Introduction And Classification
Question 1. What information is provided by the reaction mechanism?
- The bonds broken and formed
- The reaction intermediates
- The relative rates of discrete steps, especially the slowest one
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Solution: These are characteristics known from the mechanism of a reaction.
Read And Learn More: NEET General Organic Chemistry Notes, Question And Answers
Question 2. Which one of the following is s-butyl phenylvinyl methane?
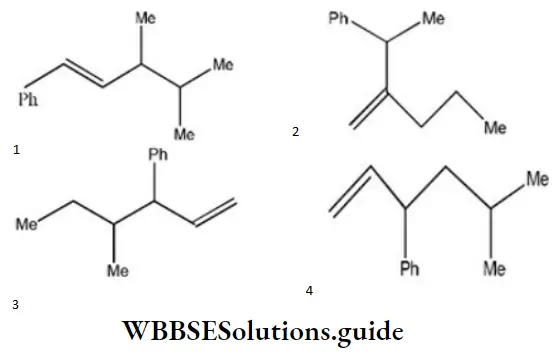
Answer: 3
Solution: Follow the nomenclature rule
NEET General Organic Chemistry Classification Questions and Answers
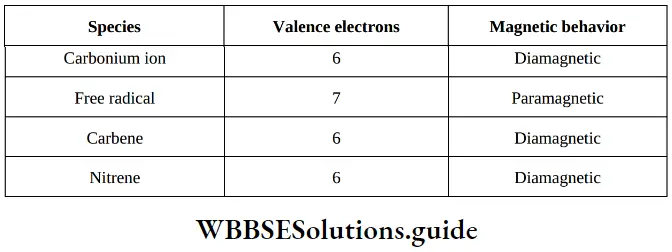
Question 3. Which of the following species is paramagnetic in nature?
- Carbonium ion
- Free radical
- Carbene
- Nitrene
Answer: 2. Free radical
Solution:
Question 4. The property by virtue of which a compound can turn the plane of polarization of light is known as?
- Photolysis
- Phosphorescence
- Optical activity
- Polarization
Answer: 3. Optical activity
Solution: It is the definition of optical activity.
Question 5. The ratio of c-to n-bonds in benzene is:
- 2
- 4
- 6
- 8
Answer: 2. 4
Solution: C6H6 has 12σ and 3π-bonds.
Question 6. The most stable carbocation is:
- CH3+
- CH3 C+ H2
- (CH3)2 C+ H
- (CH3)3 C+
Answer: 4. (CH3)3 C+
Solution: 3° Carbonium ions are more stable as the positive inductive effect disperses the positive charge on the carbon atom.
Question 7. Select the most reactive cycloalkane:
- Cyclopropane
- Cyclobutane
- Cyclopentane
- Cyclohexane
Answer: 1. Cyclopropane
Solution: Follow Baeyer’s strain theory for stability of cycloalkanes.
Question 8. In the compound, the Configuration at C2 and C3 atoms are
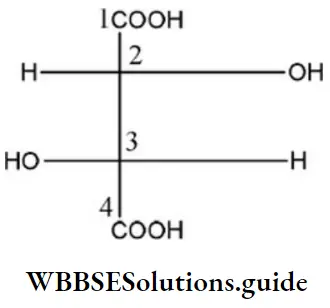
- S, S
- R, S
- S, R
- R, R
Answer: 4. R, R
Question 9. Resonance arises due to the:
- Migration of atoms
- Migration of proton
- Delocalization of c-electron
- Delocalization of n-electron
Answer: 4. Delocalization of n-electron
Solution: Resonance in a molecule arises due to the delocalization of n-electrons.
Question 10. Sometimes the behavior of a compound is explained by assuming that it exists in nature between two or more different possible structures. This phenomenon is called
- Isomerism
- Resonance
- Mutarotation
- Allotropism
Solution: The various structures derived for a molecule but none of them truly represents all the properties of that molecule are said to be canonical forms and the molecule is said to exhibit resonance.
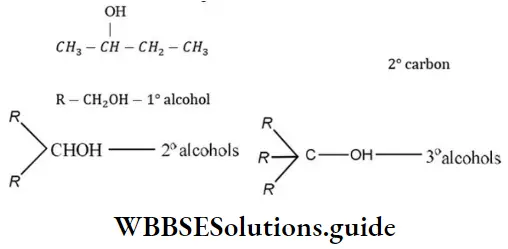
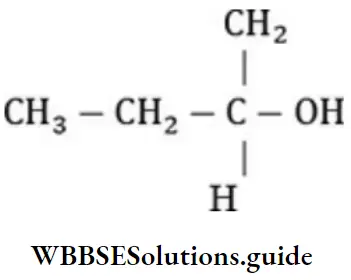
Question 11. Which one of the following is a secondary alcohol?
- 2-methyl-1-propanol
- 2-methyl-2-propanol
- 2-butanol
- l-butanol
Answer: 3. 2-butanol
Solution: 2-butanol has following structure
Question 12. The angle of rotation of plane of polarized light depends upon:
- The nature of the light beam
- The number of the molecules
- The number of asymmetric carbon atoms in the molecule of the substance
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Solution: Follow optical activity.
Question 13. The number of 4° carbon atoms in 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl pentane:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer: 2. 2
Solution:
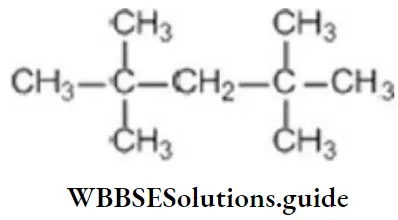
only two are quaternary carbons.
Question 14. Delocalized electrons are present in
- 1, 3- butadiene
- C6H6
- 1,3,5-hexatriene
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Solution: Delocalized electrons are present in benzene, 1, 3-butadiene and 1,3,5-hexatriene
Question 15. Which of the following contain only three pairs of electrons?
- Carbocation
- Carbanion
- Free radical
- None of these
Answer: 1. Carbocation
Solution: A carbocation contains three pairs of electrons in the valence shell.
Question 16. Fischer projection indicates:
- Horizontal substituents above the plane
- Vertical substituents above the plane
- Both horizontal and vertical substituents below the plane
- Both horizontal and vertical substituents above the plane
Answer: 1. Horizontal substituents above the plane
Solution: Fisher projections are for illustration of optical isomers.
Question 17. When the hybridization state of a carbon atom changes from sp3 to sp2 and finally to sp, the angle between the hybridized orbitals:
- Is not affected
- Increases progressively
- Decreases considerably
- Decreases gradually
Answer: 2. Increases progressively
Solution: sp3 ,sp2 and sp-orbitals are at 109°28′,120° and 180°.
Question 18. How many delocalized π-electrons are there in the below compound?
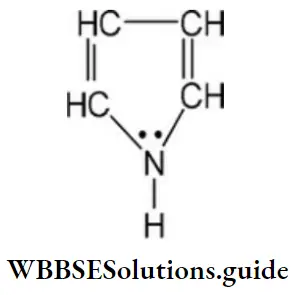
- 8
- 2
- 4
- 6
Answer: 4. 6
Solution: In the given compound four n- electrons of double bond and 1 lone pair on the nitrogen atom leads to the delocalization of six electrons.
Classification of Organic Compounds NEET MCQs with Answers
Question 19. In the following the most stable conformation of n-butane is:
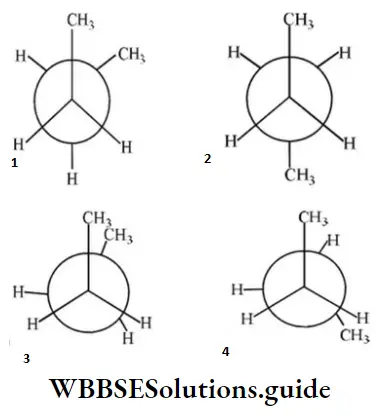
Answer: 2
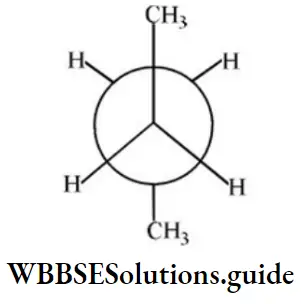
Solution: Anti-conformation is the most stable form of n-butane (Bulky groups far apart).
Question 20. Ease of abstraction of hydrogen is greater when attached to:
- 1° carbon
- 2° carbon
- 3° carbon
- neo-carbon
Answer: 3. 3° carbon
Solution: The reactivity order for the H atom is 3°>2°>1°; Neocarbon do not possess H atoms.
Question 21. Number of tertiary carbon atoms in tertiary butyl alcohol is:
- 1
- 2
- Zero
- 4
Answer: 1. 1
Solution: In tertiary alcohol, the carbon atom is joined with an alcohol group and three other carbon atoms.
Question 22. Which of the following compounds can exist in an optically active form?
- 1-butanol
- 2-butanol
- 3-pentanol
- 4-heptanol
Answer: 2. 2-butanol
Solution: Due to the presence of asymmetric carbon atoms, for example,
∴ \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \cdot \stackrel{\bullet}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{HOHCH}_3 \)
Question 23. The resonating structures
- Differ only in the arrangement of electrons
- Differ in number of paired and unpaired electrons
- Differ largely in their energy contents
- Do not lie in the same plane
Answer: 1. Differ only in the arrangement of electrons
Solution: Follow resonance characteristics.
Question 24. The number of 1° and 2° carbon atoms in n-pentane are respectively:
- 2, 3
- 3, 2
- 2, 4
- 1, 3
Answer: 1. 2, 3
Solution: CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 is n-pentane.
Question 25. A secondary (2°) carbon is one that is joined to:
- 1-alkyl group
- 2-alkyl groups
- 3-alkyl groups
- None of these
Answer: 2. 2-alkyl groups
Solution: A 2° Carbon is one of which two valencies are attached to the carbon atom.
Question 26. The maximum number of alkyl groups in C8 H18 is:
- 6
- 5
- 4
- 2
Answer: 1. 6
Solution: (CH3)3C-C(CH3)3 has a maximum number of alkyl groups in it.
Question 27. Who is called the ‘Father of Chemistry’?
- Faraday
- Priestley
- Rutherford
- Lavoisier
Answer: 4. Lavoisier
Solution: It is an honor to Lavoisier.
Question 28. An organic compound X having molecular formula C6H7O2N has 6 carbons in a ring system, two double bonds, and also a nitro group as substituent. X is?
- Homocyclic but not aromatic
- Aromatic but not homocyclic
- Homocyclic and aromatic
- Heterocyclic
Answer: 1. Homocyclic but not aromatic
Solution: For a compound to be aromatic, it must have (4n+2) n electrons. Here two double bonds are present, 4n electrons are present in the compound. Therefore, it is anti-aromatic.
Homocyclic compounds are ring structures that consist only of carbon atoms within the ring. A nitro group is attached to the ring system as a substituent, so, C6H7O2N is homocyclic but not aromatic.
An organic compound X having molecular formula C6H7O2N has 6 carbons in a ring system, two double bonds, and also a nitro group as substituent. X is Homocyclic but not aromatic
Question 29. A straight-chain hydrocarbon has the molecular formula C8 H10. The hybridization for the carbon atoms from one end of the chain to the other are respectively sp3,sp2,sp2,sp3,sp2,sp2, sp, and sp. The structural formula of the hydrocarbon would be:
- CH3-C=C-CH2-CH=CH-CH=CH2
- CH3-CH2-CH= CH-CH=CH-CH=CH
- CH3-CH=CH-CH2-C=C-CH=CH2
- CH3-CH=CH-CH2-CH=CH-C =CH
Answer: 4. CH3-CH=CH-CH2-CH=CH-C =CH
Solution: Count σ-and π-bonds on each carbon and report hybridization.
Question 30. Correct order of stability is
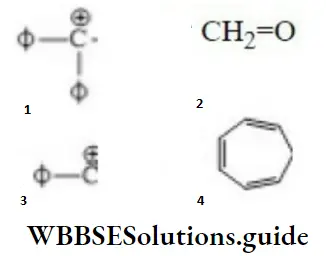
- 1>4>2>3
- 1>2>3>4
- 1>2>4>3
- 1>3>4>2
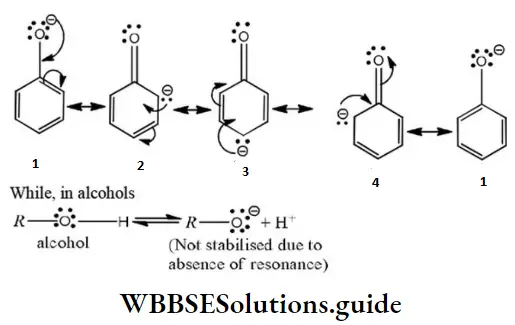
Answer: 1. 1>4>2>3
Solution: ø is phenyl group, the question can be solved on the basis of the number of conjugative
structures.
Question 31. The order of stability of the alkenes
- R2C=CR2,
- R2C=CHR,
- R2C=CH2,
- RCH=CHR,
- RCH=CH2
- 1>2>4>3>5
- 1>2>3>4>5
- 2>1>4>3>
- 5>4>3>1>2
Answer: 1. 1>2>4>3>5
Solution: Greater the substituents across the double bond of alkenes, greater is the stability.
Question 32. Which type of strain is present in fully eclipsed conformation of butane?
- Angle strain
- Steric strain
- Both (1) and (2)
- Neither (1) nor (2)
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
Solution: Eclipsed conformation of butane contains both angle and steric strain. Follow conformation.
