Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers Greenhouse Effect, Global Warming and Ozone Depletion
Question 1. Earth’s climate
- Has Been Stable Over The History Of The Planet
- Is Changing As A Result Of Natural And Human Processes
- Will Stabilise Over The Next Century, According To The Predictions Of Most Scientists
- Has been documented to have changed once due to the evolution of green photosynthesising plants
Answer: 2. Is Changing As A Result Of Natural And Human Processes
Earth’s climate is changing as a result of natural and human processes.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 2. …………………… is defined as the natural phenomenon of warming of the earth’s surface due to certain gases in the atmosphere.
- Global warming
- Ozone depletion
- Greenhouse effect
- El Nino effect
Answer: 3. Greenhouse effect
the most potent greenhouse gas in terms of efficiency is
Greenhouse gases are those gases, which are transparent to solar radiation, but retain and partially reflect back long-wave heat radiations CFCs, CO2, CH4 and NO2 are greenhouse gases. The phenomenon of keeping the earth warm due to the presence of these gases in the atmosphere is called the greenhouse effect.
Question 3. The climate of the world is threatened by
- Increasing Concentration Of Atmospheric Oxygen
- Decreasing Amount Of Atmospheric Oxygen
- Increasing Amount Of Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide
- Decreasing the amount of atmospheric carbon dioxide
Answer: 3. Increasing Amount Of Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide
The increase in the level of greenhouse gases (e.g. CO2, CH4, CFC, N2O, etc.) has led to the considerable heating of the earth’s surface leading to global warming. The relative contributions of various greenhouse gases to global warming are CO2 (60%) > CH4 (20%) > CFC (14%) >N2O(6%).
Thus, option 3 is correct.

NEET Biology Greenhouse Effect, Global Warming, and Ozone Depletion MCQs with Answers
Question 4. What keeps the atmosphere around Earth warm?
- Warm air cannot escape, as in a greenhouse
- Molecules in the atmosphere absorb reflected radiations from the earth and retain that heat
- Fossil fuels release heat
- Plants release CO2 which is a warm gas
Answer: 2. Molecules in the atmosphere absorb reflected radiations from the earth and retain that heat
The atmosphere around the earth is warmed because molecules in the atmosphere are warmed by radiation from the earth and retain that heat.
Question 5. The greenhouse effect is warming due to
- Infrared Rays Reaching Earth
- Moisture Layer In Atmosphere
- Increase In Temperature Due To Increase In Carbon Dioxide Concentration Of Atmosphere
- The ozone layer of the atmosphere
Answer: 3. Increase In Temperature Due To Increase In Carbon Dioxide Concentration In the Atmosphere
The greenhouse effect refers to the absorption of the sun’s radiations by atmospheric gases like carbon dioxide and the trapping of these radiations within the atmosphere. These are subsequently reflected on the earth’s surface and cause an increase in the global temperature called global warming. Infrared radiation reaching the world will not increase the temperature or moisture layer in the atmosphere. Thus, does not show the greenhouse effect. The ozone layer in the atmosphere absorbs the UV within the stratosphere so that they do not reach the earth’s surface.
“which of the following is not a major greenhouse gas “
Thus, option 3 is correct.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 6. What would be the average temperature on Earth assuming that there is no greenhouse effect occurring?
- 15°C
- –18ºC
- –6°C
- No change will be seen
Answer: 2. –18ºC
If there is no greenhouse effect, the average temperature at the surface of the earth would have been –18°C.
Question 7. The greenhouse effect has the following functional gases
- Transparent To Emission From Earth Surface For Passage To Outer Space
- Transparent To Both Solar And Long Wave Radiations From Earth
- Absorption Of Long Wave Radiations From Earth
- Absorption of polar radiations for warming the atmosphere
Answer: 3. Transparent To Both Solar And Long Wave Radiations From Earth
The reduction of the surface long-wave radioactive flux drives the greenhouse effect. Greenhouse gases, such as methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (NO2), water vapour (HO2) and carbon dioxide (CO2), absorb certain wavelengths of OLR (outgoing longwave radiation), preventing the thermal radiation from reaching space, adding heat to the atmosphere.
Important MCQs on Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change for NEET
Question 8. Which of the following is true for greenhouse gases?
- It is essential for respiration
- It is responsible for global warming
- It is responsible for the cooling of the climate
- It protects ozone
Answer: 2. It is responsible for global warming
Option 1 is true for global warming. Greenhouse gas is responsible for global warming. The phenomenon is similar to that of a greenhouse in which the glass-enclosed atmosphere gets heated up due to its insulation from the rest of the environment. Hence, global warming is also known as the greenhouse effect and the gases responsible for it are called greenhouse gases.
“which of the following is a greenhouse gas “
Question 9. The given diagram represents the greenhouse effect. Four points are marked in the diagram (1, 2, 3 and 4). Identify the option that correctly describes any one of these.
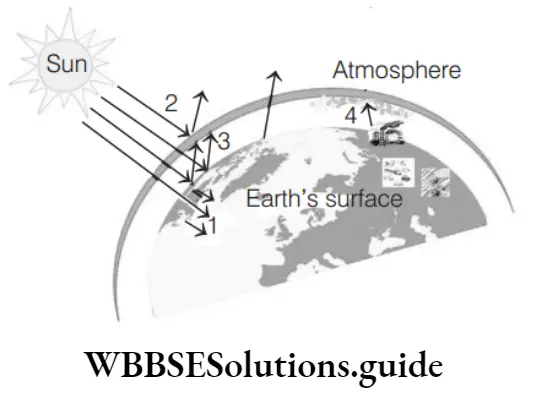
- 1 – The solar radiations pass over the earth but do not enter
- 2 – Radiations collide with the asteroid belt and are reflected away from the surface
- 3 – UV radiations emitted by plants keep the Earth warm
- 4 – Human activities release greenhouse gases that trap heat energy and increase the earth’s temperature
Answer: 4. 4 – Human activities release greenhouse gases that trap heat energy and increase the earth’s temperature
Question 10. Rise in temperature leads to deleterious changes in the environment resulting in odd climatic changes called
- Global Warming
- El Nino
- La Nina
- Greenhouse effect
Answer: 2. El Nino
The temperature of the earth has increased by 0.6º C in the last three decades, which will lead to changes in precipitation patterns. A rise in temperature leads to deleterious changes in the environment resulting in odd climatic changes called El Nino effect. The rise in temperature will lead to the increased melting of polar ice caps which will cause the rise in sea level and many coastal areas will be submerged.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 11. El Nino effect is closely associated with
- Global Warming
- Acid Rain
- Greenhouse Gases
- Tsunami
Answer: 1. Global Warming
El Nino effect is closely associated with global warming. Rise in temperature leads to deleterious changes in the environment and results in odd climatic changes.
