NEET Biology Mcqs Animal Husbandry
Question 1. ______ is the agricultural practice of feeding, breeding, and raising livestock whose primary purpose is to provide meat and milk.
- Animal husbandry
- Cattle improvement
- Both (1) and (2)
- Cattle farming
Answer: 1. Animal husbandry
Animal husbandry is the agricultural practice of feeding, breeding, and raising livestock to obtain meat and milk. It deals with the care and breeding of livestock like buffaloes, cows, pigs, horses, cattle, sheep, camels, goats, etc., that are useful to humans.
Read And Learn More: NEET Biology Multiple Choice Question And Answers
Question 2. More than 70% of the world’s livestock population is found in _____ A _______ and ____ B _______, but contribute only 25% to the world farm production.
- A–India, B–China
- A–Japan, B–China
- A–India, B–US
- A–US, B–Brazil
Answer: 1. A–India, B–China
It is estimated that more than 70% of the world livestock population is in India (A) and China (B). However, it is surprising to note that their contribution to the world farm produce is only 25%, i.e. the productivity per unit is very low.
Animal Husbandry Mcqs

NEET Biology Animal Husbandry MCQs with Answers
Question 3. The management of animals for milk and its products for human consumption is called
- Dairy farming
- Poultry
- Cattle farming
- Cattle rearing
Answer: 1. Dairy farming
The management of animals for milk and its products for human consumption is called dairying. Milk yield here is dependent primarily on the quality of breeds.
Question 4. National Dairy Research Institute is located at
- Lucknow
- Mumbai
- Chennai
- Karnal
Answer: 4. Karnal
dairy questions and answers pdf
The National Dairy Research Institute (NDRI), located in Karnal (Haryana) is a premier research organisation under the aegis of Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
Question 5. Consider the following statements.
- In dairy management, processes that improve and increase quality and yield of milk are used.
- Animals like cow, sheep, buffaloes are found in dairy.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are in correct
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
Question 6. Father of White Revolution in India is
- Dr. Verghese Kurien
- Dr. MS Swaminathan
- Alexander Fleming
- Norman Borlaug
Answer: 1. Dr. Verghese Kurien
Dr. Verghese Kurien is Father of White Revolution in India. White revolution contributed to huge production of milk and its products during the 1970s.
Question 7. The practices involving improvement in animal husbandry can be brought about by
- Better management of farm and farm animals
- Increasing the number of breeding animals
- Managing the amount of feedstock given
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Better management of farm and farm animals
The practices concerned with the improvement in animal husbandry include management of farms, farm animals, and animal breeding.
Question 8. The milk-yielding capacity of buffalo is
- More than cows
- Less than cows
- Equal to cows
- None of the above
Answer: 1. More than cows
The average annual milk yield of a buffalo is 491 liters as against 173 liters of a cow in India. So, the milk-yielding capacity of buffalo is more than cows.
Animal Husbandry Mcqs
Question 9. Milk of which breed is nutritionally superior?
- Cow milk
- Camel milk
- Goat milk
- Buffalo milk
Answer: 4. Buffalo milk
Buffalo’s milk has higher fat, calcium, and protein contents than cow’s, camel’s, and goat’s milk.
Important MCQs on Animal Husbandry for NEET
Question 10. Which of the following is observed in animal husbandry?
- Breeding of livestock buffaloes, cows, sheep, camels, etc., that is useful to humans.
- Rearing, catching, selling, etc., of fish, molluscs, and crustaceans.
- Breeding of fowls for human use.
Choose the option containing correct statements.
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer: 4. 1, 2 and 3
- All given statements are correct. In animal husbandry, meat animals include beef, cattle, sheep, and meat goats. Milk animals include cows and buffaloes.
- Fisheries is also an important source of animal food, which is concerned with rearing, catching, and selling of fish, mollusks (shellfish), crustaceans, prawns, crabs, etc. Poultry is a class of domesticated fowl used for food and for their eggs.
Question 11. India is the largest exporter of ___________
- Milk and butter
- Meat and eggs
- Hides and skin
- Wool
Answer: 3. Hides and skin
dairy questions and answers pdf
India is the largest exporter of hides and skin in the world. Animal hides are stretched, dried, and tanned for human use. Most hides are processed from domesticated animals.
Question 12. Consider the following statements.
- Most of the animals are sheared once in a year.
- The major shearing season is May to December.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 4. Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect and can be corrected as
- Most animals are shorn twice a year. The major shearing seasons are January to March, June to August, and October to December.
Animal Husbandry Mcqs
Question 13. The parameters carried out for managing dairy farm are
- Selection of high-yielding males and females showing resistance to diseases.
- Visits by a veterinary doctor on a regular basis.
- Each animal should be fed nutritious feed in a proper proportion.
- Following of good animal management and general supervision.
Which of the above statement are correct?
- 1 and 2
- 1, 2 and 3
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: 4. 1, 2, 3 and 4
- All given statements are correct. Parameters of managing dairy farm are as follows
- Selection of good breeds having high yielding potential, resistance to diseases, etc.
- Cattles have to be well looked after by experienced doctors on regular basis.
- Quality and quantity of fooder in proper ratio should be given.
- The shed must be clean spacious, possess adequate facilities of light, water, drainage, etc.
Question 14. Buffaloes are considered better than cows because
- They are resistant to diseases
- They give more milk
- They live longer
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
- Buffaloes are considered better than cows because their milk contain more calcium and other minerals like potassium, phosphorus, etc.
- Also, buffaloes are more resistant to diseases due to which they live longer as compared to cows.
Animal Husbandry Mcqs
Question 15. The yellow colouration of cow’s milk is due to the
- Presence of carotene
- Absence of albumin
- Absence of casein
- Presence of lactose
Answer: 1. Presence of carotene
dairy questions and answers pdf
The yellow colour of cow milk is due to the presence of carotene, which is a precursor for yellow colour in cow’s milk and is a derivative of vitamin-A.
Question 16. Domesticated birds used for eggs or food is called
- Poultry
- Egg farming
- Apiculture
- Fowl farming
Answer: 1. Poultry
Poultry includes the class of domesticated fowl (birds) used for food or for eggs.
Livestock Management and Animal Breeding MCQs for NEET
Question 17. The common poultry bird(s) is/are
- Geese
- Turkey
- Chicken
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
The common poultry birds are chickens, turkeys, ducks, geese, guinea fowls, and pigeons.
Question 18. The ideal floor space requirement for a layer bird is about
- 2.5 to 3 sq. ft
- 3 to 4 sq. ft
- 10 sq. ft
- 4 to 5 sq. ft
Answer: 1. 2.5 to 3 sq. ft
- Generally, egg-laying hens require about 2.5 to 3 square feet floor space for each bird.
- For example, if you build a house having 5 feet width and 6 feet long then you can raise a maximum number of 10 hens in the house.
Question 19. Which is the key factor in selecting fowl for poultry?
- It must be easily available, may or may not be prone to diseases
- It must be cheap, slowly maturing, and have low-quality of meat and egg
- It must be fast-growing, resistant against diseases, and provide more eggs and good-quality meat
- All of the above
Answer: 3. It must be fast-growing, resistant to diseases, and provide more eggs and good-quality meat
The fowls selected for poultry must be fast-growing, resistant to diseases, provide more eggs and quality meat.
Animal Husbandry Mcqs
Question 20. Bird, especially chicken, grown for meat only is known as
- Hybrid
- Broiler
- Bird management
- Bird culture
Answer: 2. Broiler
A broiler is any chicken that is breed and raised specifically for meat production.
Question 21. Fowls raised for eggs are called
- Layers
- Broilers
- Broody
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Layers
Poultry fowls are of two types, i.e. layer chicks are for egg purpose and broilers are 8-10 weeks old chicken raised specifically for meat.
Question 22. Consider the following statements.
- Typically broilers have white feathers and yellowish skin.
- Duck and pigeons are not poultry birds
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 1. Typically broilers have white feathers and yellowish skin.
Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect. Incorrect statement can be corrected as The common poultry birds are chickens, turkeys, ducks, geese, guinea fowls and pigeons.
Animal Husbandry Mcqs
Question 23. The important parameters of poultry farm management are given below.
- Selection of disease-free breed.
- Clean farm and proper disposal of wastes.
- Safe, hygienic, and pest-free food and water should be provided.
- The temperature of poultry farm should be high for egg laying.
Which of the statements given above is/are true and which is/are false?
- T T T F
- F T T T
- T T F T
- T F T F
Answer: 1. Selection of disease-free breed
Statements 1, 2, and 3 are true, but statement 4 is false. The incorrect statement can be corrected as The temperature of the poultry shed should be optimum, not too high or not too low.
dairy questions and answers pdf
Question 24. In poultry ‘broiler finish mash’ is fed to the chicks between __________ weeks.
- 1 to 6
- 7 to 10
- 10 to 15
- 15 to 20
Answer: 2. 7 to 10
Finish mash is fed to the chicks between 7 to 10 weeks. It helps to build the muscles which are mainly used for meat production.
Question 25. The yolk of avian eggs contain
- Albumin
- Provitellin
- Vitellin
- Lecithin
- All of these
Answer: 5. All of these
The yolk of avian eggs contain various proteins including vitellin, livetins, phosvitin, phosphoproteins, lipoproteins, lipovitellin, provitellin, lecithin, albumin, etc.
Question 26. Breeding of fowl is preferably done between
- Dark coloured hen and light coloured cock
- 2 years old hen and 1-year-old cock
- 1-year-old hen and 2 years old cock
- 2 years old cock and hen
Answer: 2. 2 years old hen and 1-year-old cock
For the purpose of fowl breeding, two years old hen and one-year-old cock are considered.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 27. Identify the groups including animals whose eggs are consumed by humans.
- Gallus, Turtle, Chantecler
- Turkey, Fowl, Duckbill platypus
- Rana hexadactyla, Varanus, Gallus
- Python, Gallus, Chantecler
Answer: 1. Gallus, Turtle, Chantecler
The chicken (Gallus gallus domesticus) is a type of domesticated fowl. Turtle’s eggs are usually eaten raw or very lightly heated and their taste is said to be more flavourful than chicken eggs though some experience a ‘musky’ aftertaste. The Chantecler is as edible breed of chicken that originated in Canada.
Question 28. In India, which state occupies the first position in poultry farming?
