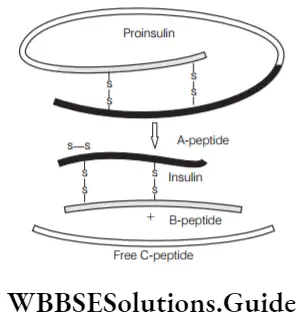
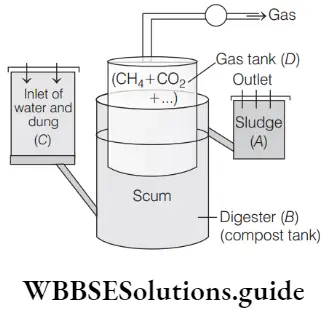
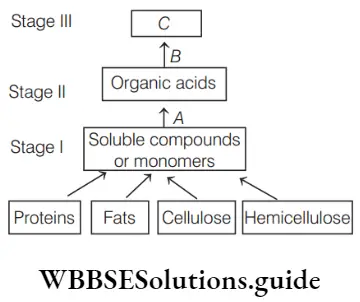
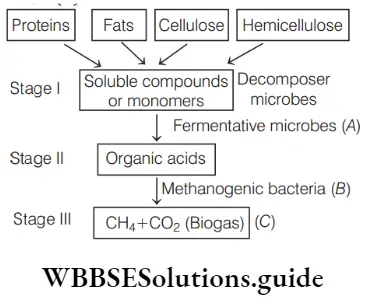
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET Transgenic Animals And Ethical Issues
Question 1. Multicellular organisms that carry a specific genetic change in each cell because of an intervention at the embryo level are a
- Transversion
- Transition
- Transgenic
- Transformant
Answer: 3. Transgenic
A multicellular organism that carries a specific genetic change in each cell because of an intervention at the fertilized egg stage is transgenic.
Question 2. The maximum number of existing transgenic animals is of
- Fish
- Mice
- Cow
- Pig
Answer: 2. Mice
In the world, a maximum number of existing transgenic animals are mice.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 3. The first transgenic mouse grew twice the normal size after drinking water containing ……….
- Cu
- Fe
- Zn
- Ra
Answer: 3. Zn
- In 1974, Rudolf Jaenisch created a transgenic mouse by introducing foreign DNA into its embryo, making it the world’s first transgenic animal. When the transgenic mice were a few weeks old, they were given drinking water containing zinc (Zn).
- Mice carrying the transgene grew to twice the size of their litter mates because the metallothionein enhancer sequence stimulated by zinc has increased growth hormone production.
what is transgenic animals class 12
Question 4. The transgenic animals are those which have
- Foreign RNA in all its cells
- Foreign dna in some of its cells
- Foreign dna in all its cells
- Both (1) and (3)
Answer: 3. Foreign dna in all its cells
Transgenic animals are those which have foreign DNA in all their cells.
Question 5. Transgenesis is useful in which of the following?
- To understand the development of disease.
- To test the newly discovered vaccine.
- To test the safety of chemicals.
- To understand the mechanism of regulation of genes.
Choose the correct option.
- Only 1
- 2 And 3
- Only 4
- 1, 2, 3 And 4
Answer: 4. 1, 2, 3 And 4
All the given statements are useful in transgenesis. Thus, option (4) is correct.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET

NEET Biology transgenic animals MCQs with answers
Question 6. Transgenic animals are produced by injecting foreign genes into the
- Egg
- The nucleus of an unfertilized egg
- The nucleus of a fertilized egg
- Nucleus of sperm
Answer: 3. Nucleus of fertilized egg
Transgenic animals are produced by injecting a foreign gene into the nucleus of a fertilized egg. This fertilized egg divides mitotically to form the whole organism so that all the cells of the organism will carry the transferred gene. The transferred genes are known as transgenes.
Question 7. The introduction of transgenes will result in
- The formation of a new species
- The formation of a new protein
- Altering a biosynthetic pathway
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer: 4. Both (2) and (3)
The introduction of transgenes will result in the formation of a new protein and the altering of a biosynthetic pathway. Thus, option (4) is correct.
