Biology MCQs With Answers For NEET Loss Of Biodiversity And Its Causes
Question 1. The number of species facing the threat of extinction worldwide is
- 14,500
- 14,000
- 15,000
- 15,500
Answer: 4. 15,500
The number of species facing the threat of extinction world wide is 15,500.
Question 2. In IUCN Red list, documents the extinction of 784 species includes
- 335 vertebrates, 360 invertebrates and 89 plants
- 337 vertebrates, 362 invertebrates and 88 plants
- 338 vertebrates, 359 invertebrates and 87 plants
- 340 vertebrates, 357 invertebrates and 87 plants
Answer: 3. 338 vertebrates, 359 invertebrates and 87 plants
“viable material of endangered species can be preserved by “
Accrding to IUCN Red list (2004), 338 vertebrates, 359 invertebrates and 87 plants are extinct in the last 500 yrs.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 3. Which organisation publishes the Red Data Book?
- GEF
- IUCN
- UNEP
- WWF
Answer: 2. IUCN
The Red Data Book is a public document which is created for recording endangered and rare species of plants, animals, fungi as well as some local subspecies. It contains the complete list of threatened (endangered) species. Currently the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) maintain the Red Data Book

“biodiversity questions “
Question 4. How much percentage of the species will be lost by end of the 21st century on earth if the current rate of loss continues?
- 10%
- 20%
- 50%
- 40%
Answer: 3. 50%
The current rate of global diversity loss is estimated to be 100 to 1000 times higher the previous extinction rate. If the current rate of loss continues 50% of the species will be lost by the end of 21st century on earth.
Question 5. According to IUCN Red list, during the last two decades, the maximum increase in the number of threatened species is among
- Amphibians
- Reptiles
- Birds
- Mammals
Answer: 1. Amphibians
Threatened species is the one which is liable to become extinct if not allowed to realise its full biotic potential by providing protection from exotic species, human exploitation and other activities. According to IUCN Red list, during the last two decades, the maximum increase in the number of threatened species is among amphibians.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 6. Red list of plants in India is completed by
- Botanical Survey of India
- Zoological Survey of India
- Geological Survey of India
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Botanical Survey of India
In India, Red list of plant species is prepared by Botanical Survey of India. It is government of India ministry of environment, forest and climate change’s organisation for the survey, research and conservation of plant resources, flora and endangered species of India. It was founded on 13 February in 1890, by the East India company.
Question 7. Red list contains data or information on
- All economically important plants
- Plants Whose Products Are In International Trade
- Threatened Species
- Marine vertebrates only
Answer: 3. Threatened Species
IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) maintains Red list, which is a catalogue for threatened species. A threatened species is any species which is vulnerable endangered or critically endangered.
NEET Biology Loss of Biodiversity MCQs with answers
Question 8. According to IUCN Red list, what is the status of red panda (Ailurus fulgens)?
- Critically endangered species
- Vulnerable species
- Extinct species
- Endangered species
Answer: 4. Endangered species
According to IUCN Red list, red panda comes under endangered species. These species facing a high risk of extinction in the wild in the near future due to decrease in its habitat, excessive predation or poaching.
“biodiversity questions and answers pdf “
Question 9. Species listed in Red list which presently have sufficient population, but are facing the risk of extinction in medium term future are called
- Endangered Species
- Vulnerable Species
- Rare Species
- Extinct species
Answer: 2. Vulnerable Species
Presently, the population of vulnerable species is sufficient, but is undergoing depletion due to some factors, so that it is facing risk of extinction in medium term future, e.g. Antelope cervicapra.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 10. According to Red list in India, ………… plant species are critically endangered.
- 132
- 50
- 60
- 80
Answer: 1. 132
According to the Red list of 2012, 132 species are critically endangered in India.
Question 11. List of endangered species was released by AFMC
- IUCN
- BBC
- WCC
- UN
Answer: 1.
The Red Data Book is a public document which is created for recording endangered and rare species of plants, animals, fungi as well as some local subspecies. It contains the complete list of threatened (endangered) species. Currently the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) maintain the Red Data Book
Important MCQs on Loss of Biodiversity for NEET
Question 12. Number of endangered species of angiosperms in India is
- 15,000
- 487
- 3000
- 5000
Answer: 3.