Question 33. The stability of the free radical’s allyl, benzyl, 3°,2°,1° and CH3 is in the order
- Benzyl > allyl >3°>2°>1°>CH3
- Allyl >3°>benzyl>2°>1°>CH3
- 3°>2°>1°>CH3>allyl > benzyl
- 3°>2°>1°>CH3>allyl=benzyl
Answer: 1. Benzyl > allyl >3°>2°>1°>CH3
Solution: Benzyl, allyl both are stabilized by resonance and 3°, 2°, and 1° are stabilized by hyperconjugation and +I effect. The combined effect of three methyl groups of 3° carbocation marginally exceeds the resonance effect of benzene in benzyl carbocation.
Question 34. Considering the state of hybridization of carbon atoms, find out the molecule among the following which is linear?
- CH3—CH2—CH2—CH3
- CH3—CH=CH—CH3
- CH3—C≡C —CH3
- CH2=CH—CH2 —C≡CH
Answer: 3. CH3—C≡C —CH3
Solution: Alkynes are linear due to sp-sp hybridized carbon.
Question 35. C2 is rotated anticlockwise 102°C about C2-C3 bond. The resulting conformer is
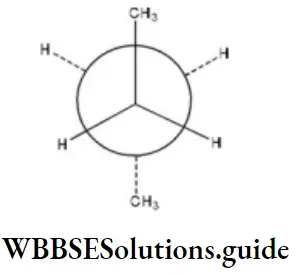
- Partially eclipsed
- Eclipse
- gauche
- Staggered
Answer: 3. gauche
Solution:
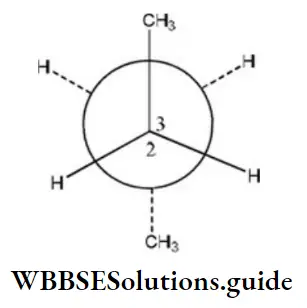
Here, when C2 is rotated anticlockwise 120° about C2-C3 bond the resulting conformer is Gauche conformer. Hence,
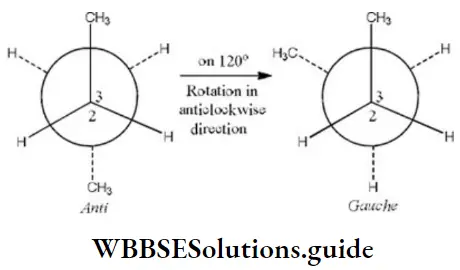
NEET Chemistry Classification of Organic Compounds Important Questions
Question 36. With a change in hybridization of the carbon bearing the charge, the stability of a carbanion increases in the order of
- sp<sp2<sp3
- sp<sp <sp2
- sp3<sp2<sp
- sp2<sp<sp3
Answer: 3. sp3<sp2<sp
Solution: Carbanion is an electron-rich species. Stability of carbanion increases with increase in s-character of hybrid orbitals of carbon-bearing the charge.
∴ sp3<sp2<sp
(25%s-character) (33%s-character) (50%s-character)
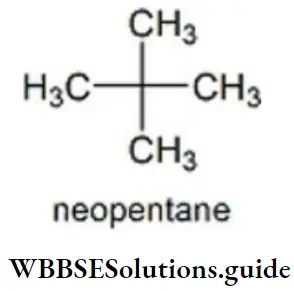
Question 37. The number of carbon atoms present in neopentane are?
- Four 1° carbon, one 4° carbon
- two 1° carbon, two 2° carbon
- one 1° carbon, three 4° carbon
- None of the above is correct
Answer: 1. Four 1° carbon, one 4° carbon
Solution: Neopentane has 4 primary carbons and 1 quaternary carbon.
Question 38. The empirical formula of an acid is CH2 O2, the probable molecular formula of the acid may be
- C2H4O2
- C3H6O4
- C2H2O4
- CH2O2
Answer: 4. CH2O2
Solution: Empirical formula of acid = CH2O2
We know that molecular formula =n (empirical formula)
- If n=1 molecular formula =(CH2O2) 1=CH2O2
- If n=2 molecular formula =(CH2O2) 2=C2H4O4
- If n=3 molecular formula =(CH2O2) 3=C3H6O6
- Thus, the probable molecular formula =CH2O2
Question 39. Find the non-staggered form(s) of ethane:
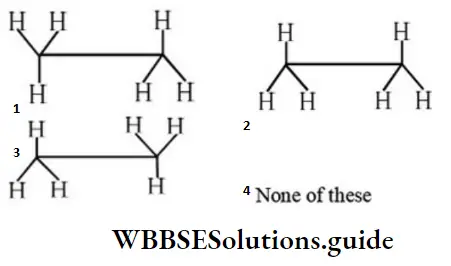
Answer: 2
Solution: Non-staggered means eclipsed form.
Question 40. 2-methyl pent-3-ene is achiral because it has:
- A Centre of symmetry
- A plane of symmetry
- Symmetry at C2 carbon
- Both Centre and a plane of symmetry
Answer: 4. Both Centre and a plane of symmetry
Solution: If the structure of the compound is drawn then we find that a plane of symmetry is present in this compound, the two halves are equal hence the compound does not have a chiral point. In addition to this it has a Centre. The two sides of the compound on the different sides of the centre atom are similar. Both reasons are present which signifies that the molecule is achiral.
Question 41. To which ring size cycloalkanes, Baeyer’s strain theory is not valid?
- 3 carbon
- 4 carbon
- 5 carbon
- ≥ 6 carbons
Answer: 4. ≥6 carbons
Solution: The closed ring cycloalkanes beyond five carbon atoms has puckered ring structure maintaining tetrahedral nature or stainless rings, example, cyclohexane has chair and boat form.
Question 42. Different structures generated due to the rotation about, C – C axis, of an organic molecule, are examples of
- Geometrical isomerism
- Conformational isomerism
- Optical isomerism
- Structural isomerism
Answer: 2. Conformational isomerism
Solution: The different arrangement of atoms in space that results from the carbon-carbon single bond free rotation by 360° are called conformations or conformational isomers and this phenomenon is called conformational isomerism.
Question 43. Carbon tetrachloride has no net dipole moment because of
- Its planar structure
- Its regular tetrahedral nature
- Similar sizes of carbon and chlorine atoms
- Similar electron affinities of carbon and chlorine
Answer: 2. Its regular tetrahedral nature
Solution: This gives rise to net resultant of four C-Cl vectors equal to zero.
Question 44. The number of π-electrons present in cyclobutadiene ion, (C4H3)– is:
- 8
- 6
- 4
- 2
Answer: 3. 4
Solution: Count π-bonds. Delocalization is not possible.
Question 45. Which of the following compounds is optically active?
- 1 – butanol
- Isopropyl alcohol
- Acetaldehyde
- 2-butanol
Answer: 4. 2-butanol
Solution: 2-butanol is optically active as it contains a chiral carbon atom.
Question 46. Which of the following is the correct order of stability of different conformations of butane?
- Staggered > Gauche > Partially eclipsed > Fully eclipsed
- Gauche > Staggered > Partially eclipsed > Fully eclipsed
- Staggered > Fully eclipsed > Partially eclipsed > Gauche
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Staggered > Gauche > Partially eclipsed > Fully eclipsed
Solution: It is the stability order for various conformers.
Question 47. Which of the following does not contain chiral carbon atoms?
- Lactic acid
- 2-chlorobutanoic acid
- Tartaric acid
- Succinic acid
Answer: 4. Succinic acid
Solution: The carbon, four valencies of which are satisfied by four different groups, is termed as chiral carbon atom. The structures of the given compounds are as
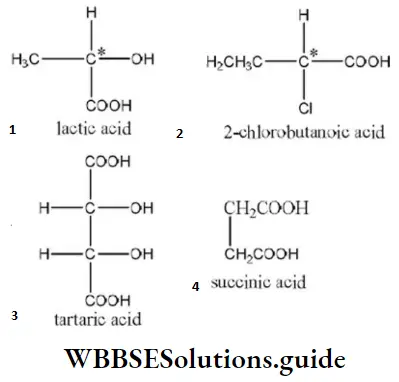
(Where C*= chiral carbon atom)
Hence, succinic acid does not contain any chiral carbon atom.
Best Practice Questions for NEET General Organic Chemistry Classification
Question 48. The yield in organic reactions is generally poor because the reactions are
- Very fast
- Non-ionic
- Between covalent compounds
- Accompanied by side reactions
Answer: 4. Accompanied by side reactions
Solution: It is a reason for the given fact.
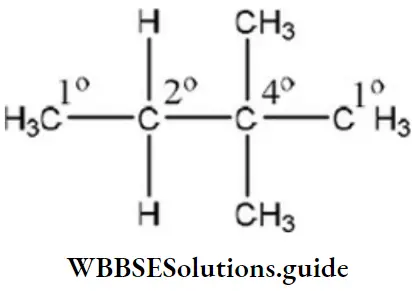
Question 49. The number of secondary hydrogens in 2, 2-dimethyl butane is
- 8
- 6
- 4
- 2
Answer: 4. 2
Solution:
- 1° Carbon is attached to one carbon atom.
- 2° Carbon is attached to two carbon atoms.
- 3° Carbon is attached to three carbon atoms.
- The hydrogen attached to 2° carbon atom is 2°.
Question 50. Which of the following Fischer’s projection formula is identical to D-glyceraldehyde?
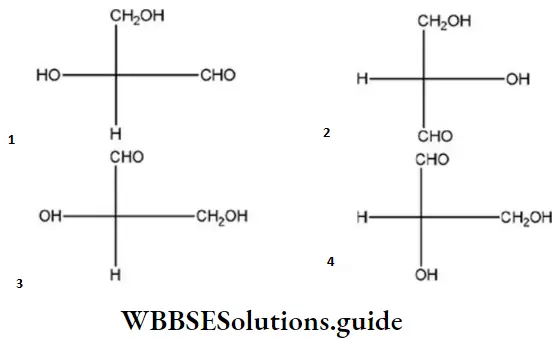
Answer: 2
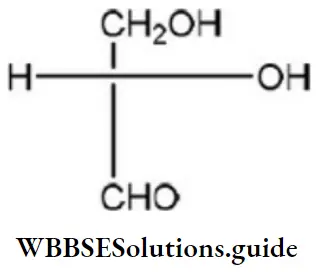
Solution:
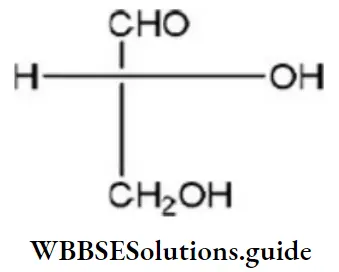
D-glyceraldehyde has the above formula. So, Fischer’s projection formula which is identical to.
Question 51. The C-H bond distance is longest in
- C2H2
- C2H4
- C2H6
- C2H2Br2
Answer: 3. C2H6
Solution: Order of bond length
σ bond (sp3) > σ bond (sp2) > σ bond (sp)
Question 52. The compound having highest dipole moment is:
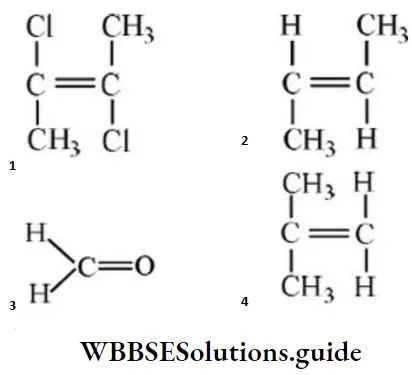
Answer: 3
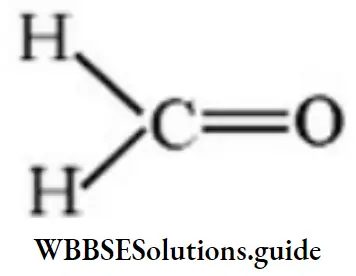
Solution: μ is more for 3 then 4.
Question 53. Orbital interaction between the o-bonds of a substituent group and a neighboring π- orbital is known as
- Hyperconjugation
- Inductive effect
- Steric effect
- Electric quadrupole interactions
Answer: 1. Hyperconjugation
Solution: Orbital interaction between σ- bonds of a substituent group and a neighboring π-orbital is known as hyperconjugation.
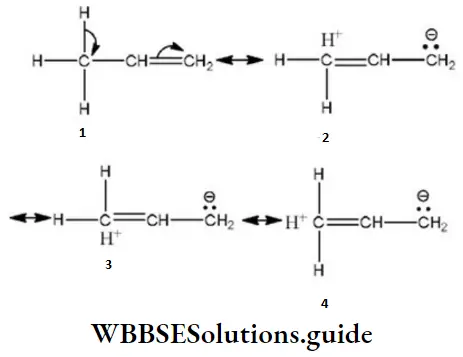
Question 54. The number of different amines corresponding to the formula C3H9 N is:
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Answer: 3. 4
Solution: Draw all structures.
Question 55. t-butyl alcohol is
- 2-methyldopa-2-ol
- 2-methyldopa-1-ol
- 3-methyl butane-1-ol
- 3-methyl butane-2-ol
Answer: 1. 2-methyldopa-2-ol
Solution: 2-methylpropan-2-ol is for-butyl alcohol.
