Short Answer Questions
Discreptions: Give answer in 2-3 sentences.
Question 1. How does a subspecies differ from a species?
Answer:
A species consists of a population (or populations) that cannot interbreed successfully with another species. A subspecies consists of a group within a species that is usually geographically isolated from other subspecies. If ranges of different subspecies do overlap, successful interbreeding can occur.
Read And Learn More: NEET Class 9 Biology Short Question And Answers
Question 2. Describe the evolution of specialized cells, tissues, and organs in the Animalia, including the name of the animal group that first showed each evolutionary innovation.
Answer:
Sponges are the group in which the first specialized cells appeared. However, sponges are merely loose collections of such cells. The cnidaria were among the first animals to evolve true, differentiated tissues. Flatworms were among the first animals to evolve true organs.
Question 3. Why do we classify organisms?
Answer:
We classify organisms because of classification:
- Makes the study of diverse forms of life easy i.e. by
studying one member of the group we can know about
the whole group. - Helps us to understand the interrelation among different
living organisms and trace the order of evolution. - Provides the basis for developments in other branches
of biology e.g. crop improvement and animal breeding.
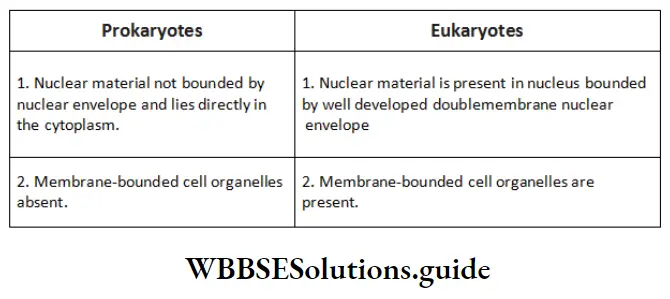
Question 4. What are the kingdoms of life?
Answer:
A five-kingdom classification system consisting of the kingdoms Monera, Protista, Animalia, Fungi and Plantae is widely used, but a new and increasingly accepted three domain system will require revisions at the kingdom level of classification. The three domains, representing the three main branches of life, are Bacteria, Archaea and Eukarya.
Question 5. The biological field of taxonomy classifies organisms based on their evolutionary relationships. Indicate the correct order for these levels of taxa Class, family, species, genus, kingdom, phylum, order
- What are the three domains of life?
- What is the binomial name for humans”
Answer:
- Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
- Archaea, Bacteria, Eukarya
- Homo sapiens.
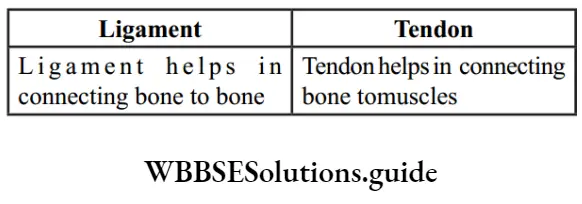
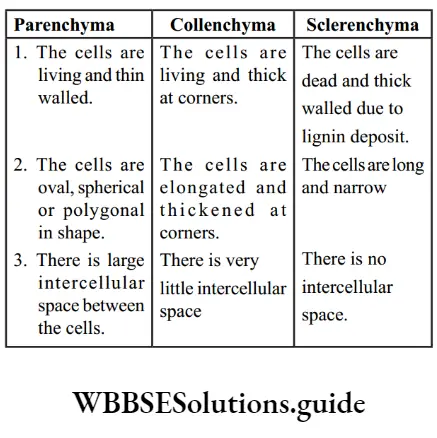
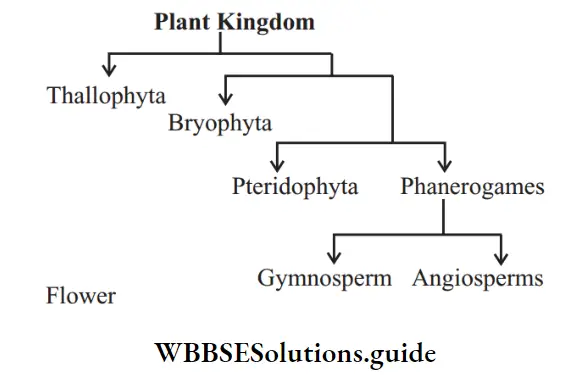
Question 6. Give the difference between Thallophyta and Bryophyta.
Answer:
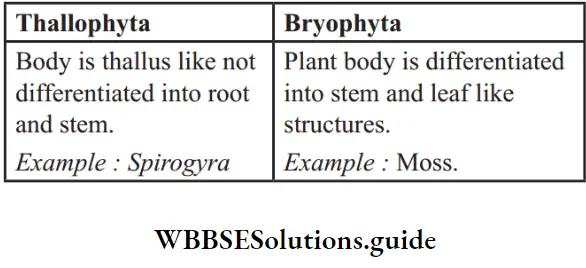
Question 7. Give the characteristics of Monera.