- Kerala
- MP
- Andhra Pradesh
- UP
Answer: 3. Andhra Pradesh
- Tamil Nadu tops in egg production after the separation of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana. Tamil Nadu’s Namakkal is famous for its eggs.
- Every day, Tamil Nadu produces 3 crore eggs. This is followed by Andhra Pradesh (2.75 crores), Telangana (2 crores) and Punjab (1 crore).
- So, out of the given options we can say that Andhra Pradesh state occupies the first position in poultry farming in India.
Question 29. The egg layer variety of birds popular all over the world is
- Plymouth rock
- Hampshire
- White leghorn
- Wyandotte
Answer: 3. White leghorn
The most common egg layer variety of bird used for commercial production throughout the world is white leghorn.
Question 30. Austra white is the hybrid vigor of
- Gallus and white leghorn
- Desi variety with exotic bird
- Australorp male and white leghorn female
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Australorp male and white leghorn female
- The Austra whites is cross between a black Australorp male and white leghorn female. It is a chicken developed for people who desire an abundance of white eggs and a calm hen to produce them.
- Austra whites are excellent layers and you can expect more than 250 eggs per year from each hen. Additionally, they can also be raised as meat birds because they possess heavyweight.
Topic-wise Animal Husbandry MCQs for NEET with Explanation
Question 31. Desi breeds of fowl are
- Plymouth rock
- Brahma
- New Hampshire
- Rhode Island
Answer: 2. Brahma
Some important indigenous breeds of domestic fowl (desi hens) include Aseel, Karaknath, Basara, Chittagong, Ghagus, Brahma, and Cochin.
Question 32. Consider the following statements.
- Desi hens are weak and do not possess natural immunity against common diseases.
- The average egg production of desi hen is very high, i.e. ~150 eggs/ annum
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 4. Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect and can be corrected as
- Desi hens are strong and possess natural immunity against common diseases, but they are small, slow growing, and lay small-sized and less number of eggs.
- The average egg production of a desi hen is about 60 eggs per annum, which is very poor. Keeping this fact in mind, a large number of poultry birds have been imported.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 33. Broodiness in layer birds can be rectified by giving the hormonal injection of
- Progesterone
- Oestrogen
- Prolactin
- Both (1) are (2)
Answer: 4. Both (1) are (2)
- Broodiness is the tendency of layer birds to stop egg-laying, eating food, and sitting morbidly.
- It can be rectified by giving them the hormonal injection of estrogen and progesterone. Broodiness is induced by the prolactin hormone.
Question 34. The process of elimination of profitable birds from a flock is called
- Brooding
- Dubbing
- Culling
- De-worming
Answer: 3. Culling
Culling is the separation and elimination of sick and non-productive birds from the flock to prevent diseases in profitable birds.
Question 35. In the poultry industry, the production of hatching eggs is more expensive than the production of market eggs mainly because
- Cost of males and their depreciation value is high
- Mortality among females is usually lower when they are mated with males
- Number of eggs produced by hatchery flock are to be sold only as market eggs
- Some of the eggs produced by hatchery flocks are not acceptable for incubation
dairy questions and answers pdf
Answer: 4. Some of the eggs produced by hatchery flocks are not acceptable for incubation
- Not all eggs laid by a breeding flock are incubated. Eggs that are cracked or dirty are usually not used for hatching.
- Very small or very large eggs do not hatch. Eggs with thin or very porous shells are not likely to hatch well because of excessive loss of water during incubation.
- So, in the poultry industry, production of hatching egg is more expensive than the production of market eggs mainly because some of eggs produced by hatchery flocks are not acceptable.
Question 36. Eggs of chicken are incubated at
- 37°C
- 45°C
- 27°C
- 10°C
Answer: 1. 37°C
Chicken eggs should be incubated at a temperature between 37 and 39°C (37.5 is often considered to be ideal) and 50 to 65% relative humidity (60% is often considered ideal).
Question 37. Match the different chickens given under Column 1 with their respective uses given under Column 2. Choose the answer. which gives the correct combination of alphabets of two columns.
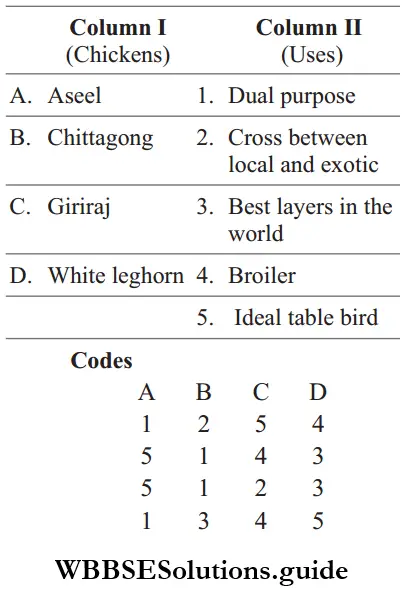
Answer: A-5, B-1, C-2, D-3
Question 38. HH 260 is a breed of
- Cock
- Pig
- Buffalo
- Hen
Answer: 4. Hen
Rhode Island Red, Black Minorca, and HH 260 are high egg-yielding breeds of hens. HH 260 is improved cross breed and highly used one. It has a very low level of climatic tolerance.
dairy questions and answers pdf
Question 39. Given below are different breeds of fowls and their characteristics
- New Hampshire – Non-American type
- Plymouth rock – Local breed
- Rhode Island Red – Mediterranean type
- White leghorn – American type
Choose the option containing incorrectly matched pairs.
- 1 and 4
- 2 and 3
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: 4. 1, 2, 3 and 4
All the given pairs are incorrectly matched pairs and can be corrected as New Hampshire is an American type. Plymouth rock is the most popular breed of the USA. Rhode Island is American class breed. White leghorn is Mediterranean type.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 40. Blackhead disease in poultry is caused by
- Haemophilus
- Histomonas
- Eimeria
- None of these
Answer: 2. Histomonas
Blackhead, also referred to as histomoniasis, is a disease caused by the protozoan, Histomonas meleagridis. This disease initially affects the intestinal ceca and liver, thus causing tissue destruction.
Question 41. Pullorum disease of poultry is otherwise known as
- Coccidiosis
- White diarrhea
- Fowl pox
- Avian diphtheria
Answer: 2. White diarrhea
Pullorum disease is caused by a bacterium, Salmonella pullorum. It results in loss of appetite, difficulty breathing, and white diarrhoea. This disease primarily affects turkeys, but other poultry species could be infected as well.
Question 42. Which is a fungal disease of poultry?
- Candidiasis
- Pox
- Cholera
- Ranikhet
Answer: 1. Candidiasis
Candidiasis is a fungal disease of poultry. Pox and Ranikhet are viral diseases. Cholera is a bacterial disease.
Question 43. One of the following is a disease of poultry.
- Ranikhet disease
- Anthrax
- Pebrine disease
- Foot and mouth disease
Answer: 1. Ranikhet disease
Ranikhet disease, also known as new castle disease. It is a contagious and highly fatal disease of fowl. In spite of the notable work done towards its control, this disease still ranks as one of the most serious viral diseases of poultry.
Question 44. The causative agent of bird flu is
- fungus
- bacteria
- protozoan
- virus
Answer: 4. virus
Bird flu is caused by a virus called H5N1.
Question 45. Consider the following statements.
- Bird flu is caused by H5N1 virus.
- H5N1 can infect humans.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 1 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 1 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
dairy questions and answers pdf
Bird flu resembles influenza and is caused by a virus H5N1. The virus enters the man through the uncooked chicken.
NEET Biology Mcq Chapter Wise
Question 46. If chicken and eggs are cooked properly (above 100°C), then the chances of catching bird flu are
- Very high
- High
- Moderate
- Nil
Answer: 4. Nil
The chances of catching bird flu from properly cooked chicken and egg are nil. It is confirmed by UN Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) and World Health Organisation (WHO)
Question 47. Fowl pox is caused by
- Ectoparasites
- Endoparasites
- Bacteria
- Virus
Answer: 4. Virus
Fowl pox causes warty lesions on the feet, on combs, and eyelids. It is caused by the genus of the virus Avipoxvirus.
Question 48. Which of the following is a fungal disease in poultry?
- Thrush
- Fowl pox
- Cholera
- Ranikhet
Answer: 1. Thrush
Thrush or mycosis or sour crop is a fungal disease of the digestive tract of various avian species, including chickens, turkeys, and quail.
Question 49. ‘Thrush disease’ in poultry is caused by
- Candida
- Aspergillus
- Puccinia
- None of these
Answer: 1. Candida
Thrush is caused by fungus, Candida albicans. It is also called Moniliasis disease and other fungal diseases include aspergillosis and aflatoxicosis.
Question 50. Gumboro disease in poultry is caused by
- Bacteria
- Virus
- Fungi
- Eimeria
Answer: 2. Virus
Gumboro disease leads to loss of appetite, diarrhea, and enlargement of the Bursa. It is caused by the bursal disease virus.
Question 51. Coccidiosis in poultry is caused by
- Protozoan parasite, eimeria
- Helminth parasites
- Virus
- Fungi
Answer: 1. Protozoan parasite, eimeria
Coccidiosis is an intestinal disease caused by intracellular protozoan parasites. It occurs when pathogenic populations of the causative agent rapidly build up. Most coccidias in poultry belongs to the genus- Eimeria, which are highly host-specific.
Question 52. Aspergillosis disease of fowl is a
- Fungal disease
- Bacterial disease
- Viral disease
- None of these
Answer: 1. Fungal disease
Aspergillosis is a disease caused by a fungus (or mold) called Aspergillus. So, it is a fungal disease.
Question 53. Coryza disease in poultry is spread by
- Litter feed
- Water
- Air
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Coryza is caused by a bacterium, Haemophilus pargallinarum. It spreads through airborne bacteria consuming contaminated feed or water. Symptoms include nasal and eye discharge with a foul smell, acute respiratory problems, and inflamed and swollen eyes.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 54. Chronic respiratory disease in poultry is caused by
- Algae
- Fungi
- Bacteria
- Virus
Answer: 3. Bacteria
Chronic Respiratory Disease (CRD) is one of the most common causes of disease in backyard fowls. CRD occurs when chickens and turkeys that are infected with Mycoplasma gallisepticum are stressed. The bacteria then cause major damage to the bird’s respiratory system.