Question 12. During the past 150 years, the concentration of CO2 has increased approximately from
- 200 ppm to 300 ppm
- 120 ppm to 280 ppm
- 280 ppm to 370 ppm
- 350 ppm to 450 ppm
Answer: 3. 280 ppm to 370 ppm
During past 150 years, the concentration of carbon dioxide has enormously increased from 280 ppm to about 370 ppm. This is because of more industrialisation, increased emission of exhaust gases, combustion of fossil fuels, deforestation, etc.
Causes and Consequences of Global Warming MCQs for NEET
Question 13. Checking of re-radiating heat by atmospheric dust, O3, CO2 and water vapours is
- Greenhouse Effect
- Solar Effect
- Ozone Layer Effect
- Global warming
Answer: 1. Greenhouse Effect
“which of the following are greenhouse gases “
Checking of re-radiating heat by atmospheric dust, ozone (O3), CO2 and water vapours is greenhouse effect. The sunlight that reaches the earth warms both atmosphere and the earth surface. The earth’s atmospheric system then radiates the heat as infrared radiation. Water vapour and several other gases, including carbon dioxide, methane and CFCs, warm the earth’s atmosphere because they absorb and re-emit radiation. This is called the greenhouse effect.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 14. The greenhouse effect was coined by
- Fourier
- Tansley
- Arrhenius
- Odum
Answer: 3. Arrhenius
Svante Arrhenius was a Swedish scientist who was first to claim in 1896 that fossil fuel combustion may eventually result in enhanced global warming. He proposed a relation between atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration and temperature. He found that the average surface temperature of the earth is about 15°C because of the infrared absorption capacity of water vapour and carbon dioxide. This is called natural greenhouse effect.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 15. Assertion Global warming (greenhouse effect) occurs due to the penetrability of low wavelength radiation through ozone layer. Reason (R) CFC is a greenhouse gas which results in the impenetrability of long wavelength radiation through CO2 of the atmosphere.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. The greenhouse effect refers to circumstances, where the short wavelength of visible light from the sun pass through a transparent medium and are absorbed, but the longer wavelength of the infrared re-radiation from the heated objects are unable to pass through that medium. The trapping of the long wavelength radiation leads to more heating and a higher resultant temperature. The CHNO2, ozone, CFC strongly absorbs infrared and does not allow as much of it to escape into space.
Question 16. The consequences of global warming.
- The average global temperature has increased almost by 0.6°C is last three decades, which will lead to change in precipitation patterns.
- Rise in temperature will lead to increased melting of polar ice caps leading to the rise in sea level and many coastal areas will be submerged.
- Warmer temperatures will intensify weed growth and eruption of diseases and pests, thus decreasing crop productivity.
Choose the correct option.
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer: 4. 1,2, and 3
- All the given statements are consequences of global warming.
- Global warming will raise the sea level due to the thermal expansion of sea water and the melting of glaciers and green land ice sheets.
- Global warming will lead to explosive growth of weeds, increased incidence of plant diseases and pest as well as increased basal rate of respiration in plants.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 17. Global warming has adverse effects on
- Terrestrial Life
- Aquatic Life
- Agriculture
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
All of the given options show adverse effect of global warming.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 18. Identify the inappropriate approach towards reducing global warming.
- Limiting the use of fossil fuels
- Increasing vegetation cover for utilisation of CO2
- Minimise use of nitrogen fertilisers in agriculture
- Increase the use of air conditioners and refrigeration unit
Answer: 4. Increase the use of air conditioners and refrigeration unit
‘Global warming’ is the warming/heating up of earth’s atmosphere due to depletion of ‘ozone’ in the stratosphere. Major pollutants responsible for this depletion are Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons. CFCs are widely used as coolants in air conditioners, refrigerators, cleaning solvents, aerosol propellants and in foam insulation. So, decreasing the use of air conditioners, jet planes, greenhouse gases, etc., or developing the substitutes of CFCs will help to reduce global warming.
“which of the following effect is responsible for global warming “
Question 19. The molecular action of ultraviolet light is mainly reflected through
- Photodynamic Action
- Destruction Of Hydrogen Bonds Between Dna Strands
- Formation Of Pyridine
- Destruction of ester bonds
Answer: 2. Destruction Of Hydrogen Bonds Between Dna Strands
UV rays are highly injurious to living organisms since DNA and proteins of living organisms preferentially absorb UV rays and its high energy breaks the chemical bond of hydrogen within there molecule UV-B damage DNA and mutation may occur. They cause ageing of the skin, damage to skin cells and various types of skin cancer.
Question 20. Global warming can be controlled by
- Reducing Deforestation
- Planting Trees (Afforestation)
- Slowing Down The Growth Of Human Population
- Reduction Of Emission Of Greenhouse Gases Into The Atmosphere
- Cutting down the use of fossil fuels
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
- 2, 3, 4 and 5
- 1, 3, 5 and 4
- 1, 2, 4 and 5
Answer: 4. 1,2,4, and 5
All statements are correct except 3 because an Increase in the level of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere causes a rise in the global mean temperature, called as global warming. Strategies for reducing global warming are
- Reducing deforestation
- Plantation
- Reduction of emission of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere
- Cutting down the use of fossil fuels
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 21. A major contribution to greenhouse gases is from
- Germany
- USA
- Pakistan
- New Zealand
Answer: 2. USA
According to Holmes et. al. (1933), the USA is responsible for the largest portion of man-made contributions to the greenhouse effect (21%), followed by Russia (14%), European countries (14%), India (4%) and the rest of the world (36%).
“which of the following effect is responsible for global warming “
Question 22. The CO2 content in the atmospheric air is about
- 0.034%
- 0.34%
- 3.34%
- 6.5%
Answer: 1. 0.034%
The content of CO2 in atmospheric air is 0.034%. The main contributors to air are N2 and O2.