The number of endangered species of angiosperms in India is 3000.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 13. A threatened species category included
- Only Endangered Species
- Only Vulnerable Species
- Endangered And Rare Species
- Endangered, vulnerable and rare species
Answer: 4. Endangered, vulnerable and rare species
The species which can extinct in future comes under the threatened species. All the types of endangered, vulnerable and rare species are included under category of threatened species.
Question 14. Given below are pie diagram A, B, C, D and E related to the percentage of various categories of threatened species of angiosperms, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals, respectively. Identify what each shaded slice of the pie chart refer to?
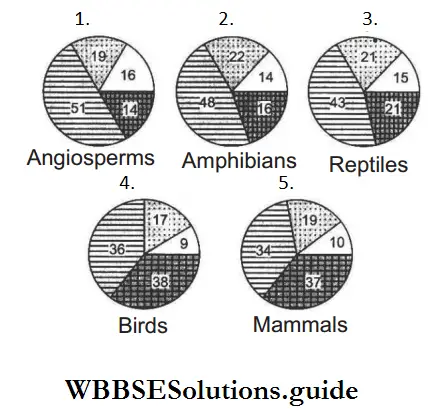
Critically study and identify the following regions
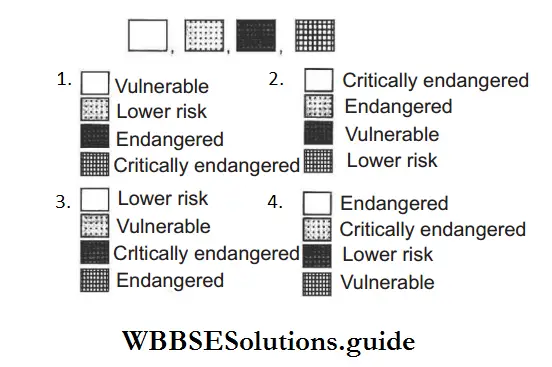
Answer: 2. Amphibians
- 10% mammals, 9% birds, 15% reptiles, 16% amphibians and 16%
angiosperms are facing very high risk of extinction in the wild and can become extinct any moment in the immediate future. - The percentage number of endangered species in the list of
threatened species is 19% mammals, 17% birds, 21% reptiles, 22% amphibians and 19% angiosperms. - Percentage of depleted (vulnerable) species out of the total threatened species is 34% mammals, 36% birds, 43% reptiles, 48% amphibians and 51 % angiosperms.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 15. Which one of the following is an endangered plant?
- Lycopersicum
- Dalbergia
- Cedrus
- Rauwolfia
Answer: 4.
Rauwolfia is a source of antihypertensive drug reserpine. It is used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension). It is an endangered plant due to its hyper-exploitation.
Question 16. The endangered member of flora is
- one horned rhino
- Drosera indica
- flying squirrel
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Drosera indica
Drosera indica L. is a threatened and endangered insectivorous plant. It is native to tropical countries.
Question 17. Which group of vertebrates comprises the highest number of endangered species?
- Birds
- Mammals
- Fishes
- Reptiles
Answer: 2. Mammals
Mammals have 177 endangered species which represent 3.8% of all the species. Similarly, birds have 188 endangered species which represent 1.9% of all the species. Reptiles, amphibians and fishes have 47, 32 and 158 endangered species representing 0.7%, 0.7% and 0.6%, respectively of all the species. So, the mammals of vertebrates comprise the highest number of endangered species.
Causes of Biodiversity Loss MCQs for NEET
Question 18. Asiatic lion (Panthera leo persica) is now
- Endangered
- Extinct In Wild
- Vulnerable
- Critically endangered
Answer: 1. Endangered
Asiatic lion is restricted to the Gir National Park and environs in Gujarat. On the IUCN Red list, it is listed under its former scientific name, Panthera leo persica as endangered because of its small population size and area of occupancy.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 19. Most of the endangered species are victims of
- Competition With Introduced Species
- Habitat Destruction
- Overhunting
- Acid Rain
Answer: 2. Habitat Destruction
The most important cause of the driving animals and plants to extinction is habitat loss and fragmentation which comes under habitat destruction. Due to various human activities, when large habitats are destructed, various animals are badly affected, leading to population decline. So, most of the endangered species are victims of habitat destruction.
