3
= x6+y6
(x2 + y2) (x4 – x2y2 + y4) = x6+y6
Question 12. Let’s try to factorize the following algebraic expression with the help of identity no. V
1. p3q3 + 1
Solution:
Given p3q3 + 1
= p3q3 + 1
= (pq)3 + (1)3
= pq+1×p2q2-pq+1
p3q3 + 1 = pq+1×p2q2-pq+1
Question 13. Let’s find the product of the following algebraic expression with the help of identity no. VI
1. (p – 2q) (p2 + 2pq + 4q2)
Solution:
Given (p – 2q) (p2 + 2pq + 4q2)
= (p – 2q) (p2 + 2pq + 4q2)
= (P – 2q) {p2+ p x 2q + (2q)2}
= (p)3 – (2q)3 [ By identity no. V ]
= (p)3-8q3
(p – 2q) (p2 + 2pq + 4q2) = (p)3-8q3
2. (x2 – 1) (x4 + x2 + 1)
Solution:
Given (x2 – 1) (x4 + x2 + 1)
= (x2 – 1) {(x2)2 + x2 x 1 + 12}
= ((x2)3-(1)3)
= x6-1
(x2 – 1) (x4 + x2 + 1) = x6-1
3. 2x {(4x – 3)2 + (4x – 3) (2x – 3) + (2x – 3)2}
Solution:
Given 2x {(4x – 3)2 + (4x – 3) (2x – 3) + (2x – 3)2}
= {(4x – 3) – (2x – 3)} {(4x – 3)2 + (4x – 3) + (2x – 3)2}
[Since : (4x – 3) – (2x – 3)} = 4x – 3 – 2x + 3 = 2x]
Let 4x – 3 = a and 2x – 3 = b = (a – b) {a2 + ab + b2}
= a3 – b3 [ With the help of identity no. VI]
= (4x – 3)3– (2x -3)3 [By replacing a = 4x – 3 and b = 2x – 3]
= {(4x)3 – 3.(4x)2 x 3+3.4x.33-(3)3}-{(2x)3-3(2x)2 3+3 x 2x x 32.33}
= 64x3 – 144x2 + 108x – 27 – {8x3 – 36x2 + 54x – 27}
= 56x3 – 108x2 + 54x
2x {(4x – 3)2 + (4x – 3) (2x – 3) + (2x – 3)2} = 56x3 – 108x2 + 54x
“WBBSE Class 8 Chapter 5 Maths, Cubes step-by-step solutions”
Question 14. Let’s factorize the following algebraic expressions with the help of identity no. VI
1. 64 I3 – 343
Solution:
Given 64 I3 – 343
= (4l)3-(7)3
= (4l-7)×(16l2+28l+49)
64 I3 – 343 = (4l-7)×(16l2+28l+49)
2. (x+2)3-(x-2)3
Solution:
Given (x+2)3-(x-2)3
= {(x + 2) – (x – 2)} {(x + 2)2 + (x + 2) (x – 2) + (x – 2)2}
= (x + 2 – x + 2) {x2 + 4x + 4 + x2 – 4x + 4}
= 4x3x2+4
(x+2)3-(x-2)3 = 4x3x2+4
Question 15. Let’s factorize the following algebraic expressions with the help of identity no. 4
1. 8m3 + 12m2n + 6mn2 + 2n3
Solution:
Given 8m3 + 12m2n + 6mn2 + 2n3
= (2m)3 + 3(2m)2 n+3.2mn2 + n3 + n3
= (2m + n)3 + n3
= 2m + 2n x
8m3 + 12m2n + 6mn2 + 2n3 = 2m + 2n x
2. a3 – 9b3 + (a + b)3
Solution:
Given a3 – 9b3 + (a + b)3
= a3 – b3 – 8b3 + (a + b)3
= a3 – b3+ x(a + b)3 – (2b)3
= (a – b) (a2 + ab + b2)+(a + b – 2b)x{(a + b)2 + 2b(a + b)+4b2}
= (a – b) (a2 + ab + b2 + a2 + 2ab + b2 – 2ab – 2b2 + 4b2}
= (a – b)×(2a2+ab+4b2)
a3+b3=a+b×a2+ab+b2)
a3-b3=(a-b)×(a2-ab+b2)
a3 – 9b3 + (a + b)3 = (a – b)×(2a2+ab+4b2)
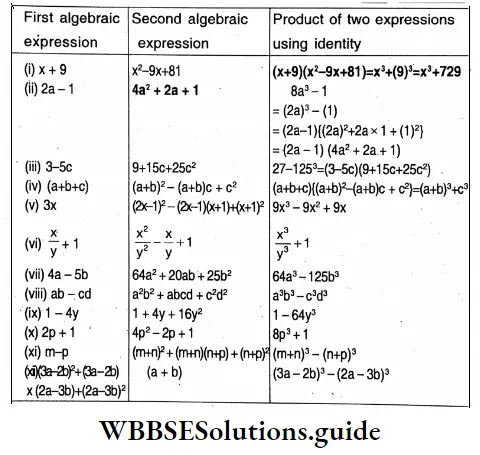
Let’s simplify using formula :
1. (a + b) (a – b) (a2 + ab + b2) (a2 – ab + b2)
Solution:
Given (a + b) (a – b) (a2 + ab + b2) (a2 – ab + b2)
= (a + b) (a2 – ab + b2) (a – b) (a2 + ab + b2)
= (a3+b3) (a3-b3)
= (a3)2-(b3)2 = a6 – b6
(a + b) (a – b) (a2 + ab + b2) (a2 – ab + b2) = a6 – b6
2. (a – 2b) (a2 + 2ab + 4b2) (a³ + 8b³)
Solution:
Given (a – 2b) (a2 + 2ab + 4b2) (a³ + 8b³)
= (a – 2b) {(a)2 + a. 2b + (2b)2} (a3 + 8b3)
= {(a)3 – (2b)3} (a3 + 8b3) = (a3-8b3) (a3 + 8b3)
= (a3)2 – (8b3)2
= a6 – 64b6
(a – 2b) (a2 + 2ab + 4b2) (a3 + 8b3) = a6 – 64b6
“WBBSE Maths Class 8 Cubes, Chapter 5 key concepts”
3. (4a2 – 9) (4a2 – 6a + 9) (4a2 + 6a + 9)
Solution:
Given (4a2 – 9) (4a2 – 6a + 9) (4a2 + 6a + 9)
= {(2a)2 – (3)2} (4a2 – 6a + 9) (4a2 + 6a + 9)
= (2a + 3) (2a – 3) (4a2 – 6a + 9) (4a2 + 6a + 9)
= (2a + 3) {(2a)2 – 2a.3 + (3)2} (2a – 3) {(2a)2 + 2a.3 + (3)2}
= {(2a)3 + (3)3} {(2a)3 – (3)3} .
= (8a3 + 27) (8a3 – 27)
= (8a3)2 – (27)2
= 64a6-729
(4a2 – 9) (4a2 – 6a + 9) (4a2 + 6a + 9) = 64a6-729
4. (x-y) (x2+xy+y2) + (y-z) (y2+yz+z2) + (z-x) (z2+zx+x2)
Solution:
Given (x-y) (x2+xy+y2) + (y-z) (y2+yz+z2) + (z-x) (z2+zx+x2)
= x3 – y3 + y3 – z3 + z3 – x3 = 0
(x-y) (x2+xy+y2) + (y-z) (y2+yz+z2) + (z-x) (z2+zx+x2) = 0
5. (x+1) (x2-x+1) + (2x-1) (4x2+2x+1 )-(x-1) (x2+x+1)
Solution:
Given (x+1) (x2-x+1) + (2x-1) (4x2+2x+1 )-(x-1) (x2+x+1)
= (x)3 + (1 )3 + (2x)3 – (1 )3 (x)3 – (1 )3}
= x3 + 1 + 8x3 – 1- (x3 – 1)
