Biology MCQs with answers for NEET Water Pollution
Question 1. The addition of hazardous material or heat to water which is harmful to humans, animals or desirable aquatic life is called
- Water Pollution
- Air Pollution
- Soil Pollution
- Noise pollution
Answer: 1. Water Pollution
The contamination of water bodies due to the changes in physical, chemical and biological properties of water that can be harmful to humans, animals or desirable aquatic life i
s called water pollution.
Question 2. When the pollutant flow is conveyed in well-defined channels as municipal or industrial waste, it is called
- Diffuse Source
- Non-Point Source
- Point source
- All of these
Answer: 3. Point source
There are two types of sources of water pollution, i.e. point sources and non-point sources.
Point sources are the sources of water pollution which are fixed at a place and have a specific location for discharging pollutants into a particular water body. These are factories, power plants, underground coal mines and oil wells situated close to the water sources. The point sources of water pollution discharge their pollutants directly into the water source.
“water pollution questions “
Non-point sources are the sources of water pollution which are scattered and do not have any specific location for discharging pollutants into a particular water body. These are runoff from fields, lawns and gardens, many small drains, rain water from roads and streets and dirty water from the different construction sites. Thus, when the pollutant flow is conveyed in well-defined channels or industrial waste it is called point source.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 3. Water pollution
- Increases Oxygenation
- Decreases Turbidity
- Increases Turbidity And Deoxygenation
- Increases photosynthesis
Answer: 3. Increases Turbidity And Deoxygenation
Discharge of untreated sewage, surface runoff water from agricultural fields and industrial wastes lead to eutrophication and exclusive growth of planktons and blue-green alga. This increase turbidity and reduces level of dissolved oxygen (i.e. deoxygenation). Thus, killing aquatic animals like fishes.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET

NEET Biology water pollution MCQs with answers
Question 4. The greatest problem of water conservation is to reduce the amount of
- Precipitation
- Runoff Water
- Groundwater
- Evaporation
Answer: 2. Runoff Water
The greatest problem of water conservation is to reduce the amount of runoff water. It is the flow of water that occurs when excess stormwater, meltwater or other sources flow over the earth’s surface.
Question 5. Water pollution is caused due to
- Industrial Effluents
- Agricultural Discharges
- Sewage and other wastes
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Oil spills and refinery discharge prevent oxygenation of water, inhibit plant growth and kill animal life. Fertilisers and pesticides used in agriculture are washed down into water bodies during rains. Both of them pollute water. Industrial effluents or wastes are also passed into water bodies. They contain a number of toxic chemicals which not only poison aquatic life, but also make the water unfit for domestic or agricultural use. Similarly treated or untreated sewage of municipalities, boats, ships, etc. is poured into water bodies.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
“questionnaire about water pollution “
Question 6. Water is normally not polluted by
- Sewage
- Radioactive Waste
- Oil Spills
- Aquatic plants
Answer: 4. Aquatic plants
Water is normally not polluted by aquatic plants. Aquatic plants play an important role in maintaining a healthy water garden or pond. They not only absorb carbon dioxide but also release oxygen into the water. They also improve the aquatic environment for fish, by absorbing nutrients from the water. Aquatic plants are critical to our freshwater ecosystems.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 7. Which one of the following is not a bioindicator of water pollution?
- Sludge worms
- Blood worms
- Stone flies
- Sewage fungus
Answer: 3. Stone flies
Stone flies (e.g. Perla sp.) belong to order–Plecoptera of class–Insecta,which has the terrestrial mandibles. These are not bioindicators of water pollution.
Question 8. Assertion Liquid waste product from industrial processes and domestic activity are termed as effluents. Reason (R) Fertiliser factories, steel and textile sugar mills are some industries which release effluents.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R both are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 2. Both A and R both are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A. Effluents are liquid industrial wastes released from steel, textile mills and fertiliser factories as a waste product.
Water pollution multiple choice questions for NEET
Question 9. Which of the following pollutant increases the hardness of water?
- H2SO4
- DDT
- Pb
- Cu
Answer: 1. H2SO4
Sulphuric acid (H2SO4) is highly reactive in water. It is also toxic and corrosive therefore increases the hardness of water.
Biology MCQs with answers for NEET
Question 10. Drinking of mineral water with very low level of pesticides (about 0.02 ppm) for long periods may
- Produce Immunity Against Mosquito
- Cause Leukaemia (Blood Cancer) In Most People
- Cause Cancer Of The Intestine
- Lead to the accumulation of pesticide residues in body fat
Answer: 4. Lead to accumulation of pesticide residues in body fat
In India, prolonged use of DDT (pesticide) can be detected in the body fat of the people, highest in the world. Most toxic pollutants such as pesticides do not degrade easily and therefore, accumulate within the body of an organism, especially in fat deposited portions. This process is known as biochemical concentration.
“water scarcity results in a higher incidence of- “

Important water pollution questions for NEET Biology exam
Question 11. Which of the following is the main factor of water pollution?
- Smoke
- Industrial waste
- Ammonia
- Detergents
Answer: 2. Industrial waste
Industrial waste is the main factor of water pollution. It is discharged into a river. Sewage agricultural chemical and industrial waste constitute the major water pollutant.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 12. Identify the Act formulated in 1974.