Question 23. CO2 increases atmospheric temperature as a result of
- Ozone Depletion
- Greenhouse Effect
- Blackman Effect
- Global warming
Answer: 4. Global warming
An increase in CO2 concentration leads to the formation of a thick layer of CO2 which functions as a glass panel of a greenhouse that prevents the heat from being re-radiated out of the earth’s surface which increases the temperature of the earth is called global warming.
Topic-wise Greenhouse Effect and Ozone Depletion MCQs for NEET with Explanation
Question 24. The greenhouse effect is the cumulative result of the influence of certain gases. Identify the gas which is not involved in this influence.
- Methane
- Chlorofluorocarbon
- Carbon dioxide
- Nitrogen
Answer: 4. Nitrogen
Nitrogen is not involved in the greenhouse effect. The relative contributions of various greenhouse gases to global warming are CO2, CH4, CFC, and NO2.
Question 25. An increase in the percentage of fauna and a decrease in flora may be dangerous because it enhances
- Percentage Of CO2 Up
- Percentage Of Radioactive Fallout
- Percentage Of O2
- Percentage of diseases
Answer: 1. Percentage Of CP2 Up
Because the increase in the percentage of fauna (animals) will increase the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere and the decrease in flora (plants) will decreasethe utilisation of CO2 via photosynthesis thereby increasing the percentage of CO2 in the atmosphere.
Question 26. Which of the following produces the least of the greenhouse effect?
- Water vapour
- Carbon dioxide
- Hydrogen gas
- Ozone
Answer: 1. Water vapour
Greenhouse gases that occur both naturally and from human activities include water vapour, carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (NO2 ) and ozone (O3 ).
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 27. CO2, CH4, H2O and CFCs are called greenhouse gases because they can absorb
- Ultraviolet Radiations
- Long Wave Infrared Radiations
- Visible Light Radiations
- Radiations
Answer: 2. Long Wave Infrared Radiations
The greenhouse gases are called so because they absorb the long wave infrared radiation reflected from earth surface and trap them such that they do not get reflected back to space. This trapping of long wave infrared radiation cause an increase in the temperature of the atmosphere called global warming.
Question 28. The trace gas which is produced in rice fields and is associated with global warming is
- Methane
- Carbon Dioxide
- Hydrogen Sulphide
- Chlorine
Answer: 1. Methane
Methane gas which is also called marsh or trace gas is produced in the paddy (rice) fields due to the decay of garbage, aquatic, vegetation, etc. Carbon dioxide, methane and chlorofluorocarbons are associated with global warming. They warm the earth’s atmosphere because they absorb and re-emit radiations.
Question 29. Which important greenhouse gas other than methane is being produced from the agricultural fields?
- Sulphur dioxide
- Ammonia
- Nitrous oxide
- Arsine
Answer: 3. Nitrous oxide
Some of the important greenhouse gases are CO2, CFCs, nitrous oxide, ozone, methane, etc. Nitrous oxide is produced by denitrifying bacteria acting on artificial fertilisers applied to poorly aerated soil.
Question 30. Which of the following would most likely help to slow down the greenhouse effect?
- Converting tropical forests into grazing land for cattle
- Ensuring that all excess paper packaging is burned to ashes
- Redesigning landfill dumps to allow methane to be collected
- Promoting the use of private rather than public transport
Answer: 3. Redesigning landfill dumps to allow methane to be collected
Redesigning landfill dumps to allow methane to be collected helps to slow down the greenhouse effect.
NEET Biology MCQ Chapter Wise
Question 31. Which one of the following gases contributes maximum to the ‘greenhouse effect’ on the earth?
- Carbon dioxide
- Chlorofluorocarbon
- Freon
- Methane
Answer: 1. Carbon dioxide
Due to excessive combustion activity, the content of CO2 in the atmosphere has been steadily rising. As carbon dioxide accumulates in the atmosphere, it absorbs more and more of the reflected infrared radiation. This could cause an increase in temperature referred to as the greenhouse effect. Other options are explained as Methane also causes the greenhouse effect, but comparatively lesser than CO2. Chlorofluorocarbons and freon cause the depletion of ozone layers.
Question 32. Carbon dioxide is called a greenhouse gas because it is
- Used In Greenhouse To Increase Plant Growth
- Transparent To Heat, But Traps Sunlight
- Transparent To Sunlight, But Traps Heat
- Transparent to both sunlight and heat
Answer: 3. Transparent To Sunlight, But Traps Heat
The excess amount of CO2 forms a thick ‘blanket’ in the atmosphere which is transparent to sunlight but absorbs infrared radiation trapping heat near the earth’s surface. In this way, due to the CO2 blanket, the earth’s atmosphere works very much like a greenhouse which causes a warming up of the interior. So, carbon dioxide is called a greenhouse gas.
Question 33. CO2, CH4, NO2 and CFCs are called greenhouse gases because they absorb and emit
- UV rays
- Heat rays
- X-rays
- Gamma rays
Answer: 2. Heat rays
The gases responsible for the greenhouse effect are CO2 CH4, NO2, CFCs, etc. The earth’s atmosphere with a high concentration of greenhouse gases is transparent to incoming short-wave solar radiations but absorbs outgoing long-wave infrared radiations, particularly the earth’s thermal radiation (heat rays), trapping heat near the earth’s surface. In this way, the earth’s atmosphere works very much like a greenhouse by warming the interior.
NEET Biology Role of Greenhouse Gases in Climate Change MCQs
Question 34. Identify the greenhouse gases A, B, C and D and their percentage makeup in the atmosphere.
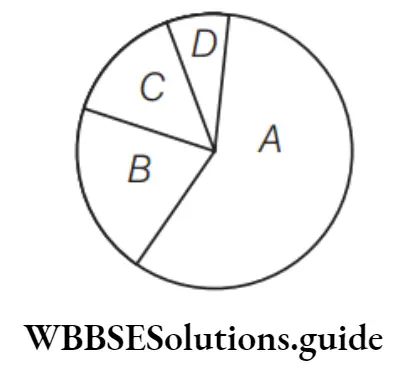
- A–CO2 (40%), B–CH4 (20%), C–CFCs (14%), D–NO2 (36%)
- A–CO2 (60%), B–CH4 (20%), C–CFCs (14%), D–NO2 (6%)
- A–CO2 (60%), B–CH4 (10%), C–CFCs (24%), D–NO2 (6%)
- A–CO2 (10%), B–CH4 (80%), C–CFCs (4%), D–NO2 (6%)
Answer: 2. A–CO2 (60%), B–CH4 (20%), C–CFCs (14%), D–NO2 (6%).