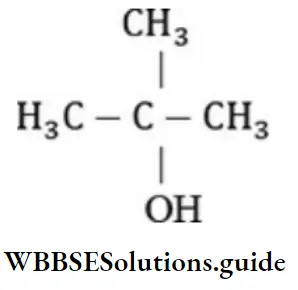
Question 56. The compound is an example of:

- Aromatic compound
- Heterocyclic compound
- Annulene
- Xanthates
Answer: 3. Annulene
Solution: This is annulene.
NEET Chemistry Functional Groups and Homologous Series MCQs with Solutions
Question 57. The structure representing a heterocyclic compound is:
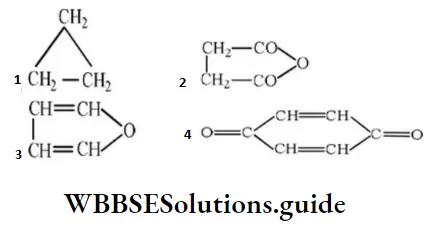
Answer: 3
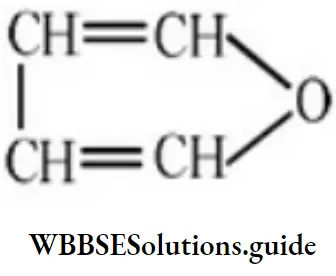
Solution: It is the structure of furan, a heterocyclic compound.
Question 58. Species containing carbon with three bonds and an electron is called as?
- Carbenes
- Carbanions
- Carbocation
- Free radicals
Answer: 4. Free radicals
Solution: It’s a fact.
Question 59. The general formula CnH2nO2 for open chain could be
- Diketones
- Carboxylic acids
- Diols
- Dialdehydes
Answer: 2. Carboxylic acids
Solution: CnH2nO2 is a general formula for an open-chain acid and ester.
n = 3 C3H6O2
Question 60. The correct structure of dimethyl butane is:
- CH3CH2—C≡C —CH2CH3
- (CH3) 3C — C≡CH
- CH3—C=CCH(CH3) 2d)
Answer: 2. (CH3) 3C — C≡CH
Solution: Follow the rules.
Question 61. Glyoxal is
- CH2OH-CH2OH
- CHO-CH2OH
- COOH-CO-COOH
- CHO-CHO
Answer: 4. CHO-CHO
Solution: CHO-CHO is called glyoxal
Question 62. The maximum bond energy is present
- C-H
- C-C
- C-N
- C-O
Answer: 1. C-H
Solution:

Question 63. Geometry of methyl free radical is
- Pyramidal
- Planar
- Tetrahedral
- Linear
Answer: 2. Planar
Solution: Number of hybrid orbitals =number of σ-bonds+number of Ips
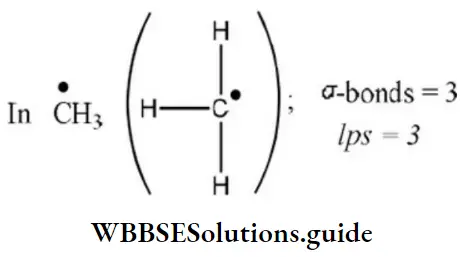
∴ Number of hybrid orbitals =3+0=3
Hence, hybridization is sp2 and geometry is planar.
Question 64. The formula of 3-chloro-2,2-dimethylbutane is
- CH(CH3)C(CH3)2 Cl
- CH3 (CH3)2 CH2Cl
- CH3C(CH3)2CH2Cl
- CH3CHClC(CH3)3
Answer: 4. CH3CHClC(CH3)3
Solution: The formula of 3-chloro-2,2-dimethyl butane is CH3CHClC(CH3)3
Question 65. Which of the following compounds has the maximum number of n-bonds?
- HC=C-CH=CH2
- CH2=CH-CH=CH2
- CH3CH2COCH3
- C6H5-COOH
Answer: 4. C6H5-COOH
Solution: In C6H5 ring there are three n-bonds and one n-bond is present in COOH group. Therefore, in all there are four π- bonds in C6H5-COOH. In C6H5COOH there is only one π- bond in C=O group, in CH2=CH-CH=CH2 there are two n-bonds while in HC≡C-CH=CH2 there are three π- bonds.
Question 66. Removal of hydrogen atom is easier when it is attached to:
- 1° carbon
- 2° carbon
- 3° carbon
- Same in all
Answer: 3. 3° carbon
Solution: The reactivity order is 3°H>2°H>1°H.
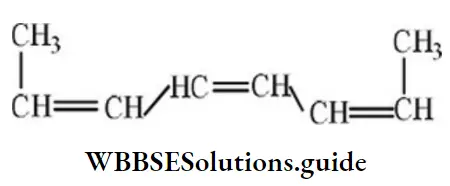
Question 67. The structure of cis-bis (propenyl) ethane is:
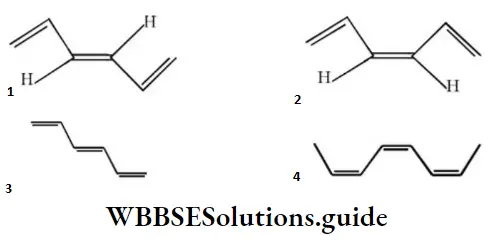
Answer: 4

Solution: The two propenyl group attached to 1,2-position of carbon in cis-form.
Question 68. The percentage of ‘s’ character of the hybrid orbital of carbon in ethane, ethane, and ethyne respectively are:
- 25, 33, 50
- 20, 50, 33
- 25, 50, 75
- 33, 66, 99
Answer: 1. 25, 33, 50
Solution: Ethane, ethene, and ethyne have sp3,sp2, and sp-hybridization respectively.
General Organic Chemistry NEET Notes on Classification with Solved Questions
Question 69. The reason for the loss of optical activity of lactic acid when -OH group is changed by H is that
- Chiral center of the molecule is destroyed
- Molecules acquires asymmetry
- Due to change in configuration
- Structural changes occurs
Answer: 1. Chiral center of the molecule is destroyed
Solution: When -OH group of lactic acid is replaced by H, then chiral carbon is lost.
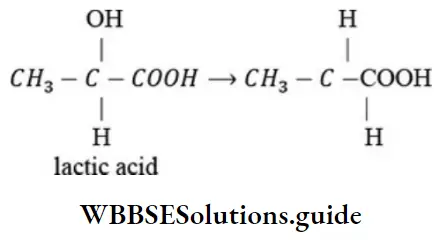
∴ Its optical activity is lost.
Question 70. In case of a homologous series each member differs from the preceding or the succeeding member by:
- a CH2 group
- a CH3 group
- Two hydrogen atoms
- Four hydrogen atoms
Answer: 1. a CH2 group
Solution: Two successive homologous differ in their formula by CH2 or have a difference of 14 units in their molecular weight.
Question 71. The number of asymmetric carbon atoms and the number of optical isomers in CH3(CHOH)2 COOH are respectively:
- 3 and 4
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 4
- 2 and 3
Answer: 3. 2 and 4
Solution: n = 2 and a = 2n = 22 = 4.
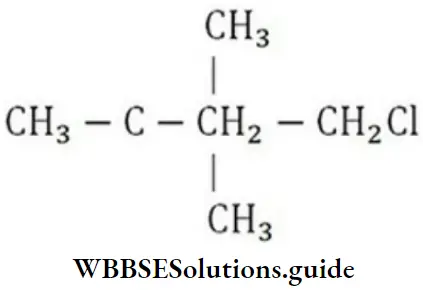
Question 72. Which of the following is a primary halide?
- Isopropyl iodide
- Secondary butyl iodide
- Tertiary butyl bromide
- Neo hexyl chloride
Answer: 4. Neo hexyl chloride
Solution: Neohexyl chloride is a primary halide as in it, Cl-atom is attached to a primary carbon.
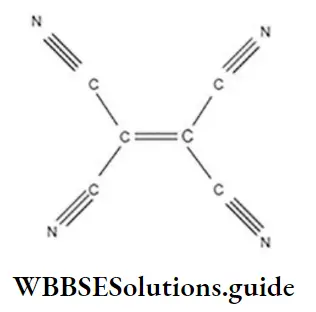
Question 73. In which of the following structures the number of sigma bonds are equal to the number of π-bonds?
- 1,2-propadiene
- 2,3-dicyanobut-2-ene
- Tetracyanoethylene
- None of these
Answer: 3. Tetracyanoethylene
Solution:
Question 74. What is the structural formula of fumaric acid?
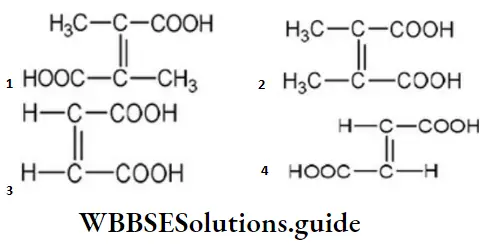
Answer: 4
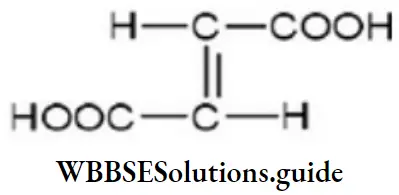
Solution: The structural formula of fumaric acid
Question 75. The correct acidity order of the following is
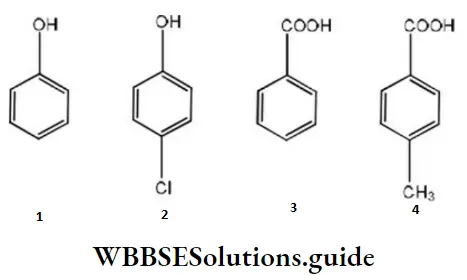
- 3>4>2>1
- 4>3>1>2
- 3>2>1>4
- 2>3>4>1
Answer: 1. 3>4>2>1
Solution: A carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol, hence both 3 and 4 are stronger acids than both 1 and 2. Also, 4 has a methyl group that gives electrons donating inductive effects and decreases the acid strength.
Therefore, 3 is a stronger acid than 4. Between 1 and 2, the dominant electron-withdrawing inductive effect of chlorine increases the acid strength of phenol slightly, hence 2 is stronger of phenol slightly, hence, 2 is a stronger acid than 1.
Thus, the overall order is: 1. 3>4>2>1
NEET Study Material for Classification of Organic Compounds
Question 75. How many π-electrons are there in the following structure?
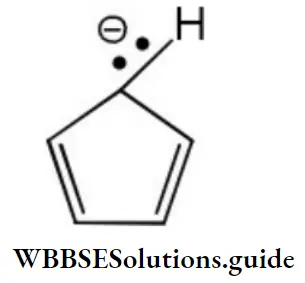
- 2
- 4
- 6
- 8
Answer: 3. 6
Solution: Each π-bond contributes two π electrons and the two electrons of the lone pair are present in a p-orbital. Therefore, total number of π electrons are six.
Question 76. The number of π-electrons in benzene molecule are?
- 3 x 2
- 23
- 3 x 3
- 32
Answer: 1. 3 x 2
Solution: C6H6 has six delocalized n-electrons.
Question 77. The hybridization of carbon atoms in C-C single bond of HC=C-CH=CH2 is
- sp3-sp
- sp3-sp3
- sp2-sp3
- sp-sp2
Answer: 4. sp-sp2
Solution: The hybridization of carbon atoms in C-C single bond of HC=C-CH=CH2 is sp-sp2.
One C atom is bonded to another C atom by a triple bond and is sp hybridised. The other C atom is attached to another C by a double bond and is sp2 hybridised.
Question 78. In which of the compounds given below there is more than one kind of hybridization (sp,sp2,sp3) for carbon?
- CH3CH2CH2CH3
- CH3CH=CH-CH3
- CH2=CH-CH=CH2
- H-C≡C-H
- 2 and 4
- 1 and 4
- 2 and 3
- 2
Answer: 4. 2
Solution:
- CH3-CH2-CH2-CH3 (Only sp3 hybridized carbons)
- CH3-CH=CH-CH3 (Both sp2 and sp3 hybridized carbons)
- CH2=CH-CH=CH2 (Only sp2 hybridized carbons)
- H-C ≡ C-H (Only sp hybridized carbons)
Question 79. How many structures can a compound with molecular formula C7H9N have?
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
Answer: 1. 5
Solution:
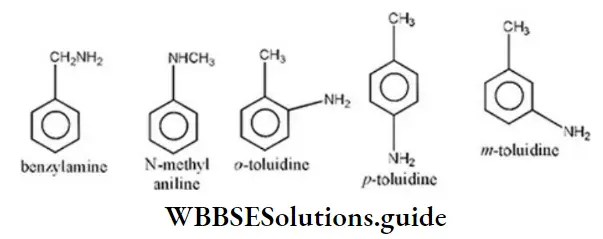
∴ Total of five isomers are possible by formula C7H9N.