- The Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act
- The Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act
- The Noise (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act
- The Environment (Protection) Act
Answer: 1. The Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act
The Government of India has passed The Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act in, 1974, to safeguard our water resources.
Question 13. Water be come polluted due to the presence or addition of
- Inorganic Substances
- Organic Substances
- Biological agents
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Water is the prime necessity of life. Water pollution is mainly caused by industrial wastes, sewage (household waste), insecticides and herbicides. Microorganisms such as protozoan, bacteria and virus also pollute water. So, water become polluted due to the presence of inorganic, organic and biological substances.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
“water scarcity results in a higher incidence of “
Question 14. With the rise of water temperature, dissolved oxygen
- Remains Unchanged
- Increases In Amount
- Decreases In Amount
- Is More available to the aquatic organisms
Answer: 3. Decreases In Amount
Amount of dissolved oxygen decreases with the rise in temperature of water. Hot wastewater is produced by many industries, thermal power plants and oil refineries. It is drainedout into water bodies. Consequently temperature of the water bodies rises, which decreases content of dissolved oxygen.
Question 15. Polluted water can be purified by using
- Microorganisms
- Algae
- Pesticides
- Fishes
Answer: 1. Microorganisms
Polluted water can be purified by using microorganisms. Sewage water can be prevented by treating sewage before passing into the water bodies. Domestic sewage primarily contains biodegradable organic matter, which readily decomposer by bacteria and other microorganisms, which can multiply by using these organic substances as substrates and hence reduce some of the components of sewage.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 16. What will happen if our water resources are continued to be polluted by industrial wastes?
- Sufficient food will not be available to water organism
- Sufficient O2 will not be available to water organism
- BOD value of water will decrease
- Drinking water will not be available
Answer: 4. Drinking water will not be available
Polluted water is unsuitable for drinking, recreation, agriculture and industry. It diminishes the aesthetic quality of lakes and rivers. More seriously, contaminated water destroys aquatic life and reduces its reproductive ability.
“which is the most polluted river in the world “
Question 17. The effluents from industries contain which of the following heavy metals?
- Cadmium
- Lead
- Mercury
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
The effluents from industries contain cadmium, lead and mercury.
Thus opiton 4 is correct.
Question 18. Which of the following metal is a pollutant in water and causes sterility in human being?
- Manganese
- Mercury
- Chromium
- Arsenic
Answer: 1. Manganese
Manganese causes sterility, eye diseases, loss of memory or loss of vision in human beings. High percentage of manganese as water pollutant can be seen in water bodies along with thermal power stations and fungicides.
Solved MCQs on water pollution for NEET
Question 19. Blue baby syndrome is caused by
- Cadmium Pollution
- Mercury Poisoning
- Chronic Exposure To Arsenic
- Excess nitrate in drinking water
Answer: 4. Excess nitrate in drinking water
Blue baby syndrome is blood related condition found in babies due to nitrate poisoning (poisoning limits blood’s ability to carry oxygen thereby causing baby to look blue) known as methemoglobinemia.
Biology MCQ For NEET With Answers
Question 20. Cadmium polluted water affects
- RBCs
- bones
- liver
- Both 2 and 3
Answer: 4. Both 2 and 3
Consumption of cadmium causes bone disorder and cancer of lungs and liver. Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 21. Itai-itai disease is due to
- Cadmium Poisoning
- Lack Of Pituitary Hormones
- NO2 poisoning
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Cadmium Poisoning
Itai-itai disease is chronic cadmium poisoning with renal tubular dysfunction followed by osteomalacia.
Question 22. Which of the following diseases is not caused by polluted water?
- Cholera
- Pneumonia
- Jaundice
- Dysentery
Answer: 2. Pneumonia
Pneumonia is caused due to air pollution not water pollution. Rest other disease are caused by polluted air.
“which is the most polluted river in the world “
Question 23. Chronic arsenic poisoning causes
- Ltai-Itai Disease
- Foot And Mouth Disease
- Blue Baby Syndrome
- Black foot disease
Answer: 4. Black foot disease
In China (Province of Taiwan), exposure to arsenic, via. drinking water has been shown to cause a severe disease of the blood vessels, which leads to gangrene, known as black foot disease. This disease has not been observed in other parts of the world, and it is possible that malnutrition contributes to its development.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 24. Heavy metals like ‘Ni’ can be separated from water by
- Carboxymethyl Chitosan
- Biological Treatment
- Ultrafiltration
- Filtration
Answer: 2. Biological Treatment
Heavy metals present in the waste water are the major concern of the environmental pollution. Different methods that can be used for the removal of heavy metals are biosorption (using microorganisms), biofilter, activated sludge treatment,etc. In biological treatment, microorganism under anaerobic conditions acts like biosorption which absorbs heavy metal by the transfer of ions from solution phase to cellular phase and removes the metallic waste from water.