Question 35. Match the following columns.
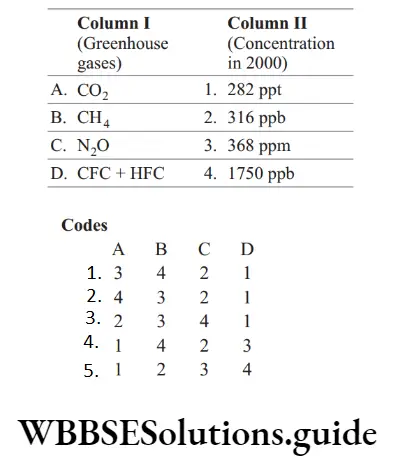
Answer: 1. A–3, B–4, C–2, D–1
Question 36. If there was no carbon dioxide in the earth’s atmosphere, the temperature of earth would be
- Dependent On The Amount Of Oxygen In The Atmosphere
- Higher Than The Present
- Lower Than The Present
- The same of now
Answer: 3. Lower Than The Present
If there was no carbon dioxide in the earth’s atmosphere, the temperature of earth would be lower than the present.
Question 37. Under Column 1, list of gases that are known to have a ‘greenhouse effect’ is given. Relate them to their main source selecting from the list given under Column 2.
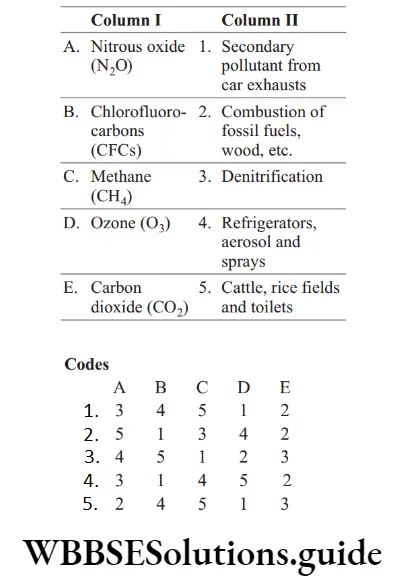
Answer: 1. A–3, B–4, C–5, D–1, E–2
Question 38. The best solution to combat the greenhouse effect is
- To Use Diesel Vehicles
- To Stop Infrared From Entering The Earth
- Afforestation and grow abundant plants
- All of the above
Answer: 3. Afforestation and grow abundant plants
Tree planting is becoming an increasingly popular tool to combat climate change. So, the best solution to combat the greenhouse effect is afforestation and growing abundant plants.
Global Warming Control Measures and Sustainable Practices MCQs for NEET
Question 39. Assertion Methane component of greenhouse gases contributing to global warming is about 20%. Reason (R) Introduction of multipoint fuel injection engines in automobiles has decreased methane content in the exhausts.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 3. A is true, but R is false
A is true, but R is false. The reason can be corrected as the Introduction of efficient engines in automobiles such as multipoint fuel injection engine have reduced the unburnt hydrocarbon (methane) content in the exhausts.
Question 40. Assertion The concentration of methane in the atmosphere has more than doubled in the last 250 years. Reason (R) Wetlands and rice fields are the major sources of methane.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. The burning of fossil fuel, wetland and rice fields wastewater fermentation are the major sources of methane which increase after industrialisation. It is a greenhouse gas whose concentration is double now than it was 200 year ago. It contributes to 20 % of greenhouse gases which the global warming
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 41. UV-B radiation from sun causes which of the following disorder of eyes?
- Cataract
- Glaucoma
- Dilation of pupil
- Some defect in retina
Answer: 1. Cataract
UV radiation is a caused factor for cataract. Epidemiological studies have shown certain types of cataract are associated with a history of higher exposure of UV and especially UV-B radiation. It is mainly damaging to the retinal tissue. 10% decrease in stratospheric ozone causes UV-B radiation (Ultraviolet blue radiation).
Question 42. Greenhouse effect is contributed by
- Refrigerators
- Rice Fields
- Greenhouse gases released by herbivores
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
All given options are contributed from the greenhouse effect.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 43. Today, the concentration of greenhouse gases is very high because of
- Use Of Refrigerator
- Increased Combustion Of Oils And Coal
- Deforestation
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
All given reasons in options are very high concentration of greenhouse gases.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 44. If global warming continues, the organism which may face more severe threat is
- Cow
- Dog
- Snow Leopard
- Dolphin
Answer: 3. Snow Leopard
If global warming continues then all the polar ice and glaciers will melt first. Hence, in the given option, snow leopard is the organism, which will face more severe threat due to destruction of habitat and other influences of ecological imbalance.
Question 45. An observance not occurring due to global warming.
- Rising sea level
- Increased agricultural productivity worldwide
- Worsening health effects
- Increased storm frequency and intensity
Answer: 2. Increased agricultural productivity worldwide
Increased agricultural productivity is not a consequence of global warming.
Question 46. Kyoto protocol has specified the commitments of different countries
- To Mitigate Climate Changes
- Limit Production Of Chlorofluorocarbons
- To prepare a world climate programme
- None of the above
Answer: 1. To Mitigate Climate Changes
Kyoto protocol has specified the commitments of different countries to mitigate climate changes.
Effects of UV Radiation and Ozone Layer Protection MCQs for NEET
Question 47. ‘Kyoto protocol’ is a multination international treaty for
- Phasing Out Greenhouse Gases
- Controlling Ozone Destroying Substances
- Management Of Hazardous Wastes
- Conservation of biodiversity
Answer: 1. Phasing Out Greenhouse Gases
International conference held in Kyoto, Japan obtained commitments from different countries for reducing overall greenhouse gas emissions at a level 5% below 1990 level by commitment 2008-2012. It is called Kyoto protocol (December 1997).
Question 48. Kyoto protocol was endorsed
- CoP-5
- CoP-6
- CoP-4
- CoP-3
Answer: 4. CoP-3
The Kyoto protocol was adopted at the third session of the conference of parties to the UNFCCC (CoP-3) in 1997 in Kyoto, Japan. The Kyoto protocol is an International treaty (agreement) so reduce green house gas emissions, based on the premise that global warming exists and human-made CO2 emissions have caused it.