“what are transgenic animals class 12 “
Question 8. Which transgenic animal is the polio vaccine tested on for safety purposes before administering to humans?
- Transgenic cow
- Transgenic monkey
- Transgenic mice
- Transgenic sheep
Answer: 3. Transgenic mice
Transgenic mice are developed to test the safety of the polio vaccine before being used on humans.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 9. Mice are the preferred choice for transgenesis because
- They have a short generation time
- A superovulated mouse can yield up to 40 eggs
- Reimplantation is relatively easy
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
All given options are the preferred choice for transgenesis in mice. Thus, option (4) is correct.
Transgenic animals and ethical issues multiple choice questions for NEET
Question 10. The giant mouse is produced by
- Gene manipulation
- Gene cloning
- Gene mutation
- Gene duplication
Answer: 1. Gene manipulation
- The first example of foreign transfer into an animal by rDNA was the insertion and expression of a rat gene, the Metallothionein (MT) gene for growth hormone in mice.
- It resulted in larger progeny than the parents and the transgenic mouse was called a ‘super (giant) mouse’. So, the giant mouse is produced by gene manipulation.
Question 11. ‘Rosie’ a transgenic animal is known to produce a type of milk which
- Has a protein content of 2.4 g/l.
- Has human α-lactalbumin.
- Is more nutritionally balanced for human babies than natural cow milk.
Which of the above statements is correct?
- 1 And 2
- 1 And 3
- 2 And 3
- 1, 2 And 3
Answer: 4. 1, 2 And 3
All given statements are correct. In 1997, the first transgenic cow, Rosie produced human protein-enriched milk (2.4 g/L). The milk contained the human α-lactalbumin and was more nutritionally balanced for human babies than natural cow milk. Thus, option (4) is correct.
“what are transgenic animals class 12 “
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 12. Which gene was introduced in the first transgenic cow?
- Human α-lactalbumin
- Β-1-antitrypsin
- Α-1-antitrypsin
- Cryl ac
Answer: 1. Human α-lactalbumin
The gene for human alpha (α) lactalbumin was introduced into the genes of the first transgenic cow, which made the milk nutritionally richer.
Question 13. Consider the following statements about ‘Rosie’.
- Rosie is the first transgenic sheep.
- Rosie produced human protein-enriched milk.
- The milk contained the human α-lactalbumin and scientist behind the research believes that the milk from the cow could provide an alternative to human breast milk.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1 And 2
- 1 And 3
- 2 And 3
- 1, 2 And 3
Answer: 3. 2 And 3
Statements 2 and 3 are correct whereas statement I is incorrect because. Rosie is a transgenic cow, not sheep.
Important transgenic animals questions for NEET Biology
Question 14. Transgenic animals are produced for
- To study normal physiology and development.
- To study diseases.
- To obtain useful biological products.
- To test the vaccine safety.
- To test the chemical safety.
Which of the above statements is correct?
- 1, 2 And 3
- 2, 3 And 4
- 1, 2, 3 And 5
- 1, 2, 3, 4 And 5
Answer: 4. 1, 2, 3, 4 And 5
(4) All given statements are correct.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 15. Which property of transgenic animals is used in chemical safety testing?
- Insensitivity to toxic substances
- Sensitivity to a toxic substance
- Resistance to a toxic substance
- Both (1) and (3)
Answer: 2. Sensitivity to a toxic substance
The property of sensitivity to toxic substances is used in chemical safety testing. Transgenic animals are useful as disease models and producers of substances for human welfare.
Question 16. In transgenics, the expression of the transgene in the target tissue is determined by
- Enhancer
- Trans gene
- Promoter
- Reporter
Answer: 4. Reporter
When plant cells are transformed by any of the transformation methods, it is necessary to isolate the transformed cells/tissue. There are certain selectable marker genes present in vectors that facilitate the selection process. These marker genes are reporter genes.
“what are transgenic animals class 12 “
Question 17. Today, transgenic models have been developed to cure many human diseases, such as
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Cancer
- Cystic fibrosis
Choose the correct option.