Question 25. Minamata disease was caused due to the consumption of
- Sea Food Containing Lot Of Cadmium
- Fish Contaminated With Mercury
- Oysters With Lot Of Pesticide
- Sea Food contaminated with selenium
Answer: 2. Fish Contaminated With Mercury
A chemical factory belonging to Chicco Corporation, Japan release wastewater containing methylmercury from 1932 to 1968. This toxic chemical accumulated in the organisms in the Minamata Bay and slowly started bioaccumulation in shell fish and fishes. People surrounding the bay consumed these organisms which resulted in mercury poisoning. By 2004, a total compensation of 86 million dollars were paid and were order to clean up the contamination. Mercury consumption mainly affects central nervous system. This results impairment of vision, trembling, hair loss and inability to coordinate. Extreme poisoning can lead to insanity, paralysis which may lead to coma and eventually death. So, Minamata disease was caused due to the consumption of fish contaminated with mercury.
Best multiple choice questions on water pollution for NEET preparation
Question 26. Based on toxicological characteristics, the important forms of mercury is/are
- Elemental
- Inorganic
- Organic
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
The three forms of mercury are elemental mercury, inorganic mercury
compounds (primarily mercuric chloride) and organic mercury compounds (primary methyl mercury). All the three forms adversely effect the human health.
“which is the most polluted river in the world “
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 27. In Minamata Bay, Japan, the animals which remained free from Minamata disease are
- Pigs
- Rabbits
- Dogs
- Cats
Answer: 2. Rabbits
Release of mercury in water causes pollution. Mercury enters the food chain killing fishes. Human beings feeding on such fishes will suffer from Minamata disease. Similarly, all carnivores feeding on fishes will develop this disease except rabbit because it is herbivore.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 28. Water pollution can be stopped best by
- Treating Effluents To Remove Injurious Chemicals
- Rearing More Fishes
- Fumigation
- Spraying With Ddt
Answer: 1. Treating Effluents To Remove Injurious Chemicals
The industrial effluents with many injurious or hazardous chemicals must be treated before they are released in river, lake, pond or sea.
“which is the most polluted river in the world “
Question 29. Which of the following is not used for disinfection of drinking water?
- Chlorine
- Ozone
- Chloramine
- Phenyl
Answer: 4. Phenyl
Chlorine, ozone, chloramine are used for disinfection of drinking water. Phenyl does not use for this purpose.
Question 30. Municipal waste, containing human and animal excreta, food residues, detergents, and rich in bacteria and organic substances, is called
- Sewage
- Sewer
- Sewerage
- None of these
Answer: 1. Sewage
Sewage is domestic, municipal or industrial liquid waste products disposed of, via. a pipe or similar structure. The composition of each sewage stream varies widely, but sewage derived from a large city can be expected to contain water, non-pathogenic bacteria, pathogens, organic particles, soluble organic material, inorganic particles, soluble inorganic material, animals, macrosolids, gases, emulsions and toxins.
Question 31. The below chart shows the sources of water pollution. Identify the option with correct combination.
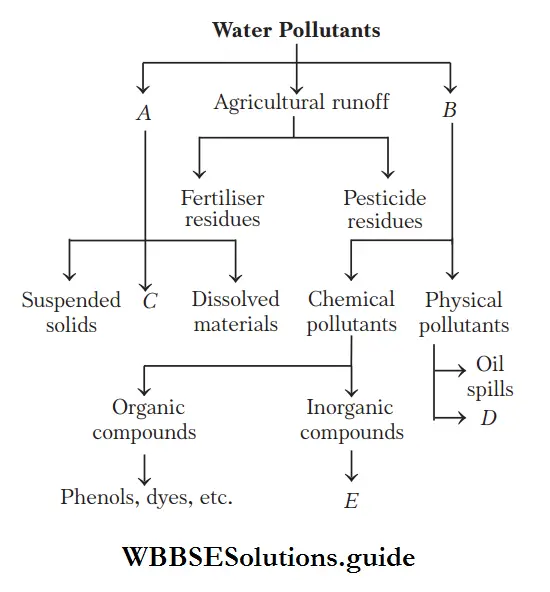
- A–Domestic sewage, C–Colloidal solids, E–Heavy metals
- B–Industrial waste, D–Colloidal solids, E–Noble gases
- C–Colloidal solids, D–Domestic wastewater, E–Heavy metals
- A–Domestic sewage, D–Thermal (hot) wastewater, E–Wood debris
Answer: 1. A–Domestic sewage, C–Colloidal solids, E–Heavy metals
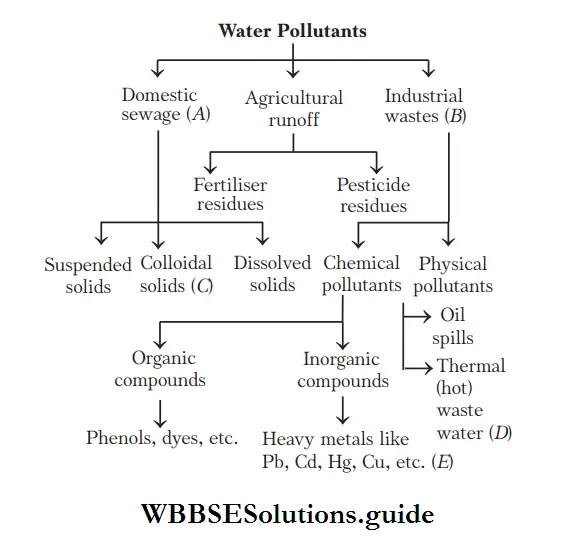
NEET Biology eutrophication and water pollution MCQs
Question 32. Domestic sewage contains
- Suspended Solid
- Colloidal Material
- Dissolved material
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Domestic sewage contain Suspended solids, e.g. sand, silt and clay. Colloidal materials, e.g. faecal matter, bacteria, paper and cloth fibres. Dissolved materials, e.g. nitrates, ammonia, phosphate, sodium, calcium salt.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 33. Domestic sewage mainly consists of …A… material which is easily decomposed by …B…
- A–inorganic, B–virus
- A–biodegradable, B–decomposers
- A–non-chemical, B–chemical processes
- A–synthetic, B–bacteria
Answer: 2. A–biodegradable, B–decomposers
Question 34. Expanded form of BOD is Odisha JEE
- Biochemical Oxygen Demand
- Biosynthetic Oxygen Demand
- Bird Oxygen Demand
- Biogeochemical Oxygen Demand
Answer: 1. Biochemical Oxygen Demand is expanded form of BOD.
