Improvement In Food Resources Long Answer Questions
Question 1. What does the Variety Improvement of crops aim at?
Answer: The aim of Variety Improvement of crops is for:
- Higher Yield: To develop high-yielding varieties so as to increase the productivity of crop per acre.
- Improved Quality: With changes in lifestyles of people, there is an increased demand for better quality. Quality considerations vary from crop to crop like baking quality in wheat, protein quality in pulses, oil quality in oil crops and preserving quality of fruit and vegetables.
- Biotic and Abiotic Resistance: Crop yields decrease due to biotic and abiotic stresses under different situations. Varieties resistant to these stresses are needed to improve crop production.
- Change in Maturity Duration: A shorter duration of the crop from sowing to harvesting makes the variety more economical.
- Wider Adaptability: Varieties capable of growing successfully under different
- environmental conditions to help in stabilising the crop production at places having different environment.
- Desirable Agronomic Characteristics: Developing varieties of desired agronomic characters help in giving higher productivity
Read And Learn More: NEET Class 9 Biology Long Question And Answers
Question 2. Describe the objectives of plant breeding.
Answer: The various objectives of plant breeding are listed below :
1. High yield: It is the primary concern of the plant breeder to produce a crop variety having increased productivity per acre. It is achieved by developing and selecting more effiient genotype.
2. Improved quality : In addition to quantity, it is necessary for the breeder to consider the quality of the Plant produce. For example, sweet, juicy and seedless oranges are preferred over a large number of sour, pithy ones.
3. Biotic and abiotic resistance. Under natural conditions, the crop plants are prone to certain biotic (diseases caused by bacteria, fungi, nematodes, etc. or damage caused by insects) and abiotic (drought, salinity, water lodging, heat, cold and frost) stresses which cause a great loss of production.
4. Change in maturity duration: Production of a crop can be increased many times by reducing the time duration from sowing to harvesting. It saves time, labour, irrigation, fertilizers and money.
5. Wider adaptability: An ability to withstand the extremes of moisture, drought, temperature and other conditions, by the cultivated plants, is another desirable trait by the breeders.
6. Development of novel varieties: Developing a new variety with increased food production is not enough. The breeder is always on the lookout for novel varieties which attract the consumer. Seedless tomatoes, oranges, lemons, stoneless lums, and peaches are some of the products of the breeder’s honest efforts which have captured the market.
NEET Biology Class 9 Improvement in Food Resources Long Questions
Question 3. State one indicator each for infestation by insects and rodents in stored food grains. Describe one method each for controlling the population of insects and rodents.
Answer: The presence of cocoons, webs and weevilled grain indicates the infestation by insects. Presence of excreta and holes in the bags indicates the infestation by rats.
- Method of controlling insects in storage by fumigation: Fumigation is the most effective method for controlling the insects without affecting the grains, example. , ethylene dibromide.
- Depending on the quantity of grains to be fumigated, a certain number of EDB ampules wrapped in cloth are inserted a little below the surface of the grain and broken gently. The structure is left air-tight and undisturbed for a week. Toxic fumes diffuse and kill the insects.
Method of controlling rodents: Using single or multiple doses of rodenticide is an effective method of killing rodents. The baits can be prepared by mixing flur of cereals with jaggery or sugar with edible oil and rodenticide in right proportion, .example zinc phosphide.
Improvement in Food Resources NEET Long Questions and Answers
Question 4. What are manures? Give its classifiation.
Answer: Manures contain large quantities of organic matter and supplies small quantities of nutrients to the soil. It is prepared naturally by the decomposition of animal waste, excreta and plant waste.
- It helps in the soil enrichment with nutrients.
- It helps in improving the soil structure.
- It helps in increasing the water holding capacity in sandy soils.
- In clayey soils it helps in the water drainage and prevent water logging. Manure is classified based on the kind of biological material used to make it.
- Compost
- Vermicompost
- Green manure.
Compost: The farm waste and livestock excreta, along with vegetable waste. Sewage wastes weeds, straws, etc. are allowed to decompose in a pit is called compost. The compost is rich in nutrients.