- 1 And 2
- 2 And 4
- 1, 2 And 4
- 1, 2, 3 And 4
Answer: 4. 1, 2, 3 And 4
Transgenic models have been developed for many human diseases like cancer, cystic fibrosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and Alzheimer’s disease. Thus, option (4) is correct.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 18. Consider the following statements.
- Transgenic animals are more sensitive to toxic substances than non-transgenic animals.
- Useful biological products can be produced by introducing a portion of dna into transgenic animals which codes for a particular product.
- Brazzein is a protein produced by a West African plant, pentadiplandra brazen which is approximately 2000 times as sweet as sugar.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
- 1, 2 And 3
- 1 And 2
- 1 And 3
- None of these
Answer: 1. 1, 2 And 3
All given statements are correct.
- Transgenic animals are made to carry genes that make them more sensitive to toxic substances than non-transgenic animals.
- Useful biological products can be produced by introducing the portion of DNA (genes) into transgenic animals which code for a particular product, for example. human protein (α-1-antitrypsin) is used to treat emphysema.
- Brazzein is a protein produced by a West African plant, Pentadiplandra brazen, which is approximately 2000 times as sweet as sugar. It is used as a low-calorie sweetener.
Thus, option (1) is correct.
Solved MCQs on genetic engineering in animals for NEET
Question 19. A regulatory body working under Moef for the release of transgenic crops is
- Nbpgr
- Geac
- Nsc
- Nipgr
Answer: 2. Geac
GEAC is the regulatory body working under MOEF for the release of transgenic crops, i.e. GEAC–Genetic Engineering Approval Committee MOEF–Ministry of Environment and Forest
“what are transgenic animals class 12 “
Question 20. In India, research in genetic modification of organisms and safety issues are controlled by
- Debt
- Cari
- Csir
- Geac
Answer: 4. Geac
In India, research in genetic modification of organisms and safety issues are controlled by GEAC.
Question 21. Which step has been taken by the government of India to cater to the requirements of patent terms and other emergency provisions in this regard?
- Passing the biopiracy act
- Passing the Indian patents bill
- Forming the gear
- Passing the bioethics act
Answer: 2. Passing the Indian patents bill
Some nations are developing laws to prevent unauthorized exploitation of their bioresearch and traditional knowledge. To check these problems, the Indian parliament has recently cleared the second amendment of the Indian Patents Bill that takes such issues into consideration.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 22. The laws and rules to prevent una
- Biopatenting
- Bioethics
- Bioengineering
- Biopiracy
Answer: 1. Biopatenting
A monopoly granted to a person who has either invented a new and useful article made improvements in an existing article, or invented a new process of making an article is called biopatent. It prevents unauthorized exploitation of bioresources.
Applications of transgenic animals NEET MCQs with answers
Question 23. Which of the following statements about biopatents is/are correct?
- Biopatents protect the intellectual property rights of an inventor.
- Biopatents of all products are subjected to commercialization.
- Biopatents should be granted carefully and impartially.
- Biopatenting requires the examination of legal, ethical, and social issues.
Choose the correct option.
- Only 2
- 1, 3 And 4
- 2 And 4
- 1, 2, 3 And 4
Answer: 2. 1, 3 And 4
All given statements are correct about biopatents except 2. Biopatent is a patent granted by the government to the inventor for biological entities and for products obtained from them. These are not always for commercialization, but some are for scientific research benefits.
Question 24. Consider the following statements about the responsibility of geac.
- Geac takes decisions regarding the validity of the gm research.
- It checks the safety of introducing gm organisms to public services for their large-scale use.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
The aim and objectives of GEAC are
- To permit the use of GM organisms and their products for commercial applications.
- To adopt the procedures for restriction, production scale, import, export, and application of GM organisms.
- Approval to conduct large-scale field trials and release of transgenic crops in the environment.
- To authorize agencies or persons to have large-scale production and the release of GM organisms into the environment or curb and take punitive action against them.
“what are transgenic animals class 12 “
Question 25. Which variety of rice was patented by our company even though the highest number of varieties of this rice is found in India?