Question 35. Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) is a measure of
- Industrial Wastes Poured Into Water Bodies
- Extent To Which Water Is Polluted With Organic Compound
- Amount Of Carbon Monoxide Inseparably Combined With Haemoglobin
- Amount Of Oxygen Needed By Green Plants During Night
Answer: 2. Extent To Which Water Is Polluted With Organic Compound
The microorganism in polluted bodies use dissolved oxygen to metabolise organic matter in polluted water. This is called biochemical oxygen demand. The more organic matter in sewage an polluted bodies, greater the BOD and hence less oxygen is left availabel for higher animals like fishes.
Question 36. Arrange the following options in ascending order of their BOD value.
- Sample of highly polluted pond water.
- Sample from unpolluted pond water.
- Distilled water.
Choose the correct option.
- 3,1,2
- 2,3,1
- 3,2,1
- 1,3,2
Answer: 3. 3,2,1
If the organic concentration is high, there will be high BOD because more dissolved oxygen will be used to breakdown the organic mass by bacteria. So, high BOD marks high pollution. Distilled water has no content of the organic substance as it has been treated and filtred. Unpolluted water pond will not have polluted source of organic mass, but the existing organisms die and their dead bodies contribute to a little raised BOD. Highly polluted water will show a very high BOD as it will take a lot of dissolved oxygen to breakdown the organic mass in water body. So, distilled water is least polluted, followed by unpolluted pond water and then highly polluted pond water.
Thus, option 3 is correct.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 37. A lake with inflow of domestic sewage rich in organic waste may result in
- Drying Of The Lake Very Soon Due To Algal Bloom
- An Increased Production Of Fish Due Increase In Nutrients
- Death Of Fish Due To Lack Of Oxygen
- Increased Population Of Aquatic Food Web Organisms
Answer: 3. Death Of Fish Due To Lack Of Oxygen
A lake rich in domestic sewage nutrients will lead to eutrophication. Eutrophication is when the environment becomes enriched with nutrients. This can be a problem in marine habitats such as lakes as it can cause algal bloom and other aquatic plants following this overcrowding occurs and plants compete for sunlight, space and oxygen. It deoxygenates the water enough to kill the fish and other animals.
Question 38. What will be the effect of the addition of organic material on water?
- COD remains unaffected
- BOD remain unaffected
- Increases BOD
- Reduces BOD
Answer: 3. Increases BOD
The decomposition of organic matter by microbes requires oxygen. The degree of organic impurity of water is measured in terms of BOD. BOD is the oxygen in milligrams required by microorganisms to metabolise organic waste. When more organic matter are added to water the BOD of water will increase.
Role of pollutants in water contamination NEET MCQs with answers
Question 39. In which one of the following the BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand) of Sewage (S), Distillery Effluent (DE), Papermill Effluent (PE) and Sugarmill Effluent (SE) have been arranged in ascending order?
- SE < PE < S < DE
- PE < S < SE < DE
- S < DE < PE < SE
- SE < S < PE < DE
Answer: 3. S < DE < PE < SE
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) is the amount of oxygen required to decompose the organic material by the microorganisms. The more oxygen required for microorganisms that means there is more organic material. According to the central pollution control board, limit of BOD prescribed is 30ppm (mg/d) for 3 days at 27ºC. The BOD of the given pollutants in ascending order is S<DE<PE<SE.
Question 40. If a large quantity of domestic sewage is continuously emptied into a small stream, it leads to Punjab PMET
- Depletion Of Oxygen Content In-Stream Water
- Depletion Of Nutrients In The Stream Water
- Enrichment Of Oxygen Content In-Stream Water
- Increase in the total amount of life in the stream water
Answer: 1. Depletion Of Oxygen Content In-Stream Water
If large quantities of domestic sewage are continuously emptied into a small stream, it leads to depletion of oxygen content in stream water as microbes that develop to degrade the organic matter shall consume the oxygen and reduce its amount.
Question 41. The limit of BOD prescribed by the Central Pollution Control Board for the discharge of industrial and municipal wastewater into natural surface waters, is
- < 10 ppm
- < 100 ppm
- < 30 ppm
- < 3.0 ppm
Answer: 1. < 10 ppm
The Central Pollution Control Board has prescribed the limit of BOD for the discharge of industrial and municipal waste in order to regulate the water pollution and for efficient water treatment and it is < 10 ppm.