Question 80. Angle strain in cyclopropane is
- 24°44’
- 9°44’
- 44’
- -5°16’
Answer: 1. 24°44’
Solution: Angle strain, α = 1/2 [109°28′ — θ]
In case of cyclopropane, θ = 60°
∴ α = 1/2 [109°28′ — 60°] = 24°44’
Angle strain in cyclopropane is 24°44’
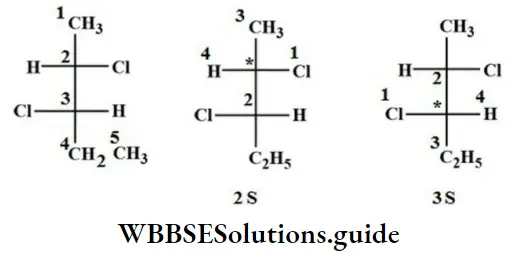
Question 81. The absolute configuration of the following
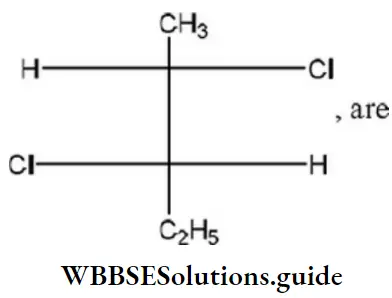
- 2S, 3R
- 2S, 3S
- 2R, 3S
- 2R, 3R
Answer: 2. 2S, 3S
Solution:
Question 82. In 2-methyl-l-propanol, the hybrid carbons of sp3,sp2 and sp are respectively:
- 3, 2, 1
- 4, 3, 0
- 4, 0, 0
- 1, 2, 3
Answer: 3. 4, 0, 0
Solution: Alkanes have all C in sp3 hybridized state irrespective of their degree (primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary)
Question 83. Which of the following compounds is not chiral?
- 1-chloro-2-methyl pentane
- 2-chloroethane
- 1-chloroethane
- 3-chloro-2-methyl pentane
Answer: 3. 1-chloroethane
Solution: To be optically active, compound or structure should possess a chiral or asymmetric carbon atom. 1-chloromethane is not chiral.
Question 84. Among the following orbital bonds, the angle is minimum between:
- sp3 – sp3 bonds
- px and py -orbitals
- H—O—H in water
- sp-sp bonds
Answer: 2. px and py-orbitals
Solution: p-orbitals are at 90° to each other.
Question 85. The correct structure of 4-bromo-3-methyl-but-1-ene.
- Br-CH=C(CH3)2
- CH2=CH-CH(CH3)-CH2 Br
- CH2=C(CH3)CH2 CH2 Br
- CH3-C(CH3)=CHCH2 -Br
Answer: 2. CH2=CH-CH(CH3)-CH2 Br
Solution: Follow the rules.
Question 86 Which of the following represents Neo-pentyl alcohol?
- CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH2OH
- (CH3)3C-CH2OH
- CH3(CH2)3OH
- CH3CH2CH(OH) C2H5
Answer: 2. (CH3)3C-CH2OH
Solution: (CH3)3C-CH2OH n is neo -pentyl alcohol
Question 87. The large number of organic compounds are due to:
- Catenation property of carbon
- Covalent bond formation
- Isomerism
- polymerization
Answer: 1. Catenation property of carbon
Solution: Catenation is the tendency to unite atoms of an element to form a long carbon chain or ring.
Question 88. The (R) and (S) enantiomers of an optically active compound differ in
- Their reactivity
- Their optical rotation of plane-polarized light
- Their melting point
- Their solubility in achiral reagents
Answer: 2. Their optical rotation of plane-polarized light
Solution: The R and S enantiomers of an optically active compound differ in their optical rotation of plane polarized light.
Question 89. Which of the following is singlet carbine?
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \ddot{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{HCH}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_5 \ddot{\mathrm{C}}-\mathrm{H}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_2=\mathrm{CH}-\stackrel{\oplus}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2\)
- \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3 \mathrm{C}^{+}\)
Answer: 2. \(\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_5 \ddot{\mathrm{C}}-\mathrm{H}\)
Solution: An organic reaction intermediate, neutral species having a divalent carbon atom with six valence electrons out of which two are present in the same orbital with opposite spin is called singlet carbene.
Question 90. In cyclopropane, Cyclobutane, and cyclohexane, the common group is
- -C
- -CH2
- -CH3
- -CH
Answer: 2. -CH2
Solution: The structure of cyclopropane, Cyclobutane, and cyclohexane are as
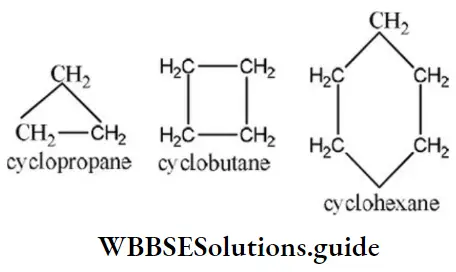
Hence, the common group in cyclopropane, Cyclobutane, and cyclohexane is -CH2 group.
Question 91. The first organic compound, urea was synthesized in the laboratory by:
- Kekule
- Liebig
- Lavoisier
- Wohler
Answer: 4. Wohler
Solution: Wohler prepared urea from KCNO and (NH4)2SO4
Question 92. In the dehydration reaction \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CONH}_2 \stackrel{\mathrm{P}_2 \mathrm{O}_5}{\rightarrow} \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{C}=\mathrm{N} \text {, },\) the hybridization state of carbon change from
- lsp3 to sp2
- lsp to sp
- lsp2 to sp
- lsp to sp3
Answer: 3. lsp2 to sp
Solution: Acetamide (CH3CONH2) contains an amide group (-CONH2) in which a carbon atom is attached to an oxygen atom by a double bond. Hence, this carbon atom is sp2 hybridized.
Acetonitrile (CH3CN) contains a nitrile group (-CN) in which the carbon atom is attached to a nitrogen atom by a triple bond. Hence, this carbon atom is sp2 hybridized.
Thus, during conversion of acetamide to acetonitrile, the hybridization of the carbon atom changes from sp2 to sp.
Question 93. Which statement is correct about the hybridization of carbon atoms in,
⇒ \(\mathrm{H} \stackrel{1}{\mathrm{C}} \equiv \stackrel{2}{=}-\stackrel{3}{\mathrm{C}} \equiv \stackrel{4}{=} \mathrm{C} \mathrm{H} \text { ? }\)
- C1 and C4 are sp2 – hybridized
- C2 and C3 are sp2 – hybridized
- All are sp – hybridized
- All are sp2 – hybridized
Answer: 3. All are sp – hybridized
Solution: Each carbon has two σ and two π-bonds.
Question 94. Hydride shift from C-2 will give the most stable resonance stabilized carbocation as
- CH3 at C-4
- “H” at C-4
- CH3 at C-2
- “H” at C-2
Answer: 4. “H” at C-2
Solution: In the following carbocation; H/CH3 that is most likely to migrate to the positively charged carbon is
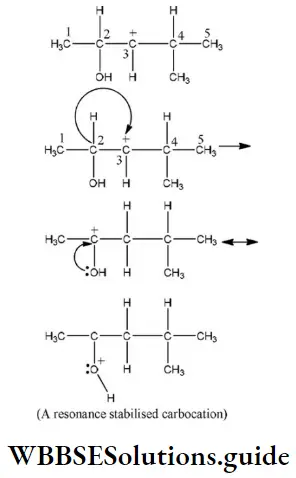
Question 95. The shape of the π electron cloud in acetylene is
- Linear
- Planar
- Cylinder
- Doughnut
Answer: 3. Cylinder
Solution: The shape of n electron cloud in acetylene in cylindrical.
Question 96. Which of the following molecules is expected to rotate the plane of plane-polarized light?
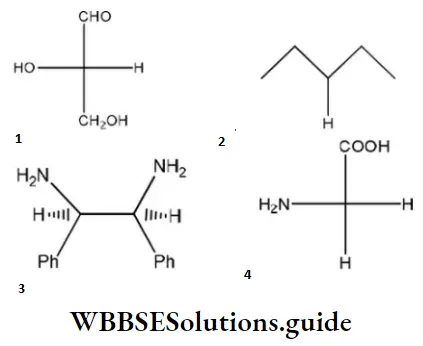
Answer: 1
Solution: The molecule, which is optically active, has a chiral center and is expected to rotate the plane of polarized light.
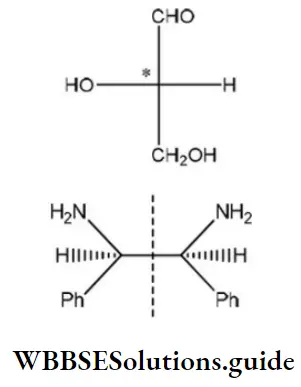
One chiral center ⇒ optically active
Two chiral centers, but plane of symmetry within molecule ⇒ optically inactive.
Classification of Organic Compounds Class 11 NCERT Questions and Answers for NEET
Question 97. Which of the following hydrocarbons is most unsaturated?
- C2H4
- C2H2
- C2H6
- CH3CH=CH2
Answer: 2. C2H2
Solution: C2H2 has two π-bonds.
Question 98. Maximum enol content is in
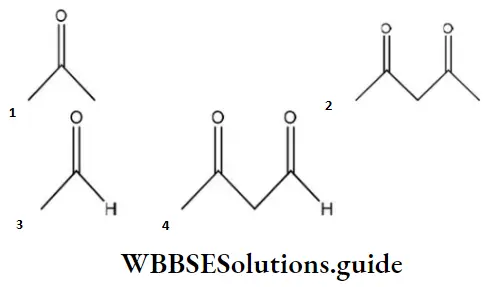
Answer: 2
Solution: Keto and enol forms are interconvertible. The enol content will be maximum when the enol form is stabilized by hydrogen bonding.
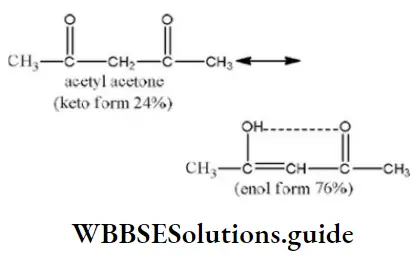
In acetylacetone, the enol form is stabilized by H-bonding, hence it has more enol content than the other.
Question 99. The compound Abd C—C Abd will exist in?
- 3 forms
- 4 forms
- 5 forms
- 2 forms
Answer: 1. 3 forms
Solution: Two similar asymmetric carbon atoms;
∴ a = 2n+1 . Also meso form = 2n/2-1
Total = a + m.
Question 100. The general formula for cycloalkanes is:
- CnH2n+2
- CnH2n
- CnH2n-2
- CnHn
Answer: 2. CnH2n
Solution: Both alkene and cycloalkane have general formulaCnH2n
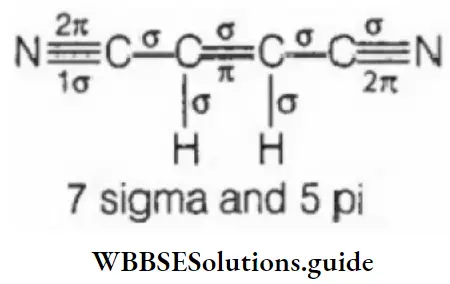
Question 101. How many sigma and pi bonds are there in the molecule of dicyanoethane (CN- CH=CH-CN)?
- 3 sigma and 3 pi
- 5 sigma and 2 pi
- 7 sigma and 5 pi
- 2 sigma and 3 pi
Answer: 3. 7 sigma and 5 pi
Solution:
Question 102. The Cl—C—Cl bond angle in dichloromethane will be:
- >109°28′
- <109°28′
- 109°28′
- 120°
Answer: 3. 109°28′
Solution: CH2Cl2 has sp3 -hybridization and tetrahedral nature.
Question 103. Overlap of which of the following atomic orbitals would be maximum to form the strongest covalent bond?
- 1s-2s(σ)
- 1s-2p(σ)
- 2P-2P(π)
- 2P-2-P(σ)
Answer: 2. 1s-2p(σ)
Solution: More directionally concentrated orbitals show more overlapping. Also closer are shells to the nucleus, more is the overlapping.
Question 104. Which of the following conformations of cyclohexane is chiral?
- Twist boat
- Rigid
- Chair
- Boat
Answer: 3. Chair
Solution:
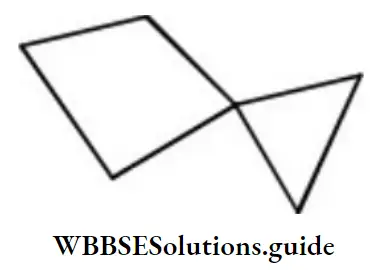
Chair form is unsymmetrical due to absence of any element of symmetry.
Question 105. Which is not deflected by a non-uniform electrostatic field?
- Water
- Chloroform
- Nitrobenzene
- Hexane
Answer: 4. Hexane
Solution: Hexane is a nonpolar molecule.
Question 106. The number of meso forms in the following compound is HOOC.CH(CH3).CH(OH).CH(Cl).CH(OH)CH(CH3).COOH
- 3
- 4
- 8
- 16
Answer: 2. 4
Solution: Number of mesostructures in compound having odd number of chiral carbon atoms and symmetrical molecule = \(2^{\left(\frac{n}{2}-\frac{1}{2}\right)}\)
Given, n=5
∴ Number of meso forms = \(2^{\left(\frac{5}{2}-\frac{1}{2}\right)}\) = 4
Question 107. Base strength of,
- \(\mathrm{H}_3 \stackrel{\ominus}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{CH}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{C}=\stackrel{\ominus}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_{\mathrm{H}}\)
- \(\mathrm{H}-\mathrm{C}=\stackrel{\ominus}{\mathrm{C}}\) is in the order of
- 3 > 2 > 1
- 1 > 3 > 2
- 1 > 2 > 3
- 2 > 1 > 2
Answer: 3. 1 > 2 > 3
Solution: Stronger the acid, weaker is its conjugate base.
Acidic nature: CH = CH > CH2 = CH2 > CH3 — CH3
Conjugate basic: CH = C- < CH2 = CH- < CH3 — CH2– nature.
Question 108. The epoxide ring consists of which of the following?