So, the correct answer is CoP-3.
NEET Biology MCQ Chapter Wise
Question 49. The second commitment period for Kyoto protocol was decided
- Cancun
- Durban
- Bali
- Doha
Answer: 4. Doha
The Kyoto protocol is an international agreement linked to the United Nations Framework Convention on climate change which commits its parties by setting internationally binding emissions reduction targets. In Doha, Qatar on 8th December in 2012, the ‘Doha Amendment to the Kyoto Protocol’ was adopted. The second commitment period was from 1st January in 2013 to 31st December in 2020.
Question 50. Temperature increases with height in which of the spheres?
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
- None of these
Answer: 2. Stratosphere
Stratosphere (second layer) extends up to 30-50 km. It shows increase in temperature from a minimum of about – 60°C to maximum of 5°C. This increase in temperature is due to ozone formation under the influence of UV-rays of solar radiation. Troposphere (first layer of atmosphere) and mesosphere (third layer) show a decrease of temperature with height.
Question 51. Assertion Ozone is a powerful oxidising agent in comparison to O2. Reason (R) Ozone is diamagnetic, but O2 is paramagnetic.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 2. Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A. Due to the case with which it can liberate nascent oxygen, O3 (ozone) act as a powerful oxidising agent.
O2 → O2 + O
Ozone is a diamagnetic as there is no unpaired, but O2 is paramagnetic due to the presence of two unpaired electrons in pi molecular orbitals.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 52. The presence of ozone in the atmosphere of earth
- Hinders Higher Rate Of Photosynthesis
- Has Been Responsible For Increasing The Average Global Temperature In Recent Past
- Helps In Checking The Ultraviolet Rays To Earth
- Is Advantageous Since It Supplies Oxygen For People Travelling In Jets
Answer: 3. Helps In Checking The Ultraviolet Rays To Earth
The stratosphere present in the atmosphere contains ultraviolet radiation absorbs the harmful UV radiation and protect us from several chronic diseases. Only ozone effectively absorb the most energetic UV light, known as UV- C and UV-B, which cause biological damage. The protective role of the ozone layer in the upper atmosphere is so vital that scientist believe life on land probably would not have evolved and could not exist today without it.
So, the presence of ozone in the atmosphere of earth helps in checking the ultraviolet rays to earth.
Question 53. Ozone is spread in the swimming pool because
- It Acts As Disinfectant
- To Absorbs Uv Radiations
- Ozone is easily available from O2
- All of the above
Answer: 1. It Acts As Disinfectant
Another common sterilising treatment for swimming pools other
than chlorination is ozone treatment. Ozone has several advantages over chlorine in that it is an effective bactericide and it is also effective against viruses. So, it acts as disinfectant.
Question 54. The thickness of ozone in a column of air from the ground to the top of the atmosphere is measured in terms of
- Decibel units
- Pascal units
- Svedberg units
- Dobson units
- Angstrom units
Answer: 4. Dobson units
The thickness of the ozone in a column of air from the ground to the top of the atmosphere is measured in terms of Dobson Units (DU).
Question 55. Which form of UV radiation can pass through the ozone layer?
- UV-A
- UV-B
- UV-C
- None of these
Answer: 1. UV-A
UV-A is the least harmful form of UV radiation having a wavelength of 320-390 nm. So, UV-A form of UV radiation can pass through the ozone layer.
Question 56. Which one of the following is a wrong statement?
- Greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon
- Eutrophication is a natural phenomenon in freshwater bodies
- Most of the forests have been lost in tropical areas
- Ozone in upper part of atmosphere is harmful to animals
Answer: 4. Ozone in upper part of atmosphere is harmful to animals
Statement in option 4 is wrong and can be corrected as The troposphere is the lowest layer of earth’s atmosphere. Bad ozone formed in troposphere and is harmful to plants and animals. Rest statements are right.
Question 57. Which one of the following gases can deplete ozone layer in the upper atmosphere?
- Ammonia
- Methane
- Carbon monoxide
- Sulphur dioxide
Answer: 2. Methane
Methane (hydrocarbons), aerosols, freon gas and nitrogen oxides destroy ozone layer in upper atmosphere (stratosphere).
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 58. The zone of atmosphere in which the ozone layer present is called
- Ionosphere
- Mesosphere
- Stratosphere
- Troposphere
Answer: 3. Stratosphere
The zone of atmosphere in which the ozone layer or shield is present in the stratosphere. It is also called ozonosphere where 90% of atmospheric ozone is present. In stratosphere, ozone is being formed and photodissociated. It dissipates the energy of UV radiations.
Question 59. In stratosphere, which of the following elements acts as a catalyst in degradation of ozone and release of molecular oxygen?
- Carbon
- Oxygen
- Fe
- Cl
Answer: 4. Cl
Chlorine acts as a catalyst in the degradation of ozone and release of molecular oxygen. The reaction occurs as follows
\(\begin{aligned}\mathrm{Cl}+\mathrm{O}_3 & \rightarrow \mathrm{ClO} \\
\mathrm{ClO}+\mathrm{O}_3 & \rightarrow \mathrm{Cl}+2 \mathrm{O}_2
\end{aligned}\)
So, the correct answer is option 4.
Question 60. Which of the chemical reaction is not correct?
- \(\mathrm{CFCL}_3 \stackrel{\mathrm{UV}-\mathrm{C}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{CFCL}_2+\mathrm{CL}\)
- \(\mathrm{CF}_2 \mathrm{CL}_2 \stackrel{\mathrm{OV}-\mathrm{C}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{CF}_2 \mathrm{CLCL}\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}+\mathrm{O}_3 \stackrel{h v}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{NO}_3+\mathrm{O}\)
- \(\mathrm{NO}_2+\mathrm{O}_3 \stackrel{h v}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{NO}_3+\mathrm{O}_2\)
Answer: 3. \(\mathrm{NO}+\mathrm{O}_3 \stackrel{h v}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{NO}_3+\mathrm{O}\)
Chemical reaction shown in option 3 is not correct and can be corrected as
\(\mathrm{NO}+\mathrm{O}_3 \stackrel{\mathrm{hv}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{NO}_3+\mathrm{O}_2\)Nitric oxide (NO) released by jets reacts with ozone to form O2.