Question 42. Assertion BOD of a river polluted by sewage is more than 20 ppm. Reason (R) Polluted river contains excess of organic matter.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. Degree of impurity of water due to organic matter is measured in terms of BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand). BOD is the oxygen in milligrams required for five days in one litre of water at 20°C for the microorganisms to metabolise organic waste. It is measured in the milligrams of oxygen taken up in one litre of sewage. The effluent that is legally allowed to be discharged into a river or stream should be such that BOD at 20°C should not be more than 20 ppm, i.e. 20 mg per litre.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 43. The domestic sewage in large cities
- Has A High Bod As It Contains Both Aerobic And Anaerobic Bacteria
- Is Processed By Aerobic And Then Anaerobic Bacteria In The Secondary Treatment In Sewage Treatment Plants (Stps)
- When Treated In Stps Does Not Really Require The Aeration Step As The Sewage Contains Adequate Oxygen
- Has very high amount of suspended solids and dissolved salts
Answer: 2. Is Processed By Aerobic And Then Anaerobic Bacteria In The Secondary Treatment In Sewage Treatment Plants (Stps)
Sewage water can be purified by passing it through Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs) with the action of heterotrophic microorganisms. There are three stages of this treatment, i.e. primary, secondary and tertiary. Primary treatment removes floating and suspended solids from sewage. In secondary treatment, a large number of aerobic heterotrophic microbes grow in the aeration tank.
The sediment of settling tank is called activated sludge. The remaining is passed into a large tank called anaerobic sludge digester. It is designed for continuous operation. The aerobic microbes present in the sludge get killed. Anaerobic microbes digest the organic mass as well as aerobic microbes of the sludge. Methanogenic bacteria produce a mixture of gases containing methane, H S2 and CO2.
Question 44. Relationship between DO and BOD is that they
- Are Directly Proportional
- Are Inversely Proportional
- Are Not Related
- Always remain equal to each other
Answer: 2. Are Inversely Proportional
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) is the amount of oxygen required by microorganisms to decompose organic waste matter present in water. Dissolved oxygen (DO) is the amount of oxygen dissolved in water. BOD and DO are inversily proportional to each other, i.e. a decline in DO levels reflects a high level of BOD.
Question 45. Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) may not be a good index for pollution for water bodies receiving effluents from
- Domestic Sewage
- Dairy Industry
- Petroleum Industry
- Sugar industry
Answer: 3. Petroleum Industry
Petroleum industry releases inorganic chemical pollutants which cannot be degraded by microbes. Thus, its BOD index cannot be measured.
Question 46. Biomagnification of DDT in an aquatic, food chain starting from water having a concentration of 0.003 ppm may go, in fish eating birds, upto
- 2 ppm
- 25 ppm
- 50 ppm
- 100 ppm
Answer: 2. 25 ppm
Biomagnification is well-known for mercury and DDT. In this manner, the concentration of DDT is increased at successive trophic level, e.g. it is started at 0.003 ppm in water. It can ultimately reach upto 25 ppm in fish eating birds.
Question 47. Choose the correct statement regarding the biomagnifications of DDT in an aquatic food chain.
- Biomagnification is seen only up the trophic level and sometimes
the lower levels have higher concentrations of toxicant. - High concentrations of DDT disturbs calcium metabolism in birds, causing thinning of egg shell and premature breaking.
- Carnivorous fish have more concentration of DDT than the water itself and are consumed by humans.
Choose the option containing correct statements.
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1,2 and 3
Answer: 3. 1 and 2
Statements 1 and 2 are correct, but 3 is incorrect because River water may have a very low concentration of DDT, but the carnivorous fish in that river contain very high concentration of DDT due to biomagnification. This carnivorous fish is taxic if consumed by human beings.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 48. DDT shows biomagnification (bioconcentration). It is found maximum in milk cream. Its concentration in human fat in India has reached a level of
- 5 to 10 ppm
- 51 to 75 ppm
- 13 to 31 ppm
- 100 to 145 ppm
Answer: 3. 13 to 31 ppm
Chlorinated hydrocarbons, such as DDT, are not very soluble in water. It generally contains only 1 to 2 parts of pesticide per billion parts of water. However, these compounds are very soluble in fats. Aquatic microorganisms absorb them in fat and oils where they accumulate to form concentrations many times greater than in water. The increased accumulation of toxic substances in the food pyramid is called biological magnification. In
Question 49. Find the correct order of biomagnification of DDT in an aquatic food chain.
- Water (0.003 ppm), zooplankton (0.5 ppm), small fish (0.04 ppm), large fish (2 ppm), fish-eating birds (25 ppm)
- Water (0.003 ppm), zooplankton (0.04 ppm), small fish (0.5 ppm), large fish (2 ppm), fish-eating birds (25 ppm)
- Water (0.003 ppm),fish-eating birds (25 ppm), zooplankton (0.5 ppm), small fish (0.04 ppm), large fish (25 ppm)
- Water (0.003 ppm), small fish (0.04 ppm), zooplankton (0.5 ppm), large fish (2 ppm), fish-eating birds (25 ppm)
- Water (0.003 ppm), large fish (0.04 ppm), small fish (0.5 ppm), zooplankton (2 ppm), fish-eating birds (25 ppm)
Answer: 2. Water (0.003 ppm), zooplankton (0.04 ppm), small fish (0.5 ppm), large fish (2 ppm), fish-eating birds (25 ppm)
Biomagnification involves a gradual increase in the concentration of chemicals like pesticides, e.g. DDT towards higher trophic levels in a food chain. In the given question, the food chain is Water → Zooplankton → Small fish → Large fish → Fish-eating birds Thus, the concentration of DDT must be lowest in water, highest in fish-eating birds and gradually increasing with intermediate trophic levels.