Question 55. In poultry birds, nasal and eye discharge with a foul smell, acute respiratory problem, and inflamed and swollen eyes are the symptoms of
- Chronic respiratory disease
- Infectious coryza disease
- Brooder pneumonia disease
- Marek’s disease
Answer: 2. Infectious coryza disease
All the given symptoms in question are of infectious coryza disease in poultry birds.
Question 56. A serious disease of poultry that reduces immunity and spreads through contaminated food is
- Ranikhet disease
- Aflatoxicosis
- Thrush
- Marek’s disease
Answer: 2. Aflatoxicosis
Aflatoxicosis represents one of the serious diseases of poultry, livestock, and other animals. The cause of this disease in poultry and other food-producing animals has been attributed to the ingestion of various feeds contaminated with A. flavus.
Question 57. Which of the following is a disease-resistant, high-yielding breed of poultry developed in Karnataka?
- Aseel
- White leghorn
- Giriraja
- Plymouth rock
Answer: 1. Aseel
Aseel is an indigenous breed. It is one of the best table birds, but it cannot be raised for commercial purposes because of its poor growth and low fertility.
Question 58. Poultry diseases include
- Fowl typhoid, blue tongue, Ranikhet
- Fowl typhoid, tick fever, blue tongue
- Ranikhet, blue tongue, tick fever
- Fowl, cholera, Ranikhet, tick fever
Answer: 4. Fowl, cholera, Ranikhet, tick fever
dairy questions and answers pdf
Poultry birds suffer from a variety of diseases like – nutritional (rick), viral (Ranikhet), bacterial (fowl cholera, salmonellosis), and tick fever.
Question 59. Which one of the following is a viral disease of the poultry?
- Coryza
- New castle disease
- Pasteurellosis
- Salmonellosis
Answer: 2. New castle disease
New Castle disease is a highly contagious disease of birds caused by a paramyxovirus.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 60. Avian diphtheria is caused by
- Bacteria
- Virus
- Fungi
- Eimeria
Answer: 1. Bacteria
Avian diphtheria is a bacterial disease that commonly affects young chicks.
Question 61. Identify the main objective of animal breeding.
- Improved growth rate.
- Increase in production of milk, meat, egg, wool, etc.
- Superior quality of milk, meat, eggs, wool, etc.
- Improved resistance to various diseases.
Choose the correct option.
- 1 and 1
- 1, 1 and 3
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: 4. 1, 2, 3 and 4
All the listed objectives are correct with respect to animal breeding.
Question 62. A group of animals which are related by descent and share many similarities are referred to as
- Breed
- Race
- Variety
- Species
Answer: 1. Breed
A group of animals, which are related by descent and share many similarities are referred to as breed.
Question 63. The process of mating two closely related individuals within the same breed for 4 to 6 generations is called
- Heterosis
- Self-breeding
- Inbreeding
- Hybridization
Answer: 3. Inbreeding
The process of breeding, which occurs between closely related individuals of the same breed, is called inbreeding.
Question 64. The steps involved in the process of inbreeding are
- Mating these superior males and females with each other.
- Identifying superior males and females of the same breed.
- Examining and choosing progeny with superior traits.
- Superior progenies thus obtained are further mated.
Arrange the above given steps in correct sequence and select the correct answer.
- 1 → 3 → 3 → 4
- 2 → 1 → 3 → 4
- 3 → 1 → 2 → 4
- 3 → 2 → 1 → 4
Answer: 2. 2 → 1 → 3 → 4
- The correct sequence of steps in inbreeding is 2 → 1 → 3 → 4. Firstly, the superior males and females of same breed having desired characteristics are identified and then mated to obtain progenies.
- The resultant progenies are examined for desired traits and those possessing the quality traits are chosen for further mating. This process is continued for atleast 4-6 generations
Question 65. The process which enables in identification superior males and superior females of the same breed is
- Inbreeding
- Outbreeding
- Outcrossing
- None of these
Answer: 1. Inbreeding
Inbreeding helps in identifying superior males and superior females of same breed.
Question 66. Homozygous pure lines in cattle can be obtained by
- Mating of related individuals of same breed
- Mating of unrelated individuals of same breed
- Mating of individuals of a different breed
- Mating of individuals of different species
Answer: 1. Mating of related individuals of same breed
Inbreeding results in an increase in homozygosity. Hence, the mating of the related individuals of same breed will increase homozygosity. Homozygous pure lines in cattle are obtained by this method only.
NEET Biology Mcq
Question 67. Inbreeding depression is
- Reduced motility and immunity due to close inbreeding
- Decreased productivity due to mating of superior male and inferior female
- Decrease in body mass of progeny due to continued close inbreeding
- Reduced fertility and productivity due to continued close inbreeding
Answer: 4. Reduced fertility and productivity due to continued close inbreeding
Inbreeding depression is continued inbreeding, especially close breeding which reduces fertility and even productivity in animals. This problem is usually overcome by outbreeding.
dairy questions and answers pdf
Question 68. Inbreeding in animal husbandry is beneficial as it
- Increases vigour
- Improves the breed
- Increases heterozygosity
- Increases homozygosity
Answer: 4. Increases homozygosity
Increasing homozygosity due to inbreeding results in a decrease in variation within the group and stabilization of a particular type, i.e. pure line.
Question 69. In order to overcome inbreeding depression, the few animals are mated with
- Unrelated superior animals
- Related inferior animals
- Unrelated inferior animals
- Related superior animals
Answer: 1. Unrelated superior animals
In case of an inbreeding depression condition, the selected animal of the breeding population should be mated with superior animals of the same breed, but they should be unrelated to the breeding population.
Question 70. Select the incorrect statement.
- Inbreeding increases homozygosity
- Inbreeding is essential to evolve pure lines in any animal
- Inbreeding selects harmful recessive genes that reduce fertility and productivity
- Inbreeding helps in the accumulation of superior genes and the elimination of undesirable genes
Answer: 3. Inbreeding selects harmful recessive genes that reduce fertility and productivity
- The statement in option (3) is incorrect and can be corrected as Inbreeding exposes harmful recessive genes that are eliminated by selection.
- It also helps in accumulation of superior genes and the elimination of less desirable genes. Therefore, due to selection at each step, it increases the productivity of inbreed population. The rest statements are correct.
Question 71. Breeding of unrelated animals even those belonging to the same breed and with no common ancestor for minimum four generations is called
- Outbreeding
- Inbreeding
- Inbreeding depression
- Hybridization
Answer: 1. Outbreeding
- Outbreeding refers to the mating of unrelated animals belonging to
- The same breed but have no common ancestors.
- The different breeds (cross-breeding).
- Different species (interspecific hybridization).
- Thus, out-breeding may be divided into three different types on the basis of the individual selected for mating. These are outcrossing, cross-breeding, interspecific hybridization, and controlled breeding using artificial insemination.
Question 72. Outbreeding is an important strategy of animal husbandry because it
- Is useful in overcoming inbreeding depression
- Exposes harmful recessive genes that are eliminated by selection
- Helps in the accumulation of superior genes
- Is useful in producing pure lines of animals
Answer: 1. Is useful in overcoming inbreeding depression
- Outbreeding is the breeding of unrelated animals, which may be between individuals of the same breed (but having no common ancestors) or between different breeds (cross-breeding) or different species (interspecific hybridization).
- Outbreeding is an important strategy of animal husbandry as it helps to overcome inbreeding depression.
Question 73. Which method of animal breeding is used for cattle which are below average in milk production and growth rate in beef?
- Outcrossing
- Crossbreeding
- Inbreeding
- Interspecific hybridization
Answer: 1. Outcrossing
- Outcrossing or outbreeding means the crossing between different breeds with no common ancestors.
- This is the practice of introducing unrelated genetic material into a breeding line. Thus, it could be used for cattle having below-average milk production and growth rate in beef.
Question 74. Mating of superior males of one breed with superior females of other breed is
- Inbreeding
- Outbreeding
- Outcrossing
- Interspecific breeding
- Crossbreeding
Answer: 5. Crossbreeding
Crossbreeding refers to the cross of superior males of one breed with superior females of another breed, e.g. Hisardale (a new sheep breed) was obtained in Punjab by crossing Bikaneri ewes and Merino rams.
Question 75. By which method was a new breed ‘Hisardale’ of sheep formed by using Bikaneri ewes and Marino rams?
- Mutational breeding
- Crossbreeding
- Inbreeding
- Outcrossing
Answer: 2. Crossbreeding
Question 76. Crossbreeding
- Refers to the cross of superior male with superior females of different breeds.
- Helps to accumulate desired genes of two breeds in a progeny.
- Progeny with desired characters may be used for commercial production.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer: 4. 1, 2 and 3
All given statements are correct with respect to cross-breeding.
Question 77. Consider the following statements about outcrossing.
- Involves the breeding of animals within the same breed without common ancestors for 4-6 generations.
- It is done to increase milk production and growth rate in animals.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Mating between unrelated members of the same breed is called outcrossing. However, the mating partners should not have common ancestors on either side of their pedigree upto 4-6 generations.
- Outcrossing is usually preferred in animals having poor productivity of milk, poor growth rate, and suffering from inbreeding depression. Thus, to overcome this problem, outbreeding is done.
Question 78. In which method of animal breeding two different species of male and female animals are mated?
- Crossbreeding
- Interspecific hybridisation
- Outbreeding
- Outcrossing
Answer: 2. Interspecific hybridization
dairy questions and answers pdf
- In interspecific hybridization, male and female animals of two different species are mated. The progeny obtained from such a mating is usually different from both the parental species.
- But in some cases, the progeny may combine the desirable characteristics of both parents. Mule is produced from a cross between a female horse (mare) and a male donkey. Mules are sturdier than their parents and are well-suited for hard work in mountainous regions.
Question 79. Mule is a result of
- Inbreeding
- Artificial insemination
- Interspecific hybridisation
- Intraspecific hybridisation
Answer: 3. Interspecific hybridisation
Question 80. Mule is a cross between ________ and _________
- Female horse, male donkey
- Male horse, female donkey
- Male horse, female horse
- Male donkey, female donkey
Answer: 1. Female horse, male donkey
Question 81. Fill in the blanks. Choose the correct option depicting A to C.