Question 20. One of endangered species of Indian medicinal plants is that of
- Podophyllum
- Ocimum
- Garlic
- Nepenthes
Answer: 1. Podophyllum
Podophyllum emodi (medicinal plant) is an Indian endangered flora. It is an verge of extinction due to overexploitation. Its dried roots and rhizomes are used in chronic, constipation and tumour growth.
Question 21. Which endangered animal is the source of the world’s finest, lightest, warmest and most expensive wool the ‘Shahtoosh’?
- Nilgai
- Cheetal
- Kashmiri goat
- Chiru
Answer: 4. Chiru
A special shawl, which is woven with the down hair of the Tibetan antelope (Chiru), by craftsmen and women of Kashmir is called as ‘Shahtoosh’. Being an endangered species, Chiru is now being protected. Thus, the shawl is now legally banned. Shahtoosh is the world’s finest lightest, warmest and most expensive wool having the lowest micron count.
“which one is an endangered species in the following “
Question 22. Which one of the following plant species is in endangered list?
- Eucalyptus
- Nepenthes
- Ceratophyllum
- Delonix
Answer: 2. Nepenthes
Nepenthes species are endangered plant. They are mainly insectivorous plant, which grows in nitrogen deficient soils. It traps insects for nitrogen requirement. Due to deforestation, they have become an endangered species.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 23. Which one is a critically endangered animal species?
- Antelope cervicapra
- Ailurus fulgens
- Calotes versicolor
- Hyla
Answer: 2. Sus salvanius
Pygmy hog (Sus salvanius/Porcula salvania) is an endangered species of small wild pig, previously spread across India, Nepal and Bhutan but now only found in Assom. The current world population is about 150 individuals or fewer. Recent conservation measures have improved the prospects of survival in the wild of this critically endangered species.
Question 24. Golden langur (Trachypithecus geei), is considered as
- Endangered Species
- Vulnerable Species
- Rare Species
- Extinct species
Answer: 1. Endangered Species
The golden langur, Trachypithecus geei, is an endangered species, endemic to India and Bhutan. Its distribution is limited to a small forest belt in Western Assom in Northeast India and Bhutan, between the River Manas in the East.
NEET quiz on Biodiversity Loss and Its Causes with solutions
Question 25. The endangered largest living lemur Indri indri is found in
- Sri Lanka
- Madagascar
- Mauritius
- India
Answer: 2. Madagascar
The lemurs are the inhabitants of Madagascar and the Comoro Islands. It is currently facing extinction. The major threat to the extinction of lemur, Indri indri is the deforestation.
Question 26. Which one of the following sets is endangered?
- Musk deer and Himalayan bear
- Tiger and Bustard
- Peacock and Pheasant
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
All of the given species are endangered. Himalayan musk deer is endangered because of overexploitation. The Himalayan brown bear is critically endangered due to poaching for their fur and claws. The Siberian tiger and peacocks both are endangered. The great Indian bustard are critically endangered because it has an extermely small population. Pheasants are one of the most endangered groups of birds in the world.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 27. Which one of the following is a pair of endangered species?
- Garden lizard and Mexican poppy
- Rhesus monkey and Sal tree
- Indian peacock and carrot grass
- Hornbill and Indian aconite
Answer: 4. Hornbill and Indian aconite
In India, aconite and hornbill are endangered species. Hornbill illegally hunting for its casque. Indian aconite belongs to family–Ranunculaceae. It is exploited due to its medicinal properties.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 28. Which of the following plant is an endangered species in India?
- Lycopodium sp.
- Pinus roxburghii
- Hydrilla
- Cedrus deodara
Answer: 1. Lycopodium sp.
Lycopodium (Phlegmariurus nutans) is a fern, which is an endangered species in India. It has been used in treatment of disorder of the locomotor system, skin, liver.
Question 29. Which of the following are rare species?
- Indian desert cat
- Wild yak
- Gharial
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
A rare species is a group of organisms that are very uncommon, scarce or infrequently encountered. Indian desert cat, wild yak, gharial comes under rare species.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
NEET expected MCQs on Biodiversity Loss 2025
Question 30. Which one of the following is an endangered animal?