= 9x3 – x3 + 1
= 8x3+ 1
(x+1) (x2-x+1) + (2x-1) (4x2+2x+1 )-(x-1) (x2+x+1) = 8x3+ 1
6. If x + \(\frac{1}{x}\)= -1 then find the value of (x3 – 1).
Solution:
Given x + \(\frac{1}{x}\)= -1
\(\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right) x=-1(x)\)x2+x+1=0[by transposition]
x3-1
or, (x-)x × x2+x+1
=(x-1)×0=0
The value of (x3 – 1)=0
7. If a + \(\frac{9}{a}\)= 3 then find the value of (a3 + 27).
Solution:
Given a + \(\frac{9}{a}\)= 3
or, \(\frac{a^2+9}{a}\) = 3
or, a2+9=3a
or, a2 – 3a + 9 = 0
= a3+ 27 = (a)3+ (3)3
= (a + 3) {(a)2 – a.3 + (3)2}
= (a + 3) (a2 – 3a + 9)
= (a + 3) x 0 = 0
The value of (a³ + 27) = 0
8. If \(\frac{a}{b}+\frac{b}{a}\)= 1 then find the value of (a3 + b3).
Solution:
Given \(\frac{a}{b}+\frac{b}{a}\)= 1
= \(\frac{a}{b}+\frac{b}{a}\)= 1
= \(\frac{a^2+b^2}{a b}=1\)
a2 +b2=ab
or, a2-ab+b2= 0
∴ a3 + b3
= (a + b) (a2 – ab + b2)
= (a + b) x 0 = 0
The value of (a³ + b³) = 0
9. Let’s factorize the following algebraic expressions :
1. 1000a3+ 27b6
Solution:
Given 1000a3+ 27b6
= (10a)3 + (3b2)3
= (10a + 3b2) {(10a)2 – 10a.3b2 + (3b2)2}
= (10a + 3b2) (100a2 – 30ab2 + 9b4)
1000a3+ 27b6 = (10a + 3b2) (100a2 – 30ab2 + 9b4)
2. 1-216z3.
Solution:
Given 1-216z3
=(1)3-(6z)3
= (1- 6z) {(1)2 + 1.6z + (6z)2}
= (1-6z) (1 + 6z + 36z2)
1-216z3 = (1-6z) (1 + 6z + 36z2)
3. m4-m
Solution:
Given m4-m
= m (m3 – 1)
= m{(m)3-(1)3}
= m (m-1) (m2 + m + 1)
m4-m = m (m-1) (m2 + m + 1)
4. 192a3 + 3
Solution:
Given 192a3 + 3
= 3 (64a3 + 1)
= 3 {(4a)3 + (1)3}
= 3 (4a + 1) {(4a)2 – 4a. 1 + (1)2}
= 3 (4a+ 1) (16a2-4a + 1)
192a3 + 3 = 3 (4a+ 1) (16a2-4a + 1)
“WBBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 5, Cubes summary”
5. 16a4x33 + 54ay3
Solution:
Given 16a4x33 + 54ay3
= 2a (8a3x3 + 27y3)
= 2a {(2ax)3 + (3y)3}
= 2a (2ax + 3y) {(2ax)2 – 2ax.3y + (3y)2}
= 2a (2ax + 3y) (4a2x2 – 6axy + 9y2)
16a4x33 + 54ay3 = 2a (2ax + 3y) (4a2x2 – 6axy + 9y2)
6. 729a3b3c3 – 125
Solution:
Given 729a3b3c3 – 125
= (9abc)3 – (5)3