- Basmati
- Parmal
- Lerma roja
- Co-668
Answer: 1. Basmati
Basmati rice is distinct for its aroma and flavour and 27 documented varieties of Basmati are grown in India. In 1997, an American company obtained patent rights on Basmati rice through the US Patent and Trademark Office. This allowed the company to sell a new variety of Basmati in the US and abroad.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 26. Biopatent means
- Right to use an invention
- Right to use biological resources
- Right to use applications
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer: 1. Right to use an invention
Biopatent is government protection for an inventor of biological material, securing to him for a specific time the exclusive right of manufacturing, exploiting, using, and selling an invention.
Question 27. Biopatent can be awarded for
- Strains of microorganisms, cell lines, genetically modified organisms
- Dna sequences and proteins encoded by them
- Biotechnological procedures, processes, products, and product applications
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
A biopatent is a patent granted by the government to the inventor for biological entities, processes, and products. A patent gives the owner exclusive rights to use the resource, process, or market the product and earn profits. Thus, option (4) is correct.
Question 28. …A… varieties of basmati rice, known for its aroma and flavor, are cultivated in …b….
- A-27, b-America
- A-30, b-America
- A-27, b-india
- A-30, b-india
Answer: 3. A-27, b-india
Basmati is unique for its aroma and flavor, whose 27 (A) varieties are cultivated in India (B).
Best multiple choice questions on transgenic animals for NEET preparation
Question 29. How many varieties of rice are estimated to be present in India?
- 2200
- 20,000
- 200,000
- 2000000
Answer: 3. 200,000
Rice is being used for thousands of years in Asia’s agricultural history of which 200,000 varieties are in India alone.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 30. Choose the correct statements about basmati rice.
- In 1997, an American company got patent rights for basmati rice through the us patent and trademark office and was allowed to sell a ‘new variety’ in the us and abroad.
- This new variety of basmati was derived from Chinese farmers’ varieties.
- Indian basmati was crossed with semidwarf varieties and claimed as an invention or a novelty.
Which of the above statements is correct?
- 1 And 2
- 1 And 3
- 2 And 3
- 1, 2 And 3
Answer: 2. 1 And 3
All statements are correct except 2. The incorrect statement can be corrected as The new variety of Basmati rice was derived from Indian farmers’ varieties.
Question 31. Which Indian plants have either been patented or attempts have been made to patent them by other nations for their use?
- Basmati rice
- Turmeric
- Neem
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
The patents have been taken out on the plants such as Basmati rice (Oryza sativa), black pepper (Piper nigrum), pomegranate (Punica granatum), Indian mustard (Brassica campestris), turmeric (Curcuma longa) and neem (Azadirachta India). US, Japanese and German companies are the principal patenting pirates.
Thus, option (4) is correct.
Question 32. Rules of conduct that are used to regulate activities with respect to the biological world are called
- Bioethics
- Bioware
- Biopiracy
- Biopatent
Answer: 1. Bioethics
Rules of conduct that may be used to regulate our activities in relation to the biological world are called bioethics.
Question 33. The use of bioresources by multinational companies and organizations without authorization from the concerned country and its people is called
- Bioinfringement
- Bioexploitation
- Biodegradation
- Biopiracy
Answer: 4. Biopiracy
Biopiracy is the term used for the unlawful exploitation of bioresources by multinational companies and othe organizations without proper authorization from the countries and people concerned with compensatory payment.
NEET Biology ethical issues in biotechnology MCQs
Question 34. Which of the following statement(s) is true?
- Bioware is the use of biological weapons against humans, crops, and animals.
- Bioethics is the unauthorized use of bioresources and traditional knowledge related to bioresources for commercial benefits.
- Biopatent is the exploitation of bioresources from other nations without proper authorization.
Choose the correct option.
- Only 2
- Only 1
- 1 And 2
- 1 And 3
- 2 and 3
Answer: 2. Only 1
Statement 1 is true whereas statements 2 and 3 are false. Incorrect statements can be corrected as
- Rules of conduct that may be used to regulate our activities in relation to the biological world are called bioethics.
- A patent is a right granted by the government to an inventor to prevent others to make commercial use of one’s invention. It is known as biopatent.