- Three membered rings with two carbon and one oxygen
- Four membered rings with three carbon and one oxygen
- Five membered rings with four carbon and one oxygen.
- Six membered rings with five carbon and one oxygen.
Answer: 1. Three membered rings with two carbon and one oxygen
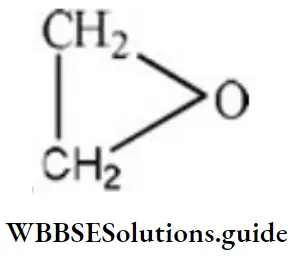
Solution: The structural formula of epoxide is It consists of three-membered rings with two carbon and one oxygen.
Question 109. The hybridization of carbon in diamond, graphite and acetylene is in the order:
- sp3,sp2,sp
- sp2,sp3,sp
- sp,sp2,sp3
- sp2,sp,sp3
Answer: 1. sp3,sp2,sp
Solution: Diamond (sp3), Graphite (sp2), Acetylene (sp).
Question 110. Which one of the following will most readily be dehydrated in acidic conditions?
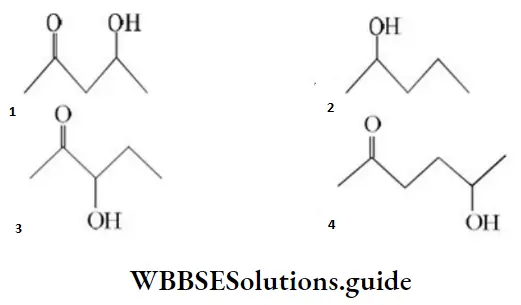
Answer: 1
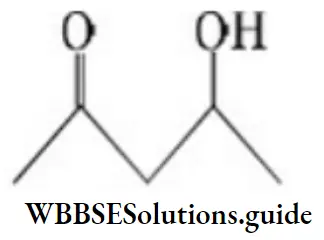
Solution: It undergoes dehydration easily as the product obtained is conjugated and more stable.
Question 111. A free radical is
- Non-existing
- Short-lived
- Diamagnetic
- Fairly stable
Answer: 2. Short-lived
Solution: Free radical state is a transient state and thus, has a short life.
Question 112. The strain in bonds of cyclopropane is:
- 0°44′
- 24°44′
- 9°44′
- 5°16′
Answer: 2. 24°44′
Strain = 1/2[Normal valence angel-valence angel] = 1/2[109°28′ – 60°] = 24°44′.
Question 113. Arrange p-toluidine (1) N, N-dimethyl-p- toluidine (2) p- nitroaniline (3), and aniline (4) in order of decreasing basicity
- 1>4>3>2
- 1>2>3>4
- 2>1>4>2
- 3>1>2>4
Answer: 3. 2>1>4>2
Question 114. Which among the following statements is wrong?
- In general, organic compounds have low melting and boiling points.
- Isomerism is common in organic compounds
- Organic compounds cannot be synthesized in the laboratory
- The number of organic compounds is fairly large
Answer: 3. Organic compounds cannot be synthesized in the laboratory
Solution: This statement is not true now.
Question 115. Which has the maximum percentage of chlorine?
- Pyrene
- PVC
- Chloral
- Ethylidene chloride
Answer: 1. Pyrene
Solution: Pyrene is CCl4.
Question 116. Naphthalene molecule contains:
- 10π-electrons
- 8π-electrons
- 12π-electrons
- 14π-electrons
Answer: 1. 10π-electrons
Solution: Total n bonds = 5; Total number of electrons = 10
Question 117. Select the correct order of basic nature:
- CH3 CH2– > CH2 = CH- > CH=C–→ OH–
- CH3 CH2– > CH = C- > CH2 =CH– > OH–
- CH3 CH2– > OH– > CH = C– > CH2 = CH–
- OH– > CH = C– > CH2 = CH- > CH3—CH2–
Answer: 1. CH3 CH2– > CH2 = CH- > CH=C–→ OH–
Solution: The acidic nature is H2O>C2 H2>C2 H4>C2 H6.
Question 118. A student named the compound as 1,4-butadiene:
- The name is correct
- He committed an error in the selection of carbon chain
- He committed an error in position of double bond
- Unpredictable
Answer: 3. He committed an error in position of double bond
Solution: Double bond should be at the 3rd position.
Question 119. The tautomeric form which is least stable is called?
- Anion form
- Cation form
- Labile form
- All of these
Answer: 3. Labile form
Solution: It is a fact.
Question 120. Stability order of… is in order
- \(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_5-\stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_2=\mathrm{CH}-\stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2\)
- \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)_3 \mathrm{C}^{+}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_2=\stackrel{+}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}\)
- 4<3<2<1
- 4<2<1<3
- 1<2<3<4
- 4<1<3<2
Answer: 1. 4<3<2<1
Solution: Benzylic and allylic carbocations (where the positively charged carbon is conjugated to one or more non-aromatic double bonds) are significantly more stable than even tertiary alkyl carbocations. Vinylic carbocations, in which the positive charge resides on a double-bonded carbon, are very unstable and thus unlikely to be formed as intermediates in any reactions.
Question 121. Acetonitrile is
- CH3CN
- CH3COCN
- C2H5CN
- C6H5CN
Answer: 1. CH3CN
Solution: CH3 C=N is known as acetonitrile or methyl cyanide.
Question 122. Isobutyl chloride is:
- CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl
- (CH3)2CHCH2Cl
- CH3CH2CHClCH3
- (CH3)3C-Cl
Answer: 2. (CH3)2CHCH2Cl
Solution: It should contain (CH3)2CH- group to be named as iso.
Question 123. The minimum number of carbon atoms which a ketone may contain is:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer: 3. 3
Solution: CH3COCH3 is the simplest ketone.
Question 124. The structure of tertiary butyl carbonium ion is:
- Pyramidal
- Trigonal planar
- Tetrahedral
- Square planar
Answer: 2. Trigonal planar
Solution: A carbonium ion is sp2-hybridized.
Question 125. Percentage of hydrogen is maximum in
- C2H4
- CH4
- C2H2
- C6H6
Answer: 2. CH4
Solution: CH4 has highest ratio of H to C
Question 126. The compound, whose stereo-chemical formula is written below, exhibits x geometrical isomers and y optical isomers The values of x and y are
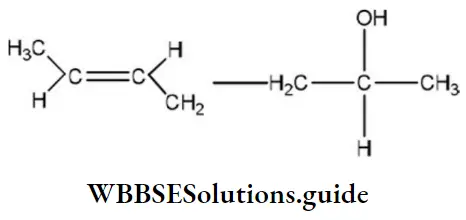
- 4 and 4
- 2 and 2
- 2 and 4
- 4 and 2
Answer: 2. 2 and 2
Solution: The given compound forms two geometrical isomers and two optical isomers.
Question 127. Which of the following is heterocyclic aromatic species?
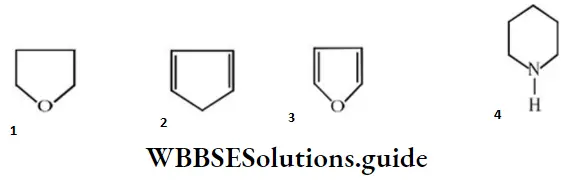
Answer: 3

Solution: Furan is heterocyclic and aromatic due to the Huckel’s rule of aromaticity, i.e., 6π- electrons.
Types of Organic Compounds: Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes NEET Questions
Question 128. Cyclohexane is:
- Aliphatic compound
- Alicyclic compound
- Aromatic compound
- Heterocyclic compound
Answer: 2. Alicyclic compound
Solution: Benzene and all its derivatives along with heteroaromatics possess aromatic nature. Rest all possess aliphatic nature.
Question 129. On monochlorination of 2-methyl butane, the number of chiral compounds formed are:
- 2
- 4
- 6
- 8
Answer: 2. 4
Solution:
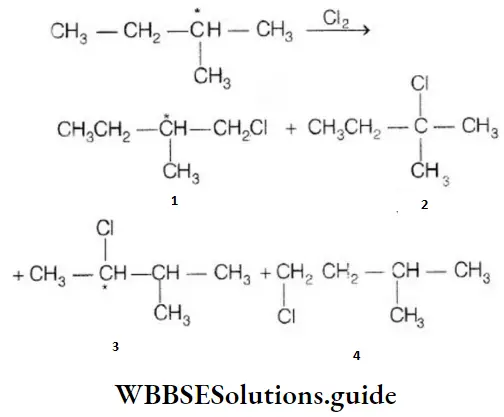
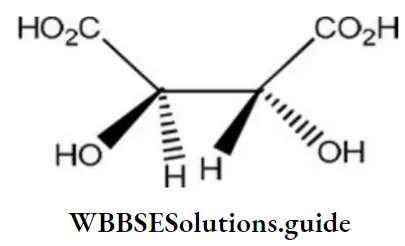
Question 130. The absolute configuration of
- S, S
- R, R
- R, S
- S, R
Answer: 2. R, R
Solution: If you rotate the curve in a clockwise manner, the absolute configuration is termed as R (rectus) configuration. On the other hand, the absolute configuration is termed as S (sinister) configuration if the curve is rotated in a counter-clockwise direction.
The lowest priority functional group should be located on the vertical line. Otherwise, the absolute configuration is reversed. The order of priority for functional group in decreasing order is given as follows:
carboxylic acid > sulphonic acid > esters > amide > nitrile > aldehydes > ketones > alcohol > amines > hydrocarbons > ethers > alkyl halides
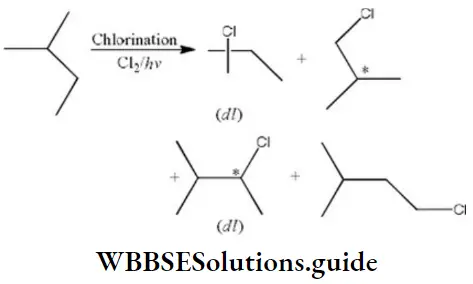
Question 131. How many chiral compounds are possible on mono chlorination of 2-methyl butane?
- 2
- 4
- 6
- 8
Answer: 1. 2
Solution: On chlorination of 2-methyl butane 2-chiral compounds are formed.
Question 132. Amongst the following compounds, the optically active alkane having lowest molecular mass is
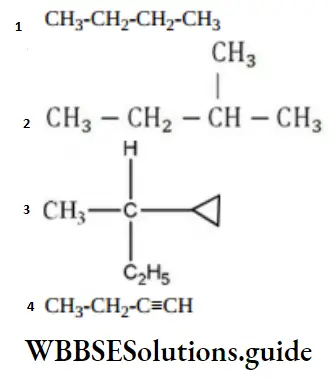
Answer: 3
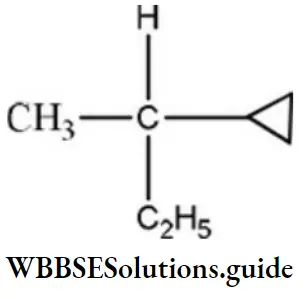
Solution:
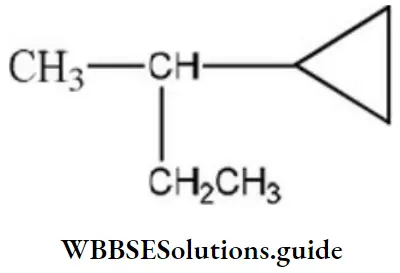
contains asymmetric carbon, thus optically active.
Question 133. An organic compound X(mol. formula C6H5O2N) has six carbons in a ring system, three double bonds, and also a nitro group as substituent. X is:
- Homocyclic but not aromatic
- Aromatic but not homocyclic
- Homocyclic and aromatic
- Heterocyclic
Answer: 3. Homocyclic and aromatic
Solution: The given compound is nitrobenzene.
Question 134. The hybrid orbitals at carbon 2 and 3 in the compound CH3 CH=CHCH3 are:
- sp3, sp
- sp2, sp2
- sp, sp
- sp2, sp
Answer: 2. sp2,sp2
Solution: Both these carbon atoms have 3σ-and 1π-bond. Recall hybridized orbitals never form π-bonds.
Question 135. The bond energy for catenation next to carbon is:
- N
- S
- Si
- P
Answer: 3. Si
Solution: The bond energy of catenation order is C > Si > S > P.
Question 136. Least stable conformer of cyclohexane is
- Chair
- Boat
- Twist boat
- Planar hexagon
Answer: 4. Planar hexagon
Solution: Planar hexagon conformer has considerable angle strain due to the fact that its bonds are not 109.5°. It also has torsional strain. Due to the presence of these strains, the planar hexagon conformer of cyclohexane is least stable.
Question 137. Which one of the following compounds is the most polar?
- CH2I2
- CH2F2
- CH2Cl2
- CH2Br2
Answer: 2. CH2F2
Solution: The electronegativity of F is maximum and thus, the C—F bond is more polar.
Question 138. Ammonia molecule is:
- A nucleophile
- An electrophile
- A homolytic
- An acid
Answer: 4. An acid
Solution: It contains lone pair electrons on the “N” atom.
Question 139. The formula of ethanenitrile is:
- C2H5NC
- C2H5CN
- CH3CN
- None of these
Answer: 3. CH3CN
Solution: Follow nomenclature rules
Question 140. The most abundant organic compound in the world is:
- CH4
- Chlorophyll
- Alkaloids
- Cellulose
Answer: 4. Cellulose
Solution: A lot of plant kingdom is made up of cellulose.