= (9abc – 5) {(9abc)2 + 9abc.5 + (5)2}
= (9abc – 5) (81a2b2c2 + 45abc + 25)
729a3b3c3 – 125 = (9abc – 5) (81a2b2c2 + 45abc + 25)
7. \(\frac{27}{a^3}-\frac{1}{27 b^3}\)
Solution:
Given \(\frac{27}{a^3}-\frac{1}{27 b^3}\)
⇒ \(\left(\frac{3}{a}\right)^3-\left(\frac{1}{3 b}\right)^3 \)
⇒ \(\left(\frac{3}{a}-\frac{1}{3 b}\right)\left\{\left(\frac{3}{a}\right)^2+\frac{3}{a} \cdot \frac{1}{3 b}+\left(\frac{1}{3 b}\right)^2\right\} \)
⇒ \(\left(\frac{3}{a}-\frac{1}{3 b}\right)\left(\frac{9}{a^2}+\frac{1}{a b}+\frac{1}{9 b^2}\right)\)
\(\frac{27}{a^3}-\frac{1}{27 b^3}\)= \(\left(\frac{3}{a}-\frac{1}{3 b}\right)\left(\frac{9}{a^2}+\frac{1}{a b}+\frac{1}{9 b^2}\right)\)
8. \(\frac{x^3}{64}-\frac{64}{x^3}\)
Solution:
Given \(\frac{x^3}{64}-\frac{64}{x^3}\)
⇒ \(\left(\frac{x}{4}\right)^3-\left(\frac{4}{x}\right)^3\)
⇒ \( \left(\frac{x}{4}-\frac{4}{x}\right)\left\{\left(\frac{x}{4}\right)^2+\frac{x}{4} \cdot \frac{4}{x}+\left(\frac{4}{x}\right)^2\right\} \)
⇒\( \left(\frac{x}{4}-\frac{4}{x}\right)\left\{\left(\frac{x}{4}\right)^2+2 \cdot \frac{x}{4} \cdot \frac{4}{x}+\left(\frac{4}{x}\right)^2-\frac{x}{4} \cdot \frac{4}{x}\right\} \)
⇒ \(\left(\frac{x}{4}-\frac{4}{x}\right)\left\{\left(\frac{x}{4}+\frac{4}{x}\right)^2-1\right\} \)
⇒ \( \left(\frac{x}{4}-\frac{4}{x}\right)\left\{\left(\frac{x}{4}+\frac{4}{x}\right)^2-(1)^2\right\} \)
⇒ \(\left(\frac{x}{4}-\frac{4}{x}\right)\left(\frac{x}{4}+\frac{4}{x}+1\right)\left(\frac{x}{4}+\frac{4}{x}-1\right)\)
\(\frac{x^3}{64}-\frac{64}{x^3}\)= \(\left(\frac{x}{4}-\frac{4}{x}\right)\left(\frac{x}{4}+\frac{4}{x}+1\right)\left(\frac{x}{4}+\frac{4}{x}-1\right)\)
9. x3 + 3x2y + 3xy2 + 2y3
Solution:
Given x3 + 3x2y + 3xy2 + 2y3
= x3 + 3x2y + 3xy2 + y3 + y3
= (x + y)3 + y3
= (x + y + y) {(x + y)2 – (x + y) y + (y)2}
= (x + 2y) (x2 + 2xy + y2– xy – y2 + y2)
= (x + 2y) (x2 + xy + y2)
x3 + 3x2y + 3xy2 + 2y3 = (x + 2y) (x2 + xy + y2)
10. 1 + 9x + 27x2 + 28x3
Solution:
Given 1 + 9x + 27x2 + 28x3
= 1 + 9x + 27x2 + 27x3 + x3 .
