Diversity in Living Organism Very Short Answer Questions
Directions: Give an answer in one word or one sentence.
Question 1. What does hierarchy in the systems of classification mean?
Answer: Hierarchy is the frame-work of classification in which these groups are arranged in the order of increasing or decreasing levels of similarities.
Question 2. What is the criterion for the classification of organisms belonging to kingdom Monera or Protista?
Answer: Absence and presence of a well-defined nucleus and organelles in the kingdom Monera and Protista.
Question 3. Define diploblastic animal.
Answer: Animals in which cells are arranged in two germ or embryonic layers, ectoderm and endoderm, are called diploblastic animals, e.g., Coelenterates.
Read And Learn More: NEET Class 9 Biology Very Short Answer Question And Answers
Question 4. Name a marine annelid?
Answer: Nereis.
Question 5. Name two phyla, which have radial symmetry.
Answer:
- Echinodermata.
- Coelenterate.
Question 6. Which type of circulatory system is present in annelids?
Answer: Annelids have closed circulatory system.
“class 9 science chapter 7 exercise question answer “
Question 7. Give the scientific name of
Answer:
- Frog-Rana tigrina.
- Tree frog-Hyla.
Question 8. If plants produce no seeds, then how do they reproduce?
Answer: They produce spores that germinate and develop into gametophytes that produce gametes.
Question 9. What kind of symmetry you have?
Answer: Humans have bilateral symmetry.

NEET Biology Diversity in Living Organisms notes
Question 10. What are elements of the biological hierarchy and how are they arranged in their proper relationship with respect to one another, from smallest to largest order?
Answer: The elements of the biological hierarchy are: molecules, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, individual organisms, populations species, communities, ecosystems, biomes, biosphere.
Question 11. List five characteristics by which biologists classify protozoan.
Answer:
- Mode of locomotion
- Nutrition
- Reproduction
- Type and number of nuclei
- Symbiotic or free-living
Question 12. State the basic characteristics of bryophytes.
Answer: Bryophytes are small, compact plants that lack vascular tissue. They absorb nutrients and water directly from the ground, rainwater and dust.
Question 13. What is an animal?
Answer: A animal is heterotrophic, unicellular or multicellular organism with eukaryotic cells that lack cell walls.
Question 14. Name the fresh water sponge.
Answer: Spongilla
Question 15. What is the space between epidermis and gastrodermis in coelenterates known as?
Answer: Mesogloea
Question 16. Name the organism in which asexual reproduction takes place by budding.
Answer: Hydra
Important questions from Diversity in Living Organisms for NEET
Question 17.What is alternation ofgenerations?
Answer: When asexual and sexual generations alternate in the life cycle, it is called alternation of generations or metagenesis, e.g., coelenterates.
Question 18. What is the body symmetry of coelenterates?
Answer: Radial symmetry
Question 19. What is the skeleton of sponges made up of?
Answer: Skeleton of sponges is made up of spicules. Spicules are formed of calcium carbonate, silica or spongin fires.
Question 20. What is enterocoelom?
Answer: Enterocoelom is a true coelom which develops as lateral pouches from embryonic gut, e.g., echinodermata, chordata.
Question 21. What do you mean by diploblastic animals?
Answer: They are animals having two germinal layers in the embryo, outer ectoderm and inner endoderm, e.g., porifera, coelenterata.
NCERT solutions for Diversity in Living Organisms Class 9
Question 22. Define choanocytes.
Answer: Choanocytes or collar cells are biflagellate oval sponge cells that have a transparent contractile collar.
Question 23. What are parazoa?
Answer: Parazoa includes animals whose body consists of loosely aggregated cells, e.g., Porifera.
Question 24. What are non-chordates?
Answer: Non-chordates are those animals in which notochord is totally absent.
Question 25. What is cell level organization?
Answer: It is a type of organization based on cells which are not organised into tissues.
Question 26. Which type of body organization is present in platyhelminthes?
Answer: Organ system level of organization.
Five kingdom classification NEET notes
Question 27. Give the scientific name of the following:
Answer:
- Round-worm
- Ascaris lumbricoides
- Filarial worm
- Wuchereria bancrofti
Question 28. Give the scientific name of the following:
Answer:
- Earthworm
- Pheretima Posthuma
- Leech
- Hirudinaria
Question 29. What is the body symmetry of echinoderms?
Answer: Radial symmetry (in adults).
Difference between plant and animal kingdom NEET
Question 30. Which type of eyes are present in insects?
Answer: Compound eyes
Question 31. Give two examples of mollusca.
Answer: Pila and Oyster
Question 32. Name the organ of echinoderms which helps in respiration and locomotion.