Question 61. The ionosphere is between
- Stratosphere And Mesosphere
- Mesosphere And Thermosphere
- Troposphere And Stratosphere
- Troposphere and thermosphere
Answer: 2. Mesosphere And Thermosphere
The ionosphere is a region of earth’s upper atmosphere from about 60 km to 1000 km altitude and includes the thermosphere, parts of mesosphere and exosphere. It is distinguished because it is ionised by solar radiation. So, ionosphere is between mesosphere and thermosphere.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 62. Ozone in stratosphere extends
- 10-20 km
- 20-30 km
- 15-30 km
- 25-40 km
Answer: 2. 20-30 km
The ozone layer is a shield which is present in stratosphere which is also called ozonosphere. It lies at an altitude of 20-30 km over equator.
Question 63. ‘Good ozone’ is found in the
- Mesosphere
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
- Ionosphere
Answer: 3. Stratosphere
Good ozone occurs naturally in the earth’s upper atmosphere 10-30 miles above earth’s surface (stratosphere) where it forms a protective layer that shield us from the sun’s harmful ultraviolet rays.
Question 64. ‘Bad’ ozone is observed in
- Atmosphere
- Ionosphere
- Stratosphere
- Troposphere
Answer: 4. Troposphere
Bad ozone is formed in troposphere. It is harmful to plants and animals.
Question 65. Good ozone absorbs harmful…………………… from the sun.
- UV-rays
- Infrared Radiation
- Visible radiation
- X-rays
Answer: 1. UV-rays
Good ozone absorbs harmful UV-rays from the sun.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 66. Which of the following statements is correct about ozone?
- Tropospheric ozone protects us from UV radiations
- Stratospheric ozone is ‘bad’
- Tropospheric ozone is ‘good’
- Stratospheric ozone protects us from UV radiations
Answer: 1. Tropospheric ozone protects us from UV radiations
The statement in option 1 is correct. Rest statements are not correct and can be corrected as Ultraviolet radiation in the stratosphere are absorbed by ozone.
Question 67. Which of the following is a photochemical reaction product?
- CO and CO2
- SO2
- O3
- Fluorides
Answer: 3. O3
The ozone molecule is formed due to the action of the UV-rays with the oxygen molecule. When the UV-rays penetrate in earth’s atmosphere, the radiation react with the O2 molecules to form oxygen atoms which react again to form O3. This reaction is Known as photochemical reaction in which light and radiation form ozone.
Question 68. A prime health risks associated with exposure to harmful UV radiation due to depletion of stratospheric ozone.
- Damage to digestive system
- Neurological disorder
- Increased skin cancer
- Both 2 and 3
Answer: 4. Both 2 and 3
Increasing skin cancer, damages in DNA and proteins of living organisms (neurological disorder) are the result of ozone depletion.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 69. UV rays are non-ionising type and are lethal due to the inactivation of
- Proteins
- Pigments
- Nucleic acid
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Ultraviolet (UV) light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. It is classified as non-ionising radiation and can cause inactivation of protein, pigments and nucleic acids.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
NEET Biology MCQ Chapter Wise
Question 70. Which of the following is not ionising radiation?
- Alpha rays
- Beta rays
- UV rays
- Infrared
Answer: 4. Infrared
The ionising radiations include X-rays, gamma rays, emission of α and β-particles. Some radiations with shorter wavelengths like UV rays, due to their light energy content are capable of causing harm to microorganisms and damage only the surface tissues of animals (including man) and plants. So, infrared is not ionising radiation.
NEET Biology MCQ Chapter Wise
Question 71. In coming years, skin related disorders will be more common due to
- Pollutants In Air
- Use Of Detergents
- Water Pollution
- Depletion of the ozone layer
Answer: 4. Depletion of the ozone layer
The ozone layer is a shield which is present in the stratosphere which is also called the ozonosphere. Depletion in the concentration of ozone over a restricted area as springtime decline over Antarctica is called an ozone hole. Thinning of the ozone layer increases the amount of UV-B radiation reaching the earth. It would increase the occurrence of cataracts, skin cancers, herpes, dimming of eyesight, photo burning, and deficient functioning of the immune system. So, in coming years’ skin related disorders will be more common due to depletion of ozone layer.
Question 72. Consider the following statements.
- UV rays play a key role in the production and degradation of ozone.
- Ozone in ionosphere acts as a shield to absorb UV radiations from the sun.
- One fourth of the incoming solar radiation is reflected by the atmospheric gases and clouds and only half of the incoming solar radiation falls on the earth’s surface, heating it.
Choose the option containing correct statements.
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer: 2. 2 and 3
All given statements are correct except 2. Incorrect statement can be corrected as Ozone present in stratosphere acts as a shield absorbing UV radiations coming from the sun.
Question 73. Fill up the blanks.
- The part of the electromagnetic spectrum of the sun that causes mutations – A
- Exposure of eyes to harmful UV radiations causes inflammation of this part of the eye – B
- Isotope of oxygen that combines with O2 to form ozone – C
- A natural phenomena that occurs once in few years which results change in weather patterns – D
Choose the correct option.
- A – UV-A, B – Retina, C – HO2, D – El Nino effect
- A – UV-B, B – Cornea, C – O (nascent oxygen), D – El nino effect
- A – Rays, B – Iris, C – O (nascent oxygen), D – Greenhouse effect
- A – Visible light, B – Cornea, C – NO2, D – Greenhouse effect
Answer: 2. A – UV-B, B – Cornea, C – O (nascent oxygen), D – El nino effect
Question 74. Fill up the blanks.
- When UV radiations in the …A… come in contact with CFCs …B… are released.
- These chloride atoms catalyse the reaction leading to the formation of …C…
- …D… present in the troposphere is harmful to life.
- Good ozone found in the stratosphere absorbs the incoming …E… from the sun.
Choose the correct option.
- A–stratosphere, B–chloride ions, C–O2, D–Bad ozone, E–UV radiations
- A–stratosphere, B–nitrogen ions, C– CO2, D–Bad ozone, E–infrared radiations
- A–ionosphere, B–chloride ions, C– N2O, D–Sulphur, E–UV radiations
- A–troposphere, B–oxygen ions, C– H2O, D–Bad ozone, E–UV radiations
Answer: 1. A–stratosphere, B–chloride ions C–O2, D–Bad ozone, E–UV radiations
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 75. Ozone hole means
- Same Concentration Of Ozone
- Decrease In The Concentration Of Ozone
- Increase In The Concentration Of Ozone
- Hole In The Stratosphere
Answer: 2. Decrease In The Concentration Of Ozone
The ozone layer is a shield which is present in the stratosphere which is also called the ozonosphere. Depletion in the concentration of ozone over a restricted area as springtime decline over Antarctica is called ozone hole. Thinning of the ozone layer increases the amount of UV-B radiation reaching the earth. It would increase the occurrence of cataracts, skin cancers, herpes, dimming of eyesight, photo burning, and deficient functioning of immune system. So, in the coming years’ skin related disorders will be more common due to the depletion of the ozone layer.