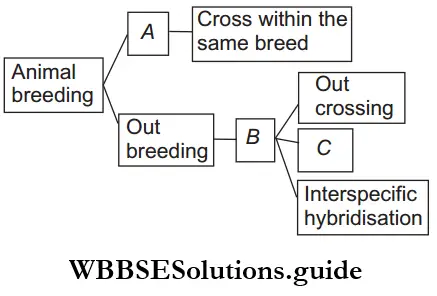
- A–Inbreeding, B–Cross between animals of different breeds, C–Crossbreeding
- A–Cross inbreeding, B–Cross between animals of same breed, C–Outcrossing
- A–Crossbreeding, B–Cross between animals of a different breed, C–Cross hybridization
- A–Inbreeding, B–Cross between animals of same breed, C–Outbreeding depression
Answer: 1. A–Inbreeding, B–Cross between animals of different breeds, C–Crossbreeding
NEET Biology Animal Breeding and Dairy Farming MCQs
Question 82. In cattle, the superior female is the ______ A _____, which produces more ______ B _____ Superior males are _______ C ______ from which superior quality _____ D ______ is obtained.
- A–cow, B–milk per lactation, C–bull, D–sperm
- A–buffalo, B–male, C–bull, D–superior progeny
- A–cow, B–milk per progeny, C–bull, D–inferior progeny
- A–buffalo, B–male, C–bull, D–inferior progeny
Answer: 1. A–cow, B–milk per lactation, C–bull, D–sperm
Question 83. MOET refers to
- Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer technology
- More Ovulation Embryo Transfer technology
- Multiple Ovulation Embryo Test technology
- None of the above
Answer: 1. Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer technology
Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer (MOET) technologies is a hybridization technique for herd improvement in animals like cattle, sheep, rabbits, and buffaloes. In this, high milk-yielding breeds of females are breed with high-quality meat-yielding bull to increase herd size in lesser time.
Question 84. MOET (Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer) is the method of
- Fish cultivation
- Hybridization of cattle
- Birth control
- Cloning of sheep
Answer: 2. Hybridisation of cattle
Question 85. In order to induce follicular maturation and superovulation during MOET in a cow, which of the following hormones are administered?
- Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
- Progesterone
- Androgen
- Oestrogen
Answer: 1. Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
- MOET is program for herd improvement in animals like cattle sheep, and rabbits. buffaloes, mares, etc. A cow is administered FSH-like activity hormones to induce follicular maturation and superovulation.
- The cow produces 6-8 eggs instead of one egg (produced normally). It is now, either mated with an elite bull or artificial insemination is carried out.
- When the fertilized eggs attain 8-32 cells stage, they are non-surgically removed and transferred to a surrogate mother. The genetic mother can be superovulated again.
Question 86. In MOET technology, what cell stage is transferred to surrogate mothers?
- 2-4 cell stage
- 4-8 cell stage
- 32-34 cell stage
- 8-32 cell stage
Answer: 4. 8-32 cell stage
dairy questions and answers pdf
Question 87. The semen of a bull meant for artificial insemination is preserved in
- Liquid N2
- Liquid O2
- Liquid CO2
- Refrigerated at temperature below 10ºc
Answer: 1. Liquid N2
- Liquid nitrogen (N2) plays a vital role in storing the frozen semen straws, at a temperature of-196°C for longer periods.
- Artificial Insemination (AI) is the process of collecting sperm cells from a male animal and manually depositing them into the reproductive tract of a female.
Question 88. _________ technique involves mating of high milk-yielding female breeds with high-quality meat bulls to obtain a better breed in short time.
- MOET
- Artificial insemination
- Crossbreeding
- Induced mutation
Answer: 1. MOET
Question 89. The yellow-colored milk secreted by cattle soon after the birth of a calf is called
- Chyme
- Chyle
- Cholesterol
- Colostrum
Answer: 4. Colostrum
Colostrum is a breast fluid produced by humans, cows, and other mammals during the onset of lactation. It promotes growth and health in infants and newborn animals.
Question 90. What will you conclude, when a cow is crossed to a bull and the female progeny is yielding more milk than its mother?
- More number of genes for high-yielding milk is inherited, only from the female parent
- More number of genes for high-yielding milk is inherited only, from the male parent
- More number of genes for high-yielding milk is inherited from both the parents
- The progeny through mutation achieved more genes for high-yielding milk
Answer: 3. More number of genes for high-yielding milk is inherited from both the parents
In the given situation, more genes for high-yielding milk are inherited by progeny from both parents because it is a polygenic trait.
Question 91. Identify A, B, C, and D.
- A–Cross of superior males of one breed with superior females of another breed.
- B–Controlled breeding involving semen transfer into the reproductive tract of selected female.
- C–Cross between male and female animals of two different species.
- D–Programme for herd improvement in animals like cattle, sheep, buffaloes, etc.
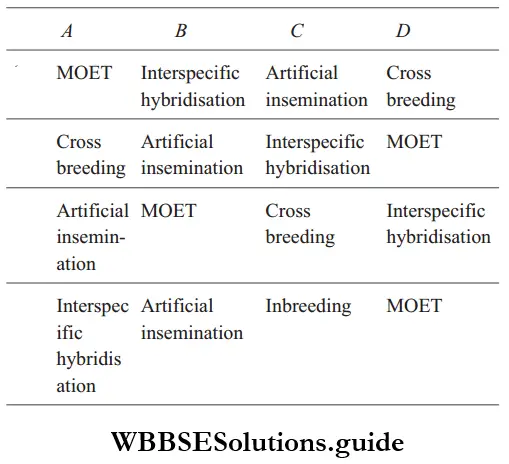
Answer: 2. B–Controlled breeding involving semen transfer into the reproductive tract of selected female.
- Crossbreeding (A) refers to the cross of superior males of one breed with superior females of another breed, for example, Hisardale.
- Artificial insemination (B) is a method of controlled breeding in which semen from the selected male parent is injected into the reproductive tract of the selective female parents.
- Interspecific hybridization (C) refers to crossing between male and female animals of two different species, for example, a mule was obtained by crossing a male donkey and a female horse.
- MOET (D) is a programme for herd improvement in animals.
Question 92. In the cloning of cattle, a fertilised egg is taken out of the mother’s womb and
- In the eight-cell stage, cells are separated and cultured until small embryos are formed which are implanted into the womb of other cows
- In the eight-cell stage, the individual cells are separated under an electrical field for further development in culture media
- From this upto eight identical twins can be produced
- The egg is divided into 4 pairs of cells
- which are implanted into the womb of other cows
Answer: 1. In the eight-cell stage, cells are separated and cultured until small embryos are formed which are implanted into the womb of other cows
- In the cloning of cattle, a fertilized egg divides into 2, 4, and then into 8 celled stage. This embryo is carefully removed from the womb in eight-cell stage.
- The embryonic cells are then separated using enzymes. Each isolated cell is kept in a nutrient medium and cultured until small embryos are formed. These are later implanted into the womb of a different ‘host mother’ cow.
Question 93. Infertility of local breeds of cattle can be overcome by the use of
- Cross-breeding with exotic breeds
- Good nourishment
- Stilbesterol
- Gonadotropin
Answer: 4. Gonadotropin
Infertility in local breeds of cattle can be overcome through the use of pregnant serum gonadotropin.
Question 94. Sahiwal is a breed of
- Buffalo
- Horse
- Dog
- Cattle
Answer: 4. Cattle
- Sahiwal is a breed of Zebu cattle which is primarily used in dairy production.
- The name Sahiwal originates from the Sahiwal district of Punjab province in Pakistan and is found in Ferozpur, Amritsar, and Sri Ganganagar in India.
Question 95. Jaffrabadi is a variety of
- Cow
- Buffalo
- Sheep
- Goat
Answer: 2. Buffalo
Jaffarabadi is one of the heaviest buffalo breeds.
Question 96. The Jaffrabadi breed is distributed in
- Gujarat
- Malvi
- Halliker
- None of these
Answer: 1. Gujarat
Jaffarabadi is a native of the Saurashtra region of Gujarat around the Gir forest. It is also known as Bhavanagri, Gir, or Jaffari. It is named after the town of Jaffarabad of Gujarat.
Question 97. Dual breed variety of cattle is
- Jersey
- Ayrshire
- Brown swiss
- All of the above
Answer: 2. Ayrshire
Ayrshire is dual breed of cattle from Ayrshire in South-west Scotland. It is used for dairy and meat production. Jersey and Brown Swiss are exotic milch breeds of cattle.
Question 98. Assertion (A) Cattle breeds can be improved by superovulation and embryo transplantation.Reason (R) Superovulation in high milk-yielding cows is induced by hormonal injection.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 2. Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- Cattle breeds can be improved by superovulation and embryo transplantation as it helps to produce higher number of quality eggs in short period of time. Superovulation in high milk-yielding cows is induced by hormonal injection.
Question 99. Match the breeds of cattle given under Column 1 with the place of their origin listed under Column 2. Choose the answer which gives the correct combination of alphabets of the two columns.
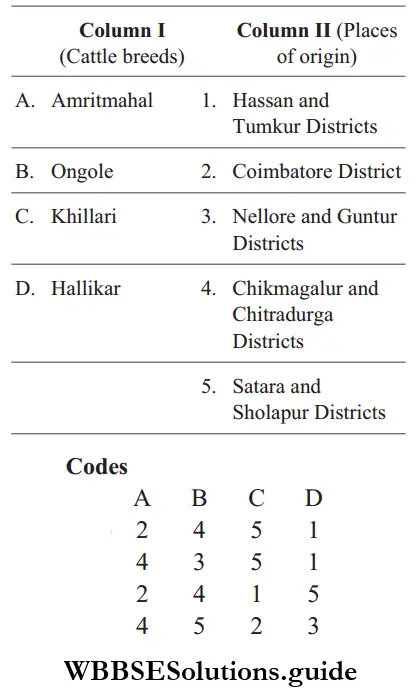
Answer: A-4, B-3, C-5, D-1
Question 100. Which of the following is an exotic breed of cattle?
- Brown jersey
- Friesian
- Holstein
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Holstein-Friesian is a native cow of Holland which it is called Friesian and is exotic dairy breed of cattle. Jersey is native cow of Jersey Island and is an exotic breed.
dairy questions and answers pdf
Question 101. Holstein-Friesian cattle were developed from the breeds of
- Denmark
- English channel
- Netherlands
- Switzerland
Answer: 3. Netherlands
Holstein cows come from a region in northern Germany, while Friesians originally came from the Netherlands. Thus, Holstein-Friesian cattle were developed from the breeds of Netherlands.
Question 102. Given below are different breeds of buffalo and their characteristics.