Answer: Tube feet.
Question 33. Give one example of
Answer:
- Cartilaginous fish
- Scoliodon (dog-fish)
- Bony fish.
- Rohu
“the living organisms characteristics and habitats extra questions “
Question 34. Name two classes of chordates in which clawed digits are present.
Answer: Reptilia and Aves
Question 35. Mention one unique feature of mammals.
Answer: Presence of diaphragm
Question 36. Name two classes having cold-blooded animals.
Answer: Amphibia and pisces
Classification of living organisms NEET questions
Question 37. Name the following:
Answer:
1. Organism in which external ear (pinna) is present.
Answer: Man
2. Organism in which nictitating membrane is present.
Answer: Frog.
Question 38. Name the reptile in which heart is four-chambered.
Answer: Crocodile
Question 39. What is the position of notochord in
- Urochordata
- Cephalochordata?
Answer:
- Tail region
- Notochord extends up to anterior end of the body.
Question 40. How many chambers are present in the heart of
- Fishes
- Frogs
Answer:
- Two chambers
- Three chambers.
Question 41. Name the phylum in which pharyngeal gill slits are present.
Answer: Chordata
Question 42. What do you mean by the term chondrichthyes?
Answer: Cartilaginous fishes.
Mnemonics for biological classification NEET
Question 43. Which tissue is called loose connective tissue?
Answer: Areolar tissue.
Question 44. Write one important character of permanent tissues.
Answer: They originate from meristematic tissue and become
permanent at field positions in the plant body.
Question 45. Name the components of xylem.
Answer: Tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fires.
Question 46. Which tissue is the principal component of tendons and ligaments?
Answer: Dense regular connective tissue.
Question 47. Name the three parts of a neuron.
Answer: Cyton (cell body), Dendrons and Axon.
Question 48. Where do you find meristematic tissues in plants?
Answer: In apical, intercalary and lateral positions in plants.
Best books for Diversity in Living Organisms NEET
Question 49. Name the three types of meristematic tissues.
Answer: Apical meristem, Lateral meristem and Intercalary meristem.
Question 50. Name the complex tissues in plants which help in the
“the living organisms characteristics and habitats extra questions “
1. Conduction of water and inorganic solutes.
Answer: Xylem
2. Translocation of organic solutes.
Answer: Phloem.
Question 51. What is meant by division of labour?
Answer: It refers to the distribution of different functions among
different parts of the organism’s body which get specialized
for the particular function.
Question 52. Name the muscles of heart.
Answer: Cardiac muscles
Question 53. Identify a plant tissue whose living cells form the mechanical tissue of actively growing organs and whose cell wall show cellulose thickenings often at the corners of cells.
Answer: Collenchyma.
Question 54. Nissl’s granules are present in which cells?
Answer: Neurons.
Question 55. Which cell is attached to the lateral side of sieve tube in phloem?
Answer: Companion cell.
Question 56. Which simple tissue is used for making ropes?
Answer: Sclerenchyma.
Question 57. An organism has actively dividing cells at its growing apices which continue to divide and add new cells throughout the life. To which group it belongs – plants or animals?
Answer: The organism is a plant
Question 58. What is the chief function of collenchyma?
Answer: It provides mechanical strength as well as flexibility to soft parts of plant.
Question 59. Who wrote the book “The Origin of Species”?
Answer: Charles Darwin in 1859.
Characteristics of Monera, Protista, and Fungi NEET
Question 60. Name the simple division of plant kingdom.
Answer:
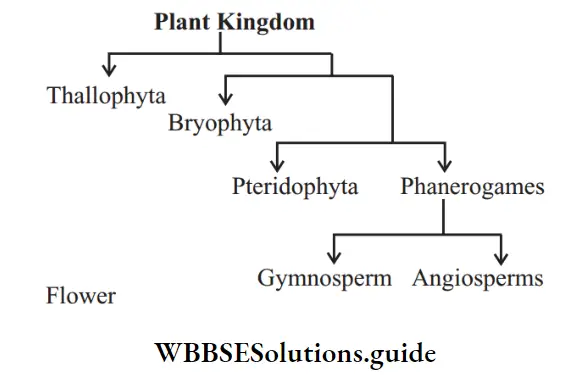
Question 61. Name the reproductive organ of plants.
Answer: Flower
Question 62. What are cotyledons?
Answer: Plant embryos in seeds are called cotyledons. They are called so because they look like seed ‘leaves’.
Question 63. Name two mammals that lay eggs.
Answer: Platypus, Echidna.
Question 64. What are Cryptogamae?
Answer: The plants with hidden reproductive organs are called cryptogamae, e.g. fern