Question 141. State of hybridization of carbon atom of carbene in the singlet state is
- sp2
- sP
- sp3
- None of these
Answer: 1. sp2
Solution: Carbon atom in singlet carbene is sp2-hybridized.
Question 142. Total number of rotational conformers of n-butane are:
- 2
- 6
- 5
- 3
Answer: 3. 5
Solution: Follow conformation; The conformers for n-butane are two gauche, two eclipsed and one anti.
Question 143. The arrangement of atoms that characterizes a particular stereoisomer is called?
- Geometry of isomer
- Configuration
- Conformers
- None of these
Answer: 2. Configuration
Solution: Different spatial arrangement of atoms leads to its configuration.
Question 144. The restricted rotation about the carbon-carbon double bond in 2-butene is due to:
- Overlap of two p-orbitals
- Overlap of one p and one sp2-hybridized orbitals
- Overlap of two sp2-hybridized orbitals
- Overlap of one s and one sp2-hybridized orbitals
Answer: 1. Overlap of two p-orbitals
Solution: Presence of the n-bond in the molecule gives rise to hindered rotation.
Question 145. Glycerol is an alcohol which can be classified as
- Trihydric
- Monohydric
- Dihydric
- Hexahydric
Answer: 1. Trihydric
Solution: Glycerol is a trihydric alcohol. It is CH2 OH-CHOH-CH2 OH. It contains three hydroxyl groups. It is present in nature in the form of oils and fats as its carboxylic esters.
Question 146. The organic liquid that mixes freely with water is:
- CHCl3
- CCl4
- CS2
- C2 H5 OH
Answer: 4. C2 H5 OH
Solution: Due to H-bonding.
Question 147. With a change in hybridization of the carbon bearing the charge, the stability of a carbanion increases in the order
- sp < sp3 < sp2
- sp < sp2 < sp3
- sp2 < sp < sp3
- sp3 < sp2 < sp
Answer: 4. sp3 < sp2 < sp
Solution: Stability of carbanions increase with increasing in s-character of hybrid orbitals of carbon-bearing charge therefore, the order is sp3 < sp2 < sp
Question 148. Which one of the following is the stable structure of cyclohexatriene?
- Chair form
- Boat form
- Half chair form
- Planar form
Answer: 4. Planar form
Solution: Benzene has a planar structure.
Question 149. Which of the following compounds is expected to be optically active?
- (CH3)2 CHCHO
- CH3CH2CH2CHO
- CH3CH2CHBrCHO
- CH3CH2CBr2CHO
Answer: 3. CH3CH2CHBrCHO
Solution: Compounds having asymmetric C-atom are optically active, for example,
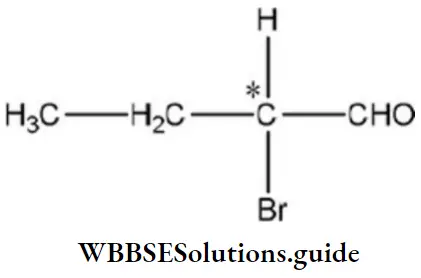
The C-atom whose four valencies are satisfied by four different groups is an asymmetric C-atom.
Question 150. How many n-electrons are there in the following?
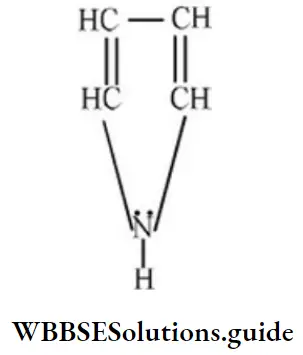
- 2
- 4
- 6
- 8
Answer: 3. 6
Solution: Four n-electrons of double bond and 1 lone pair on “N” atom leads to delocalization of six electrons.
Question 151. The number of possible alkynes with molecular formula C5H8 is
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
Answer: 1. 3
Solution: C5H8 has three possible alkynes. These are
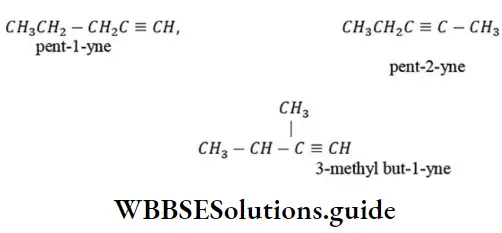
Question 152. Formulae of phenyl carbinol and chloral are respectively:
- C6H5.CH2CH2OH and CHCl2CHO
- C6H5CH2OH and CCl3CHO
- C6H5OH and CH2Cl.CHO
- C6H5CHO and CHCl2CHO
Answer: 2. C6H5CH2OH and CCl3CHO
Solution: Carbinol is trivial name for HCH2OH. Thus, C6H5 CH2 OH is phenyl carbinol and chloral is CCl3 CHO.
Question 153. The correct name for the following hydrocarbon is
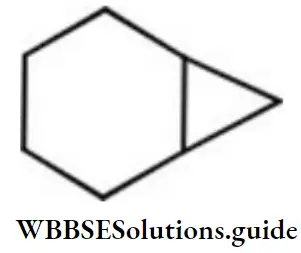
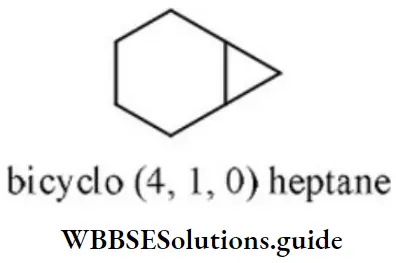
- Tricycle [4.1.0] heptane
- Bicyclo [5.2.1] heptane
- Bicyclo [4.1.0] heptane
- Bicyclo [4.1.0] hexane
Answer: 3. Bicyclo [4.1.0] heptane
Solution: This compound contains 7 carbon atoms, so the corresponding alkane is heptane. Two bridges contain 4 and 1 carbon atom respectively and one bridge does not contain any carbon atom. So, the name of the compound is bicyclo (4,1,0) heptane.
Question 154. In the following compounds which will have a zero-dipole moment?
- 1,1-dichloroethylene
- trans-1,2-dichloroethylene
- cis-1,2-dichloroethylene
- None of the above
Answer: 2. trans-1,2-dichloroethylene
Solution: Symmetrical trans-form has a non-polar nature.
Question 155. Which of the following conformers for ethylene glycol is most stable?
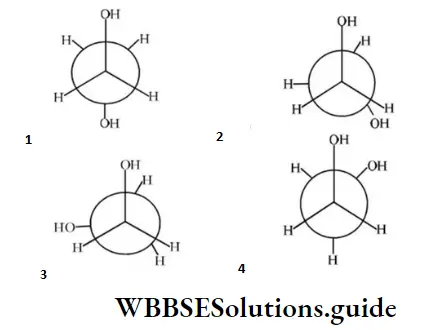
Answer: 4
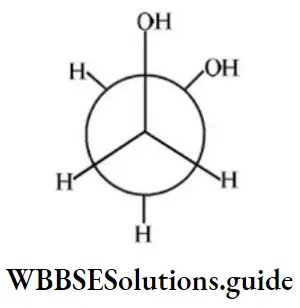
Solution: It shows intramolecular H-bonding.
Question 156. Unpaired electron in C° H3 occupies
- sp-hybrid orbital
- sp3-hybrid orbital
- p-orbital
- sp2-hybrid orbital
Answer: 3. p-orbital
Solution: Alkyl free radicals are either planar or pyramidal in structure. Spectroscopic evidence shows that methyl free radical (CH3) is planar, thus it is conveniently sp2 hybridization with unpaired electrons located primarily in p-orbital.
Question 157. Out of the following, the alkene that exhibits optical isomerism is
- 3-methyl-2-pentene
- 4-methyl-l-pentene
- 3-methyl-l-pentene
- 2-methyl-2-pentene
Answer: 3. 3-methyl-l-pentene
Solution: It has one chiral centre.
Question 158. Rotation of plane polarized light can be measured by:
- Manometer
- Calorimeter
- Polarimeter
- Viscometer
Answer: 3. Polarimeter
Solution: It is a fact.
Question 159. In the hydrocarbon, \(\underset{6}{\mathrm{CH}_3}-\underset{5}{\mathrm{CH}}=\underset{4}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}-\mathrm{CH}_2-\underset{2}{\mathrm{C}} \equiv \underset{1}{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}\). The state of hybridization of carbons 1, 3, and 5 are in the following sequence:
- sp,sp3,sp2
- sp,sp2,sp3
- sp3,sp2,sp
- sp2,sp,sp3
Answer: 1. sp,sp3,sp2
Solution:
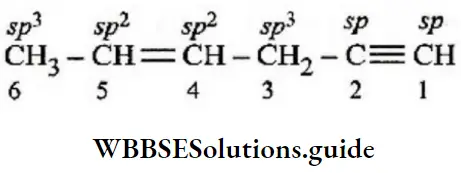
Question 160. 2, 3-dimethyl hexane contains ______ tertiary ____ secondary and _______ primary carbon atoms, respectively
- 2,2,1
- 2,4,3
- 4,3,2
- 3,2,4
Answer: 1. 2,2,1
Solution: The structure of 2, 3-dimethyl hexane is
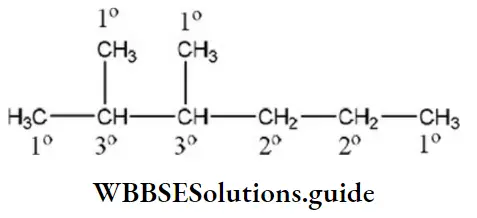
So, the number of tertiary carbon atoms=2
The number of secondary carbon atoms=2
The number of primary carbon atoms=4
Question 161. The enolic form of acetone contains
- 8σ bonds, 2π-bonds, and 1 lone pair
- 9σ bonds, 1π-bonds, and 2 lone pairs
- 9σ bonds, 2π-bonds, and 1 lone pair
- 10σ bonds, 1πr-bonds, and 1 lone pair
Answer: 2. 9π bonds, 1π-bonds, and 2 lone pairs
Solution:
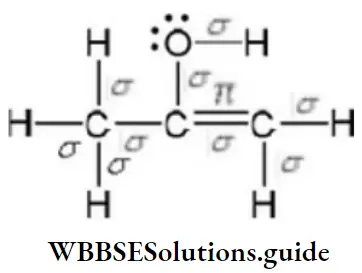
9σ bonds, 1π-bonds, and 2 lone pairs
Question 162. Which of the following molecules contain asymmetric carbon atoms?
- CH3CHClCOOH
- CH3CH2COOH
- ClCH3.CH2COOH
- Cl2CHCOOH
Answer: 1. CH3CHClCOOH
Solution: The second carbon is asymmetric.
Question 163. 2-methyl-2-butene will be represented as:
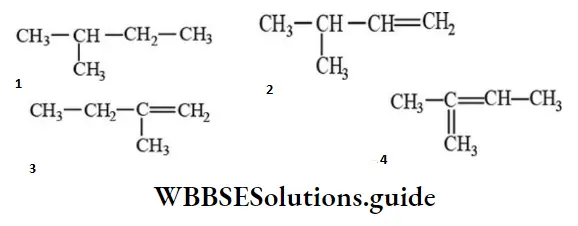
Answer: 4
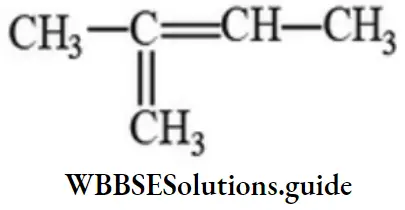
Solution: -do-
Question 164. The energy of C—C triple bond in acetylene in kcal is:
- 140
- 192
- 60
- 100
Answer: 2. 192
Solution: It is a fact.
Question 165. The chirality of the compound is
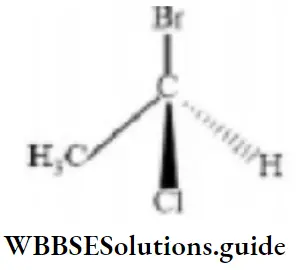
- R
- S
- Z
- I
Answer: 1. R
Solution: Highest to lowest priority (Br > Cl >CH3) is clockwise than R.
Question 166. Bond energy with the increase in number of lone pairs on the bonded atoms.
- Decreases
- Increases
- Does not change
- None of these
Answer: 3. Does not change
Solution: It is a fact.
Question 167. The family to which methoxy ethene belongs, is?
- Hydrocarbon
- Ketone
- Unsaturated ether
- Ester
Answer: 3. Unsaturated ether
Solution: Methoxy ethene is CH3O—CH = CH2 an unsaturated ether.
Question 168. Crown ethers are named as X-crown-7. In the following crown ether, X and Y are respectively
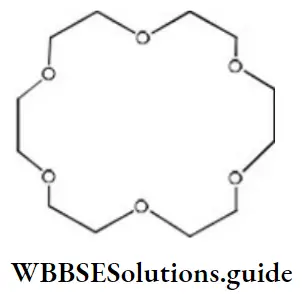
- 6 and 12
- 18 and 6
- 24 and 6
- 6 and 24
Answer: 2. 18 and 6
Solution: X-crown-Y, 18-crown-6
The first number X is the total number of ‘C’ and ‘O atoms in the ring and the second number Y is the number of oxygen atoms in the ring.