Question 50. The term ‘biomagnification’ refers to the
- Growth Of Organisms Due To Food Consumption
- Increase In Population Size
- Blowing Up Of Environmental Issues By Man
- Increase in the concentration of non-degradable pollutants as they pass through food chain
Answer: 4. Increase in the concentration of non-degradable pollutants as they pass through food chain
Biomagnification is defined as the gradual increase in the concentration of harmful pesticides (non-degradable pollutants) in the food chain, with an increase in trophic level.
Question 51. Which among the following is likely to have the highest levels of DDT depositions in its body?
- Seagull
- Phytoplankton
- Eel
- Crab
Answer: 1. Seagull
Biomagnification is the increase in the concentration of a compound in the tissue of an organism as the compound passes up a food chain usually as a result of food intake. Level of concentration of the compound increases in higher trophic levels as shown in the following chain Water → Phytoplanktons → Zooplanktons → Insects → Fish → Large fish Higher the trophic level higher will be the accumulation of organic compound. Hence, seagull is likely to have the highest level of DDT deposition in its body.
Question 52. What is true for DDT?
- It is not a pollutant
- It is a non-biodegradable pollutant
- It is an antibiotic
- It is an antiseptic agent
Answer: 2. It is a non-biodegradable pollutant
Option 2 is true for DDT. DDT, plastics, polythene, bags, insecticides, pesticides, mercury, lead, arsenic, metal articles like aluminium cans, synthetic fibres, glass objects, iron products and silver foils are non-biodegradable pollutants.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 53. In an area where DDT had been used extensively, the population of birds declined significantly because
- Snake Was Feeding Exclusively On Birds
- Many Of The Birds Laid Eggs, But Did Not Hatch
- Bird Stopped Laying Eggs
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Many Of The Birds Laid Eggs, But Did Not Hatch
In an area where DDT had been used extensively, the population of birds declined significantly because many of the birds laid eggs, which did not hatched.
Question 54. The maximum biological magnification of DDT through the food web is seen in
- Algae
- Bacteria
- Higher Plants
- Man
Answer: 4. Man
Those pollutants which either degrade very slowly or do not degrade at all are called non-degradable pollutants. They usually join the food chain and enter the body of an organism where their concentration always increases. This phenomenon is called biological magnification. These pollutants may degrade or destroy the resources, e.g. DDT, phenolic compounds. As man occupies the topmost trophic level of all the food chain, man cannot pass the toxicant to any other organism.
Hence, the correct option is 4.
Question 55. If a water body is contaminated with a toxicant, its biomagnification will be more marked in
- Water
- Planktons
- Small Fishes
- Birds
Answer: 4. Birds
The more contaminated phytoplankton, zooplankton eats, the more pollutants it will have in it body. This is because the consumer at the successive trophic level to fulfil the energy requirement. Due to this toxicant keep on accumulating in successive trophic level. So, planktons will have least and birds will have the most toxicant present.
Question 56. Algal blooms in a lake
- Lead To Oxygen Depletion
- Increase CO2 Level
- Kill fishes and other organisms
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Algal bloom in a lake occurs when it becomes rich in nutrient growth of macrophytes leads to oxygen depletion and increase CO2 level. Due to the lack of oxygen, fishes and other organisms are prone to death.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 57. The term ‘Terror of Bengal’ corresponds to
- Eichhornia crassipes
- Decreased Biological Oxygen Demand
- Biomagnification
- Algal Bloom
Answer: 1. Eichhornia crassipes
Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) also called Terror of Bengal’ is one such plant that sometimes chokes ponds, lakes and rivers resulting in imbalance of ecosystem, dynamics of water bodies.
Question 58. Eutrophication of water bodies is associated with water
- Hole
- Water Hyacinth
- Lily
- None of these
Answer: 2. Water Hyacinth
Eutrophication is the pollution of water bodies. It occurs due to reduction of dissolved oxygen resulting from rich growth of algae and other microorganisms (due to rich in nutrients in lake or water body in which fertilised fields, domestic sewage are the main source). In eutrophic, water bodies sudden death of fishes takes place because of oxygen depletion. Such water bodies support the growth of plants like water hyacinth.
Question 59. What renders algal blooms and its distinctive colour in water?
- Their pigments
- Excretion of coloured substance
- Absorption of light by algal cell wall
- Formation of coloured chemicals in water
Answer: 1. Their pigments
Algal blooms impart a distinct colour to water due to their pigments.
Question 60. Consider the following statements.
- Algal blooms are formed by free floating algae.
- Algal bloom causes fish mortality and deterioration of water quality.