Question 76. The ozone hole was first discovered over
- Arctic
- Antarctica
- Tropic
- Polar region
Answer: 2. Antarctica
An ozone hole was discovered over Antarctica by Farnanet et. al, 1985.
Question 77. The ozone hole was discovered in the year ………… over ………………….
- 1984, Antarctica
- 1985, Antarctica
- 1986, Arctic
- 1987, Arctic
Answer: 2. 1985, Antarctica
The depletion of ozone is particularly marked over the Antarctica region in 1985. This has resulted in the formation of a large area of thinned ozone layer, commonly called as the ozone hole.
Question 78. Snow blindness in Antarctica region is due to
- Inflammation of cornea due to high dose of UV-B radiation
- High Reflection Of Light Form Snow
- Damage To Retina Caused By Infrared Rays
- Freezing Of Fluids In The Eye By Low Temperature
Answer: 1. Inflammation of cornea due to high dose of UV-B radiation
Snow blindness in Antarctica region is due to inflammation of cornea due to high dose of UV-B radiation. It is a painful, temporary loss of vision due to overexposure to the sun’s UV rays. It also called photokeratitis (photo–light, keratitis– inflammation of the cornea).
Question 79. The maximum threat to the world is from
- Global Warming
- Ozone Hole
- Water Pollution
- Soil erosion
Answer: 2. Ozone Hole
Ozone hole is not an actual hole but an area of extreme reduction in ozone concentration in the ozone layer in stratosphere. Depletion or thinning of ozone layer allows harmful UV-rays to reach earth and causes skin ageing, skin cancer, cataract, etc. Thus, maximum threat of the world is from ozone hole.
Question 80. Which country has the greatest contribution for the ‘hole’ in the ozone layer?
- Russia
- Japan
- USA
- Germany
Answer: 3. USA
Depletion in the concentration of ozone over a restricted area as springtime decline over Antarctica is called an ozone hole. Depletion of ozone is due to action of sunlight over pollutants which release chemicals (e.g. chlorine) that destroy ozone. The major are chlorofluorocarbons (14% of total depletion), nitrogen oxides (3.5% depletion), sulphur dioxide, halon, carbon tetrachloride, methyl chloroform, chlorine, etc. The major contributor of these gases is USA.
NEET Biology MCQ Chapter Wise
Question 81. Ozone depletion in stratosphere shall result in
- Forest Fires
- Greenhouse Effect
- Global Warming
- Increased incidence of skin cancer
Answer: 4. Increased incidence of skin cancer
Ozone depletion in stratosphere shall result in increased incidence of skin cancer and cataract.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 82. The ozone hole over Antarctica develops each year between
- Late December And Early February
- Late February And Early April
- Late April And Early June
- Between The Months Of September And November
- None of the above
Answer: 4. Between The Months Of September And November
The ozone hole now occurs every year in Antarctica between the months of September and November, which is the South Pole’s springtime.
Question 83. …………… leads to reduction in the ozone umbrella protecting us from harmful UV rays.
- CFCs
- CO2
- PAN
- Coal burning
Answer: 3. PAN
Ozone protects us from the harmful UV radiation from the sun. Major pollutants responsible for the depletion of ozone layer are chlorofluorocarbons, nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons. The threat to O3 is mainly from CFCs, which are known to deplete O3 by 14% at the current emission rate.
Question 84. Peeling of ozone umbrella, which protects us from UV- rays, is caused by
- CO2
- PAN
- CFCs
- Coal burning
Answer: 3. CFCs
Peeling of the ozone umbrella, which protects us from UV rays is caused by CFCs. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and halons deplete ozone in stratosphere. CFCs are 20,000 times more efficient than CO2 in trapping energy in lower atmosphere. CFCs are also powerful greenhouse gases.
Question 85. The chemical name of freon is
- Dichlorofluoromethane
- Trichlorotrifluoroethane
- Dichlorofluorine
- Dichloroethane
Answer: 1. Dichlorofluoromethane
Dichlorodifluoromethane is a colourless gas usually sold under the brand name freon-12 and a chlorofluorocarbon halomethane used as a refrigerant and aerosol spray propellant.
Question 86. Which of the following is a chlorofluorocarbon?
- CFSO2
- CF2Cl2
- FClCO2
- ClF2C
Answer: 2. CF2Cl2
Chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) is a class of synthetic chemicals that are odourless, non-toxic, non-flammable and chemically inert. It is a molecule that contains chlorine, fluorine and carbon atoms. CFCs have been used as propellants in aerosol cans, as refrigerants in refrigerators and air conditioners and in the manufacture of foam packaging. They are partly responsible for the destruction of the ozone layer. Dichlorodifluoromethane (CCl2F2) is an example of a CFC and it was once used as a refrigerant before it was discovered that CFCs can cause ozone depletion.
Question 87. The common refrigerants chlorofluoromethane (freon) and NO2 is a severe pollutant because
- It Lowers Atmospheric Temperature
- It Prevents Cloud Condensation
- It Destroys Haemoglobin
- It Disrupts O3 Layer
Answer: 4. It Disrupts O3 Layer
Chlorofluorocarbons and freon cause depletion of ozone layers. CFCs are used as refrigerants. They are discharged in the lower part of the atmosphere from there they move upward and reach the stratosphere. In the stratosphere, UV rays act on them releasing Cl atoms, Cl degrade ozone releasing molecular oxygen. Cl atoms are not consumed in the reaction. Hence, whatever CFCs are added to the stratosphere, they have permanent and continuing effects on the ozone layer.