- Rhesus monkey
- Antelope
- Langur
- Lion tailed macaque
Answer: 4. Lion-tailed macaque
The lion-tailed macaque, endemic to the evergreen forests of the Western ghats in Southern India. With less than 2500 individuals remaining in the wild and about 400 more in zoos, the lion-tailed macaque is one of the most endangered species in the world today.
Question 31. Which of the following is not endangered?
- Peacock
- Indian rhino
- Asiatic lion
- Great Indian bustard
Answer: 1. Peacock
Technically only males are peacock. Females are peahens and together, they are called peafowl. Indian peafowl are widely distributed in the wild across South Asia and protected both culturally in many areas and by law in India. Conservative estimates of the population put them at more than 1,00,000. So, peacock is not an endangered species. Whereas Indian rhino, Asiatic lion and Great Indian bustard belong to endangered species.
Question 32. Which one of the following species is no more an endangered species and has been given the status of ‘vulnerable’, recently?
- Tiger
- Giant panda
- Elephant
- Deer
Answer: 2. Giant panda
The Giant panda is an endangered species, threatened by continued habitat loss and by very low birth rate, both in wild and in captivity. The numbers are slowly increasing due to widespread conservation efforts and it has moved into the vulnerable category of IUCN’s Red list.
NEET Biology MCQ
Question 33. Among various categories of threatened species, the percentage of angiosperms categorised as vulnerable is about
- 14%
- 19%
- 41%
- 51%
Answer: 4. 51%
Out of total threatened species 34-51% are vulnerable (34% mammals, 36% birds, 43% reptiles, 48% amphibians and 51% angiosperms).
Question 34. Organisms are susceptible to extinction as a result of
- Their Large Body Size
- Their Small Population
- Their High Trophic Level
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
- Organisms are susceptible to extinction is due to
- Large body size, e.g. elephant, rhinoceros, Bengal tiger, lion.
- Small population size.
- Low reproductive potential, e.g. blue whale, giant panda.
- The higher status of trophic level, e.g. bald eagle, Bengal tiger, due to all these reasons, they are unable to sustain and hence comes under organisms which are susceptible to extinction.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 35. The rate of extinction in the tropics is
- High
- Moderate
- Low
- Negligible
Answer: 3. Low
There are various hypotheses for the presence of higher diversity in tropical areas. One of them is, the rate of extinction is low in tropics because climatic conditions are favorable and stable.
Question 36. Which animal has gone extinct in recent times in India?
- Panthera leo
- Acinonyx jubatus
- Antilope cervicapra
- Rhinoceros unicornis
Answer: 2. Acinonyx jubatus
Acinonyx jubatus, commonly called cheetah, has gone extinct in recent times in India due to the rapid destruction of its habitat, high rate of mortality of the cubs, and the killing by hunters.
Question 37. The bird ‘dodo’ became extinct because of
- Its Beautiful Feathers
- Its Flesh
- Its Curved Beak
- Its melodious songs
Answer: 2. Its Flesh
The dodo (Raphus cucullatus) was first described in 1601 from the island of Mauritius. By 1681, it had become extinct as a result of hunting by Dutch colonists. It becomes extinct because of its flesh and the bird was flightless too, which increased its predation and poaching.
NEET Biology MCQ
Question 38. A species facing an extremely high risk of extinction in the immediate future is called CBSE AIPMT
- Vulnerable
- Endemic
- Critically Endangered
- Extinct
Answer: 3. Critically Endangered
The taxon under critically endangered category are facing very high risk of extinction in the wild and can become extinct at any moment in the immediate future.
Question 39. If the Bengal tiger becomes extinct then
- Hyenas And Wolves Will Become Scarce
- The Wild Areas Will Be Safe For Man And Domestic Animals
- Its Gene Pool Will Be Lost Forever
- The population of beautiful animals like deer will get stabilised
Answer: 3. Its Gene Pool Will Be Lost Forever
If the Bengal tiger becomes extinct, its gene pool is lost forever. The combination of all the genes present in a given population is called the gene pool of that population. Extinction leads to deletion of gene from the resultant genome in course of evolution.
Question 40. Which of the following birds is on the verge of extinction in India?