Question 169. In the following compounds, the order of basicity is:
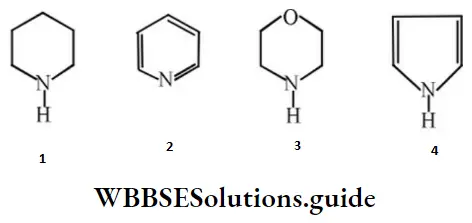
- 4 > 1 > 3 > 2
- 3 > 1 > 4 > 2
- 2 > 1 > 3 > 4
- 1 > 3 > 2 > 4
Answer: 4. 1 > 3 > 2 > 4
Solution: In 2 and 4 lone pairs are involved in resonance.
Question 170. The hybridization of central carbon atom in 1,2- propadiene (allene) is
- sp3
- sp2
- sp
- None of these
Answer: 3. sp
Solution: The simplest cumulated diene is 1,2-propadiene, CH2=C=CH2, also known as allene. Indeed, cumulated dienes are often called allenes. The central carbon in such compounds is sp- hybridized (it has only two bonding partners), and the double-bond array is linear as a result.
Question 171. Which structure can be explained by taking ground state configuration of atoms?
- BeH2
- BF3
- CH4
- H2O
Answer: 4. H2O
Solution: “O” has two unpaired electrons in the ground state.
Question 172. Among the following, which one has more than one kind of hybridization?
- CH3CH2CH2CH3
- CH3CH=CHCH3
- CH2=CH-CH=CH
- CH = CH
- 2 and 3
- 2 and 1
- 3 and 4
- 4
Answer: 1. 2 and 3
Solution:
- has sp3;
- has sp2, sp3;
- has sp2, sp;
- has sp.
Question 173. C – H bond energy is about 101 kcal/mol for methane, ethane and other alkanes but is only 77kcal/mol for C – H bond of CH3 in toluene. This is because
- Of inductive effect due to -CH3 in toluene
- Of the presence of benzene ring in toluene
- Of resonance among the structures of benzyl radical in toluene
- Aromaticity of toluene
Answer: 3. Of resonance among the structures of benzyl radical in toluene
Solution: Y C – H bond in toluene has partial double bond character due to resonance. C – H bond in toluene has less energy as compared to others.
Question 174. The energy difference between the chair and boat form of cyclohexane is:
- 44 kJ mol-1
- 24 kJ mol-1
- 34 kJ mol-1
- 68 kJ mol-1
Answer: 1. 44 kJ mol-1
Solution: It is a fact.
Question 175. Allyl isocyanide has:
- 9σ and 4π-bonds
- 8σ and 5π-bonds
- 9σ, 3π, and 2 non-bonded electrons
- 8σ, 3π, and 4 non-bonded electrons
Answer: 3. 9σ, 3TT and 2 non-bonded electrons
Solution: Single bond has 1 sigma bond double bond has a sigma and a pi bond and triple bond has 2 pi and 1 sigma bond.
Question 176. Which of the following represents the given mode of hybridization sp2-sp2-sp-sp from left to right?
- CH2=CH-OCH
- HOC-ON
- CH2=C-C=CH2
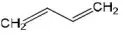
Answer: 1. CH2=CH-OCH
Solution: CH2=CH-OCH (sp2-sp2-sp-sp)
Question 177. In which case the carbon-carbon bond length is the same?
- 2-butene
- Benzene
- 1-butene
- 1-propyne
Answer: 2. Benzene
Solution: Due to resonance in benzene.
Question 178. The compounds CH3 NH2 and CH3 CH2.NH2 are:
- Isomers
- Isobars
- Homologous
- Allotropes
Answer: 3. Homologous
Solution: Both differ by a -CH2 group.
Question 179. The C—C bond length of the following molecules is in the order of.
- C2H6 > C2H4 > C6H6 > C2H2
- C2H2 < C2H4 < C6H6 < C2H6
- C6H6 > C2H2 > C2H6 > C2H4
- C2H4 > C2H6 > C2H2 > C6H6
Answer: 2. C2H2 < C2H4 < C6H6 < C2H6
Solution: C-C, C = C, and C = C bond length are 1.54 A, 1.34A, and 1.20A respectively.
In benzene C = C is 1.40A.
Question 180. Vital force theory of the origin of organic compounds was discarded by:
- Kolbe’s synthesis
- Haber’s synthesis
- Wohler’s synthesis
- Berthel it’s a synthesis
Answer: 3. Wohler’s synthesis
Solution: Wohler prepared urea from inorganic compounds and rejected the vital force theory that organic compounds can only be synthesized from living organisms.
Question 181. Which of the following orders is true regarding the acidic nature of COOH?
- Formic acid > acetic acid > propanoic acid
- Formic acid > acetic acid < propanoic acid
- Formic acid < acetic acid > propanoic macid
- Formic acid > acetic acid < propanoic acid
Answer: 1. Formic acid > acetic acid > propanoic acid
Solution: This can be judged by comparing the stabilities of carboxylate ions formed. The most stable carboxylate ion is formed by the strongest acid
Question 182. A compound containing 80% C and 20% H is likely to be
- C6H6
- C2H6
- C2H6
- C2H2
Answer: 2. C2H6
Solution:
\(\begin{aligned}& \mathrm{C} \frac{80}{12}=6.6, H \frac{20}{1}=20 ; \text { ratio }=1: 3 \\
& \mathrm{EF}=\mathrm{CH}_3 \\
& \mathrm{MF}=\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_6
\end{aligned}\)
Question 183. With a change in hybridization of the carbon bearing the charge, the stability of a carbanion increases in the order
- sp<sp2<sp3
- sp<sp3<sp2
- sp3<sp2<sp
- sp2<sp<sp3
Answer: 3. sp3<sp2<sp
Solution: Carbanion is an electron-rich species. Stability of carbanion increases with increase in the s-character of hybrid orbitals of carbon-bearing the charge.
∴ sp3 < sp2 < sp
(25%s-character) (33%s-character) (50%s-character)
Question 184. The basic strength of
- \(\mathrm{CH} \equiv \overline{\mathrm{C}}\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_2=\overline{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H},\)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \overline{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{H}_2\) will be in order
- 1<2<3
- 2<3<1
- 3<2<1
- 3<1<2
Answer: 1. 1<2<3
Solution: Weak base —> strong conjugate acid \(\mathrm{CH} \equiv \mathrm{C}^{-} \rightarrow \mathrm{CH} \equiv \mathrm{CH}\) weakest base (strongest acid among the given) CH3-CH2– CH3 CH3
Question 185. In the following groups,
- OAC1
- OMe2
- OSO2Me
- OSO2CF3 the order of leaving group ability is:
- 1 > 2 > 3 > 4
- 4 > 3 > 1 > 2
- 3 > 2 > 1 > 4
- 2 > 3 > 4 > 1
Answer: 2. 4 > 3 > 1 > 2
Solution: Leaving group ability depends upon the basicity of the group.
Question 186. The compound in which carbon uses only its sp3 hybrid orbitals for bond formation is
- (CH3)3COH
- HCOOH
- CH3CHO
- (H2N)2CO
Answer: 1. (CH3)3COH
Solution:
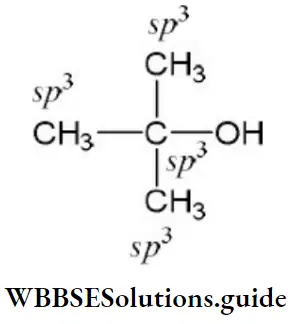
All bonds are σ- bonds hence C uses only its sp3-hybrid orbitals. In all other compounds there is one C=O double bond, therefore, this carbon is sp2– hybridized
Question 187. The structural formula of methyl aminomethane is:
- (CH3)2CHNH2
- (CH3)3N
- (CH3)2NH
- CH3NH2
Answer: 3. (CH3)2NH
Solution: IUPAC name is N-methyl methanamine.
Question 188. Which of the following is not chiral?
- 3-bromopentane
- 2-hydroxy propanoic acid
- 2-butanol
- 2,3-dibromo pentane
Answer: 1. 3-bromopentane
Solution: 3-bromopentane is not a chiral molecule due to the absence of chiral C-atom.
Question 189. The C—C bond angle in cyclopropane is:
- 60°
- 120°
- 109°28′
- 180°
Answer: 1. 60°
Solution: The arrangement of the three carbon atoms of the cyclopropane ring is of the form of an equilateral triangle thus bonds angles are 60 degrees each.
Question 190. How many σ and π bonds are there in the molecule of tetracyanoethylene?
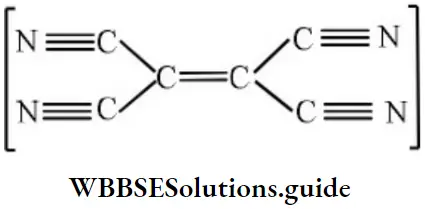
- 9σ and 9π
- 5σ and 9π
- 9σ and 7π
- 5σ and 8π
Answer: 1. 9σ and 9π
Solution: Count σ and n-bonds.
Question 191. The correct name for CH3 COCH2 OH is:
- 2-keto propanol
- 1-hydroxy propan-2-one
- Propan-2-one-l-ol
- 3-hydroxy propane-2-one
Answer: 2. 1-hydroxy propan-2-one
Solution: Follow IUPAC rules.
Question 192. The group named as benzal possesses nature.
- Monovalent
- Bivalent
- Trivalent
- Tetravalent
Answer: 2. Bivalent
Solution: Benzal is C6 H5 CH group.
Question 193. The study of the three-dimensional structure of molecule is called
- Stereochemistry
- Solid state chemistry
- Chirality
- None of these
Answer: 2. Solid state chemistry
Solution: It is a fact.
Question 194. Who proposed the tetrahedral mirror image structures to a pair of enantiomers
- Kekule
- Wohler
- Van’tHoff
- None of these
Answer: 3. Van’tHoff
Solution: It is a fact
Question 195. Which of the following statements is not correct?
- Primary carbocation is more stable than secondary ones
- Secondary free radicals are more stable than primary free radicals
- Tertiary free radicals are more stable than secondary ones
- Tertiary carbonium ions are more stable than primary ones
Answer: 1. Primary carbocation is more stable than secondary ones
Solution: In the tertiary carbocation the three alkyl groups help to stabilize the positive charge. In a secondary carbocation, only two alkyl groups would be available for this purpose, while a primary carbocation has only one alkyl group available. Thus, the observed order of stability for carbocations is as follows: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl.
Question 196. Which one of the following is the most energetic conformation of cyclohexane?
- Boat
- Twisted boat
- Chair
- Half chair
Answer: 4. Half chair
Solution: The stability order of conformation of cyclohexane is chair>twist boat>boat>half chair. Hence, the half chair is less stable due to torsional and angle strain.
Question 197. Cyclic hydrocarbon molecule (A) has all the C and H atoms in a single plane. All the C-C bonds have same length, less than 1.54 A but more than 1.34A. The∠ (angle) CCC is:
- 190°28′
- 100°
- 180°
- 120°
Solution: The conditions given are for C6 H6.
Question 198. A molecule of benzene contains:
- Twelve sigma-bonds and three pi-bonds
- Eighteen sigma-bonds and three pi-bonds
- Twelve pi-bonds and three sigma-bonds
- Six hydrogen-bonds, six sigma-bonds and three pi-bonds
Answer: 1. Twelve sigma-bonds and three pi-bonds
Solution: Benzene has 6 C—C and 6 C—H σ-bonds and 3 C = C π-bonds.
Question 199. The maximum number of carbon atoms arranged linearly in the molecule, CH3– OC-CH=CH2 is
- 5
- 4
- 2
- 3
Answer: 3. 2
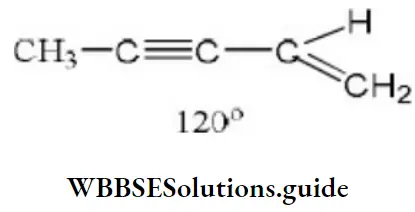
Solution: The C-atoms attached to the triple bond lie in a straight line while the carbon of the CH2 group is inclined at an angle of 120°. Therefore, only 2 carbon atoms are linearly arranged.
Question 200. Homologous compounds have:
- Same chemical properties
- Same molecular weight
- Same physical properties
- Same melting point and boiling point.
Answer: 1. Same chemical properties
Solution: Due to the same functional group.
Question 201. The species which use sp2-hybrid orbitals in its bonding:
- PH3
- NH3
- CH3+
- CH4
Answer: 3. CH3+
Solution: CH3+ has planar structure.
Question 202. Reactivity of hydrogen atoms attached to different atoms in alkanes has the order:
- 3°>1°>2°
- 1°>2°>3°
- 3°>2°>1°
- None of these
Answer: 3. 3°>2°>1°
Solution: The reactivity order for H atom is 3°H > 2°H > 1°H.
Question 203. Eclipsed and staggered forms of n-butane are called a pair of:
- Diastereomers
- Conformers
- Isomers
- Enantiomers
Answer: 2. Conformers
Solution: Follow conformation.
Question 204. In the case of homologous series of alkanes, which one of the following statements is incorrect?
- The members of the series have the general formula CnH2n+2, where n is an integer
- The difference between any two successive members of the series corresponds to 14 unit of relative atomic mass
- The members of the series are isomers of each other
- The members of the series have similar chemical properties
Answer: 3. The members of the series are isomers of each other
Solution: Homologous differ by a group —CH2 and cannot be isomer.