- Water hyacinth, the world’s most problematic aquatic weed is also called ‘Terror of Bengal’.
Choose the option containing correct statements.
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1,2 and 3
Answer: 4. 1,2, and 3
All given statements are correct. The excess growth of planktonic algae that causes colouration of water is called algal blooms. They are toxic to animals and humans. In some cases, eutrophic water bodies support excessive growth of floating plants.
Question 61. Water hyacinth is grown in water to
- Absorb O2 Of Water
- Kill Microorganisms
- Absorb Heavy Metals And Radioactive Elements
- Supply food to aquatic animals
Answer: 3. Absorb Heavy Metals And Radioactive Elements
Microorganisms and certain plants like water hyacinth usually absorb heavy metals and radioactive elements present in water.
Question 62. Eutrophication is excessive growth of algae, plants and animals in water bodies due to nutrient enrichment particularly with
- Nitrogen And Phosphorus
- Calcium And Phosphorus
- Sodium And Calcium
- Nitrogen and calcium
Answer: 1. Nitrogen And Phosphorus
Eutrophication is excessive growth of algae, plants and animals in water bodies due to nutrient enrichment particularly with nitrogen and phosphorus.
Question 63. The accelerated ageing of lakes due to sewage and agricultural and industrial waste is called
- Nutrient Enrichment
- Accelerated Eutrophication
- Biomagnification
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Accelerated Eutrophication
Pollutants like effluents from the industries and sewage speed up this ageing process. This is called accelerated or cultural eutrophication. Hot wastewater from electricity generating units, thermal power plants is important pollutants.
Question 64. Nutrient enrichment of a lake will cause
- Eutrophication
- Stratification
- Biomagnification
- Bioaccumulation
Answer: 1. Eutrophication
Eutrophication is increase in amount of nutrients in water due to detergents, pesticides, etc., and it leads to organic loading, depletion of O2, etc.
Question 65. Eutrophication results in reduction of
- Mineral Salts
- Dissolved Oxygen
- Parasitic Protozoan
- Dissolved nitrate
Answer: 2. Dissolved Oxygen
Eutrophication is the phenomenon of nutrient enrichment of a water body that initially supports a dense growth of plants and animal life. The extensive increase of algal growth in water bodies is called water bloom (algal bloom). Due to death of these algae, their organic matter gets decomposed, due to which oxygen gets depleted and the aquatic animals die. Hence, eutrophication results in the reduction of dissolved oxygen.
Question 66. Consider the following statements about eutrophication.
- It is defined as the natural ageing of a water body due to nutrient enrichment.
- This accelerated ageing is as a result of sewage, agricultural and industrial wastes being dumped into the water body.
- Excessive nitrates and phosphates are responsible for eutrophication.
- Algae grow abundantly in the presence of nitrates and phosphates and using the oxygen present in the water body thereby reducing its availability to other organisms.
Choose option containing correct statements.
- 1 and 2
- 1,2 and 3
- 1,3 and 4
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: 1,2,3 and 4
All the given statements are correct.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 67. Which one of the following statements is correct?
- Both Azotobacter and Rhizobium fix atmospheric nitrogen in root nodules of plants
- Cyanobacteria such as Anabaena and Nostoc are important mobilisers of phosphates for plant nutrition in the soil
- At present, it is not possible to grow maize without chemical fertilisers
- Extensive use of chemical fertilisers may lead to eutrophication of nearby water bodies
Answer: 4. Extensive use of chemical fertilisers may lead to eutrophication of nearby water bodies
The statement in option 4 is correct, but other options are incorrect. Incorrect statements can be corrected as At present, it is possible to grow maize without chemical fertiliser by using organic manures and compost. This is known as organic farming. Excessive use of chemical fertilisers contaminates water bodies due to runoff excess water and lead to increased algal growth due to nutrient enrichment of the water bodies. This is known as eutrophication. Azotobacter is a free-living bacterium in soil that fixes nitrogen whereas Rhizobium forms a symbiotic association with the root nodules of the plants and fix nitrogen. Cyanobacteria, i.e. Anabaena and Nostoc have specialised cells known as heterocysts which help in nitrogen fixation. Hence, these cyanobacteria are important mobilisers of nitrogen.
Question 68. Ganga Action Plan was started in Punjab
- 1947
- 1956
- 1982
- 1985
Answer: 4. 1985
Ganga is the major river in Northern India. To observe the implementation of Ganga Action Plan (GAP) for cleaning polluted stretches of the Ganga, the Central Ganga Authority (CGA) was setup in February 1985.
Question 69. The trickling filter method involves
- Pumping Of Sewage Water Into Aeration Tank Which Contains Sludge
- Passing Of Sewage Water Through A Thick Bed Of Gravel Stones
- Recycling Of Sewage Water
- Treatment of sewage with alum
Answer: 2. Passing Of Sewage Water Through A Thick Bed Of Gravel Stones
A trickling filter is a type of wastewater treatment system. It consists of a fixed bed of rocks, coke, gravel, slag, polyurethane foam, Sphagnum peat moss, and ceramic or plastic media over which sewage or other wastewater flows downward and causes a layer of microbial slime (biofilm) to grow, covering the bed of media. So, the trickling filter method involves passing of sewage water through a thick bed of gravel stones.