- Murrah – Found in Punjab and Haryana
- Mehsana – Breed of water buffalo
- Jaffarabadi – Low-weight breed
Choose the option containing incorrectly matched pairs.
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
Answer: 3. 2 and 3
- Pairs 2 and 3 are incorrectly matched, but I is a correctly matched pair. Incorrect matched paris can be corrected as
- The Murrah buffalo is a breed of water buffalo mainly kept for milk production. It originates in Punjab and Haryana.
- Mehsana is a dairy breed of buffalo found in Mehsana, Sabarkanda, and Banaskanta Districts in Gujarat and adjoining Maharashtra state. The breed is evolved out of cross-breeding between the Surti and the Murrah.
- Jaffarabadi is one of the heaviest buffalo breeds and is a native of the Saurashtra region of Gujarat around Gir forest.
Question 103. Which of the following breeds of milk-yielding cows has been formed from Indian and Swiss cows?
- Red Sindhi
- Sahiwal
- Sunandini
- Deoni
Answer: 3. Sunandini
Sunandini is a composite breed of cattle developed in India by crossing Indian cattle with Brown Swiss, Jersey cattle, and Holstein-Friesian cattle.
Question 104. Consider the following statements.
- The progeny of cross-breeding may be used for commercial production.
- In case of artificial insemination, the semen can be used immediately or can be frozen for later use.
- Controlled breeding experiments are carried out using artificial insemination and MOET technology.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer: 4. 1, 2 and 3
- All the given statements are correct.
- Crossbreeding refers to the cross of superior males of one breed with superior females of another breed.
- The progeny may be used for commercial production, for example, Hisardale. In case of artificial Insemination (AI), the semen can be used immediately or can be frozen in liquid nitrogen for later use.
- Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer (MOET) technology is a programme for herd improvement. Controlled breeding programs involve the use of AI and MOET technologies.
Question 105. Highest milk yielding variety of cattle in the world is
- Brown Jersey
- Ongole
- Holstein-Friesian
- Hallikar
Answer: 3. Holstein-Friesian
Holstein-Friesian gives 5000 L /lactation. It is the highest milk-yielding variety of cattle in world.
Question 106. Lactation in sterile cows is induced by giving
- Stilbestrol
- Gonadotropin
- Vitamin-B12
- None of these
Answer: 1. Stilbestrol
The majority of Indian cattle have been on marginal inputs and are infertile and poor milk yielders. Stilbestrol tablets are administered to induce lactation in sterile cows and immature females. Stilbestrol is a synthetic non-steroidal oestrogen.
Question 107. Milch breeds are
- Good meat-producing bulls
- Good milk-producing cows
- Good working bullocks
- None of the above
Answer: 2. Good milk-producing cows
Milch breeds are cows that produce large quantities of milk per lactation.
Question 108. The milch breed of cattle are
- Hillikar, Nageri and Malvi
- Gir, Sahiwal and Deoni
- Kankrej, Haryana and Ongole
- Tharpakar, Kangayan
Answer: 2. Gir, Sahiwal and Deoni
Milch cattle are kept for the purpose of milk production. Sahiwal, Gir, Deoni, Red Sindhi, and Rathi are examples of milch breed of cattle.
Question 109. Dual purpose breed is
- Jersey
- Brown Swiss
- Krishna valley
- All of these
Answer: 3. Krishna valley
- Krishna valley is a dual-purpose breed of recent origin with an inherent ability to toil in extremely hot and humid climatic conditions. They are a draught breed and are mainly used for agricultural purposes.
- The cows are moderate milk producers while the bulls are known for their strength and endurance.
Question 110. Cattle fed with spoilt hay of sweet clover which contains dicumarol
- Are healthier due to a good diet
- Catch infections easily
- May suffer vitamin-K deficiency and prolonged bleeding
- May suffer from beri -beri due to deficiency of vitamin-B6
Answer: 3. May suffer vitamin-K deficiency and prolonged bleeding
Dicumarol is an anticoagulant which inhibits the synthesis of prothrombin in the liver. Thus, it may cause prolonged bleeding by inhibiting the coagulation of blood.
Question 111. Mad cow disease in cattle is caused by an organism which has
- Inert crystalline
- Abnormally folded protein
- Free RNA without protein coat
- Free DNA without protein coat
Answer: 2. Abnormally folded protein
Mad cow disease in cattle is a progressive fatal neurological disorder that is caused from an infection by a prion. It is an abnormally folded protein with the ability to transmit misfold shape to other proteins.
Question 112. Given below are the animals useful to us in several ways. Select an appropriate code to match the animals to their utility.

Answer: A-4, B-1, C-2, D-3
NEET Exam Animal Husbandry Most Repeated MCQs
Question 113. Match the following columns and choose the correct option.
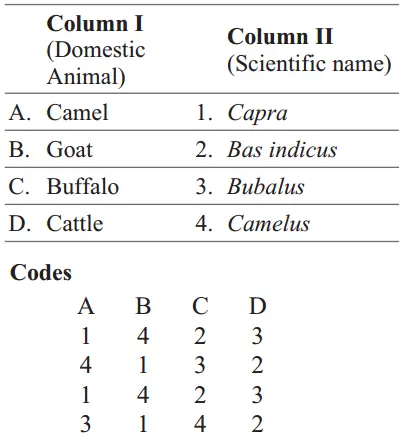
Answer: A-4, B-1, C-3, D-2
Question 114. Hinny is a hybrid of male
- Horse and female donkey
- Donkey and female horse
- Goat and female lamb
- Sheep and female goat
Answer: The hybrid between the female donkey and male horse is called hinny.
Question 115. The breeds of sheep which give good-quality wool are
- Lohi and Nellore
- Rampur and decani
- Nellore and decani
- Nali and lohi
Answer: 4. Nali and lohi
- Nali is a good carpet-quality wool breed, with the densest and heaviest fleeces among the breeds of Rajasthan.
- Lohi sheep is found in Southern Punjab in India. It is used for its carpet-quality wool and meat production. The body is white and the head is usually black or brown.
Question 116. Superior quality wool is obtained from the sheep raised in
- Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh
- Bihar and Tamil Nadu
- Maharashtra and Gujarat
- Odisha and Rajasthan
Answer: 1. Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh
Pashmina is the most sought-after wool in the world because of its superior quality. It is found in Himachal Pradesh and Kashmir in India.
Question 117. The world’s highly prized wool-yielding ‘Pashmina’ breed is
- Sheep
- Goat of high himalayan altitudes
- Goat-sheep cross
- Kashmir Afghan sheep cross
Answer: 2. Goat of high himalayan altitudes
Pashmina is the underfur of Kashmiri and Tibetan goats, indigenous to high altitudes of the Himalayan Range Belt of Asia.
Question 118. Match the following columns.
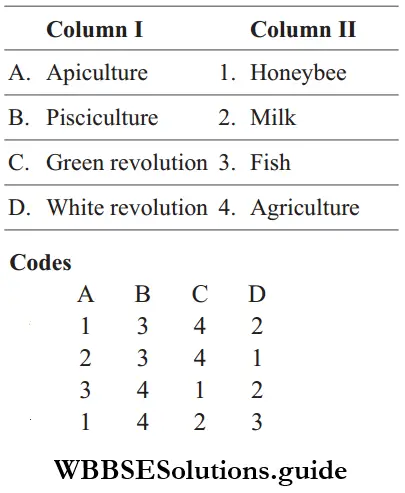
Answer: A-1, B-3, C-4, D-2
Question 119. Domestication of honeybees is called
- Sericulture
- Apiculture
- Tissue culture
- Pisciculture
Answer: 2. Apiculture
Apiculture or bee culture is the rearing of honeybees by culturists in different parts of the world to obtain honey and bees wax on commercial scale.
dairy questions and answers pdf
Question 120. Queen bee is specified for
- Administration
- Making hive
- Egg laying
- Collection of food
Answer: 3. Egg laying
- The term queen bee is typically used to refer to an adult, mated female (gyne) that lives in a honeybee colony or hive.
- She is usually the mother of most, of the bees in the beehive. Queens are developed from larvae selected by worker bees and specially fed in order to become sexually mature and lay eggs.
Question 121. In which bee, wax glands are found?
- Queen bee
- Drone
- Workers
- Both (1) and (3)
Answer: 3. Workers
- The wax gland in the honeybee colony is found in workers. The wax gland complex of the honeybee worker consists of 3 cell types, epithelial cells, oenocytes, and adipocytes, which act synergistically to secrete wax.
- It is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons, fatty acids, and proteins (lipoproteins).
Question 122. In which part of the body, does honeybee keep the nectar for some time?
- Crop
- Mouth
- Gizzard
- Pollen basket
Answer: 1. Crop
Nectar ingested by bee is mixed with saliva and collected in the honey sac or crop until honey is regurgitated into hive cell.
Question 123. The name ‘honey stomach’ in bees is applied for
- Gizzard
- Pharynx
- Stomach
- Crop
Answer: 4. Crop
In stinging bees, oesophagus enlarges to form crop to store the liquid. Later on, it is regurgitated as honey. It may contain 75 mg of nectar and known as honey stomach.
Question 124. In which of the following is parthenogenesis observed?
- Honeybee
- Silkworm
- Earthworm
- Housefly
Answer: 1. Honeybee
Parthenogenesis is a form of asexual reproduction in which growth and development of embryos occur without fertilisation. This occurs in honeybees. Males (drones) are produced parthenogenetically from unfertilised eggs.
Question 125. In honeybees, the drones (males) are produced from
- Unfertilised eggs
- Fertilized eggs
- Larvae fed by royal jelly
- Fasting larvae
Answer: 1. Unfertilised eggs
Question 126. Drone is
- Sterile male
- Fertile male
- Sterile female
- Fertile female
Answer: 2. Fertile male
A drone is a fertile male honeybee. Unlike the female worker bee, drones do not have stingers and gather neither nectar nor pollen. A drone’s primary role is to mate with an unfertilised queen.
Question 127. Lifespan of worker bee is
- 10 days
- 15 days
- 5-6 weeks
- 10 weeks
Answer: 3. 5-6 weeks
During the active season, the lifetime of a worker is five to six weeks. Worker bees usually confine themselves to one task at a time and work without pause. The first few weeks of a worker’s life are spent working within the hive, while the last weeks are spent foraging for food and gathering pollen or nectar.