NEET Biology MCQ Chapter Wise
Question 88. Freon gas causing stratospheric ozone depletion is used mainly in
- Refrigerator
- Automobile
- Thermal Power Plant
- Steel industry
Answer: 1. Refrigerator
Freon is stable, non-flammable, low toxicity gas or liquid, which have generally been used in refrigerator and as aerosol propellants.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 89. Chlorofluorocarbons are air-polluting agents, these are produced by
- Diesel Trucks
- Jet Planes
- Rice Field
- Acid batteries
Answer: 2. Jet Planes
Chemicals released in the atmosphere with force in the form of mist or vapours are called aerosols. Jet aeroplanes release aerosols, which contain CFCs (Chlorofluorocarbons). CFCs are used as coolants in air conditioners, refrigerators, etc.
Question 90. What are the chief pollutants of the atmosphere which are most likely to deplete the ozone layer?
- Sulphur dioxide
- Nitrogen oxide and chlorofluorocarbons
- Carbon dioxide
- Carbon monoxide
Answer: 2. Carbon dioxide
Chlorofluorocarbons or CFCs and nitrogenous compounds such as NO2, NO, and NO2 are highly responsible for the depletion of the ozone layer.
Question 91. Aerosols are
- Chemicals Released In Air In The Form Of Mist Or Vapour With Force
- Gases Released From Exhaust Pump
- Mixture Of Carbon Particles And Mist
- A Suspension of fine solid particles or liquid droplets
Answer: 4. A Suspension of fine solid particles or liquid droplets
An aerosol is a suspension of fine solid particles or liquid droplets, in air or another gas. Aerosols can be natural or anthropogenic. Examples of natural aerosols are fog, dust, forest exudates and geyser steam. Examples of anthropogenic aerosols are haze, particulate air pollutants and smoke.
NEET Biology MCQ Chapter Wise
Question 92. Aerosols reduce primary productivity by
- Decreasing O2 Concentration In Atmosphere
- Reducing Photosynthesis
- Competing With CO2
- Being toxic to chloroplast
Answer: 4. Being toxic to chloroplast
Both liquid and solid aerosols are present in atmosphere, which are called particulate matter by Hodges (1973). Chemicals released in the atmosphere with force in the form of mist or vapours are called aerosols. Jet aeroplanes release aerosols, which contain CFC (chlorofluorocarbon). It is strong enemy of ozone and caused depletion of ozone layer. Aerosols affect the rate of photosynthesis and hence decrease primary productivity.
Question 93. The major aerosol pollutant in jet plane emission is
- Sulphur dioxide
- Carbon monoxide
- Methane
- Fluorocarbon
Answer: 4. Fluorocarbon
Aerosols are chlorofluoro hydrocarbon compounds released into air with force in the form of vapour. Main source of aerosols is the emission of jet planes, where fluorocarbon is used. These chlorofluorocarbons deplete the ozone layer in the higher atmosphere. These CFCs have produced a hole in the ozone layer.
Question 94. Which one of the following statements is not valid for aerosols?
- They are harmful to human health
- They alter rainfall and monsoon patterns
- They cause increased agricultural productivity
- They have negative impact on agricultural land
Answer: 3. They cause increased agricultural productivity
Aerosols are microscopic liquid or solid particles that are given out into the atmosphere either through man-made or natural processes such as burning of fossil fuels and volcanoes, respectively. Aerosols can be harmful for agriculture directly or indirectly. It can reduce precipitation by reducing the size of droplets, if aerosol particles are heavy, in nature it can settle on the ground, it can also add to global warming, etc.
Question 95. The supersonic jets cause pollution by the thinning of
- O2 layer
- O3 layer
- CO2 layer
- SO2 layer
Answer: 2. O3 layer
90% of naturally occurring atmospheric ozone occurs in the stratosphere. It removes all incoming UVA and 70% of the incoming UV-B at the equator, and 90% at\ poles. All aircraft produce water, CO2, CO, etc., in exhaust gases.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 96. Assertion Major cause of ozone depletion is CFCs, but greenhouse gases also have a negative effect on the ozone layer. Reasons (R) Greenhouse gases increase the temperature of the troposphere, but decrease the temperature of the stratosphere which facilitates ozone depletion.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. Greenhouse gases lower the temperature of the stratosphere and lower temperature facilitates ozone depletion, so greenhouse gases indirectly affected the ozone layer or ozone depletion.
Question 97. Consider the following statements.
- Chlorofluorocarbons deplete ozone.
- Chlorofluorocarbons contain chlorine, bromine and fluorine.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 1. Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect. Incorrect statement can be corrected as Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) contain carbon and some combination of fluorine and chlorine atoms.
NEET Biology MCQ Chapter Wise
Question 98. Which one of the following pairs is mismatched?
- Fossil fuel burning – Release of CO2
- Nuclear power – Radioactive wastes
- Solar energy – The greenhouse effect
- Biomass burning – Release of CO2
Answer: 3. Solar energy – The greenhouse effect
Option 3 is mismatched pair and can be corrected as Solar energy coming to the earth is not responsible for the greenhouse effect. It is the increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like CO2 which is released by the complete combustion of fossil fuels or biomass in industries or transportation vehicles that prevent the re-radiation of infrared radiation from the earth and result in an increase in the temperature of the earth. Rest options are correctly matched pairs.
Question 99. Which of the following protocols did aim for reducing the emission of chlorofluorocarbons into the atmosphere?
- Montreal protocol
- Kyoto protocol
- Gothenburg protocol
- Geneva protocol
Answer: 1. Montreal protocol
To control the deleterious effect of the stratospheric ozone depletion an international treaty was signed at Montreal, Canada in 1987. It is popularly known as the Montreal Protocol. The protocol aimed at reducing of the emission of chlorofluorocarbons into the atmosphere.
NEET Biology MCQ Chapter Wise
Question 100. Montreal protocol was signed in 1987 control for
- Emission Of Ozone Depleting Substances
- Release Of Greenhouse Gases
- Disposal Of E-Wastes
- Transport of genetically modified organisms from one country to another
Answer: 1. Emission Of Ozone Depleting Substances
Montreal Protocol was signed in 1987 to control the emission of ozone-depleting substances. It is a global agreement to protect the stratospheric ozone layer by phasing out the production and consumption of Ozone-Depleting Substances (ODS).
Question 101. World Ozone Day is celebrated on
- 5th June
- 22nd April
- 16th September
- 21st April
Answer: 3. 16th September
World Ozone Day is celebrated on the 16th of September. Other options are explained as 5th June – World Environment Day 21st April – National Yellow Bat Day 22nd April – National Earth Day