Question 205. During pyrolysis of an alkane, the C—C bond breaks faster than the C—H bond because:
- C—C bond is stronger
- C—H bond is weaker
- C—C bond involves π-bond in alkane
- The bond energy of C—C bond is less than that of C—H bond
Answer: 4. The bond energy of C—C bond is less than that of C—H bond
Solution: Lesser is bond energy of 2p-2p overlapping in C—C, more is its reactivity than C—H bond showing 2p-ls overlapping.
Question 206. Which one of the following compounds is most acidic?
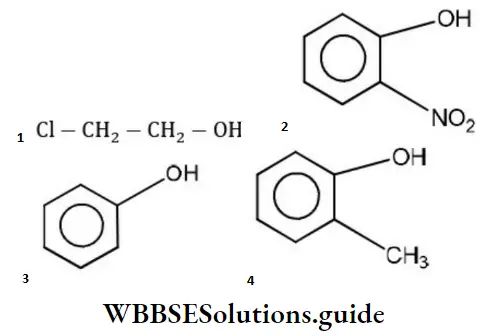
Answer: 2
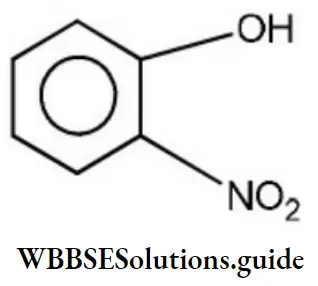
Solution: Phenols are much more acidic than alcohol due to the stabilization of phenoxide ion resonance.
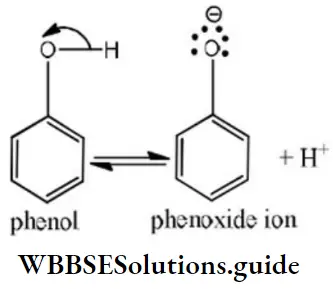
Phenoxide ions are stabilized due to the following resonating structures.
ortho nitrophenol is most acidic because in -NO2 electron attracting group is attached to ortho position which helps in stabilizing the negative charge on the oxygen of phenoxide ion. Hence, due to this reason acidic character of phenol is increased, while on attachment of -CH3 group (electron donating group) acidic strength of phenol is decreased in cresol due to the destabilization of phenoxide ion.
Question 207. The correct definition for organic chemistry is:
- Chemistry of carbon compounds
- Chemistry of compounds derived from living organisms
- Chemistry of hydrocarbons and their derivatives
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Chemistry of hydrocarbons and their derivatives
Solution: It is the latest modified definition of organic chemistry.
Question 208. The nodal plane in the π-bond of ethene is located in
- The molecular plane
- A plane parallel to the molecular plane
- A plane perpendicular to the molecular plane which bisects the carbon-carbon sigma bond at right angle
- A plane perpendicular to the molecular plane which contains the carbon-carbon sigma bond
Answer: 1. The molecular plane
Solution: A π-bond has a nodal plane passing through the two bonded nuclei, i.e., molecular plane.
Question 209. Given that the decreasing order of the acidic character is
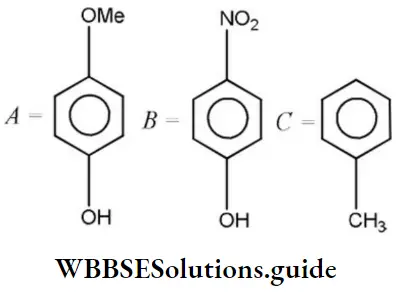
- A>B<C
- B>A>C
- B>C>A
- C>B>A
Answer: 3. B>C>A
Solution: According to Lewis, electron-acceptor compounds are called acids. Therefore, compounds having a tendency to accept electrons will be more acidic. The correct order of acidic character is as follows:
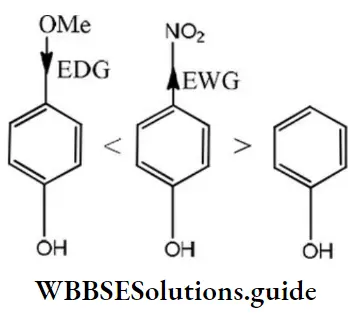
Question 210. Select the molecule having only one n-bond
- CH≡CH
- CH2 = CH—CHO
- CH3-CH=CH2
- CH3-CH=CHCOOH
Answer: 3. CH3-CH=CH2
Solution: CH3-CH=CH2 (Propene) has only one Pi-bond.
Question 211. The Cl—C—Cl angle in 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethene and tetrachloromethane respectively will be about:
- 120° and 109.5°
- 90° and 109.5°
- 109.5° and 90°
- 109.5° and 120°
Answer: 1. 120° and 109.5°
Solution: CCl2=CCl2 has ethene like structure (z.e.,sp2-hybridization); CCl4 has CH4 like structure,i.e.,sp3-hybridization.
Question 212. The name of the compound is
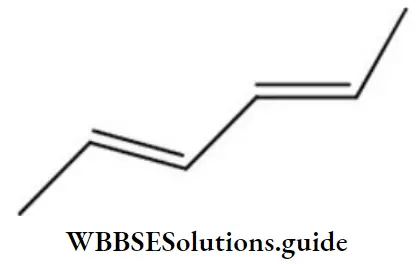
- (2Z,4Z)-2, 4-hexadiene
- (2Z-, 4E)-2, 4-hexadiene
- (2E, 4Z)-2, 4-hexadiene
- (4E, 4Z)-2, 4-hexadiene
Answer: 1. (2Z,4Z)-2, 4-hexadiene
Solution: The name of the compound is (2Z,4Z)-2, 4-hexadiene.
Question 213. The change in optical rotation with time of freshly prepared solution of sugar is known as:
- Specific rotation
- Inversion
- Rotatory motion
- Mutarotation
Answer: 2. Inversion
Solution: The hydrolysis of sugar solution (dextrorotatory) leads to formation of laevorotatory mixture due to formation of glucose (dextrorotatory) and fructose (laevorotatory).
Question 214. A strong base can abstract an a-hydrogen from:
- Amine
- Ketone
- Alkane
- Alkene
Answer: 2. Ketone
Solution: Removal of H from ketone gives resonance stabilized carbanion.
Question 215. What is the formula of tertiary butyl alcohol?
- CH-CH(CH3)-CH2-OH
- CH3-(CH2)2OH
- CH3-CH(OH)-CH2-CH3
- (CH3)3.C-OH
Answer: 4. (CH3)3.C-OH
Solution:
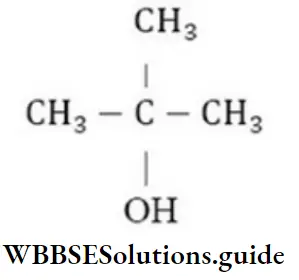
is the formula of tertiary butyl alcohol as in it – OH group is attached to tertiary carbon.
Question 216. Which of the following compounds (s) has ‘Z’ configuration?
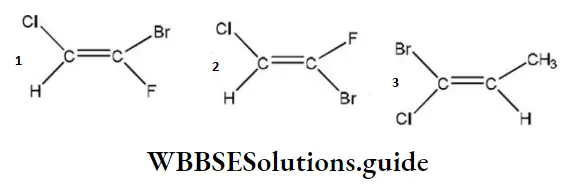
- 1 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1 and 3
Answer: 4. 1 and 3
Solution: When the groups with higher priority (i.e., with high atomic number) are present on the same side of the double bond, then the configuration is Z but when present on the opposite side of the double bond, the configuration is E.
Question 217 The number of sp3– hybrid carbons in 2-butyne is:
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
Answer: 3. 2
Solution: Butyne-2 is CH3-C=C-CH3; Two carbon of corner are sp3-hybridized.
Question 218. Which of the following possesses a sp-hybridized carbon in its structure?
- CCl2=CCl2
- CH2=C=CH2
- CH2=CH—CH=CH2
- CH2=CCl—CH=CH2
Answer: 2. CH2=C=CH2
Solution: The middle carbon has 2σ-and 2π-bonds.
Question 219. The shape of CH3° is?
- Linear
- Planar
- Pyramidal
- None of these
Answer: 3. Pyramidal
Solution: sp’-hybridization with one position occupied by lone pair like NH3.
Question 220. Which one is the senior most functional group in the nomenclature of an organic compound if it possesses more than one functional group?
- —CHO
- —COOH
- —OH
Answer: 2. —COOH
Solution: -COOH is on top in the preference table.
Question 221. The number of valence electrons in the excited carbon atom is:
- Two in s and two in p-orbitals
- 4 singles p-orbitals
- One in s and three in p-orbitals
- None of the above
Answer: 3. One in s and three in p-orbitals
Solution: Excited state of carbon is 2s1 2p3.
Question 222. In benzene, all the C-C bonds are of equal length because of:
- Isomerism
- Resonance
- Tautomerism
- Inductive effect
Answer: 2. Resonance
Solution: Resonance in benzene gives rise to identical C—C bond lengths.
Question 223. Correct structural formula of the compound-5-nitro-3-methoxy-3-methylhexanoyl chloride is
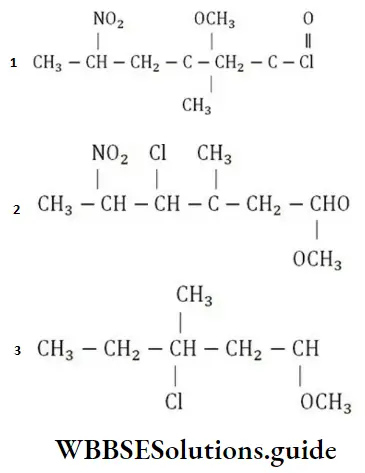
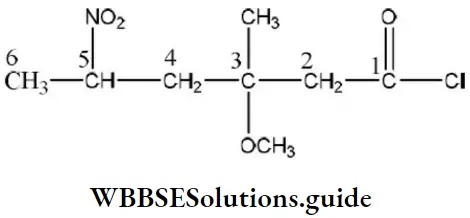
Solution: The structural formula of the compound 5-nitro-3-methoxy-3-methyl hexanoyl chloride is
Question 224. Enol content is highest in
- Acetone
- Acetophenone
- Acetic acid
- Acetyl acetone
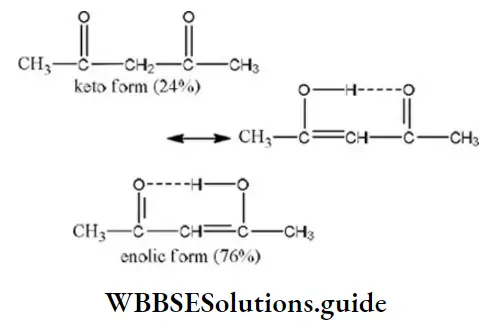
Answer: 4. Acetyl acetone
Solution: The amount of enolic form is highest in acetyl due to the stabilization of enolic form by hydrogen bonding
Question 225. Pyridine is:
- An aromatic compound and a primary base
- A heterocyclic amino compound and a tertiary base
- An aromatic amino compound and forms salts
- A cyano derivative of benzene and secondary base
Answer: 2. A heterocyclic amino compound and a tertiary base
Question 226. The sigma bond energy of C—H bond in C2 H6 is:
- 99 kcal
- 140 kcal
- 200 kcal
- 60 kcal
Answer: 1. 99 kcal
Solution: It is a fact.
Question 227. The name of the compound, is:

- 2-pentanone
- Pentanone-2
- Pentan-2-one
- All are correct
Answer: 3. Pentan-2-one
Solution: -do-
Question 228. Which of the following does not have a resonance structure?
- Benzene
- Benzaldehyde
- Acetaldehyde
- Benzylamine
Answer: 3. Acetaldehyde
Solution: All aromatic compounds are resonance hybrids.
Question 229. Which reaction sequence would be best to prepare 3-chloro-aniline from benzene?
- Chlorination, nitration, reduction
- Nitration, chlorination, reduction
- Nitration, reduction, chlorination
- Nitration, reduction, acylation, chlorination, hydrolysis
Answer: 2. Nitration, chlorination, reduction
Solution: This synthesis involves adding two substituents to the benzene ring. In this case, we need to consider the order of substitution. Cl is an ortho-para director. That means, if Cl is first added to the benzene, the next substituent will be placed in the ortho/para position and that will not work since, in the desired product, NH2NH2 is meta to Cl. That means we need to add Cl in the last. NH2NH2 is also an ortho-para director, so that means we can’t add Cl after forming aniline.
Assertion Reasoning Type
Each question contains Statement l(Assertion) and Statement 2(Reason).
Each question has the 4 choices (1), (2), (3), and (4) out of which only one is correct.
- Statement 1 is True; Statement 2 is True;
Statement 2 is the correct explanation for Statement 1 - Statement 1 is True; Statement 2 is True; Statement 2 is not correct explanation for Statement 1
- Statement 1 is True, Statement 2 is False
- Statement 1 is False, Statement 2 is True
Question 230.
- Statement 1: Carbanion-like ammonia has pyramidal shape
- Statement 2: The carbon atom carrying negative charge has an octet of electrons
Answer: 2. Statement 1 is True; Statement 2 is True; Statement 2 is not correct explanation for Statement 1
Solution: Carbon in carbanion is sp3-hybridized with one orbital occupied by a lone pair
Question 231.
- Statement 1: The empirical formula of glucose is CH2O which represents the relative number of atoms of each atom present in this molecule
- Statement 2: In glucose, the elements C, H, and O have combined in the ratio 1:2:1
Answer: 1. Statement 1 is True; Statement 2 is True;
Statement 2 is correct explanation for Statement 1
Solution: The empirical formula of compound in the simplest formula deduced from its percentage composition showing its composition by