- Peacock AMU 2001
- Pintail ducks
- Hornbill
- Great Indian bustard
Answer: 4. Great Indian bustard
The great Indian bustard is a tall, long legged bird which is on the verge of extinction in India. It’s numbers have now dwindled to just 150 felling by 100 since 2011.
NEET Biology Loss of Biodiversity MCQs with explanations
Question 41. Which of the following is the most important cause for animals and plants being driven to extinction?
- Habitat loss and fragmentation
- Drought and floods
- Economic exploitation
- Alien species invasion
Answer: 1. Habitat loss and fragmentation
Habitat loss and fragmentation is the most important cause driving animals and plants to extinction. When large habitats are broken up into small fragments due to various human activities, mammals and birds requiring large territories and certain animals with migratory habits are badly affected.
NEET Biology MCQ
Question 42. Main cause behind destruction of biodiversity is
- Deforestation
- Illegal Hunting
- Air Pollution
- Interspecific competition
Answer: 1. Deforestation
Deforestation leads to loss of various species of plants and animals dependent on them. This leads to habitat loss for many animals. Deforestation also results in less rainfall in that area. So, main cause behind destruction of biodiversity is deforestation.
Question 43. A species is prone to extinction as a result of
- Drastic Environmental Changes And Population Characteristics
- Large Body Size And Large Population Size
- Drastic Environmental Changes And Mass Extinction
- Population Characteristics And Pollution
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Drastic Environmental Changes And Population Characteristics
A species becomes prone to extinction due to the two categories of attributes, drastic environmental changes and population characteristics. Population traits are small population size, large body size, higher status of trophic level, etc
Question 44. At present, the most significant cause of dwindling biodiversity is probably
- The Deterioration Of Ozone Layer
- The Destruction Of Habitat
- Biological Magnification Of Ddt
- Global warming
Answer: 2. The Destruction Of Habitat
Habitat destruction affects the survival of populations and reduces biodiversity. The major causes of biodiversity decline are pollution, changes in atmospheric CO2 concentrations, changes in the nitrogen cycle and acid rain, climate alterations and the introduction of exotic species, all coincident to human population growth.
Question 45. Which of the following is the natural cause of extinction of species?
- Pollution of soil, water and air
- Earthquakes, floods, landslides
- Cutting of forest trees, overgrazing
- Uprooting of orchids and medicinal plants
Answer: 2. Earthquakes, floods, landslides
Extinction occurs when species are diminished because of environmental forces (habitat loss, fragmentation, global change), natural disaster (earthquakes, floods, landslides, etc.), overexploitation of species (for human use) or because of evolutionary changes in their members (genetic inbreeding, poor reproduction, decline in population numbers). So, earthquakes, floods and landslides are the natural cause of extinction of species.
Question 46. Identify the causes of biodiversity loss.
- Overexploitation
- Alien species
- Coextinction
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
The world is facing accelerated rate of biodiversity losses due to human interference. The four major causes are the overexploitation, coextinctions, alien-species invasions, habitat loss and fragmentation, etc.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 47. Wildlife is destroyed the most when
- There Is Lack Of Proper Care
- Mass Scale Hunting For Foreign Trade
- Its Natural Habitat Is Destroyed
- Natural calamity
Answer: 3. Its Natural Habitat Is Destroyed
Destruction of natural habitats causes the most serious threat to the biodiversity, i.e. endangering many animals. Habitats are destroyed/fragmented by many human activities like developmental work, deforestation, pollution, etc. Overhunting and poaching also have harmful effect. Thus, wildlife is destroyed the most when its natural habitat is destroyed.
Question 48. Extinction vertex includes
- Genetic Factors
- Demographic Factors
- Both 1 And 2
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Both 1 And 2
Extinction vertex is a combination of genetic and demographic factors. Genetic factors are involved due to restricted mating opportunities, in breeding becomes more likely. If populations remain small and isolated for many generations, they loose genetic variation necessary to respond to environmental challenges. The small and isolated populations are threatened by extinction. Thus, environmental demographic and genetic factors can interact and reinforce each other in a downward spiral, extinction vertex.
Thus, option 3 is correct.