Question 128. In which part of the body ‘pollen basket’ is found in the honeybee?
- Prothoracic leg
- Mesothoracic leg
- Metathoracic leg
- At union of thorax and abdomen
Answer: 3. Metathoracic leg
Each metathoracic leg of a honeybee has a large tibia with a cavity having bristles forming a pollen basket or corbicula. It is used for storing pollen during collection.
Question 129. For its committed functions, a worker bee is provided with
- Powerful wings
- Mouthparts for sucking
- Legs as carriers of pollen grains
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Worker bees perform all the work of the colony. For this purpose, they are provided with mouth parts suitable for sucking nectar, leg suitable for carrying pollen, wax glands, stings and powerful wings.
Question 130. The Nobel Prize for studing honey bees was given to
- Karl Korrens
- Karl von Frisch
- Hugo de Vries
- Parkinson
Answer: 2. Karl von Frisch
- Honeybees, despite their small size, have one of the most sophisticated communication systems.
- In a series of classic experiments dating from the 1920s, the Austrian Biologist Karl von Frisch investigated how honeybees communicate with each other.
- He received Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine, with K. Lorenz and N. Tinbergen for his achievements in comparative behavioral, physiology, and pioneering work in communication between insects (1973).
Question 131. Honeybees exhibit a type of dance to communicate the location of food. This is known as
- Waggle dance
- Tap dance
- Round dance and waggle dance
- Breakdance
Answer: 3. Round dance and waggle dance
- Bees perform two types of dances, the ‘round’ and ‘waggle tail’ dance. The round dance is performed by the scouts when the food source is within a couple of 100 m of the hive.
- The waggle dance is performed when food sources are away, greater than a couple of 100 m.
Question 132. In bees, dance is meant for
- Only reproduction
- Communication
- Visiting the source of food
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer: 4. Both (2) and (3)
Bees perform two types of dances to communicate about the source of food at various angles and the movements of dance help the bees to visit the food source.
Question 133. The stimuli through which a dancing scout bee communicates the location of a food source to other worker bees in a hive are
- Visual
- Acoustic
- Contact
- Both (1) and (3)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (3)
During the dance, the scouts move their body in different angles and locations to send visuals signals to the community. They also pass signal of nectar to other workers, which is a form of contact communication.
Question 134. Which one of the following statement is correct in relation to honeybees?
- Apis indica is the largest sized wild honey bee in India
- Honey is predominantly sucrose and arabinose
- Bee wax is a waste product of honeybees
- Communication in honeybees was discovered by Karl von Frisch
Answer: 4. Communication in honeybees was discovered by Karl von Frisch
- The statement in option (4) is correct whereas other statements are incorrect. Incorrect statements can be corrected as Apis dorsata is a bigger bee than Apis indica (a medium-sized bee).
- Honey is predominantly glucose and fructose. Beeswax is secreted by special wax glands to make compartments. Thus, it is not a waste product.
Question 135. Assertion (A) The behaviour of honeybees to come out of the hive in large number is called swarming. reason (R) It relieves the crowding and provides a means of founding new colonies.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 1. Both A and R are true and R is the orrect explanation of A
- Swarming is the process by which a new honeybee colony is formed when the queen bee leaves the colony with a large group of worker bees.
- In the prime swarm, about 60% of the worker bees leave the original hive location with the old queen.
- Swarming is a honeybee colony’s natural means of reproduction.
Question 136. Assertion (A) The honeybee queen opulates only once in her lifetime. eason (R) The honeybee queen an lay fertilised as well as fertilised eggs.
- Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true, but R is false
- Both A and R are false
Answer: 2. Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- Queen is the only fertile female in a beehive. She lays about 2000 or more eggs in a day.
- The fertilised eggs are laid in a worker or queen cell or honeycomb, while unfertilised eggs are laid in a drone cell, the latter develops parthenogenetically. The queen mates only once in a lifetime.
- The sperms stored in her spermatheca fertilise her eggs as long as she lives.
Question 137. At times of need, a worker bee can e converted into a queen by
- Placing the worker bee in the queen’s chamber
- Suspension of worker’s duties
- Feeding the worker bee with ‘royal early during its larval period
- None of the above
Answer: 3. Feeding the worker bee with ‘royal early during its larval period
- A bee becomes a queen bee by the efforts of the existing worker bees in the hive. A young larva (newly hatched baby insect) is fed special food called ‘royal jelly’ by the worker bees.
- Royal jelly is richer than the food given to worker larvae and is necessary for the larva to develop into a fertile queen bee.
Question 138. Sting apparatus in honeybees is a modified form of
- Ovipositor
- Wax glands
- Alkaline glands
- Podical valves
Answer: 1. Ovipositor
A bee’s abdomen have one notable appendage the stinger, which is a modified ovipositor or egg depositor.
dairy questions and answers pdf
Question 139. Which of the following is correctly matched?
- Apiculture – Honeybee
- Pisciculture – Silk moth
- Sericulture – Fish
- Aquaculture – Mosquitoes
Answer: 1. Apiculture – Honeybee
- Option (1) is correctly matched pair. Apiculture is the rearing of bees or beekeeping for the production of honey and wax. Other options represent incorrectly matched pairs and can be corrected as
- Pisciculture is the rearing of fish.
- Sericulture is silk farming.
- Aquaculture is culture of freshwater amimals.
Question 140. Silk, honey, and lac are
- The secretory substance of insects
- Secretory substance of plants
- Artificial chemicals
- All of the above
Answer: 1. Secretory substance of insects
Silk, honey, and lac all are secretory substances of insects. Silk is produced from the insect Bombyx mori. Honey is produced from the Apis indica, whereas lac is produced from insects Laccifer lacca.
Question 141. Which among the following is the real product of the honeybee?
- Pollen
- Bee wax
- Honey
- Propolis
Answer: 2. Bee wax
- Bee wax is the natural secretion of the worker bees and is poured out in thin delicate flakes. It is made of
- Even numbered alcohols.
- Even numbered fatty acids.
- Odd-numbered normal paraffin.
- Honey and propolis are derived from beehives whereas pollens are products of flower.
Question 142. The wax glands in honeybee are present
- On the ventral side of the last segment
- On the ventral side of last four abdominal segments
- On the dorsolateral side of first two abdominal segments
- On the lateral side of last two abdominal segments
Answer: 2. On the ventral side of last four abdominal segments
Worker bees (females) have eight wax-producing glands on the ventral side of abdominal segments 4 -7, to produce bee wax.
Question 143. The product used to manufacture cosmetics, shaving creams, and polishes of various kinds is
- Bee wax
- Honey
- Latex
- Resin
Answer: 1. Bee wax
Bee wax is used to manufacture cosmetics, shaving creams, and polishes.
Question 144. A waxy substance produced by honeybees to repair combs is called
- Propolis
- Honeydew
- Nectar
- Sporopollenin
Answer: 1. Propolis
Propolis is a mixture of resin that honeybees collect from flower saps or buds of plant and is used as a seal in repairing hives.
Question 145. Honey is
- Acidic
- Alkaline
- Neutral
- Acidic when fresh and alkaline when old
Answer: 1. Acidic
The pH of honey ranges from 3.4 to 6.1, the average being 3.9. Thus, it is acidic in nature.
Question 146. In honey, the percentage of maltose and other sugars is
- 9.2
- 8.81
- 10.5
- 11.2
Answer: 2. 8.81
Honey is a natural sweet syrup extracted from the hives of honey bees. The chemical composition of honey is ash 01.00%, enzyme and pigments 2.21%, maltose and other sugar 8.81 %, water 17.20%, dextrose 21.28%, and levulose 88.90%.
Question 147. The composition of honey is
- Water, sucrose and dextrine
- Fructose, glucose, water, maltose,
- Water, protein, sucrose and dextrin
- Water, sucrose, glucose and dextrin
Answer: 2. Fructose, glucose, water, maltose,
Honey is primarily fructose (38%), glucose (31%), water (17%), maltose (7%), and small amounts of trisaccharides, other higher carbohydrates, sucrose, minerals, vitamins, and enzymes.
Question 148. Honey is
- A natural valuable tonic for human body.
- Of high medicinal value as it contains important enzymes, vitamins, and disaccharide sugars mainly glucose and fructose.
- Consumed alongwith a number of ayurvedic medicines.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 3
Answer: 4. 1, 2 and 3
All the given statements are correct.
dairy questions and answers pdf
Question 149. Identify the flower that is pollinated by honeybees.
- Sunflower
- Apple and pear
- Brassica
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Bees are the pollinators of many of crop species, such as sunflower, Brassica, apple, and pear.
Question 150. Consider the following statements.
- Keeping beehives in crop fields during flowering period increases both crop yield and honey yield.
- Successful bee-keeping requires management of beehives during different seasons.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Usually, the most common places for keeping beehives are the courtyard, on the roof, in the crop fields during flowering period, etc.
- The beehives when kept in the fields, increase the pollination efficiency of flowering plants and improve the yields. Successful bee-keeping requires management of beehives during different seasons.
Question 151. Bee venom is used for the preparation of medicines against
- Slipped disc
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Tuberculosis
- Cancer
Answer: 2. Rheumatoid arthritis
Bee venom is collected on a commercial scale for the treatment of snake bite, rheumatoid arthritis, and many other diseases.
Question 152. Most common honeybee species in India is
- Apis indica
- Apis florea
- Apis mellifera
- Apis dorsata
Answer: 1. Apis indica
The most common species of honeybee is Apis indica. Relatively non-aggressive and rarely exhibiting swarming behavior, it is ideal for bee-keeping.
Question 153. European bee is called as
- Apis indica
- Apis florea
- Apis dorsata
- Apis mellifera
Answer: 4. Apis mellifera
An exotic European variety of bees is Apis mellifera (an Italian variety). It is used in apiaries for large-scale production of honey and wax.
Question 154. The highest amount of honey is made available by
- Apis indica
- Apis mellifera
- Apis calculate
- Apis florea
Answer: 2. Apis mellifera
- The average yield of honey from Apis mellifera is 45 to 180 kg/ year/colony. It is the highest quantity among all the honeybees.
- So, the highest amount of honey is made available by Apis mellifera.
Question 155. Which of the following is a ferocious bee?
- Apis mellifera
- Apis florea
- Apis indica
- Apis dorsata
Answer: 4. Apis dorsata
Apis dorsata generally live in hilly areas. So, they are called ‘rock bees’. Sometimes they are called monster bees. This bee is the biggest, very fearful, and ferocious nature, among all the bee species.