Answer:
- Organisms are unicellular, do not have a defined nucleus.
- Organisms may have cell wall or may not have cell wall.
- Mode of nutrition is either autotrophic or heterotrophic
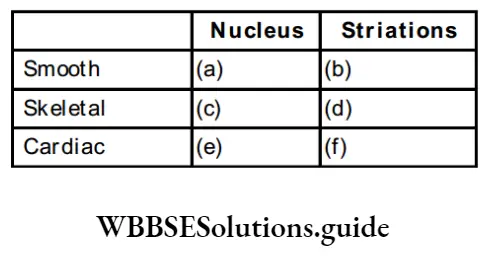
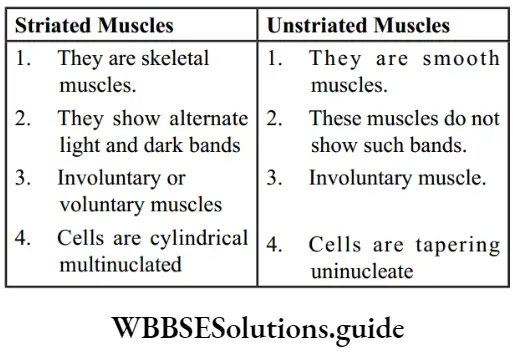
Question 8. Give the difference between the two types of symmetry that animals show.
Answer:
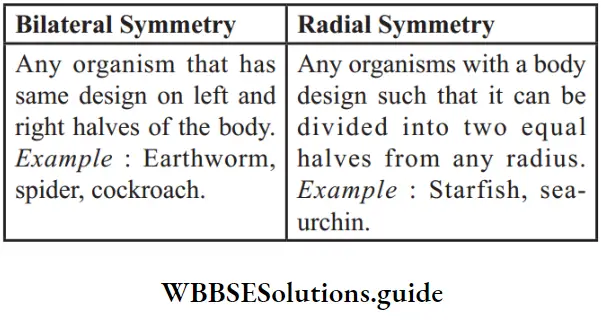
Question 9. Differentiate between Vertebrates and Invertebrates.
Answer:
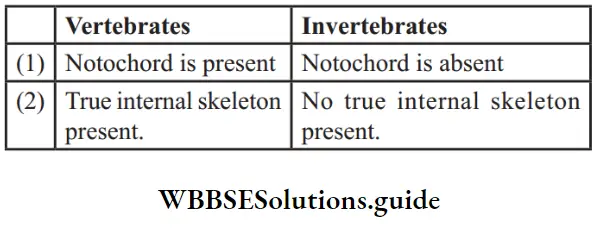
Question 10. How are pores or holes all over the body of porifera important?
Answer: The pores or holes present all over the body of the organisms lead to a canal system that helps in circulating water throughout the body to bring in food and oxygen.
Question 11. State the features of all chordates.
Answer:
All chordates possess the following features:
- Have A Notochord
- Have A Dorsal Nerve Cord
- Are Triploblastic
- Have paired gill pouches
Question 12. Name the phylum of the following animals.
- Tapeworm
- Starfish
- Jellyfish
- Octopus
Answer:
- Tapeworm – Phylum Platyhelminthes
- Starfish – Phylum Echinodermata
- Jelly fish – Phylum Coelenterata
- Octopus – Phylum Mollusca
Question 13. Give general characteristics of Platyhelminthus’?
Answer:
- These are flatworms.
- Most of them are parasites.
- Animals are triploblastic.
- No true internal body cavity.
Examples: Tapeworm, Planaria, Liver fluke
Question 14. Give the characteristics of Arthropoda with two examples.
Answer:
- Arthropoda means ‘Jointed legs’.
- Animals are bilaterally symmetrical and segmented.
- It has an open circulatory system.
- They have open circulatory system.
Example: Spider, scorpions, crabs house flies.
Question 15. Give specific characteristics of coelenterata.
Answer:
- Water-living animals.
- Body is made of two layers of cells.
- Some of them live in colonies corals, while others have solitary life-span (Hydra).
- Body cavity present.
Question 16. Give the characteristics of mammals.
Answer:
- Mammals are warm-blooded animals.
- Four chambered heart
- Mammary glands for production of milk to nourish their younger one.
- Skin has hairs and sweat and oil glands.
- Most of them produce their young ones (viviparous)
Question 17. Differentiate between algae and fungi.
Answer:
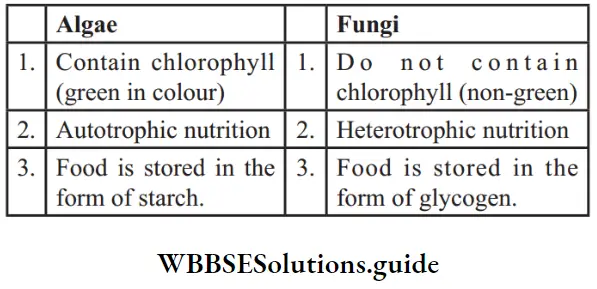
Question 18. Give the characteristics ofAves.