Question 49. India’s biodiversity is in jeopardy and major reason for this is
- Population Explosion
- Habitat Destruction
- Pollution and animal poaching
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Today, with the population explosion, more and more land is being cleared for agriculture, habitation destruction and other developmental projects. Pollution by heavy metals, persistent biocides, organic wastes, removal of sand from riverbeds and agricultural runoff have spoilt the river ecosystem. Poaching of animals for their skin, fur, tusk, horns and meat for medicinal purposes are a major threat to birds, mammals, plants and reptiles.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Mock test on Loss of Biodiversity for NEET preparation
Question 50. Extinction abetted by human activities is called
- Natural Extinction
- Mass Extinction
- Coextinction
- Anthropogenic extinction
Answer: 4. Anthropogenic extinction
Anthropogenic extinctions are the extinctions abetted by human activities like settlements, hunting,overexploitation and habitat destruction.
Question 51. Loss of biodiversity may lead to
- Lower resistance to environmental stress.
- Decrease in plant production.
- Breakdown in functioning the ecosystem processes.
- Increase in genetic diversity.
Choose the correct option.
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 4
- 1 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer: 4. 1, 2 and 3
All statements are correct except
Incorrect statement can be corrected as Loss of biodiversity may lead to decrease in genetic diversity.
Question 52. Decline in the population of Indian native fishes due to introduction of Clarias gariepinus in river Yamuna can be categorised as
- Coextinction Neet
- Habitat Fragmentation
- Overexploitation
- Alien-species invasion
Answer: 4. Alien-Species Invasions
Introduction of the African catfish, Clarias gariepinus for aquaculture purposes, has become athreat to indigenous catfishes in our rivers. It is an example of alien species, as it has come from outside for the invasion communities in Yamuna.
Question 53. Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) is an example of …………………………… . It was introduced in Indian waters for its beautiful flower.
- Disturbance And Degradation
- Coextinctions
- Alien-Species Invasions
- Overexploitation
Answer: 3. Alien-Species Invasions
Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) introduced in Indian waters. It is an example of alienspecies invasions. These causes dense mate of biomass on the water surface, which reduces dissolved oxygen.
Question 54. Which of the following is an exotic species?
- Lantana
- Parthenium
- Eichhornia
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
All of the given species are exotic species. An exotic species is one that is not native to a given area. It is a plant, animal or insect that has been brought to an area, often by immigrants.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
NEET practice test on Loss of Biodiversity and Its Causes
Question 55. Which of the following is an example of alien species invading a new ecosystem resulting in biodiversity losses?
- Introduction of Nile Perch into Lake Victoria in East Africa
- Introduction of water hyacinth into India
- Introduction of African catfish into Indian rivers
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
All given options are an example of alien-species invading a new ecosystem resulting in biodiversity losses. When alien species are introduced unintentionally or deliberately they result in decline in biodiversity, e.g. when Nile perch was introduced into Lake Victoria in East Africa, it led to extinction of cichlid fish in the lake.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 56. American water plant that has become a troublesome water weed in India is
- Cyperus rotundus
- Eichhornia crassipes
- Typha latifolia
- Trapa bispinosa
Answer: 2. Eichhornia crassipes
Eichhornia crassipes is an American origin plant and now water weed in India.
Question 57. A weed which has invaded many forest lands of India.
- Ocimum sanctum
- Papaver somniferum
- Lantana camara
- Oryza sativa
Answer: 3. Lantana camara
Lantana camara is considered to be a weed in large areas of the Paleotropics, where it has established itself. In agricultural areas or secondary forests, it can become the dominant understorey shrub, crowding out other native species and reducing biodiversity. So, Lantana camara has invaded many forest lands of India.
Question 58. Which of the following is not an invasive species?
- Parthenium hysterophorus
- Ocimum sanctum
- Lantana camara
- Eichhornia crassipes
Answer: 2. Ocimum sanctum
Ocimum sanctum (tulsi) is not an invasive species. Non-native or alien species are often introduced inadvertently for their economic and other uses. They often become invasive and drive away the local species. Lantana camara has replaced many species in forests of Central India. Parthenium hysterophorus has pushed out several herbs and shrubs from open places in the plains. Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) was introduced in Indian water to reduce pollution. It clogged water bodies including wetlands at many place resulting in death of several aquatic plants and animals.