Question 156. Which of the following is rock bee?
- Apis mellifera
- Apis indica
- Apis dorsata
- Apis florea
Answer: 3. Apis dorsata
dairy questions and answers pdf
Question 157. Largest honeybee is
- Apis mellifera
- Apis indica
- Apis dorsata
- Apis florea
Answer: 3. Apis dorsata
Question 158. The most commonly maintained species of bee by beekeepers is
- Apis mellifera
- Apis dorsata
- Apis indica
- Apis florea
Answer: 1. Apis mellifera
The most commonly maintained species of bee by beekeepers is Apis mellifera. At present time, Apis mellifera is used in apiaries for large-scale production of honey and wax.
Question 159. The silk industry is related to
- Sericulture
- Apiculture
- Pisciculture
- Horticulture
Answer: 1. Sericulture
- Sericulture or silk farming, is the cultivation of silkworms to produce silk. Apiculture is the management and study of honeybees. Pisciculture also known as fish farming is the rearing of fish for food in enclosures such as fish ponds or tanks.
- Horticulture is the branch of plant agriculture dealing with garden crops, generally fruits, vegetables, and, ornamental plants.
Question 160. The life cycle of the mulberry silkworm is completed in
- 2-3 weeks
- 4-5 weeks
- 6-8 weeks
- 5-7 weeks
Answer: 4. 5-7 weeks
The silkworm larval life has five instars, with four skin molts and four distinct development stages, to complete one generation of the species. These are ova, larvae, pupae, and imago. The life cycle takes 5-7 weeks, depending on climatic conditions.
Question 161. Caterpillar of silkworm voraciously feeds upon
- Apple leaves
- Guava leaves
- Mulberry leaves
- All of the above
Answer: 3. Mulberry leaves
Pale, naked caterpillars feed upon mulberry leaves until pupation begins.
Question 162. Voracious feeder in life history of silk moth is
- Adult female
- Eggs
- Larva
- Pupa
Answer: 3. Larva
The larva is a voracious feeder and during this period, it moults four times. When fully grown, it stops feeding and starts secreting liquid silk through spinnerets.
Question 163. In which stage of its life cycle, the silk moth begins to produce silk fiber?
- 3rd instar larva
- 4th instar larva
- 5th instar larva
- Pupa
Answer: 4. Pupa
The pupa of the silkworm spin a cocoon of one continuous white or yellow silken thread.
Question 164. The maximum length of silk fiber that surrounds the single cocoon is about
- 8000 – 12000 ft
- 1000 – 1500 m
- 800 – 1200 ft
- 8000 – 12000 m
Answer: 2. 1000 – 1500 m
Cocoon is white colored bed of pupa that gives thread of up to 1000-1500 m. It is estimated that 2500 cocoons produce one pound of silk.
Question 165. In the silkworm, if no Juvenile Hormone (JH) is present when it molts, it will
- Die
- Moult into another larval stage
- Moult into pupa
- Moult into an adult
Answer: 2. Moult into another larval stage
The presence of juvenile hormone is necessary for metamorphosis to adult. In its absence, the larva moults into another form, but it will not die or become adult.
Question 166. Silk is the secretion of
- Cephalic glands
- Gastric glands
- Buccal glands
- Salivary glands
Answer: 4. Salivary glands
The saliva from the salivary gland of silkworm is a component of silk and is produced by the larva of the silkworm (cocoon).
Question 167. Secretion of silk gland comes through a small pore. This pore is situated on
- Exopodite of 2nd maxilla
- Endopodite of 1st maxilla
- Prostheca of mandible
- Anterior part of hypopharynx
Answer: 4. Anterior part of hypopharynx
The anterior parts of both the silk glands are united to form a common duct that open through a spinneret situated on the hypopharynx which secrete the silk.
Question 168. Protein present in silk fibre is
- Collagen
- Fibroin
- Elastin
- Casein
Answer: 2. Fibroin
- Silk protein fibroin (β -keratin protein) is produced by modified salivary glands of silkworms (silk moth larvae) and by spiders, among other arthropods.
- Silk is composed of two kinds of very large molecular weight amphoteric colloidal proteins, i.e. fibroin and sericin, where fibroin constitutes about 75% and sericin is 25% of the thread.
Question 169. The silkworm larva ceases to eat and starts spinning silk around its body
- At random
- From inside to outside
- From outside to inside
- All of the above
Answer: 3. From outside to inside
In silkworm, mature caterpillar stops feeding and returns to a corner of mulberry leaves. Its salivary glands now secrete a sticky fluid. This sticky substance turns into a solid silk thread after coming in contact with air. It spins silk from outside to inside around its body.
Question 170. Given below are the different variety of silk found in India and the organisms from which it is derived.
- Mulberry silk – Bombyx mori
- Tassar silk – Attaccus ricini
- Muga silk – Antheraea mylitta
- Eri silk – Antheraea assamensis
Choose the option containing incorrectly matched pairs.
- 1 and 2
- 3 and 4
- 1, 2 and 4
- 2, 3 and 4
Answer: 4. 2, 3 and 4
Pairs 2, 3, and 4 are incorrectly matched and can be corrected as Tassar silk (Antheraea mylitta), Muga silk (Antheraea assamensis), and Erisilk (Attaccus ricin). Pair 1 is correctly matched.
Question 171. Largest silk producing state of India is
- Karnataka
- Bihar
- Assom
- Bengal
Answer: 1. Karnataka
Karnataka is the largest producer of silk in India. The state produces an average of around 8,200 metric tonnes of silk every year, which is about one-third of the total silk production in India.
Question 172. Which species produces superior-quality of silk?
- Attacus ricini
- Bombyx mori
- Antheraea assamensis
- Attacus atlas
Answer: 2. Bombyx mori
Bombyx mori is known to produce the superior-quality of silk.
dairy questions and answers pdf
Question 173. The number of eggs laid by Bombyx mori are
- 200 to 300
- 300 to 500
- 400 to 600
- 500 to 700
Answer: 2. 300 to 500
Just after copulation, female Bombyx mori starts egg laying which is completed in 1-24 hours. One moth lays 300 to 500 eggs depending upon the climatic conditions and the supply of food.
Veterinary Science and Animal Health MCQs for NEET
Question 174. The silkworm which is reared on castor plants is
- Eri silkworm
- Muga silkworm
- Oak silkworm
- Tassar silkworm
Answer: 1. Eri silkworm
- Eri silk is also known as Endi or Errandi. It is produced by Philosamia ricini which is commonly called as eri silkworm. It primarily feeds on castor leaves and is thus, reared on castor plants.
- The manufacturing process of Eri allows the pupae to develop into adults and only the open-ended cocoons are used for obtaining silk. Thus, it is also popularly known as non-violent silk.
Question 175. Food ofAntheraea assamensis is
- Terminalia arjuna
- Machilus bombycina
- Ricinus communis
- Euphorbia pulcherrima
Answer: 2. Machilus bombycina
Muga silk is the product of the silkworm Antheraea assamensis, endemic to Assom. The larvae of these moths feed on Som (Machilus bombycina) leaves. This silk is known for its glossy fine texture and durability.
Question 176. The scientific name of the oak silkworm is
- Bombyx mori
- Antheraea assamensis
- Antheraea pernyi
- Philosamia ricini
Answer: 3. Antheraea pernyi
Antheraea pernyi is the scientific name of oak silkworm.
Question 177. Tassar silk is extracted from
- Bombyx mori
- Apis indica
- Anthrerea paphia
- Apis dorsata
Answer: 3. Anthrerea paphia
- Tussar silk, also often referred to as ‘wild silk, which is an exquisite thread obtained from a wide-winged moth that is yellowish-brown in colour.
- The scientific name of these moths is Antheraea paphia and they are a part of the group known as Emperor Moths or Saturnids.
Question 178. In addition to Bombyx mori, there are several other organisms that produce commercial silk. Match the following columns given having name of the species with the correct commercial name of their produce by selecting the appropriate answer from the given codes.

Answer: A–2, B–3, C–4, D–1
Question 179. Process of twisting silk strands to make it more thicker and stronger yarn is
- Spinning
- Throwing
- Stifling
- Raising
Answer: 2. Throwing
Several silk strands are twisted together to make thicker, stronger yarn in the process called throwing. It produces various yarns, differing according to the amount and direction of the twist imparted.
Question 180. Which of the following statements is/are true?
- Salivary glands of moth secrete silk
- Larval form of moth secretes silk
- Silk is extracted from the cocoon of the moth by boiling
- Both (2) and (3)
Answer: 4. Both (2) and (3)
- Statements in options (2) and (3) are true whereas (1) is not true.
- Incorrect statement can be corrected as Silk is produced by the salivary glands of the larval stage of moth and not by moth itself.
- When pupa spin the cocoon of about 1000 m, it is killed with hot air or boiling in water, to preserve the thread intact.
Question 181. Flacherie disease of the silkworm is caused due to
- Bacteria
- Virus
- Protozoans
- Fungi
Answer: 1. Bacteria
Flacherie’s disease in silkworms is associated with bacterial infections. Wide fluctuations in temperature and humidity with poor-quality mulberry leaves are the major predisposing factors.
Question 182. Pebrine is a disease of
- Honeybee
- Fish
- Silkworm
- Lac insect
Answer: 3. Silkworm
Pebrine is caused by protozoan Nosema bombycis. It causes death of eggs or larva during their third moult. It is the worst disease of silkworms.
Question 183. Lac-producing insect is
- Lytta
- Tachardia lacca
- Bombyx mori
- Antheraea assamensis
Answer: 2. Tachardia lacca
Tachardia lacca is a lac-producing insect.
Question 184. Indian Lac Research Institute is situated at
- Ranchi
- Mysore
- Dehradun
- Nagpur
Answer: 1. Ranchi
‘Indian Lac Research Institute’ is situated in Namkum, Ranchi, Jharkhand. It is a nodal institute at the national level for research and development on all aspects of lac and other natural gums or resins such as harvesting/tapping, processing, product development, training, information repository, technology dissemination, and national/international cooperation.
Question 185. Consider the following statements.
- Lac is used in making bangles and furniture polish.
- India is largest producer of lac in world.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
Lac is used in ammunition, airplanes, furniture polish, and perfumes and in making bangles, imitation fruits, and flowers. India is the largest producer of lac in the world and contributes to about 70% of the world’s need.