Question 70. A high amount ofEscherichia coli in water indicates Chandigarh
- Hardness Of Water
- Industrial Pollution
- Sewage Pollution
- Pollution due to electromagnetic radiation
Answer: 3. Sewage Pollution
The presence of E. coli bacteria indicates possible sewage contamination of water because E. coli is found only in the mammalian intestinal tract including that of humans. E. coli bacteria belong to the coliform bacteria group. Coliforms found in mammals are called faecal coliforms. Most coliforms are E. coli. So, E. coli tests are used as an indicator of faecal coliforms.
Question 71. Primary treatment of wastewater includes
- Screening And Sedimentation Of Undissolved Solids In Raw Sewage
- Breakdown Of Organic Matter Into Harmless Materials
- Chlorination Of Water
- Precipitation of water
Answer: 1. Screening And Sedimentation Of Undissolved Solids In Raw Sewage
Primary treatment of wastewater includes screening and sedimentation of undissolved solids in raw sewage.
Question 72. Which of the following is absent in polluted water?
- Hydrilla
- Water hyacinth
- Larva of stone fly
- Both 1 and 3
Answer: 1. Hydrilla
Hydrilla is a freshwater plant. It is absent in polluted water. Stone fly (Plecoptera order) larva requires well-aerated, non-polluted water.
Question 73. Which of the following is put into an anaerobic sludge digester for further sewage treatment?
- Floating debris
- Effluents of primary treatment
- Activated sludge
- Primary sludge
Answer: 3. Activated sludge
Activated sludge is put into an anaerobic sludge digester for further sewage treatment. It contains biological flocs that contain bacteria and protozoan for further digestion of organic wastes under aerobic conditions.
Question 74. Tertiary treatment of wastewater includes
- Screening And Sedimentation Of Undissolved Solids
- Chlorination Of Water
- Removal of nitrates and phosphates by precipitation
- Both 1 and 2
Answer: 3. Removal of nitrates and phosphates by precipitation
Tertiary treatment is the final cleaning process that improves wastewater quality before it is reused, recycled or discharged to the environment. The treatment removes remaining inorganic compounds and substances, such as nitrogen and phosphorus.
Question 75. In the integrated wastewater treatment process in Arcata, heavy metals are removed by
- Only Conventional Method Of Sewage Treatment
- Biological Process In The Marsh
- Chemical Processes
- Chemical fertilisers
Answer: 2. Biological Process In The Marsh
Cleaning of wastewater in Arcata Marsh involves the removal of dissolved heavy metals through a biological process.
Question 76. A citizen group called Friends of the Arcata Marsh (FOAM) basically belongs to
- Germany
- USA
- Canada
- UK
Answer: 2. USA
FOAM (Friends of the Arcata Marsh) is a non-profit organisation which for last 20 years has advanced the knowledge and educated the public about treatment and reuse of wastewater. It belongs to the USA.
Question 77. In the town of Arcata situated on Northern coast of …A…, an integrated wastewater treatment process was developed with the help of biologists from …B… . Biologists from the Humboldt State University in Arcata developed an integrated wastewater treatment process.
- A–Florida, B–Barry University
- A–California, B–Humboldt State University
- A–Florida, B–Abilene Christian University
- A–California, B–Becker University
Answer: 2. A–California, B–Humboldt State University
Question 78. Identify the advantages of ecological sanitation.
- It is a sustainable method of human method of waste disposal.
- It is cost-effective.
- Human excreta can be recycled into natural fertilisers, to replace chemical fertilisers.
Choose the option containing correct statements.
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer: 4. 1,2, and 3
All given statements are advantages of ecological sanitation.
Thus, option 4 is correct.
Question 79. An EcoSan toilet is a sustainable method of handling human excreta by using dry composting toilets. Such toilets can be found in
- Assom and Sri Lanka
- Andhra Pradesh and Maharashtra
- Kerala and Sri Lanka
- Karnataka and Nepal
Answer: 3. Kerala and Sri Lanka
An ecologically compatible system of disposal of human excreta is the use of dry composting toilets called ‘EcoSan’ toilets. No water is required. Human excreta is used as a natural fertiliser. EcoSan toilets are already working in many parts of Kerala and Sri Lanka.
Question 80. Match the following columns.
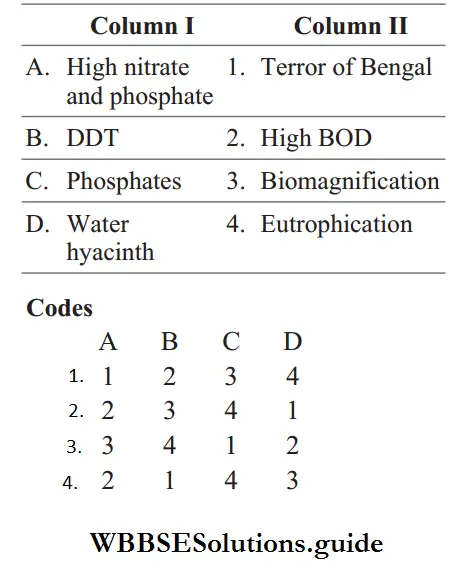
Answer: 2. A–2, B–3, C–4, D–1