Answer:
Characteristics of Aves are :
- Streamlined body
- Hollow and light bones
- Forelimbs are modified into wings, which help in fling.
- Warm blooded animals. Heart with four chambers.
- Egg laying animals
- Beak present, teeth are absent.
Question 19. Birds should feed more often than lizards. Give reasons.
Answer:
Birds are warm-blooded animals and are more active. Some of them often fl continuously for hours. So their energy requirement is more. On the other hand, lizards are coldblooded, sluggish animals and often go for hibernation. So their energy demand is relatively less. Energy is produced by the oxidation offood materials. So, to fulfi the higher energy demand, birds should feed more often than lizards.
Question 20. A, B and C are living organisms. Identify the group to which they belong to on the basis of the following features:
1. A is unicellular, microscopic, eukaryotic, and shows locomotion with the help of pseudopodia.
Answer: Organism A belongs to kingdom Protista.
2. B is unicellular, microscopic, prokaryotic, and has cell wall.
Answer: Organism B belongs to kingdom Monera.
3. C is multicellular, fiamentous, eukaryotic, autotrophic and aquatic.
Answer: Organism C belongs to kingdom Plantae; division Thallophyta and class Algae.
Question 21.What is haemocoel? Which groups of animals have it?
Answer: The coelomic cavity meant for blood circulation is termed as haemocoel. In haemocoel, the blood flws freely, so this type of blood circulation is known as open type circulation. Haemocoel is found in the animals of phylum Arthropoda.
Question 22.What is the fate of notochord in higher chordates?
Answer: In higher chordates, the notochord is transformed into vertebral column, which lies mid dorsally extending from skull to tail.
Question 23. How can we consider that green algae are similar to higher plants?
Answer: On the basis of the following points, green algae can be considered to be similar to higher plants :
- Their cell wall is made up of cellulose and pectin.
- They contain pigments like chlorophyll and carotenoid
- They contain pigments like chlorophyll and carotenoid
- They store food in the form of starch.
Question 24. Why are bryophytes called ‘amphibians of the plant world’?
Answer: Like amphibians, bryophytes, also need water for fertilisation and development. Hence, they are called amphibians of the plant world.
Question 25. Give the characteristics of Protista.
Answer:
- Organisms are unicellular, eukaryotic organisms
- Use appendages for locomotion like cilia, flagella.
- Nutrition is either autotrophic or heterotrophic, e.g. algae, protozoa.
Question 26.What are hermaphrodites? Give two examples.
Answer: When an organism has both the sexes, i.e., it can produce both sperms and eggs.
Example: sponges, earthworms.
Question 27. Give the characteristics features of Echinodermata.
Answer:
- Spikes present on skin.
- Free-living marine animals.
- Triploblastic and have a coelomic cavity.
- Have peculiar water-driven tube system called water vascular system that they use for making movement around.
- Have hard calcium carbonate structure that is used as a skeleton.
Example: Starfish, sea-urchin.
Question 28. What are the conventions followed for writing the scientific names?
Answer:
The conventions followed while writing the scientific names are:
- The name of the genus begins with a capital letter.
- The name of the species begins with a small letter.
- When printed, the scientific name is given in italics.
- When written by hand, the genus name and the species name have to be underlined separately.
Question 29. Why are vertebrates also called craniates?
Answer: All vertebrates possess skull or cranium, inside which brain ramains protected. Since cranium is always present in vertebrates they are also referred to as craniates.
Question 30. In which kingdom are viruses placed?
Answer:
Viruses are classified as living organisms because they have very simple, noncellular structure and cannot exist independently. They are on the boundary between what we regard as living and non living, and hence, are not included in any kingdom under modern classification.
Question 31. Why is Euglena called a plant-animal?
Answer:
Euglena is claimed to be a plant by botanists because it contains chloroplats and obtains its food through photosynthesis. On the other hand, zoologists consider it to be an animal as its body is covered by pellicle, it bears myonemes and reproduces by binary fision. Since Euglena possesses the features of both plants and animals, it is often called as a plant-animal.
Question 32. Identify the animal group having:
1. Spiny body and radial symmetry
Answer: Echinodermata
2. Bones are light and hollow
Answer: Aves
3. External ear or pinna present
Answer: Mammal
4. Soft-bodied animals supported by calcareous shell.
Answer: Mollusca
Question 33. What conventions are followed while writing the scientific names?
Answer:
- The scientific name should be written in italicized letters.
- Every organism must have two Latin names – the first name representing genus and the second name representing the species.
- The genus name must start with a capital letter and the species name with a small letter