Question 186. Lac is produced as
- Feces of lac insect
- Secretion from body
- Excretion from body
- Excess food oozing out of body
Answer: 2. Secretion from body
Larvae of insect, Tachardia lacca secretes resinous substance by special dermal glands located all over the body. Reisinous secretion becomes hard after coming in contact with air and it forms lac.
Question 187. The female of lac insect lays about _________ eggs at a time.
- 150-250
- 200-300
- 250-450
- 300-400
Answer: 2. 200-300
Each female lac insect lays 200-300 eggs. The eggs hatch into red-coloured larvae.
Question 188. The cultivation of aquatic animals or plants for food is called
- Aquaculture
- Pisciculture
- Sericulture
- Apiculture
Answer: 1. Aquaculture
Aquaculture is the farming of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, and aquatic plants.
Question 189. In culture fishery, the fingerlings are developed in
- Breeding happy
- Nursery pond
- Hatching happy
- Stocking pond
Answer: 2. Nursery pond
Fingerlings are juvenile fishes. In culture fishery, development upto the fingerling stage is carried out in nursery ponds.
Question 190. Hypophysation is done in major carps
- To increase size
- To increase their growth period
- To carry out breeding in the fishes
- To increase their palatability
Answer: 3. To carry out breeding in the fishes
The technique of breeding the fish by administering pituitary gland extract injection is known as induced breeding or hypophysation. The pituitary gland secretes several hormones, of which gonadotropin is the most important for breeding.
Question 191. Crustacean fishery involves
- Exploitation of oysters and crabs
- Exploitation of mussels and squids
- Exploitation of shell and cuttlefish
- Exploitation of lobster and prawn
Answer: 4. Exploitation of lobster and prawn
Crustacean fishery is concerned with exploitation of lobsters, crabs, and prawns.
Question 192. ‘Inland fisheries’ is referred to
- Culturing fish in freshwater
- Trapping and capturing fishes from sea coast
- Deep sea fishing
- Extraction of oil from fishes
Answer: 1. Culturing fish in freshwater
Freshwater fisheries and brackish water fisheries are collectively called inland fisheries. Marine fisheries is the culture of fishes in marine waters.
Question 193. Which one of the following is not amarine fish?
- Sardine
- Catla
- Mackerel
- Bombay duck
Answer: 2. Catla
- Marine fishes are sardine, mackerel, and Bombay duck.
- Freshwater fishes include rohu, Catla, calabash, mrigal, chital, common carp, etc.
Question 194. The term ‘blue revolution is associated with
- Apiculture
- Sericulture
- Dairy
- Fishery
Answer: 4. Fishery
Blue revolution refers to the growth in the aquaculture industry which includes culturing of all types of aquatic animals (fishery) and plants even those in brackish water too.
Question 195. Blue Revolution refers to
- The rapid expansion intensive commercial aquaculture.
- Increase in global food production and reduction in widespread hunger.
Which of the statements given above is/ are correct?
- Only 1
- Only 2
- 1 and 2
- None of these
Answer: 3. 1 and 2
During the last two decades, due to impact of blue revolution, there has been a rapid global expansion of commercial aquaculture and it now contribute significantly to the total global seafood production.
Question 196. Consider the following statements.
- Isinglass is a gelatinous byproduct obtained from fishes.
- Fish meal is a good source of protein.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
Isinglass is produced from the air bladder of catfishes and carps. Fish meal is a good source of protein for cattle and poultry. It is obtained from the non-edible (waste) parts of fish like tails and fins.
Question 197. The adhesive for paper, wood, etc., obtained from fish is
- Fish guano
- Fish glue
- Fish oil
- Fish chum
Answer: 2. Fish glue
- Fish glue is extracted from fish by heating the skin or bones in water.
- The purest form of fish glue is made from the membrane of the swim bladder of sturgeon and is called isinglass.
Question 198. Fish roes widely used for high biological value is rich in
- Thymine and creatine
- Lecithin and cholesterol
- Vitamin B6, C, and B12
- All of the above
Answer: 4. All of the above
Fish roe is fully ripe egg masses of fish. It is a type of seafood. It is highly nutritious as it contains vitamin- B(10%), vitamin- B12 (89%), vitamin-C (27%), cholesterol (59%), proteins (58%), and amino acids like lecithin, thymine, creatine, etc.
Question 199. Among the following edible fishes, which one is a marine fish having rich source of omega-3 fatty acids?
- Mystus
- Mangur
- Mrigala
- Mackerel
Answer: 4. Mackerel
Mackerel is a marine fish having rich quality of omega-3 fatty acid.
Poultry Farming and Fisheries MCQs for NEET with Answers
Question 200. Cod liver oil is extracted from
- Bony fishes
- Gadidae
- Buffaloes
- Whales
Answer: 2. Gadidae
Cod liver oil is a dietary supplement derived from the liver of cod fish, Gadidae. As with most fish oils, it contains omega-3 fatty acids, Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA), and Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA).
Question 201. Cod liver oil is rich in
- Iodine
- Vitamin-A
- Vitamin-B
- Vitamin-C
Answer: 2. Vitamin-A
Cod liver oil is one of the best sources of omega- 3 fatty acids (EPA and DHA) and it contains relatively high amounts of vitamin- A and vitamin- D.
Question 202. Isinglass is
- Collagen0
- Pigment obtained from scales
- A substance obtained from air bladder
- Glass preparation from fish fin
Answer: 3. Substance obtained from air bladder
Isinglass is produced from the air bladder of catfishes and carps. It is principally used for clarifying wines, and beer and making purse, honey, comb, book, and ribbon. The isinglass prepared in Russia is of the best quality in the world.
Question 203. Isinglass, a type of byproduct of fish industry is principally used for
- Feeding cattle, pigs, and poultry
- Preparation of paints and varnishes
- Clarification of vinegar, wines, and beer
- Production of insulin
Answer: 3. Clarification of vinegar, wines, and beer
Question 204. Consider the following statements.
- Pearl is produced by marine mollusks.
- Pearl oysters are major source of pearls.
Choose the correct option.
- Statement 1 is correct, but 2 is incorrect
- Statement 1 is incorrect, but 2 is correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Answer: 3. Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- Pearls is produced by marine molluscs such as pearl oyster and mussel. Pearls are intensively produced by cultivating pearl oysters.
- The most important mollusks cultivated for pearls are Pinctada vulgaris.
Question 205. Natural pearl is formed by
- A bivalve
- Prawn
- Crayfish
- Fish
Answer: 2. Prawn
Pearls are formed in molluscan bivalves (clams, oysters, mussels) of several species by the secretion of a substance known as nacre around an irritant in the outer tissue (mantle) of the organism or between the outer tissue and the shell. Nacre is also the substance that coats the inner surface of bivalve shells.
Question 206. A pearl oyster secretes pearls to
- Regenerate injured parts
- Protect itself against invading parasite
- Harden its mantle cavity
- Isolate-damaged tissues of the body
Answer: 2. Protect itself against invading parasite
Pearl is secreted by a nacreous layer of pearl oyster as a protection against foreign body such as parasite or sand particle.
Question 207. Which of the following nutrients are added to improve fish culture?
- NO3– and SO42-
- PO43- and NO3–
- SO42- and I2
- Both (1) and (2)
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2)
Fish culture is improved by mixing fish food with superphosphates (PO43-), nitrates (NO3–), and ammonium sulfates (SO42-) during culture.
Question 208. Rohu is zoologically known as
- Labeo rohita
- Catla catla
- Harpadon nehereus
- Mrigala cirrhinus
Answer: 1. Labeo rohita
The rohu is a species of fish of the carp family, found in rivers in South Asia. It is a large omnivore and extensively used in aquaculture. Its zoological name is Labeo rohita.
Question 209. Which of these is not an exotic fish?
- Gourami
- Sardine
- Anchors
- Mackerel
Answer: 1. Gourami
Exotic species of animals are those which are introduced from some other country and were not native of the present country. Gourami is a native to countries of Asia.
Question 210. Choose the freshwater fishes from the options given below.
- Catla
- Rohu
- Common carp
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Some of the common freshwater fishes are rohu, Catla, calabash, mrigal, chital, common carp, etc.
Question 211. Identify the edible marine fish.
- Hilsa
- Pomfret
- Both (1) and (2)
- Catla
Answer: 3. Both (1) and (2)
The common marine fish varieties popularly consumed as food are hilsa, sardines, mackerel, tuna, pomfrets, eel, Bombay duck, etc.
Question 212. Match the following columns.
Answer: A–2, B–1, C–4, D–3
Question 213. Which one of the following edible fishes is introduced in India by foreigners?
- Labeo rohita
- Stromateus argenteus
- Mystus singhala
- Clarias batrachus
Answer: 2. Stromateus argenteus
Stromateus argenteus or pomfret fish was introduced in India by foreigners as an edible fish.
Question 214. Bombay duck is
- Hilsa hilsa
- Harpadon nehereus
- Podiceps ruficollis
- Oreochromis mossambicus
Answer: 2. Harpadon nehereus
The Bombay duck or bummalo (Harpadon nehereus) is a lizard fish.
Question 215. ______. is a larvivorous fish, which eat larva of mosquito.
- Gambusia
- Catla
- Rohu
- Mrigal
Answer: 1. Gambusia
Gambusia is a freshwater fish which feeds on the larvae of mosquitoes. Due to this, it is also called mosquito fish.
Question 216. Gill rot disease in fishes is caused by
- Aeromonas sp.
- Bacillus polymyxa
- Branchiomyces sanguinis
- Bacillus subtilis
Answer: 3. Branchiomyces sanguinis
- Branchiomycosis affects the fish’s gills by causing them to become mottled or blotchy in appearance due to the dying tissue.
- For this reason, it is also known as ‘gill rot.’ It is a fungal disease caused by Branchiomyces sanguinis.
Question 217. Which one of the following is bacterial disease of fish?
- Gill rot
- Fin rot
- Skin lesions
- Anaemia
Answer: 2. Fin rot
Fin rot is caused by Gram-negative bacteria, Aeromonas or Vibrio. So, it is a bacterial disease of fish.
Question 218. From the options given below, the edible aquatic animals is/are
- Crab
- Lobster
- Oyster
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Crabs, oysters, lobster are edible aquatic animals.