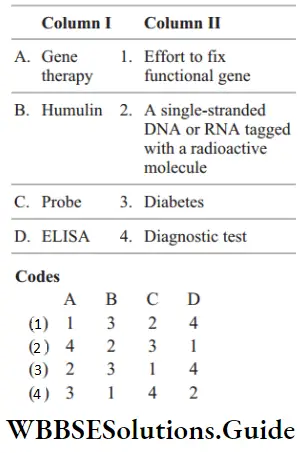
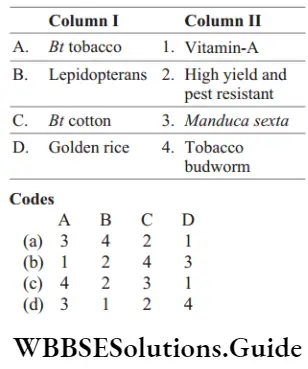
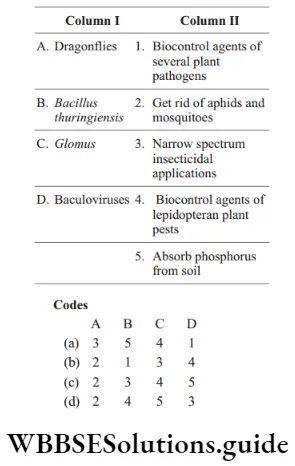
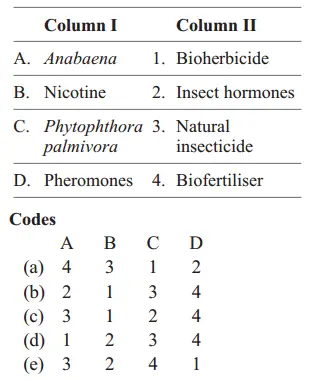
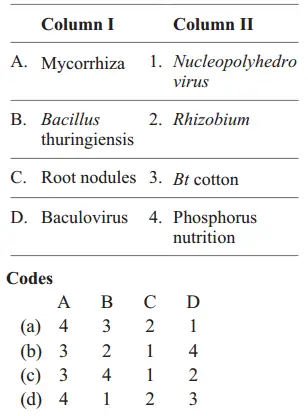
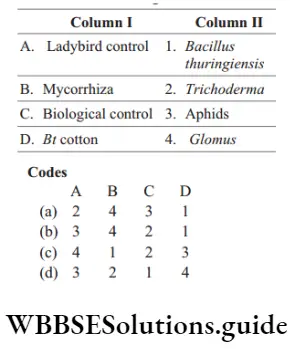
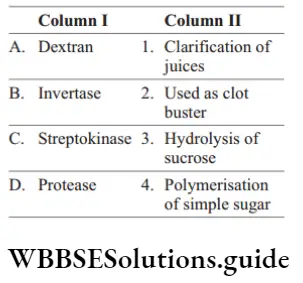
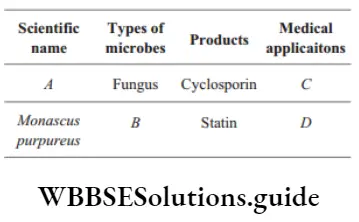
Question 35. Match the following columns.
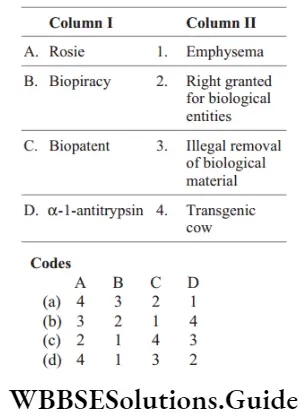
Answer: 1. A–4, B–3, C–2, D–1
Question 36. Which of the following has been covered under the broad patent category?
- Triticum
- Oryza
- Pisum sativum
- Brassica
Answer: 2. Oryza
Oryza has been covered under the broad patent category.
Question 37. The most widely used bioweapon is
- Bacillus subtilis
- Pseudomonas putida
- Bacillus anthracis
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Bacillus anthracis
- Biowar or biological war is the misuse of biological organisms (bioweapons) against human or their crops and animals, for example.
- In World War-I, Germany used anthrax and bacterial diseases to infect sheep. Bioterrorism occurred in the USA in 2000 through the use of spores of the anthrax bacterium, Bacillus anthracis.