Question 59. Consider the following statements with respect to Eichhornia.
- It drains off oxygen from water and is seen growing in standing water.
- It is an indigenous species of our country.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 1. Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect. Incorrect statement can be corrected as Eichhornia is an alien or exotic species. This plant was introduced in India because of its beautiful flowers and shape of leaves.
Question 60. When a species becomes extinct, the plant and animal species associated with it also becomes extinct, this is called
- Extinction
- Coextinction
- Fragmentation
- Proextinction
Answer: 4. Proextinction
When a species becomes extinct, the plant and animal species associated with it also becomes extinct. This is called coextinction, e.g. when a host fish species become extinct, its unique assemblage of parasites also meet the same fate.
Question 61. If the high altitude birds become rare or extinct, the plants which may disappear along with them are
- Pine
- Oak
- Orchids
- Rhododendrons
Answer: 4. Rhododendrons
Rhododendrons are woody plants that grow at high altitude which attract birds. Birds take up the nectar produced by flowers of these plants and carry out the pollination. So, both are dependent on each other and if bird species become extinct, the plant also becomes extinct.
Question 62. One out of the following is not responsible for biodiversity loss.
- Alien-species invasion
- Coextinction
- Ex situ conservation
- Deforestation
Answer: 3. Ex situ conservation
Ex situ conservation is not responsible for biodiversity loss, rather it is a method of conservation of biodiversity. It conserves selected rare plants/animals in places outside their natural homes whereas alien-species invasion, coextinction and deforestation result in extinction of many species and loss of biodiversity.
Question 63. The alien-species introduced into lake Victoria that was responsible for the extinction of cichlid fishes is
- Water Hyacinth
- Carrot Grass
- Nile Perch
- African Catfish
- Murrels
Answer: 3. Nile Perch
The Nile Perch, a voracious predator introduced to the lake Victoria as a fish food lead to the extinction of over one hundred species of native cichlid fish there.
Question 64. A pollinator specific to a plant (mutualism is seen) becomes extinct. What effect will be observed in those plants?
- Decreased pollination
- No effect as a substitute pollinator is available
- The plant would not be pollinated
- None of the above
Answer: 3. The plant would not be pollinated
If a pollinator specific to a plant becomes extinct, plant would not be pollinated anymore because both of these share mutualistic relation. Finally, it leads to extinction of plant species also.
Question 65. Assertion The current species extinction taking place is different from the earlier mass extinction. Reason (R) Present species extinction is due to natural causes, whereas the earlier extinction was due to man-made causes.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 3. A is true, but R is false
A is true, but R is false because The current species extinction are estimated to be 100 to 1000 times faster than in the prehuman times and our activities are responsible for these faster rates. Ecologists warn that if, the present trend continues, nearly half of all the species on earth might be wiped out within the next 100 years. The present occurring species extinction is different from the earlier mass extinction as the present species extinction is due to man-made causes, whereas the earlier extinction was due to the natural causes.
Question 66. An example of …………………… is the disappearance of dinosaurs along with various other organisms.
- Coextinction
- Anthropogenic Extinction
- K-T Boundary
- Extinction vertex
Answer: 3. K-T Boundary
Mass extinction occurred between cretaceous and tertiary over 60 million years ago when dinosaurs and a number of other organisms disappeared. It is also called K-T boundary.
Question 67. Many species like steller’s sea cow, passenger pigeon have been driven to the brink of extinction. A reason for this could be
- Over-Exploitation By Humans
- Pollution
- Habitat Loss
- Competition from introduced species
Answer: 1. Over-Exploitation By Humans
Excessive exploitation of a species, whether a plant or animal reduces the size of its population, so that it becomes vulnerable to extinction, e.g. steller’s sea cow, passenger pigeon, etc.
Question 68. Which of the following pairs of an animal and a plant represents endangered organisms in India?
- Bentinckia nicobarica and red panda
- Tamarind and rhesus monkey
- Cinchona and leopard
- Banyan and black buck
Answer: 1. Bentinckia nicobarica and red panda
A plant Bentinckia condapanna/nicobarica (member of family–Arecaceae) and the animal redpanda, both are declared as endangered in India.