= (1)3 + 3.(1 )2 .3x + 3.1. (3x)2 + (3x)3 + x3
= (1 + 3x)3 + (x)3
= (1 + 3x + x) {(1 + 3x)2 – (1 + 3x) x + (x)2}
= (1 + 4x) (1 + 6x + 9x2 – x – 3x2 + x2)
= (1 + 4x) (1 + 5x + 7x2)
1 + 9x + 27x2 + 28x3 = (1 + 4x) (1 + 5x + 7x2)
11. x3 – 9y3 – 3xy (x – y)
Solution:
Given x3 – 9y3 – 3xy (x – y)
= x3 – 9y3 – 3x2y + 3xy2
= x2 – 3x2y + 3xy2 – y3 – 8y3
= (x – y)3– (2y)3
= (x – y – 2y) {(x-y)2 + (x-y) 2y + (2y)2}
= (x-3y) (x2 – 2xy + y2 + 2xy – 2y2 + 4y2)
= (x – 3y) (x2 + 3y2)
x3 – 9y3 – 3xy (x – y) = (x – 3y) (x2 + 3y2)
12. 8-a3 + 3a2b – 3ab2 + b3
Solution:
Given 8-a3 + 3a2b – 3ab2 + b3
= 8- (a3 – 3a2b + 3ab2 – b3)
= (2)3 – (a – b)3
= {2 – (a -b)}{(2)2 + 2(a – b) + (a-b)2}
= (2 – a + b) (4 + 2a – 2b + a2 – 2ab + b2)
8-a3 + 3a2b – 3ab2 + b3 = (2 – a + b) (4 + 2a – 2b + a2 – 2ab + b2)
13. x6 + 3x4b2 + 3x2b4 + b6 + a3b3
Solution:
Given x6 + 3x4b2 + 3x2b4 + b6 + a3b3
= (x2)3+ 3.(x2)2.b2 + 3.x2.(b2)2 + (b2)3 + a3b3
= (x2 + b2)3 + (ab)3
= (x2 + b2 + ab) {(x2 + b2)2 – (x2 + b2) ab + (ab)2}
= (x2 + b2 + ab) (x4 + 2x2b2 + b4 – x2ab – ab3 + a2b2)
= (x2 + ab + b2) (x4 + 2x2b2 – abx2 + a2b2 – ab3 + b4)
x6 + 3x4b2 + 3x2b4 + b6 + a3b3 = (x2 + ab + b2) (x4 + 2x2b2 – abx2 + a2b2 – ab3 + b4)
14. x6+27
Solution:
Given x6+27
= (x2)3 + (3)3
= (x2 + 3) {(x2)2 – x2.3 + (3)2}
= (x2 + 3) (x4 – 3x2 +9)
x6+27 = (x2 + 3) (x4 – 3x2 +9)
15. x6 – y6
Solution:
Given x6 – y6
= (x3)2 – (y3)2 = (x3 + y3) (x3 – y3)
= (x + y) (x2 – xy + y2) (x – y) (x2 + xy + y2)
= (x + y) (x – y) (x2 – xy + y2) (x2 + xy + y2)
x6 – y6 = (x + y) (x – y) (x2 – xy + y2) (x2 + xy + y2)
16. x12– y
Solution:
Given x12– y
= (x6)2 – (y6)2
= (x6 + y6) (x6 – y6)
= {(x2)3+(y2)3} {(x3)2 – (y3)2}
= (x2 + y2) {(x2)2– x2.y2 + (y2)2} (x3 + y3) (x3 – y3)
= (x2+ y2) (x4– x2y2 + y4) (x + y).(x2– xy + y2) (x-y) (x2 + xy + y2)
= (x + y) (x – y) (x2 + y2) (x2 – xy + y2) (x2 + xy + y2) (x4 – x2y2 + y4)
x12– y = (x + y) (x – y) (x2 + y2) (x2 – xy + y2) (x2 + xy + y2) (x4 – x2y2 + y4)
“WBBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 5 Cubes, definitions and examples”
17. m3 – n3 – m (m2 – n2) + n(m – n)
Solution:
Given m3 – n3 – m (m2 – n2) + n(m – n)
= (m-n) (m2+mn+n2) -m(m+n) (m-n) +n(m-n)(m-n)
= (m-n) (ref + rpfi + rf – ryf – rprfi + mn -rf) –
= (m-n) mn = mn (m-n)
m3 – n3 – m (m2 – n2) + n(m – n) = mn (m-n)