Vermi Compost: When the above-given matter is allowed to decompose in the pit along with same earthworms, the decomposition speeds up and is called vermicomposting.

Green Manure: The same plants like sun-hemp or guar are grown and then mulched by plowing them into the soil. This is done before the sowing of crop seeds into the field. These green plants present in the soil acts as green manure which enriches the soil in nitrogen and phosphorus.
NEET Biology Improvement in Food Resources Important Long Answer Questions
Question 5. What are the different patterns of cropping?
Answer:
Different ways/patterns/systems of growing crops are:
- Mixed cropping
- Inter-cropping
- Crop-Rotation.
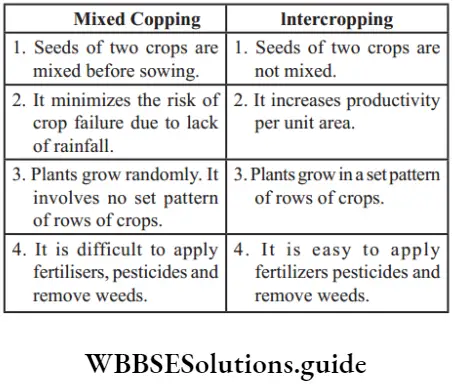
- Mixed Cropping: It is a method in which two or more crops grow simultaneously on the same piece of land. Example: Wheat + grain, Wheat + mustard, or groundnut + sunflower. This helps in the reduction of risk factors and provides insurance against the failure of one of the crops.
- Inter-Cropping: It is growing two or more crops simultaneously on the same field in a definite pattern. A few rows of one crop alternate with a few rows of a second crop Example: soybean + maize or bajra + labia
- Crop-rotation: The growing of different crops on a piece of land in a pre¬planned succession is known as crop-rotation. The availability of moisture and irrigation facility decides the choice of crop to be cultivated after one harvest.
Question 6. Explain different types of fisheries.
Answer: The different types of fisheries are marine fisheries, and Inland fisheries, capture fishing, culture fishing, mariculture, aquaculture.
Marine fisheries: Marine fish are caught using fishing nets. Large school offices are located by satellites. Some are farmed in seawater.
Mariculture: Marine fish are cultured in seawater this culture of fisheries is called mariculture.
Inland fisheries: The fisheries are done in freshwater, resources like canals, ponds, reservoirs, and rivers.
Capture fishing: It is done in seawater, estuaries, and lagoons.
Aquaculture: The culture of fish done in different water bodies is called aquaculture
Best Long Questions for Class 9 Biology Improvement in Food Resources
Question 7. What are the various methods of irrigation in India?
Answer: Most of the agriculture in India is rain-fed, and several different kinds of irrigation systems are adopted to supply water to agricultural lands. The resources are wells, canals, rivers, and tanks.
Wells: Dug wells-water is collected from bearing strata.
Tubewells: Can tap water from deeper strata.
- Canals: Most extensive irrigation system. Canals receive water from reservoirs or rivers. The main canal is divided into branch canals having further distributories to irrigate fields.
- River lift system: Water is directly drawn from the river for supplementing irrigation in areas close to
rivers. - Tanks: These are small storage reservoirs, which intercept and store the run-off of smaller catchment
areas
Improvement in Food Resources Class 9 NEET Descriptive Questions
8. Large amounts of food grains get spoiled every year in India due to improper storage of food grains. How can this be avoided?
Answer: Food grains get spoiled by insects, fungi, rodents, bacteria, moisture, and temperature in the place of storage. Storage losses can be minimized by following preventive and control measures.
- The seeds/grains that are to be stored should be dry, with no moisture in them.
- The grains should be cleaned.
- The grains should be fumigated using chemicals that kill the pest.
- The storage houses should be waterproof.
- The grains should be stored in sealed gunny bags or metal containers.
- The bags should be stacked in order in a pile for proper fumigation and should be kept few centimetres away from the wall.
- The ventilators if any should be closed tightly, to avoid birds visiting the storage house and destroy
the grains. - The walls and the floor should be water-proof with no holes in it, to avoid rodents and pests.